Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 viewsMatter Mind Map Page 6-7
Matter Mind Map Page 6-7
Uploaded by
Mr Robert G.The document defines matter, atoms, and molecules, and describes the properties of volume, density, hardness, solubility, and thermal conductivity. It discusses the types of pure substances and mixtures, including homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures. Finally, it outlines methods for separating mixtures, such as filtration, evaporation, and sieving.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Matter and Its PropertiesDocument7 pagesMatter and Its PropertiesAndrei Mae MercadoNo ratings yet
- The MatterDocument3 pagesThe Mattermarianobenlliure5dNo ratings yet
- Science 2 LectureDocument5 pagesScience 2 Lectureraymundfarinas123No ratings yet
- Gen Chem Chapt.1Document45 pagesGen Chem Chapt.1Dave Cercado BugadorNo ratings yet
- Classifying MatterDocument53 pagesClassifying MatterTanya MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Substance Chemistry Lesson 1Document28 pagesSubstance Chemistry Lesson 1samsonNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Section 5.1 - Chemical and Physical ChangeDocument4 pagesLesson 1 - Section 5.1 - Chemical and Physical ChangeshanlbyNo ratings yet
- Matter and Its PropertiesDocument10 pagesMatter and Its PropertiesGerald CatiponNo ratings yet
- Review of Chemistry ConceptsDocument15 pagesReview of Chemistry ConceptsAnele CatayasNo ratings yet
- Matter and Its Properties: Sci-CoreDocument6 pagesMatter and Its Properties: Sci-Corecrmc bedNo ratings yet
- Materi Dan PerubahannyaDocument11 pagesMateri Dan PerubahannyaAniz DmurryNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Classification of MatterDocument7 pagesChapter 2 Classification of MatterPatrice Francisco100% (1)
- CBSE Class 6 Science Notes Chapter 4 Sorting Materials Into GroupsDocument8 pagesCBSE Class 6 Science Notes Chapter 4 Sorting Materials Into Groupssaarthjain2007No ratings yet
- Diversity of Materials in The EnvironmentDocument19 pagesDiversity of Materials in The EnvironmentMarjorie TrinidadNo ratings yet
- week-1-2-Properties-of-Matter (2) NOTESDocument5 pagesweek-1-2-Properties-of-Matter (2) NOTESJerome SarsonasNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Lesson 1Document60 pagesModule 1 Lesson 107 JAVIER LLYOD GENELSON B.No ratings yet
- MatterDocument16 pagesMatterapi-454467369No ratings yet
- Chemistry, Unit 1, Matter and Its ClassificationDocument7 pagesChemistry, Unit 1, Matter and Its Classification盾謙No ratings yet
- Chemistry Checkpoint Topics Part 1Document28 pagesChemistry Checkpoint Topics Part 1esteban ferrada silvaNo ratings yet
- Pages From ChemistryDocument8 pagesPages From ChemistryKunalKaushikNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1Document5 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1Jeannie QuillanoNo ratings yet
- Lecciones Sobre La MateriaDocument21 pagesLecciones Sobre La Materiaavalkvin04No ratings yet
- Chapter1 (Matter and Its Properties)Document9 pagesChapter1 (Matter and Its Properties)Anyanna MunderNo ratings yet
- Matter, Properties, & Phases: by Emmanuel DikolelayDocument33 pagesMatter, Properties, & Phases: by Emmanuel DikolelayMaPhi ZaBeNo ratings yet
- Matter and ITS Properties: Arvin C. Diamante Master Teacher II Nicolas L. Galvez Memorial NHS June 18, 2018Document57 pagesMatter and ITS Properties: Arvin C. Diamante Master Teacher II Nicolas L. Galvez Memorial NHS June 18, 2018Arvin Corpuz DiamanteNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Module 1 & 2Document2 pagesGeneral Chemistry Module 1 & 2Claire VillaminNo ratings yet
- (CHEM) UNIT 1. Lesson 2. Properties & Characteristics of MatterDocument7 pages(CHEM) UNIT 1. Lesson 2. Properties & Characteristics of MatterTrishia Mae Gregorio BelenNo ratings yet
- Brown Aesthetic Group Project Presentation 20240207 082108 0000Document30 pagesBrown Aesthetic Group Project Presentation 20240207 082108 0000jillianaynemanaNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer MATTERDocument3 pagesScience Reviewer MATTERRACHELL SATSATINNo ratings yet
- Is Matter Around Us PureDocument14 pagesIs Matter Around Us Purepunksnotdead_t7100% (1)
- Matteru 4Document9 pagesMatteru 4Cris MonteroNo ratings yet
- JH1 - Science - Term 1 N 2Document88 pagesJH1 - Science - Term 1 N 2yetriNo ratings yet
- 3rd Quarter Science 8Document50 pages3rd Quarter Science 8John Ryan PiolNo ratings yet
- Exp SC 5 - Chapter 08Document9 pagesExp SC 5 - Chapter 08megamind publicationNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Matter in Our Surroundings - Notes 1Document2 pagesChapter 1 - Matter in Our Surroundings - Notes 1Perajothi PalanirajaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For General Chemistry 1st MonthDocument5 pagesReviewer For General Chemistry 1st MonthAhrron CapistranoNo ratings yet
- Unique Characteristics of MatterDocument20 pagesUnique Characteristics of Mattercaeameko:)0% (2)
- Chem. Lesson 1Document31 pagesChem. Lesson 1Ashlee Talento100% (1)
- Science8 Q3 W1-8Document30 pagesScience8 Q3 W1-8Maricar agawa GuntanNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem q1 w1 2Document7 pagesGen Chem q1 w1 2ARIEL ANGELIONo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Introduction To Matter: Ex. Water Into Ice CubeDocument4 pagesChapter 1: Introduction To Matter: Ex. Water Into Ice CubeIvan NenadicNo ratings yet
- Physical Science NotesDocument143 pagesPhysical Science NotesNelsonMoseMNo ratings yet
- IX Class NotesDocument60 pagesIX Class NotesNitin ThakurNo ratings yet
- Unit 01 Chapter 2Document86 pagesUnit 01 Chapter 2Pauline BatanayNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument32 pagesChemistryAndrei Angelo PantigNo ratings yet
- MatterDocument5 pagesMattererikaNo ratings yet
- Gen-Chem-1 Handout Q1 Week1Document4 pagesGen-Chem-1 Handout Q1 Week1Daphnie Pauleen PalomarNo ratings yet
- Ros Unit 2 Matter and EnergyDocument18 pagesRos Unit 2 Matter and EnergyNina GanapaoNo ratings yet
- For Prints in ScienceDocument20 pagesFor Prints in Sciencenbqp6p9v6pNo ratings yet
- Física I. T2Document7 pagesFísica I. T2Simona FourtakNo ratings yet
- Física I. T2Document7 pagesFísica I. T2Simona FourtakNo ratings yet
- 2 Matter: Solids: Liquids: Liquids Take On The Shape of Their Container But Do Not Change Their Volume. For ExampleDocument5 pages2 Matter: Solids: Liquids: Liquids Take On The Shape of Their Container But Do Not Change Their Volume. For ExampleRegz GasparNo ratings yet
- Matter - LessonDocument4 pagesMatter - LessonAnonymous hWtQueEyxNo ratings yet
- Chemestry: Matter Is Anything That Has Mass and Takes Up Space. A Book Is Matter, ADocument6 pagesChemestry: Matter Is Anything That Has Mass and Takes Up Space. A Book Is Matter, ADiana RevillaNo ratings yet
- GENERAL CHEMISTRY 1 - Lesson 1Document8 pagesGENERAL CHEMISTRY 1 - Lesson 1Fernandez, Nadine Kate T.No ratings yet
- Lesson 3 State Classifications and Properties of MatterDocument40 pagesLesson 3 State Classifications and Properties of MatterAngel MaeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Matter and Its PropertiesDocument7 pagesChapter 2 Matter and Its PropertiesJennelyn BaylonNo ratings yet
- Children Encyclopedia Chemistry: The World of KnowledgeFrom EverandChildren Encyclopedia Chemistry: The World of KnowledgeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- The Solid Truth about States of Matter with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceFrom EverandThe Solid Truth about States of Matter with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNo ratings yet
- Crust MovementsDocument2 pagesCrust MovementsMr Robert G.No ratings yet
- Air & GasesDocument3 pagesAir & GasesMr Robert G.No ratings yet
- Acids & BasesDocument4 pagesAcids & BasesMr Robert G.No ratings yet
- PRE1ADocument1 pagePRE1AMr Robert G.No ratings yet
- Acid RainDocument3 pagesAcid RainMr Robert G.No ratings yet
- Acid Rain 11Document3 pagesAcid Rain 11Mr Robert G.No ratings yet
- Europe Geo & ClimateDocument1 pageEurope Geo & ClimateMr Robert G.No ratings yet
Matter Mind Map Page 6-7
Matter Mind Map Page 6-7
Uploaded by
Mr Robert G.0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views2 pagesThe document defines matter, atoms, and molecules, and describes the properties of volume, density, hardness, solubility, and thermal conductivity. It discusses the types of pure substances and mixtures, including homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures. Finally, it outlines methods for separating mixtures, such as filtration, evaporation, and sieving.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document defines matter, atoms, and molecules, and describes the properties of volume, density, hardness, solubility, and thermal conductivity. It discusses the types of pure substances and mixtures, including homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures. Finally, it outlines methods for separating mixtures, such as filtration, evaporation, and sieving.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views2 pagesMatter Mind Map Page 6-7
Matter Mind Map Page 6-7
Uploaded by
Mr Robert G.The document defines matter, atoms, and molecules, and describes the properties of volume, density, hardness, solubility, and thermal conductivity. It discusses the types of pure substances and mixtures, including homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures. Finally, it outlines methods for separating mixtures, such as filtration, evaporation, and sieving.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
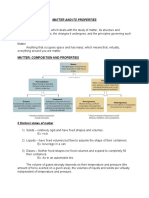
DEFINITIONS.
Matter: Is everything around us.
Atoms: Tiny particles that made out the matter.
Molecules: Groups of atoms.
PROPERTIES.
Volume: Describes how much space matter occupies. We measure it in milliliters (ml).
Density: Amount of matter in a volume. We measure it in kilograms per litre (kg/l)
Density explains why some objects float in water while other sink.
Hardness: Is the scratch-resistance of a solid. Diamonds are the hardest natural solids.
Solubility: Is the ability of a substance to dissolve in another substance and form a
solution.
Thermal conductivity: Is the ability of certain substances to conduct or transfer heat.
Metals are good conductors and wool and wood are good heat insulators.
Mass: Amount of matter in an object. We measure it in grams (g).
TYPES
Pure substances: Consist of only one type of matter. Like the table salt.
Mixtures: Made up of two or more pure substances.
- Homogeneous: We cannot see the individual substances that make it up.
Example: sea water.
- Heterogeneous: We can see individual substances that make it up. Example:
Salad.
METHODS
Filtration: When we pour the juice of a lemon through a filter, the solids stay in the
filter, and the liquid passes through it.
Evaporation: When we heat a mixture of salt and water, the liquid evaporates and
leaves only the solids which crystallise and form salt crystals
Sieving: We use a sieve to separate solids of different sizes, such as pebbles from sand.
You might also like
- Matter and Its PropertiesDocument7 pagesMatter and Its PropertiesAndrei Mae MercadoNo ratings yet
- The MatterDocument3 pagesThe Mattermarianobenlliure5dNo ratings yet
- Science 2 LectureDocument5 pagesScience 2 Lectureraymundfarinas123No ratings yet
- Gen Chem Chapt.1Document45 pagesGen Chem Chapt.1Dave Cercado BugadorNo ratings yet
- Classifying MatterDocument53 pagesClassifying MatterTanya MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Substance Chemistry Lesson 1Document28 pagesSubstance Chemistry Lesson 1samsonNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Section 5.1 - Chemical and Physical ChangeDocument4 pagesLesson 1 - Section 5.1 - Chemical and Physical ChangeshanlbyNo ratings yet
- Matter and Its PropertiesDocument10 pagesMatter and Its PropertiesGerald CatiponNo ratings yet
- Review of Chemistry ConceptsDocument15 pagesReview of Chemistry ConceptsAnele CatayasNo ratings yet
- Matter and Its Properties: Sci-CoreDocument6 pagesMatter and Its Properties: Sci-Corecrmc bedNo ratings yet
- Materi Dan PerubahannyaDocument11 pagesMateri Dan PerubahannyaAniz DmurryNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Classification of MatterDocument7 pagesChapter 2 Classification of MatterPatrice Francisco100% (1)
- CBSE Class 6 Science Notes Chapter 4 Sorting Materials Into GroupsDocument8 pagesCBSE Class 6 Science Notes Chapter 4 Sorting Materials Into Groupssaarthjain2007No ratings yet
- Diversity of Materials in The EnvironmentDocument19 pagesDiversity of Materials in The EnvironmentMarjorie TrinidadNo ratings yet
- week-1-2-Properties-of-Matter (2) NOTESDocument5 pagesweek-1-2-Properties-of-Matter (2) NOTESJerome SarsonasNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Lesson 1Document60 pagesModule 1 Lesson 107 JAVIER LLYOD GENELSON B.No ratings yet
- MatterDocument16 pagesMatterapi-454467369No ratings yet
- Chemistry, Unit 1, Matter and Its ClassificationDocument7 pagesChemistry, Unit 1, Matter and Its Classification盾謙No ratings yet
- Chemistry Checkpoint Topics Part 1Document28 pagesChemistry Checkpoint Topics Part 1esteban ferrada silvaNo ratings yet
- Pages From ChemistryDocument8 pagesPages From ChemistryKunalKaushikNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1Document5 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1Jeannie QuillanoNo ratings yet
- Lecciones Sobre La MateriaDocument21 pagesLecciones Sobre La Materiaavalkvin04No ratings yet
- Chapter1 (Matter and Its Properties)Document9 pagesChapter1 (Matter and Its Properties)Anyanna MunderNo ratings yet
- Matter, Properties, & Phases: by Emmanuel DikolelayDocument33 pagesMatter, Properties, & Phases: by Emmanuel DikolelayMaPhi ZaBeNo ratings yet
- Matter and ITS Properties: Arvin C. Diamante Master Teacher II Nicolas L. Galvez Memorial NHS June 18, 2018Document57 pagesMatter and ITS Properties: Arvin C. Diamante Master Teacher II Nicolas L. Galvez Memorial NHS June 18, 2018Arvin Corpuz DiamanteNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Module 1 & 2Document2 pagesGeneral Chemistry Module 1 & 2Claire VillaminNo ratings yet
- (CHEM) UNIT 1. Lesson 2. Properties & Characteristics of MatterDocument7 pages(CHEM) UNIT 1. Lesson 2. Properties & Characteristics of MatterTrishia Mae Gregorio BelenNo ratings yet
- Brown Aesthetic Group Project Presentation 20240207 082108 0000Document30 pagesBrown Aesthetic Group Project Presentation 20240207 082108 0000jillianaynemanaNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer MATTERDocument3 pagesScience Reviewer MATTERRACHELL SATSATINNo ratings yet
- Is Matter Around Us PureDocument14 pagesIs Matter Around Us Purepunksnotdead_t7100% (1)
- Matteru 4Document9 pagesMatteru 4Cris MonteroNo ratings yet
- JH1 - Science - Term 1 N 2Document88 pagesJH1 - Science - Term 1 N 2yetriNo ratings yet
- 3rd Quarter Science 8Document50 pages3rd Quarter Science 8John Ryan PiolNo ratings yet
- Exp SC 5 - Chapter 08Document9 pagesExp SC 5 - Chapter 08megamind publicationNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Matter in Our Surroundings - Notes 1Document2 pagesChapter 1 - Matter in Our Surroundings - Notes 1Perajothi PalanirajaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For General Chemistry 1st MonthDocument5 pagesReviewer For General Chemistry 1st MonthAhrron CapistranoNo ratings yet
- Unique Characteristics of MatterDocument20 pagesUnique Characteristics of Mattercaeameko:)0% (2)
- Chem. Lesson 1Document31 pagesChem. Lesson 1Ashlee Talento100% (1)
- Science8 Q3 W1-8Document30 pagesScience8 Q3 W1-8Maricar agawa GuntanNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem q1 w1 2Document7 pagesGen Chem q1 w1 2ARIEL ANGELIONo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Introduction To Matter: Ex. Water Into Ice CubeDocument4 pagesChapter 1: Introduction To Matter: Ex. Water Into Ice CubeIvan NenadicNo ratings yet
- Physical Science NotesDocument143 pagesPhysical Science NotesNelsonMoseMNo ratings yet
- IX Class NotesDocument60 pagesIX Class NotesNitin ThakurNo ratings yet
- Unit 01 Chapter 2Document86 pagesUnit 01 Chapter 2Pauline BatanayNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument32 pagesChemistryAndrei Angelo PantigNo ratings yet
- MatterDocument5 pagesMattererikaNo ratings yet
- Gen-Chem-1 Handout Q1 Week1Document4 pagesGen-Chem-1 Handout Q1 Week1Daphnie Pauleen PalomarNo ratings yet
- Ros Unit 2 Matter and EnergyDocument18 pagesRos Unit 2 Matter and EnergyNina GanapaoNo ratings yet
- For Prints in ScienceDocument20 pagesFor Prints in Sciencenbqp6p9v6pNo ratings yet
- Física I. T2Document7 pagesFísica I. T2Simona FourtakNo ratings yet
- Física I. T2Document7 pagesFísica I. T2Simona FourtakNo ratings yet
- 2 Matter: Solids: Liquids: Liquids Take On The Shape of Their Container But Do Not Change Their Volume. For ExampleDocument5 pages2 Matter: Solids: Liquids: Liquids Take On The Shape of Their Container But Do Not Change Their Volume. For ExampleRegz GasparNo ratings yet
- Matter - LessonDocument4 pagesMatter - LessonAnonymous hWtQueEyxNo ratings yet
- Chemestry: Matter Is Anything That Has Mass and Takes Up Space. A Book Is Matter, ADocument6 pagesChemestry: Matter Is Anything That Has Mass and Takes Up Space. A Book Is Matter, ADiana RevillaNo ratings yet
- GENERAL CHEMISTRY 1 - Lesson 1Document8 pagesGENERAL CHEMISTRY 1 - Lesson 1Fernandez, Nadine Kate T.No ratings yet
- Lesson 3 State Classifications and Properties of MatterDocument40 pagesLesson 3 State Classifications and Properties of MatterAngel MaeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Matter and Its PropertiesDocument7 pagesChapter 2 Matter and Its PropertiesJennelyn BaylonNo ratings yet
- Children Encyclopedia Chemistry: The World of KnowledgeFrom EverandChildren Encyclopedia Chemistry: The World of KnowledgeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- The Solid Truth about States of Matter with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceFrom EverandThe Solid Truth about States of Matter with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNo ratings yet
- Crust MovementsDocument2 pagesCrust MovementsMr Robert G.No ratings yet
- Air & GasesDocument3 pagesAir & GasesMr Robert G.No ratings yet
- Acids & BasesDocument4 pagesAcids & BasesMr Robert G.No ratings yet
- PRE1ADocument1 pagePRE1AMr Robert G.No ratings yet
- Acid RainDocument3 pagesAcid RainMr Robert G.No ratings yet
- Acid Rain 11Document3 pagesAcid Rain 11Mr Robert G.No ratings yet
- Europe Geo & ClimateDocument1 pageEurope Geo & ClimateMr Robert G.No ratings yet