Professional Documents
Culture Documents
EXAMPLE Bar Graph
EXAMPLE Bar Graph
Uploaded by
Cy SyOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
EXAMPLE Bar Graph
EXAMPLE Bar Graph
Uploaded by
Cy SyCopyright:
Available Formats
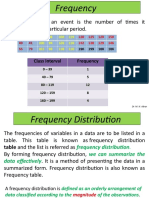
BAR GRAPH. It is a graph which uses horizontal or vertical bars to represent data.
It is a visual
display used to compare the frequency of occurrences of different characteristics of data. This type of graph
allows us to compare groups of data and make quick generalization about the data by examining the length of
the bars. Since only the lengths of the bars are important, the widths are all made equal. A gap between the
bars is spaced equally.
Steps to draw a bar graph:
1. To draw a bar graph, you to start with your frequency table.
2. From the frequency table, decide on the range and scale of the frequency data axis (vertical axis) and
the grouped data axis (horizontal axis)
3. Draw the vertical and horizontal axes and label them.
4. Write the graph title at the top.
5. Mark the data on the graph for each data group and draw the bar.
Example 2: Use the frequency table below to draw a bar graph.
Fruits Frequency Solution: Use the frequency table on the left to draw a bar graph.
Banana 35
Apple 23 The graph has a title and both axes are
Orange 18 labeled. Upon looking the graph, we can generalize quickly that the favorite fruit is
Grapes 45 grapes.
Guava 5 BAR GRAPH. It is a graph which uses horizontal or vertical bars to represent
data. It is a visual display used to compare the frequency of occurrences of different
characteristics of data. This type of graph allows us to compare groups of data and make quick generalization
about the data by examining the length of the bars. Since only the lengths of the bars are important, the
widths are all made equal. A gap between the bars is spaced equally.
Steps to draw a bar graph:
1. To draw a bar graph, you to start with your frequency table.
2. From the frequency table, decide on the range and scale of the frequency data axis (vertical axis) and
the grouped data axis (horizontal axis)
3. Draw the vertical and horizontal axes and label them.
4. Write the graph title at the top.
5. Mark the data on the graph for each data group and draw the bar.
Example 2: Use the frequency table below to draw a bar graph.
Fruits Frequency Solution: Use the frequency table on the left to draw a bar graph.
Banana 35
Apple 23 The graph has a title and both axes are
Orange 18 labeled. Upon looking the graph, we can generalize quickly that the favorite fruit is
Grapes 45 grapes.
Guava 5
Favorite Fruit
50
45
Favorite Fruit
40
50
35
45
30
Frequency
40
25
35
20
30
Frequency
15
25
10
20
5
15
0
10
5 Banana Apple Orange Grapes Guava
0
Fruits
Banana Apple Orange Grapes Guava
Fruits
You might also like
- M7Sp-Ivd-E-1: Bilbao-Uybico National High SchoolDocument3 pagesM7Sp-Ivd-E-1: Bilbao-Uybico National High SchoolRed Cruz100% (2)
- Numerical Communication WorkbookDocument77 pagesNumerical Communication WorkbookHugh Fox IIINo ratings yet
- Bar GraphDocument1 pageBar GraphCy SyNo ratings yet
- Bar Graph: Favorite FruitDocument1 pageBar Graph: Favorite FruitChristopher CabanagNo ratings yet
- Favorite Fruit: FruitsDocument1 pageFavorite Fruit: FruitsChristopher CabanagNo ratings yet
- Comp312 Chapter3 - BordonDocument14 pagesComp312 Chapter3 - BordonJULIUS BORDON100% (1)
- StatisticsDocument18 pagesStatisticsAndersonNo ratings yet
- Virtual University of PakistanDocument21 pagesVirtual University of PakistanABDUR -No ratings yet
- Presentation (STA102)Document19 pagesPresentation (STA102)Md.siful Islam Bhuiyan MahedyNo ratings yet
- 02-Descriptive StatisticsDocument17 pages02-Descriptive StatisticsAva FarjadNo ratings yet
- Unit 01 - Describing Data and Its Distributions - 1 Per PageDocument79 pagesUnit 01 - Describing Data and Its Distributions - 1 Per PageKase1No ratings yet
- Module 2 EDADocument12 pagesModule 2 EDAMa. Nerissa RabinoNo ratings yet
- CH2 - Sampling Methodologies and Frequency DistributionsDocument11 pagesCH2 - Sampling Methodologies and Frequency DistributionsGilbertoGarciaNo ratings yet
- Excercise 8Document2 pagesExcercise 8Daniel LuNo ratings yet
- 1.4! Frequency, Frequency Tables, and Levels of MeasurementDocument9 pages1.4! Frequency, Frequency Tables, and Levels of MeasurementDahanyakage WickramathungaNo ratings yet
- LESSON 4.2.1 Mean, Median and ModeDocument17 pagesLESSON 4.2.1 Mean, Median and ModeJayson Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- MA121-1 1 3-3rdDocument6 pagesMA121-1 1 3-3rdJunayed AzizNo ratings yet
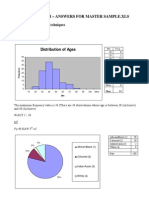
- Lfs Project I - Answers For Master Sample - XLS: Distribution of AgesDocument9 pagesLfs Project I - Answers For Master Sample - XLS: Distribution of AgesTshepiso Jamal AppieNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central Tendency GroupedDocument3 pagesMeasures of Central Tendency GroupedNoreenNo ratings yet
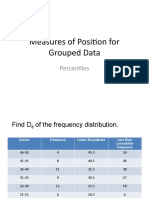
- ABSTRACTION Measures of Position For Grouped DataDocument7 pagesABSTRACTION Measures of Position For Grouped DataLeth AbagNo ratings yet
- FYM - DOE - Lecture #2 PDFDocument51 pagesFYM - DOE - Lecture #2 PDFNohaM.No ratings yet
- Data Arrangement and Presentation Formation of Tables and ChartsDocument55 pagesData Arrangement and Presentation Formation of Tables and ChartsNImra ShahNo ratings yet
- Applied Statistics and Data Analysis For Engineers (2143B) : Lecture 2: Graphical SummariesDocument30 pagesApplied Statistics and Data Analysis For Engineers (2143B) : Lecture 2: Graphical SummariesJoerg OxboroughNo ratings yet
- Robability and TatisticsDocument31 pagesRobability and TatisticsVan TranNo ratings yet
- cn4212 1Document35 pagescn4212 1upk civilNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios Faciles Fraction To PercentagesDocument2 pagesEjercicios Faciles Fraction To PercentagesJhonathan GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Lec 2Document43 pagesLec 2Muhammad AbubakerNo ratings yet
- BBS11 PPT ch02Document42 pagesBBS11 PPT ch02GUNJAN YADAVNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Probability and StatisticsDocument30 pagesIntroduction To Probability and StatisticsChe RryNo ratings yet
- Tools of Quality PDFDocument17 pagesTools of Quality PDFArivanandanNo ratings yet
- 03 - Data Table and Graphing Notes Key 1Document8 pages03 - Data Table and Graphing Notes Key 1api-292000448No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 NotesDocument3 pagesChapter 2 NotesCharlie RNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01Document30 pagesChapter 01Genelle Mae MadrigalNo ratings yet
- Bar GraphDocument7 pagesBar GraphVioleta RagiloNo ratings yet
- 2-Presentation of DataDocument62 pages2-Presentation of Dataمنوعات ساياNo ratings yet
- Tabular and Graphical Presentation of Data1Document7 pagesTabular and Graphical Presentation of Data1edniel maratas100% (1)
- Statistik Deskriptif Cara Penyajian DataDocument34 pagesStatistik Deskriptif Cara Penyajian Datariezea100% (23)
- Guide To In-Home Vision Testing: How To Set Up The TestsDocument9 pagesGuide To In-Home Vision Testing: How To Set Up The TestsSandeepNo ratings yet
- LAB#9Document6 pagesLAB#9FroPe GamingNo ratings yet
- No. Pre-Test Result Post-Test Result: Highest LowestDocument46 pagesNo. Pre-Test Result Post-Test Result: Highest LowestFRELYNNo ratings yet
- 119 125 Chapter 4.2 Data Management Presentation of DataDocument7 pages119 125 Chapter 4.2 Data Management Presentation of DataSamuel ContrerasNo ratings yet
- Math5 q2 Mod8Document19 pagesMath5 q2 Mod8Pia JalandoniNo ratings yet
- Stat 1&2Document35 pagesStat 1&2Owais KadiriNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Probability and Statistics Thirteenth EditionDocument30 pagesIntroduction To Probability and Statistics Thirteenth EditionMario Ricardo Urdaneta ParraNo ratings yet
- Stat DescrDocument51 pagesStat DescrDesryadi Ilyas MohammadNo ratings yet
- 0460 w22 QP 11-MergedDocument60 pages0460 w22 QP 11-MergedAnto Arkangel ClementsNo ratings yet
- Activitry 13 - Frequency Distribution TableDocument2 pagesActivitry 13 - Frequency Distribution Tabledoreethy manaloNo ratings yet
- Answer Key - Worksheet 2Document22 pagesAnswer Key - Worksheet 2aliNo ratings yet
- 8 Types of Progress Charts Excel CampusDocument36 pages8 Types of Progress Charts Excel Campusmaxx255117No ratings yet
- Chapter (2) Describing Data Frequency Distributions and Graphic Presentation ExamplesDocument10 pagesChapter (2) Describing Data Frequency Distributions and Graphic Presentation ExamplesABDUR REHMAN HUSSAIN KHANNo ratings yet
- Chapter (2) Describing Data Frequency Distributions and Graphic Presentation ExamplesDocument10 pagesChapter (2) Describing Data Frequency Distributions and Graphic Presentation ExamplesABDUR REHMAN HUSSAIN KHANNo ratings yet
- Diam 3 R 1Document1 pageDiam 3 R 1JORGE LUiS CAYO GUTIERREZNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Maths Unit 9Document11 pagesGrade 8 Maths Unit 9Kyal SinNo ratings yet
- Math 10 Q4 WK4 Las3Document1 pageMath 10 Q4 WK4 Las3HarleysheinNo ratings yet
- Learning Objectives: Descriptive StatisticsDocument17 pagesLearning Objectives: Descriptive StatisticsMuhammad IshaqNo ratings yet
- WEEK1Document36 pagesWEEK1Mesut ÇetinNo ratings yet
- Avl NewDocument31 pagesAvl NewBhupesh DhapolaNo ratings yet
- Math 7-Q4-Module-4Document15 pagesMath 7-Q4-Module-4Peterson Dela Cruz Enriquez100% (1)
- Statistical Process Control: Chapter ObjectivesDocument58 pagesStatistical Process Control: Chapter ObjectivesNidushan NethsaraNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Igcse Maths Stage 11 - StatisticsDocument9 pagesCambridge Igcse Maths Stage 11 - StatisticsMazuba ChibbelaNo ratings yet
- Week 45-PtMP-WiConnect-2021Document82 pagesWeek 45-PtMP-WiConnect-2021mogahedNo ratings yet
- Pie Graph5Document1 pagePie Graph5Cy SyNo ratings yet
- EXAMPLE OgiveDocument2 pagesEXAMPLE OgiveCy SyNo ratings yet
- EXAMPLE Line GraphDocument1 pageEXAMPLE Line GraphCy SyNo ratings yet
- EXAMPLE HistogramDocument2 pagesEXAMPLE HistogramCy SyNo ratings yet
- Bar GraphDocument1 pageBar GraphCy SyNo ratings yet
- Pie GraphDocument1 pagePie GraphCy SyNo ratings yet
- Line GraphDocument1 pageLine GraphCy SyNo ratings yet
- HistogramDocument1 pageHistogramCy SyNo ratings yet
- Pie Graph1Document1 pagePie Graph1Cy SyNo ratings yet
- Math3 PLPs Q4 Wk5 Day1-5-QA-doneDocument12 pagesMath3 PLPs Q4 Wk5 Day1-5-QA-doneGARZONI SOLONNo ratings yet
- WRITING TASK 1 - BOOK 1 (Charts With Trends)Document109 pagesWRITING TASK 1 - BOOK 1 (Charts With Trends)Nguyen Thi Tu TranNo ratings yet
- Tabular and Graphical Presentation Using Excel: 2.1 Summarizing Categorical DataDocument15 pagesTabular and Graphical Presentation Using Excel: 2.1 Summarizing Categorical DataAnna TaylorNo ratings yet
- Class XII (As Per CBSE Board) : Informatics PracticesDocument18 pagesClass XII (As Per CBSE Board) : Informatics PracticesShekh SultanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12Document31 pagesChapter 12John Muou Thuc Ruai100% (1)
- Assignment No:-01: Name:-Snehal - Satyavrat.Yadav ROLL - NO:-42Document12 pagesAssignment No:-01: Name:-Snehal - Satyavrat.Yadav ROLL - NO:-42poojaNo ratings yet
- NEW Lesson 3 in ST 2, Economics of Agriculture, December 25, 2023Document249 pagesNEW Lesson 3 in ST 2, Economics of Agriculture, December 25, 2023beberliepangandoyonNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Statistics (Reading)Document24 pagesIntroduction of Statistics (Reading)Riddhima VidayaNo ratings yet
- English 10 Lesson 2-1Document26 pagesEnglish 10 Lesson 2-1Liann James Doguiles100% (1)
- Bar GraphDocument15 pagesBar GraphKhan AmByNo ratings yet
- Bar Graph: Example 1 - Vertical Bar GraphsDocument9 pagesBar Graph: Example 1 - Vertical Bar GraphsHoney Jane Cantillas LumactodNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Using Visual Aids: Learning OutcomesDocument24 pagesUnit 4 Using Visual Aids: Learning OutcomesNur Haswani SufianNo ratings yet
- MATHEMATICS 4 LPDocument8 pagesMATHEMATICS 4 LPRic Adigue Official TVNo ratings yet
- STAT 111: Introduction To Statistics and Probability: Lecture 2: Data ReductionDocument28 pagesSTAT 111: Introduction To Statistics and Probability: Lecture 2: Data ReductionTrevor ChilmanNo ratings yet
- Data Collection and Bar GraphsDocument5 pagesData Collection and Bar Graphsapi-331862751No ratings yet
- Data Visualization How To Pick The Right Chart Type 1563473391Document16 pagesData Visualization How To Pick The Right Chart Type 1563473391Jasim C. RenquifoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Data VisualizationDocument9 pagesChapter 3 Data VisualizationAngela PonceNo ratings yet
- Bar Charts - Different TypesDocument6 pagesBar Charts - Different TypesBADAM NAVINA Finance2019No ratings yet
- AK - STATISTIKA - 01 - Describing DataDocument26 pagesAK - STATISTIKA - 01 - Describing DataMargareth SilvianaNo ratings yet
- Research II Q4 Module 4Document15 pagesResearch II Q4 Module 4Mhelet Dequito PachecoNo ratings yet
- STID1103 Computer Applications in Management: Topic 8 Chart & Graph (MS Excel)Document47 pagesSTID1103 Computer Applications in Management: Topic 8 Chart & Graph (MS Excel)Nur AthirahNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Data Science With R ProgrammingDocument91 pagesIntroduction To Data Science With R ProgrammingVimal KumarNo ratings yet
- QT Unit 4 PDFDocument23 pagesQT Unit 4 PDFmojnkuNo ratings yet
- IT Assignment 1Document3 pagesIT Assignment 1Neha KhanNo ratings yet
- (Use R!) Keon-Woong Moon - Learn Ggplot2 Using Shiny App (2017, Springer) PDFDocument356 pages(Use R!) Keon-Woong Moon - Learn Ggplot2 Using Shiny App (2017, Springer) PDFHoracio Miranda Vargas100% (3)
- KindergartenDocument18 pagesKindergartenTejas Jasani43% (7)
- Mathematics7 Q4 Mod3 PresentationofData-v3Document29 pagesMathematics7 Q4 Mod3 PresentationofData-v3charitocalangan605No ratings yet
- Bar Graphs and Pie ChartsDocument9 pagesBar Graphs and Pie ChartsMuhammad AwaisNo ratings yet