Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Diodes
Diodes
Uploaded by
azas asdCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Commissioning Quick Reference - PMI Auto-TuningDocument28 pagesCommissioning Quick Reference - PMI Auto-TuningDariusNo ratings yet
- Certified Secure Computer User Exam Question PrepareDocument5 pagesCertified Secure Computer User Exam Question Preparekouassi joel100% (2)
- ANDROID TERMINAL EMULATOR CODES - Tech Blog PDFDocument9 pagesANDROID TERMINAL EMULATOR CODES - Tech Blog PDFgjino67% (3)
- Syllabus CEA201 Spring 2022Document15 pagesSyllabus CEA201 Spring 2022Dang Hoang Viet (K17 HCM)No ratings yet
- Wireless Power Transfer Project by Pradeep VishnoiDocument23 pagesWireless Power Transfer Project by Pradeep VishnoiPradeep Vishnoi82% (17)
- Basic Electronics ECE 1051: Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering 1Document41 pagesBasic Electronics ECE 1051: Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering 1Nilabha DasNo ratings yet
- BASIC ELECTRONICS - Notes-M1Document18 pagesBASIC ELECTRONICS - Notes-M1Mr SpamNo ratings yet
- Lec05 SSMDDocument18 pagesLec05 SSMDTayyaba SaharNo ratings yet
- 12.diode CharacteristicsDocument8 pages12.diode CharacteristicsRaja KumarNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - DiodeDocument43 pagesModule 1 - DiodeSarthak ShastriNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3-PN JunctionDocument59 pagesLecture 3-PN JunctionKarimovaRaikhanovnaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 02Document4 pagesExperiment 02S sarkerNo ratings yet
- Sai Eshwar ReportDocument45 pagesSai Eshwar ReportSaieshwar MNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4 Study V-I Characteristics of P-N Junction DiodeDocument7 pagesExperiment 4 Study V-I Characteristics of P-N Junction DiodeTushar Sharma100% (1)
- Automotive Electrical-Electronic Systems: Fundamentals of Electrics & ElectronicsDocument55 pagesAutomotive Electrical-Electronic Systems: Fundamentals of Electrics & ElectronicsMinh TríNo ratings yet
- COMSATS Institute of Information Technology Virtual Campus IslamabadDocument47 pagesCOMSATS Institute of Information Technology Virtual Campus Islamabadrizwanspirit11No ratings yet
- Edic Lecture 1 03082005Document71 pagesEdic Lecture 1 03082005Dipin MutrejaNo ratings yet
- Lecture-9 Bio Potential ElectrodesDocument30 pagesLecture-9 Bio Potential Electrodesmdhawan1be20No ratings yet
- Diode ActionDocument6 pagesDiode ActionRashid Rind Rashid RindNo ratings yet
- CH1 Module1 DiodesDocument54 pagesCH1 Module1 DiodesParidhi kothariNo ratings yet
- EC Unit 1 Slides 4 in 1Document18 pagesEC Unit 1 Slides 4 in 1Abhishek MagadumNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 2: To Obtain V-I Characteristics of PN Junction Diode. Lab ObjectiveDocument5 pagesExperiment No. 2: To Obtain V-I Characteristics of PN Junction Diode. Lab ObjectiveMohsin Iqbal Department of Electrical EngineeringNo ratings yet
- STI 2024 DIODES, BJT and MOSFET SMALL VARYING SIGNALSDocument15 pagesSTI 2024 DIODES, BJT and MOSFET SMALL VARYING SIGNALSArthur MoloNo ratings yet
- TransistorsaDocument44 pagesTransistorsaazas asdNo ratings yet
- Selvam College of Technology, Namakkal - 03 PH: 9942099122Document28 pagesSelvam College of Technology, Namakkal - 03 PH: 9942099122Anusooya VNo ratings yet
- Electronics Chap TWODocument36 pagesElectronics Chap TWOERMIAS AmanuelNo ratings yet
- 371 Lab3Document7 pages371 Lab3m33320022No ratings yet
- Conductors-Dielectrics & CapacitanceDocument34 pagesConductors-Dielectrics & Capacitancepradeepvinaik kodavantiNo ratings yet
- Lab ProjectDocument20 pagesLab ProjectTanveerNo ratings yet
- EX # 2 (PN Diode)Document7 pagesEX # 2 (PN Diode)manishNo ratings yet
- ECE 301 Electronics 1: Measurement TolerancesDocument17 pagesECE 301 Electronics 1: Measurement TolerancesVince Hugo GutibNo ratings yet
- Analog ElectronicsDocument24 pagesAnalog ElectronicsDiptoNo ratings yet
- EXP1 PN Junction Diode CharacteristicsDocument8 pagesEXP1 PN Junction Diode Characteristicsحيدر محمدNo ratings yet
- EXP1 PN Junction Diode CharacteristicsDocument8 pagesEXP1 PN Junction Diode CharacteristicsMohammed Dyhia AliNo ratings yet
- UG - EE 2109 - CH 1 - 2023Document34 pagesUG - EE 2109 - CH 1 - 2023tahmidjewel708No ratings yet
- Module 1 Lecture 2.1 Band Formation & N Type SemiconductorDocument11 pagesModule 1 Lecture 2.1 Band Formation & N Type SemiconductorAjay KumarNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1 & 2 PDFDocument50 pagesUnit - 1 & 2 PDFSharmila ArunNo ratings yet
- UNIT3 DiodeDocument8 pagesUNIT3 DiodeOumar MandodjoNo ratings yet
- Basic ElectronicsDocument209 pagesBasic Electronicsrajatjhalani100% (1)
- Sanjay Rathore: Wireless Power TransferDocument24 pagesSanjay Rathore: Wireless Power TransferKamlesh100% (1)
- Lab Manual Electronic Devices and Circuits Practical 2Document10 pagesLab Manual Electronic Devices and Circuits Practical 2Engr Zaryab WarraichNo ratings yet
- 2 PN in Reverse BiasDocument18 pages2 PN in Reverse Biasdeathride007No ratings yet
- Field Effect TransistorsDocument73 pagesField Effect TransistorsDan ChapsNo ratings yet
- EEE 121 Lec 6Document33 pagesEEE 121 Lec 6Kenneth DalionNo ratings yet
- Electronic Materials: Chapter 4: Semiconductor DevicesDocument25 pagesElectronic Materials: Chapter 4: Semiconductor Deviceschinh buiNo ratings yet
- P-N DiodeDocument48 pagesP-N DiodeAnita PatelNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor Materials: ContentDocument42 pagesSemiconductor Materials: ContentNguyên Nguyễn SơnNo ratings yet
- VI Characteristics of DiodeDocument5 pagesVI Characteristics of DiodeRashid Rind Rashid RindNo ratings yet
- Unit-2 Junction DiodeDocument55 pagesUnit-2 Junction DiodeShubhangBaghelNo ratings yet
- 1.2 DiodesDocument32 pages1.2 DiodesMargaret lian Celeste BisaresNo ratings yet
- Anmicrowave Engineering Unit 2 Lec I 160821 - Ravi KiranBDocument9 pagesAnmicrowave Engineering Unit 2 Lec I 160821 - Ravi KiranBravi kiranNo ratings yet
- EIE101R01: Basic Electronics Engineering: Textbook and MaterialsDocument7 pagesEIE101R01: Basic Electronics Engineering: Textbook and MaterialsAdal ArasuNo ratings yet
- Be Com NotesDocument206 pagesBe Com NotesSiddharth MayyaNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: Arunai Engineering College TiruvannamalaiDocument56 pagesElectronic Devices and Circuits: Arunai Engineering College TiruvannamalaiKannan TindivanamNo ratings yet
- P-N Junction Diode Baising and Its VI CharacteristicsDocument12 pagesP-N Junction Diode Baising and Its VI Characteristicsvihan shahNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical EngineeringDocument145 pagesBasic Electrical EngineeringAkash GolwalkarNo ratings yet
- Be8253 - Unit 4Document28 pagesBe8253 - Unit 4balajiNo ratings yet
- Basic 22 M-1 - 430971214478751498Document55 pagesBasic 22 M-1 - 430971214478751498Naveen SettyNo ratings yet
- Eee1 2s1819 Lec10 Semicon 190312Document21 pagesEee1 2s1819 Lec10 Semicon 190312Rhona Liza CruzNo ratings yet
- MC 40 Vineet Exp05Document7 pagesMC 40 Vineet Exp05Sangeeta MankaniNo ratings yet
- 01 - PN Junction Diode CharacteristicsDocument26 pages01 - PN Junction Diode CharacteristicsVarsha PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisFrom EverandElectromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisNo ratings yet
- Course Plan: Department of MathematicsDocument21 pagesCourse Plan: Department of Mathematicsazas asdNo ratings yet
- DownloadDocument4 pagesDownloadazas asdNo ratings yet
- Time Table 2nd Sem B.E 2022-2023 01.04.23Document18 pagesTime Table 2nd Sem B.E 2022-2023 01.04.23azas asdNo ratings yet
- TransistorsaDocument44 pagesTransistorsaazas asdNo ratings yet
- SF500 InstructionDocument142 pagesSF500 InstructionDonig FermanianNo ratings yet
- Cisco GPLDocument3,506 pagesCisco GPLOdranoelGomesNo ratings yet
- hw2 Sols Ece570 w14Document9 pageshw2 Sols Ece570 w14dzakybdNo ratings yet
- VSP 70-04-01-00-M114Document71 pagesVSP 70-04-01-00-M114imkzbyNo ratings yet
- Iclcok360 PDFDocument2 pagesIclcok360 PDFchan_thong_1No ratings yet
- KSC5603D NPN Silicon Transistor, Planar Silicon Transistor: FeaturesDocument5 pagesKSC5603D NPN Silicon Transistor, Planar Silicon Transistor: FeaturesParag IngleNo ratings yet
- Specification RMA801Document11 pagesSpecification RMA801Mario AlcanatarNo ratings yet
- X1 User Manual V1.7Document105 pagesX1 User Manual V1.7Sandiego GomesNo ratings yet
- Data Models: Preface XVDocument8 pagesData Models: Preface XVSwapnil KumbharNo ratings yet
- Laput EE323 Quiz-2Document2 pagesLaput EE323 Quiz-2Gabriel GabuyaNo ratings yet
- AMD Operation Scorpius - The Legend of FXDocument12 pagesAMD Operation Scorpius - The Legend of FXCentrale3DNo ratings yet
- C++ Worksheet 2Document2 pagesC++ Worksheet 2Hanan FuadNo ratings yet
- Schematics (Rev 2)Document11 pagesSchematics (Rev 2)Charles AustinNo ratings yet
- HCIA 4.5 DumpDocument75 pagesHCIA 4.5 DumpAyoub MIINo ratings yet
- Sanyo Eb8-A Ce21dn9fDocument26 pagesSanyo Eb8-A Ce21dn9fvideosonNo ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet CollectionDocument35 pagesCheat Sheet CollectionwerdegastNo ratings yet
- OciuldrDocument10 pagesOciuldrjspiderNo ratings yet
- Fast Fourier Transform On HexagonsDocument7 pagesFast Fourier Transform On HexagonsYufangNo ratings yet
- Rajagiri School of Engineering and Technology: Rajagiri Valley, Kakkanad. Third SemesterDocument37 pagesRajagiri School of Engineering and Technology: Rajagiri Valley, Kakkanad. Third SemesterAmrita VenkitaramaniNo ratings yet
- MCQS On Power Electronics 1Document3 pagesMCQS On Power Electronics 1Ameen Ullah100% (1)
- Armv8-A External DebugDocument25 pagesArmv8-A External Debugnhv_lhNo ratings yet
- SDG Implementers GuideDocument260 pagesSDG Implementers GuideJeevanandhamNo ratings yet
- MDPF DocumentationDocument60 pagesMDPF DocumentationSai KarthikNo ratings yet
- Inspiron 14z 5423 Reference Guide en UsDocument6 pagesInspiron 14z 5423 Reference Guide en Usjessy vergara hondaNo ratings yet
- Dr. C. Lakshmi Devasena, IBS HyderabadDocument31 pagesDr. C. Lakshmi Devasena, IBS Hyderabadsaket kumarNo ratings yet
- SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER 2 (Solved)Document8 pagesSAMPLE QUESTION PAPER 2 (Solved)Taru GoelNo ratings yet
Diodes
Diodes
Uploaded by
azas asdCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Diodes
Diodes
Uploaded by
azas asdCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 2
• Basic Components,Devices and applications
Basic Electronics (18EECF101)
2020-2021, Even Semester
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 1
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
Topic Learning Outcomes
• At the end of the topic the student should be
able to:
1.Discuss the characteristics of semiconductor Diode.
2.Realize simple applications such as rectifier, voltage regulator,
gates using diodes.
3.Analyze and compare various configurations of rectifier circuits
with respect to their performance parameters.
CO2.Describe the characteristics of semiconductor
devices and their applications in rectifiers, switches,
regulators, gates.
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 2
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
CONTENTS
1) P-N Junction diode
2) Diode characteristics
3) Diode approximations
4) Half wave rectifier
5) Full wave rectifier with two diodes
6) Bridge rectifier with four diodes
7) All three rectifiers with filter.
8) Zener diode as voltage regulator
9) Realization of logic gates using diodes.
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 3
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES
• P-N Junction diode
• Bipolar Junction Transistor- BJT
• Field Effect Transistor - FET
• Uni Junction Transistor- UJT
• MetalOxide Semiconductor FET - MOSFET
School of Electronics and Communication Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
05-05-2021 4
P-N Junction Diode
• P-N Junction diode is a two terminal device
formed by joining P type and N type
semiconductor materials and it allows current
flow in one direction only.
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 5
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
P-N Junction diode
• Symbol
Anode Cathode
+ -
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 6
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
P-N JUNCTION DIODE
P-Type N-Type
Majority carriers Holes Electrons
Minority carriers Electrons Holes
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 7
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
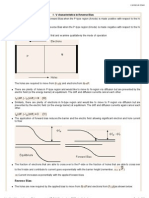
What is a Depletion region ?
• Depletion region or depletion layer is a region in a
P-N junction diode where no mobile charge carriers
are present. Depletion layer acts like a barrier that
opposes the flow of electrons from n-side and holes
from p-side
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 8
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
Forward Bias
https://circuitglobe.com
Forward bias means , the positive terminal of the
battery is connected to the p-type
semiconductor material and the negative terminal is
connected to the n-type
semiconductor material.Electrons in N type material gets
repelling force andSchool
05-05-2021 they startandmoving
of Electronics towards the
Communication
9
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
Reverse Bias
https://circuitglobe.com
Reverse bias means the n-type material is connected to the positive
terminal of the battery and the p-type material is connected to
the negative terminal .Electrons from N type,move away from junction
due to which depletion region widens and current cannot flow.
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 10
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
Reverse Bias
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 11
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 12
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
V-I Characteristics of diode
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 13
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
Parameters of diode
• Forward Voltage drop-VF
The diode forward voltage is the drop in electrical voltage that occurs when
electrical current is conducted through a diode. Diodes are two-lead
semiconductor devices that conduct an electrical signal in one direction but
not the other.
• Maximum Forward current-
It is the maximum current that can flow in a diode when it is forward biased.
• Reverse saturation current-
This is the current flowing through the diode during reverse bias due to the
flow of minority charge carriers.
• Reverse breakdown voltage-
When the diode reverse voltage (VR) is sufficiently increased,the device goes
to reverse breakdown & it can destroy a diode unless the current is limited by
a resistor.
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 14
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
•
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 15
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
Problem1: Find the static resistance of the diode whose
characteristics is shown in Fig.when the forward current is 80mA
& reverse voltage is 40V.Cut-in-voltage is 0.35V
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 16
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
Solution
•
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 17
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
Diode Approximations
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 18
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
Piecewise linear model
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 19
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
Temperature effects on diode
• An increased temperature will result in a large number of broken covalent
bonds increasing the large number of majority and minority carriers. This
amounts to a diode current larger than its previous diode current. The
above phenomenon applies both to forward and reverse current.
• The effect of increased temperature on the characteristics curve of a
PN junction diode is as shown in figure. It may be noted that the forward
characteristics shifts upwards with increase in temperature. On the other
hand, the reverse characteristics shifts downwards with the increase in
temperature.
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 20
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 21
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
Effect on power dissipation
•
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 22
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
Power-Temperature curve
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 23
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
Problem2: Find the maximum forward current at 25oc & 65oc of a diode
with 600mW max.power dissipation at 25oc& a derating factor of
5mw/oc. Assume that the forward voltage drop remains constant at 0.6v
Solution
Given T1=25oc,PT1=600mW, T2=65oc D=5mw/oc
• PT1=VT1 X IT1 ( power dissipation at T1)
• IT1=PT1/VT1=600mW/0.6v= 1A
• PT2=PT1-(T2-T1) D
• =600mW-(65-25)5=400mW
• Hence current IT2=PT2/VT2=400mW/0.6v=667mA
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 24
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
Applications of diode
• RECTIFIERS:
A rectifier is an electronic device that converts AC voltage into
DC voltage. In other words, it converts alternating current to
direct current.
A rectifier is used in almost all electronic devices. Mostly it is
used to convert the mains voltage into DC voltage in the power
supply section.
Rectifiers are classified into two categories: Half Wave Rectifier
and Full Wave Rectifier
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 25
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
Half wave Rectifier
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 26
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
Half wave Rectifier working
• A step down transformer is used to convert high voltage A.C.
to low voltage A.C.and Voltage will be reduced as per the
turns ratio of primary & secondary of transformer.
• During the positive half cycle, the diode is under forward bias
condition and it conducts current through RL (Load
resistance). A voltage is developed across the load, which is
the same as the input AC signal of the positive half cycle.
• Alternatively, during the negative half cycle, the diode is under
reverse bias condition and there is no current flow through
the diode and RL.
• Hence the output voltage is pulsating DC voltage as shown in
Fig.
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 27
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
WAVEFORMS
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 28
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
Derivations
•
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 29
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
Derivation of average current Idc
•
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 30
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
Derivation of effective/rms current
Irms
•
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 31
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
•
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 32
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
Average/DC load voltage
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 33
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
RMS Load voltage
•
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 34
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
Ripple Factor
•
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 35
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
•
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 36
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
•
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 37
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
Rectification Efficiency
•
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 38
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
•
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 39
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
Problem 3: A diode whose internal resistance is 20Ω,is used
to supply power to a 1000 Ω load in a H.W.Rectifier ckt. From
a 110V(rms)source of supply. Calculate
a)Peak load current
b)DC load current
c)AC load current
d)DC load voltage
e)Rms load voltage
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 40
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
Solution
•
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 41
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
•
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 42
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
Center-tapped Full wave Rectifier
using two diodes
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 43
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
Full wave Rectifier working
• The input AC supplied to the full wave rectifier is very high. The step-down
transformer in the rectifier circuit converts the high voltage AC into low voltage AC.
• The anode of the centre tapped diodes is connected to the transformer’s secondary
winding and connected to the load resistor. During the positive half cycle of the
alternating current, the top half of the secondary winding becomes positive while
the second half of the secondary winding becomes negative.
• During the positive half cycle, diode D1 is forward biased as it is connected to the top
of the secondary winding while diode D2 is reverse biased as it is connected to the
bottom of the secondary winding. Due to this, diode D1 will conduct acting as a short
circuit and D2 will not conduct acting as an open circuit
• During the negative half cycle, the diode D1 is reverse biased and the diode D2 is
forward biased because the top half of the secondary circuit becomes negative and
the bottom half of the circuit becomes positive. Thus in a full wave rectifiers, DC
voltage is obtained for both positive and negative half cycle.
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 44
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
Waveforms
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 45
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
Derivations
•
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 46
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
•
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 47
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
•
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 48
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
•
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 49
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
Average/DC load voltage
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 50
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
RMS Load voltage
•
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 51
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
Ripple Factor
•
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 52
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
•
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 53
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
•
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 54
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
Rectification Efficiency
•
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 55
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
•
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 56
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
Problem4:A Full wave Rectifier with two diodes having internal
resistance of 500 & load resistance of 2000.the secondary
voltage wrt center tap is 280V/calculate
a)Peak load current
b)DC load current
c)AC load current
d)DC load voltage
e)Rms load voltage
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 57
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
Solution
•
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 58
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
•
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 59
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
Bridge Rectifier
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 60
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
Bridge Rectifier Working
• When an AC signal is applied across the bridge rectifier, during the positive
half cycle, terminal A becomes positive while terminal B becomes
negative. This results in diodes D1 and D2 to become forward biased while
D3 and D4 become reverse biased.
• The current flow during the positive half-cycle is shown in the figure .
• During the negative half-cycle, terminal B becomes positive while the
terminal A becomes negative. This causes diodes D3 and D4 to become
forward biased and diode D1 and D2 to be reverse biased.
• The current flow during the negative half cycle is shown in the figure .
• Hence there is a current flow in both half cycles through the load and
hence we call it as full wave rectifier.
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 61
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
Waveforms
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 62
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
Bridge Rectifier parameters
•
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 63
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
• Problem5:a Full wave bridge rectifier,with load
resistance 100 is driven by source voltage of
100V,50HzNeglecting diode
resistances,calculate
a)average output voltage
b)average load current
c)frequency of output wavefoem
d)dc power output
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 64
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
•
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 65
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
Half-Wave Rectifier with Filter
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 66
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
Working
• Rectifier without filter produces pulsating DC. It fluctuates with respect to time.
When this fluctuating Direct Current (DC) is applied to any electronic device, the
device may not work properly. Sometimes the device may also be damaged. So
the fluctuating Direct Current (DC) is not useful in most of the applications.
Hence rectifier with filter is used which reduces the pulsations called ripples.
• During positive half cycle of input, the diode is forward biased and current flows through
the diode as well as capacitor, due to this, capacitor charges till Vm,the peak value of
transformer secondary voltage. When transformer secondary voltage falls below Vm,the
diode stops conducting. Now the capacitor discharges through the load RL and hence
current continues to flow through the load. This continues during entire negative half
cycle and till the transformer secondary voltage becomes more than the capacitor
discharged voltage.
• When the secondary voltage is more than the capacitor voltage, again the diode becomes
forward biased and starts conducting again, Now the capacitor starts charging again.
• This charging and dicharging of capacitor continues and the output is taken across the
load which is parallel to the capacitor. So the voltage across capacitor is now
smoothened,thus reducing the ripples.
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 67
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
Problem6:A H.W.Rectifier with capacitor filter is
supplying a resistive load of 500Ω.If the load ripple
content should not exceed 10%,find the value of
capacitance required,The supplyFrequency is 50 Hz
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 68
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
Full Wave Rectifier with Filter
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 69
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
Rectifier with filter waveforms
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 70
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
Problem7:In a Full wave rectifier with filter,the load
current from the circuit operating from 230V,50 Hz
supply is 10mA,Estimate the value of capacitance
required to keep the ripple factor below 1%
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 71
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
•
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 72
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
Bridge Rectifier with Filter
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 73
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
Problem8:A bridge rectifier with filter,supplies a load of
400Ω in parallel with a capacitor of 500μF.If the ac supply
voltage is 230sin314tV,find the
a)Ripple factor and
b)DC load current
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 74
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
•
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 75
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
Zener diode as Voltage Regulator
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 76
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
working
• Zener diode is a silicon semiconductor with a p-n junction that
is specifically designed to work in the reverse biased
condition. When forward biased, it behaves like a normal
signal diode, but when the reverse voltage is applied to it, the
voltage remains constant for a wide range of currents.
• Due to this feature, it is used as a voltage regulator in d.c.
circuit. The primary objective of the Zener diode as a voltage
regulator is to maintain a constant output voltage in spite of
any fluctuations at input side voltage. Let us say if Zener
voltage of 5 V is used then, the voltage becomes constant at 5
V, and it does not change.
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 77
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
•
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 78
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
•
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 79
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
Problem9:Design a zener diode voltage regulator to meet the following
specifications
dc input voltage Vi=20V-30V
dc output voltageVo=10V
Load current IL=0-25mA
Izmin=2mA
Izmax=100mA
Solution:
• Here, Vimin=20V, Vimax=30V
• ILmax=25mA, ILmin=0
• V0=10V
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 80
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
•
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 81
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
Realization of Logic gates using Diodes
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 82
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
AND gate truth table
Fig,C Fig.d
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 83
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
OR Gate Working:
• Refer Fig a.Fig d(Truth Table)
• When either of the inputs A,B,C is logic
‘1’(5V),current flows through the diode & the
resistor R. hence there is a voltage drop across
R, Vo=I x R=5v
• If all inputs are at logic ‘0’, no current flows
through the diodes and ‘R’,hence voltage drop
across ‘R’ is 0.
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 84
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
AND Gate Working
• ReferFig. b,c
• Output is taken at anode of diode.
• When either of the inputs A,B,C is logic
‘1’(5V),current flows through the diode & the
resistor R. hence there is a voltage drop across R,
and voltage at anode is at ‘0’ level
• If all inputs are at logic ‘1’, no current flows
through the diodes and ‘R’,hence voltage drop
across ‘R’ is 0.and voltage at anode is at logic’1’
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 85
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
School of Electronics and Communication
05-05-2021 86
Engineering, 2020-2021 Even
You might also like
- Commissioning Quick Reference - PMI Auto-TuningDocument28 pagesCommissioning Quick Reference - PMI Auto-TuningDariusNo ratings yet
- Certified Secure Computer User Exam Question PrepareDocument5 pagesCertified Secure Computer User Exam Question Preparekouassi joel100% (2)
- ANDROID TERMINAL EMULATOR CODES - Tech Blog PDFDocument9 pagesANDROID TERMINAL EMULATOR CODES - Tech Blog PDFgjino67% (3)
- Syllabus CEA201 Spring 2022Document15 pagesSyllabus CEA201 Spring 2022Dang Hoang Viet (K17 HCM)No ratings yet
- Wireless Power Transfer Project by Pradeep VishnoiDocument23 pagesWireless Power Transfer Project by Pradeep VishnoiPradeep Vishnoi82% (17)
- Basic Electronics ECE 1051: Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering 1Document41 pagesBasic Electronics ECE 1051: Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering 1Nilabha DasNo ratings yet
- BASIC ELECTRONICS - Notes-M1Document18 pagesBASIC ELECTRONICS - Notes-M1Mr SpamNo ratings yet
- Lec05 SSMDDocument18 pagesLec05 SSMDTayyaba SaharNo ratings yet
- 12.diode CharacteristicsDocument8 pages12.diode CharacteristicsRaja KumarNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - DiodeDocument43 pagesModule 1 - DiodeSarthak ShastriNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3-PN JunctionDocument59 pagesLecture 3-PN JunctionKarimovaRaikhanovnaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 02Document4 pagesExperiment 02S sarkerNo ratings yet
- Sai Eshwar ReportDocument45 pagesSai Eshwar ReportSaieshwar MNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4 Study V-I Characteristics of P-N Junction DiodeDocument7 pagesExperiment 4 Study V-I Characteristics of P-N Junction DiodeTushar Sharma100% (1)
- Automotive Electrical-Electronic Systems: Fundamentals of Electrics & ElectronicsDocument55 pagesAutomotive Electrical-Electronic Systems: Fundamentals of Electrics & ElectronicsMinh TríNo ratings yet
- COMSATS Institute of Information Technology Virtual Campus IslamabadDocument47 pagesCOMSATS Institute of Information Technology Virtual Campus Islamabadrizwanspirit11No ratings yet
- Edic Lecture 1 03082005Document71 pagesEdic Lecture 1 03082005Dipin MutrejaNo ratings yet
- Lecture-9 Bio Potential ElectrodesDocument30 pagesLecture-9 Bio Potential Electrodesmdhawan1be20No ratings yet
- Diode ActionDocument6 pagesDiode ActionRashid Rind Rashid RindNo ratings yet
- CH1 Module1 DiodesDocument54 pagesCH1 Module1 DiodesParidhi kothariNo ratings yet
- EC Unit 1 Slides 4 in 1Document18 pagesEC Unit 1 Slides 4 in 1Abhishek MagadumNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 2: To Obtain V-I Characteristics of PN Junction Diode. Lab ObjectiveDocument5 pagesExperiment No. 2: To Obtain V-I Characteristics of PN Junction Diode. Lab ObjectiveMohsin Iqbal Department of Electrical EngineeringNo ratings yet
- STI 2024 DIODES, BJT and MOSFET SMALL VARYING SIGNALSDocument15 pagesSTI 2024 DIODES, BJT and MOSFET SMALL VARYING SIGNALSArthur MoloNo ratings yet
- TransistorsaDocument44 pagesTransistorsaazas asdNo ratings yet
- Selvam College of Technology, Namakkal - 03 PH: 9942099122Document28 pagesSelvam College of Technology, Namakkal - 03 PH: 9942099122Anusooya VNo ratings yet
- Electronics Chap TWODocument36 pagesElectronics Chap TWOERMIAS AmanuelNo ratings yet
- 371 Lab3Document7 pages371 Lab3m33320022No ratings yet
- Conductors-Dielectrics & CapacitanceDocument34 pagesConductors-Dielectrics & Capacitancepradeepvinaik kodavantiNo ratings yet
- Lab ProjectDocument20 pagesLab ProjectTanveerNo ratings yet
- EX # 2 (PN Diode)Document7 pagesEX # 2 (PN Diode)manishNo ratings yet
- ECE 301 Electronics 1: Measurement TolerancesDocument17 pagesECE 301 Electronics 1: Measurement TolerancesVince Hugo GutibNo ratings yet
- Analog ElectronicsDocument24 pagesAnalog ElectronicsDiptoNo ratings yet
- EXP1 PN Junction Diode CharacteristicsDocument8 pagesEXP1 PN Junction Diode Characteristicsحيدر محمدNo ratings yet
- EXP1 PN Junction Diode CharacteristicsDocument8 pagesEXP1 PN Junction Diode CharacteristicsMohammed Dyhia AliNo ratings yet
- UG - EE 2109 - CH 1 - 2023Document34 pagesUG - EE 2109 - CH 1 - 2023tahmidjewel708No ratings yet
- Module 1 Lecture 2.1 Band Formation & N Type SemiconductorDocument11 pagesModule 1 Lecture 2.1 Band Formation & N Type SemiconductorAjay KumarNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1 & 2 PDFDocument50 pagesUnit - 1 & 2 PDFSharmila ArunNo ratings yet
- UNIT3 DiodeDocument8 pagesUNIT3 DiodeOumar MandodjoNo ratings yet
- Basic ElectronicsDocument209 pagesBasic Electronicsrajatjhalani100% (1)
- Sanjay Rathore: Wireless Power TransferDocument24 pagesSanjay Rathore: Wireless Power TransferKamlesh100% (1)
- Lab Manual Electronic Devices and Circuits Practical 2Document10 pagesLab Manual Electronic Devices and Circuits Practical 2Engr Zaryab WarraichNo ratings yet
- 2 PN in Reverse BiasDocument18 pages2 PN in Reverse Biasdeathride007No ratings yet
- Field Effect TransistorsDocument73 pagesField Effect TransistorsDan ChapsNo ratings yet
- EEE 121 Lec 6Document33 pagesEEE 121 Lec 6Kenneth DalionNo ratings yet
- Electronic Materials: Chapter 4: Semiconductor DevicesDocument25 pagesElectronic Materials: Chapter 4: Semiconductor Deviceschinh buiNo ratings yet
- P-N DiodeDocument48 pagesP-N DiodeAnita PatelNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor Materials: ContentDocument42 pagesSemiconductor Materials: ContentNguyên Nguyễn SơnNo ratings yet
- VI Characteristics of DiodeDocument5 pagesVI Characteristics of DiodeRashid Rind Rashid RindNo ratings yet
- Unit-2 Junction DiodeDocument55 pagesUnit-2 Junction DiodeShubhangBaghelNo ratings yet
- 1.2 DiodesDocument32 pages1.2 DiodesMargaret lian Celeste BisaresNo ratings yet
- Anmicrowave Engineering Unit 2 Lec I 160821 - Ravi KiranBDocument9 pagesAnmicrowave Engineering Unit 2 Lec I 160821 - Ravi KiranBravi kiranNo ratings yet
- EIE101R01: Basic Electronics Engineering: Textbook and MaterialsDocument7 pagesEIE101R01: Basic Electronics Engineering: Textbook and MaterialsAdal ArasuNo ratings yet
- Be Com NotesDocument206 pagesBe Com NotesSiddharth MayyaNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: Arunai Engineering College TiruvannamalaiDocument56 pagesElectronic Devices and Circuits: Arunai Engineering College TiruvannamalaiKannan TindivanamNo ratings yet
- P-N Junction Diode Baising and Its VI CharacteristicsDocument12 pagesP-N Junction Diode Baising and Its VI Characteristicsvihan shahNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical EngineeringDocument145 pagesBasic Electrical EngineeringAkash GolwalkarNo ratings yet
- Be8253 - Unit 4Document28 pagesBe8253 - Unit 4balajiNo ratings yet
- Basic 22 M-1 - 430971214478751498Document55 pagesBasic 22 M-1 - 430971214478751498Naveen SettyNo ratings yet
- Eee1 2s1819 Lec10 Semicon 190312Document21 pagesEee1 2s1819 Lec10 Semicon 190312Rhona Liza CruzNo ratings yet
- MC 40 Vineet Exp05Document7 pagesMC 40 Vineet Exp05Sangeeta MankaniNo ratings yet
- 01 - PN Junction Diode CharacteristicsDocument26 pages01 - PN Junction Diode CharacteristicsVarsha PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisFrom EverandElectromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisNo ratings yet
- Course Plan: Department of MathematicsDocument21 pagesCourse Plan: Department of Mathematicsazas asdNo ratings yet
- DownloadDocument4 pagesDownloadazas asdNo ratings yet
- Time Table 2nd Sem B.E 2022-2023 01.04.23Document18 pagesTime Table 2nd Sem B.E 2022-2023 01.04.23azas asdNo ratings yet
- TransistorsaDocument44 pagesTransistorsaazas asdNo ratings yet
- SF500 InstructionDocument142 pagesSF500 InstructionDonig FermanianNo ratings yet
- Cisco GPLDocument3,506 pagesCisco GPLOdranoelGomesNo ratings yet
- hw2 Sols Ece570 w14Document9 pageshw2 Sols Ece570 w14dzakybdNo ratings yet
- VSP 70-04-01-00-M114Document71 pagesVSP 70-04-01-00-M114imkzbyNo ratings yet
- Iclcok360 PDFDocument2 pagesIclcok360 PDFchan_thong_1No ratings yet
- KSC5603D NPN Silicon Transistor, Planar Silicon Transistor: FeaturesDocument5 pagesKSC5603D NPN Silicon Transistor, Planar Silicon Transistor: FeaturesParag IngleNo ratings yet
- Specification RMA801Document11 pagesSpecification RMA801Mario AlcanatarNo ratings yet
- X1 User Manual V1.7Document105 pagesX1 User Manual V1.7Sandiego GomesNo ratings yet
- Data Models: Preface XVDocument8 pagesData Models: Preface XVSwapnil KumbharNo ratings yet
- Laput EE323 Quiz-2Document2 pagesLaput EE323 Quiz-2Gabriel GabuyaNo ratings yet
- AMD Operation Scorpius - The Legend of FXDocument12 pagesAMD Operation Scorpius - The Legend of FXCentrale3DNo ratings yet
- C++ Worksheet 2Document2 pagesC++ Worksheet 2Hanan FuadNo ratings yet
- Schematics (Rev 2)Document11 pagesSchematics (Rev 2)Charles AustinNo ratings yet
- HCIA 4.5 DumpDocument75 pagesHCIA 4.5 DumpAyoub MIINo ratings yet
- Sanyo Eb8-A Ce21dn9fDocument26 pagesSanyo Eb8-A Ce21dn9fvideosonNo ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet CollectionDocument35 pagesCheat Sheet CollectionwerdegastNo ratings yet
- OciuldrDocument10 pagesOciuldrjspiderNo ratings yet
- Fast Fourier Transform On HexagonsDocument7 pagesFast Fourier Transform On HexagonsYufangNo ratings yet
- Rajagiri School of Engineering and Technology: Rajagiri Valley, Kakkanad. Third SemesterDocument37 pagesRajagiri School of Engineering and Technology: Rajagiri Valley, Kakkanad. Third SemesterAmrita VenkitaramaniNo ratings yet
- MCQS On Power Electronics 1Document3 pagesMCQS On Power Electronics 1Ameen Ullah100% (1)
- Armv8-A External DebugDocument25 pagesArmv8-A External Debugnhv_lhNo ratings yet
- SDG Implementers GuideDocument260 pagesSDG Implementers GuideJeevanandhamNo ratings yet
- MDPF DocumentationDocument60 pagesMDPF DocumentationSai KarthikNo ratings yet
- Inspiron 14z 5423 Reference Guide en UsDocument6 pagesInspiron 14z 5423 Reference Guide en Usjessy vergara hondaNo ratings yet
- Dr. C. Lakshmi Devasena, IBS HyderabadDocument31 pagesDr. C. Lakshmi Devasena, IBS Hyderabadsaket kumarNo ratings yet
- SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER 2 (Solved)Document8 pagesSAMPLE QUESTION PAPER 2 (Solved)Taru GoelNo ratings yet