Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Group 6
Group 6
Uploaded by
Israel AyindeCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Sheet - 01 - DifferentiabilityDocument26 pagesSheet - 01 - DifferentiabilityMankirat SinghNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3: Differential Calculus: 1 Differentiable FunctionsDocument11 pagesCHAPTER 3: Differential Calculus: 1 Differentiable FunctionsJorge SotoNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan Ke 4 Kalkulus IDocument6 pagesPertemuan Ke 4 Kalkulus IBintang BintangNo ratings yet
- Problems On Limit of A FunctionDocument2 pagesProblems On Limit of A FunctionSwapnaneel BhattacharyyaNo ratings yet
- Optimization Lectures Formal NoteDocument9 pagesOptimization Lectures Formal NoteDebdas GhoshNo ratings yet
- Calculus NotesDocument7 pagesCalculus Notesjistoni tanNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Calculus Fall 23 SolutionDocument10 pagesFinal Exam Calculus Fall 23 SolutioneynullabeyliseymurNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3: Derivatives, Maxima and Minima, Rolle's TheoremDocument2 pagesAssignment 3: Derivatives, Maxima and Minima, Rolle's TheoremvishaldeepNo ratings yet
- UPSC Civil Services Main 1986 - Mathematics Calculus: Sunder LalDocument7 pagesUPSC Civil Services Main 1986 - Mathematics Calculus: Sunder Lalsayhigaurav07No ratings yet
- Limit and ContinuityDocument7 pagesLimit and ContinuityPrastut AryalNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 6 SolutionsDocument3 pagesProblem Set 6 SolutionsMengyao MaNo ratings yet
- UPSC Civil Services Main 1981 - Mathematics Calculus: Sunder LalDocument2 pagesUPSC Civil Services Main 1981 - Mathematics Calculus: Sunder Lalsayhigaurav07No ratings yet
- Ross SolutionsDocument12 pagesRoss Solutionssoumya mirdhaNo ratings yet
- Differentiation and Its Application: 2.1 Differentiability of A FunctionDocument18 pagesDifferentiation and Its Application: 2.1 Differentiability of A FunctionAnemesh BaruaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document2 pagesLecture 5anchal shuklaNo ratings yet
- 3-7 Graphs of Rational Functions With DetailsDocument12 pages3-7 Graphs of Rational Functions With DetailsRejieNo ratings yet
- Exercises MEF - 5 - 2018 - SolutionDocument6 pagesExercises MEF - 5 - 2018 - SolutionrtchuidjangnanaNo ratings yet
- Mat202 Tutorials Sheets IDocument7 pagesMat202 Tutorials Sheets ITaffohouo Nwaffeu Yves ValdezNo ratings yet
- Kuliah 4 IFDocument13 pagesKuliah 4 IFRAMADHAN WIJAYANo ratings yet
- Elementary MathematicsDocument17 pagesElementary MathematicsPankaj BiswasNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5Document2 pagesTutorial 5monkeyng.bmedNo ratings yet
- Sheet - 01 - Differentiability NJ - 247Document17 pagesSheet - 01 - Differentiability NJ - 2471qerfdNo ratings yet
- MTH4100 Calculus I: Lecture Notes For Week 5 Thomas' Calculus, Sections 2.6 To 3.5 Except 3.3Document10 pagesMTH4100 Calculus I: Lecture Notes For Week 5 Thomas' Calculus, Sections 2.6 To 3.5 Except 3.3Roy VeseyNo ratings yet
- 2.1 The Derivative of A FunctionDocument3 pages2.1 The Derivative of A Functiontinashembofana84No ratings yet
- Calculus Cheat Sheet Part 2Document4 pagesCalculus Cheat Sheet Part 2Dave Cloud100% (8)
- Math 111 - 5 One Sided Limits, ContinuityDocument12 pagesMath 111 - 5 One Sided Limits, ContinuityMuhamad PeshrawNo ratings yet
- Solutions From The PutnamDocument4 pagesSolutions From The PutnamSai GokulNo ratings yet
- Limits WorksheetDocument2 pagesLimits WorksheethjNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10Document11 pagesLecture 10muradNo ratings yet
- Pagadian Junior College (PJC), Inc.: Module 1: Week 1 Chapter 1-Limits and ContinuityDocument8 pagesPagadian Junior College (PJC), Inc.: Module 1: Week 1 Chapter 1-Limits and ContinuityJefferson PasanaNo ratings yet
- Lectures#5 9Document22 pagesLectures#5 9Jargalmaa ErdenemandakhNo ratings yet
- Ma1010 2014 PS 3Document2 pagesMa1010 2014 PS 3s rkNo ratings yet
- Cobb DouglasDocument14 pagesCobb DouglasRob WolfeNo ratings yet
- MTH4100 Calculus I: Lecture Notes For Week 9 Thomas' Calculus, Sections 4.6 To 5.2 Except 4.7Document11 pagesMTH4100 Calculus I: Lecture Notes For Week 9 Thomas' Calculus, Sections 4.6 To 5.2 Except 4.7Roy VeseyNo ratings yet
- Instantaneous Rate of Change - The DerivativeDocument7 pagesInstantaneous Rate of Change - The DerivativeTrishul GyNo ratings yet
- Final14 15M102EDocument1 pageFinal14 15M102EMohamad TouskaNo ratings yet
- UPSC Civil Services Main 1985 - Mathematics Calculus: Sunder LalDocument5 pagesUPSC Civil Services Main 1985 - Mathematics Calculus: Sunder Lalsayhigaurav07No ratings yet
- Test 1 SolDocument5 pagesTest 1 Solken20050324No ratings yet
- Sequence of Functions Counterexamples - Lecture Note - by SA 2021Document3 pagesSequence of Functions Counterexamples - Lecture Note - by SA 2021Fazal KarimNo ratings yet
- Block 1 MEC 003 Unit 2Document20 pagesBlock 1 MEC 003 Unit 2Abhishek PatraNo ratings yet
- MA 101 (Mathematics - I) : Differentiability: Exercise Set 1Document1 pageMA 101 (Mathematics - I) : Differentiability: Exercise Set 1AdityaNo ratings yet
- Function PDFDocument3 pagesFunction PDFDany DwNo ratings yet
- Soal UTS Madas BilingualDocument1 pageSoal UTS Madas BilingualJuwita PardedeNo ratings yet
- ECON6067 Problem Set 1 SolutionDocument2 pagesECON6067 Problem Set 1 SolutionMingtao ChenNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Analysis of Functions Increasing and Decreasing FunctionsDocument7 pages4.1 Analysis of Functions Increasing and Decreasing FunctionsAnemesh BaruaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10 Local Extrema and Points of InflectionDocument4 pagesLecture 10 Local Extrema and Points of InflectionShresth SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two-MATH122Document21 pagesChapter Two-MATH122Josiah GyanNo ratings yet
- CBSE I Succeed Math 12th SP11Document10 pagesCBSE I Succeed Math 12th SP11vk7820066No ratings yet
- Calc 1 Chapter 4Document11 pagesCalc 1 Chapter 4freakysnatchNo ratings yet
- Solutions Problem Set 1 (Diff)Document4 pagesSolutions Problem Set 1 (Diff)AdityaNo ratings yet
- Https App - Oswaalbooks.com Download Sample-Qp Subsolution 350SAP-3 SolDocument11 pagesHttps App - Oswaalbooks.com Download Sample-Qp Subsolution 350SAP-3 Sol3107aloksinghNo ratings yet
- Lec.9 DifferentiationDocument13 pagesLec.9 DifferentiationNajiba HamadNo ratings yet
- Revision Test 2Document39 pagesRevision Test 2Thabo InnocentNo ratings yet
- Exercises MEF - 4 - 2018 - SolutionDocument7 pagesExercises MEF - 4 - 2018 - SolutionrtchuidjangnanaNo ratings yet
- Continuity WSDocument11 pagesContinuity WSNarendra GaddamNo ratings yet
- Limits of FunctionsDocument31 pagesLimits of FunctionsMustafaNo ratings yet
- MA 101 (Mathematics - I) : Differentiation: Exercise Set 2Document1 pageMA 101 (Mathematics - I) : Differentiation: Exercise Set 2AdityaNo ratings yet
- Functional Operators (AM-22), Volume 2: The Geometry of Orthogonal Spaces. (AM-22)From EverandFunctional Operators (AM-22), Volume 2: The Geometry of Orthogonal Spaces. (AM-22)No ratings yet
- Transformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandTransformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
Group 6
Group 6
Uploaded by
Israel AyindeOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Group 6
Group 6
Uploaded by
Israel AyindeCopyright:
Available Formats
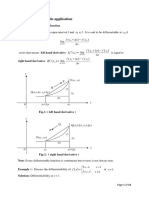
1.
Let f : R →R be a function defined by
{
x
f ( x )= e +asinx ,if ∧x <0
b (x−1)2 + x−2 , if ∧x ≥ 0
Find the values of a and b for which f is differentiable at x=0
SOLUTION
For f to be differentiable at x=0 , f must be continuous at x=0
That is left hand side limit must be equals to right hand side limit
lim ¿
That is x→ 0 −¿
f (x)= lim +¿
¿¿
x →0 f (x )¿
Solving for left hand side limit;
lim ¿
−¿
x→ 0 f (x)= lim ¿¿
x →0 (e + asinx) =e +asin ( 0)=1+ a(0 )=1¿
−¿ x 0
Solving for Right hand side limit;
+¿
lim ¿
x→ 0 f ( x )= lim ¿¿
x→0 +¿
[b (x−1) + x−2]=b(0−1) +0−2=b−2¿
2 2
Equating the two;
1=b−2
1+2=b
b=3
For f to be differentiable at x=0
' + ¿at x=0¿
That is f ' (x )−¿=f (x ) ¿
Solving for when f ( x)−¿=e +asinx , differentiating∧subtituting x=0 ;¿
x
f ' ( x )−¿=e +acos ( x)¿
0
f ' (0)−¿=e +acos (0 )¿
f ' ( 0)−¿=1+ a¿
Differentiating
2
Solving for when f ( x)+¿=b(x−1) +x−2 ,differ entiating∧ subtituting x=0 ;¿
' +¿=2 b ( x−1 ) +1 ¿
f (x)
Recall that b=3
' +¿=2(3) ( x−1 ) +1 ¿
f ( 0)
f ' ( x )+¿=6 ( x−1)+1 ¿
f ' ( 0 )+¿=6 (0−1) +1¿
' +¿=−6 +1 ¿
f ( x)
f ' ( x )+¿=−5 ¿
Equating the two;
' + ¿¿
' −¿=f (x ) ¿
f (x)
1+a=5
a=−6
Hence a=−6 and b=3 for which f is differentiable at x=0
You might also like
- Sheet - 01 - DifferentiabilityDocument26 pagesSheet - 01 - DifferentiabilityMankirat SinghNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3: Differential Calculus: 1 Differentiable FunctionsDocument11 pagesCHAPTER 3: Differential Calculus: 1 Differentiable FunctionsJorge SotoNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan Ke 4 Kalkulus IDocument6 pagesPertemuan Ke 4 Kalkulus IBintang BintangNo ratings yet
- Problems On Limit of A FunctionDocument2 pagesProblems On Limit of A FunctionSwapnaneel BhattacharyyaNo ratings yet
- Optimization Lectures Formal NoteDocument9 pagesOptimization Lectures Formal NoteDebdas GhoshNo ratings yet
- Calculus NotesDocument7 pagesCalculus Notesjistoni tanNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Calculus Fall 23 SolutionDocument10 pagesFinal Exam Calculus Fall 23 SolutioneynullabeyliseymurNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3: Derivatives, Maxima and Minima, Rolle's TheoremDocument2 pagesAssignment 3: Derivatives, Maxima and Minima, Rolle's TheoremvishaldeepNo ratings yet
- UPSC Civil Services Main 1986 - Mathematics Calculus: Sunder LalDocument7 pagesUPSC Civil Services Main 1986 - Mathematics Calculus: Sunder Lalsayhigaurav07No ratings yet
- Limit and ContinuityDocument7 pagesLimit and ContinuityPrastut AryalNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 6 SolutionsDocument3 pagesProblem Set 6 SolutionsMengyao MaNo ratings yet
- UPSC Civil Services Main 1981 - Mathematics Calculus: Sunder LalDocument2 pagesUPSC Civil Services Main 1981 - Mathematics Calculus: Sunder Lalsayhigaurav07No ratings yet
- Ross SolutionsDocument12 pagesRoss Solutionssoumya mirdhaNo ratings yet
- Differentiation and Its Application: 2.1 Differentiability of A FunctionDocument18 pagesDifferentiation and Its Application: 2.1 Differentiability of A FunctionAnemesh BaruaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document2 pagesLecture 5anchal shuklaNo ratings yet
- 3-7 Graphs of Rational Functions With DetailsDocument12 pages3-7 Graphs of Rational Functions With DetailsRejieNo ratings yet
- Exercises MEF - 5 - 2018 - SolutionDocument6 pagesExercises MEF - 5 - 2018 - SolutionrtchuidjangnanaNo ratings yet
- Mat202 Tutorials Sheets IDocument7 pagesMat202 Tutorials Sheets ITaffohouo Nwaffeu Yves ValdezNo ratings yet
- Kuliah 4 IFDocument13 pagesKuliah 4 IFRAMADHAN WIJAYANo ratings yet
- Elementary MathematicsDocument17 pagesElementary MathematicsPankaj BiswasNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5Document2 pagesTutorial 5monkeyng.bmedNo ratings yet
- Sheet - 01 - Differentiability NJ - 247Document17 pagesSheet - 01 - Differentiability NJ - 2471qerfdNo ratings yet
- MTH4100 Calculus I: Lecture Notes For Week 5 Thomas' Calculus, Sections 2.6 To 3.5 Except 3.3Document10 pagesMTH4100 Calculus I: Lecture Notes For Week 5 Thomas' Calculus, Sections 2.6 To 3.5 Except 3.3Roy VeseyNo ratings yet
- 2.1 The Derivative of A FunctionDocument3 pages2.1 The Derivative of A Functiontinashembofana84No ratings yet
- Calculus Cheat Sheet Part 2Document4 pagesCalculus Cheat Sheet Part 2Dave Cloud100% (8)
- Math 111 - 5 One Sided Limits, ContinuityDocument12 pagesMath 111 - 5 One Sided Limits, ContinuityMuhamad PeshrawNo ratings yet
- Solutions From The PutnamDocument4 pagesSolutions From The PutnamSai GokulNo ratings yet
- Limits WorksheetDocument2 pagesLimits WorksheethjNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10Document11 pagesLecture 10muradNo ratings yet
- Pagadian Junior College (PJC), Inc.: Module 1: Week 1 Chapter 1-Limits and ContinuityDocument8 pagesPagadian Junior College (PJC), Inc.: Module 1: Week 1 Chapter 1-Limits and ContinuityJefferson PasanaNo ratings yet
- Lectures#5 9Document22 pagesLectures#5 9Jargalmaa ErdenemandakhNo ratings yet
- Ma1010 2014 PS 3Document2 pagesMa1010 2014 PS 3s rkNo ratings yet
- Cobb DouglasDocument14 pagesCobb DouglasRob WolfeNo ratings yet
- MTH4100 Calculus I: Lecture Notes For Week 9 Thomas' Calculus, Sections 4.6 To 5.2 Except 4.7Document11 pagesMTH4100 Calculus I: Lecture Notes For Week 9 Thomas' Calculus, Sections 4.6 To 5.2 Except 4.7Roy VeseyNo ratings yet
- Instantaneous Rate of Change - The DerivativeDocument7 pagesInstantaneous Rate of Change - The DerivativeTrishul GyNo ratings yet
- Final14 15M102EDocument1 pageFinal14 15M102EMohamad TouskaNo ratings yet
- UPSC Civil Services Main 1985 - Mathematics Calculus: Sunder LalDocument5 pagesUPSC Civil Services Main 1985 - Mathematics Calculus: Sunder Lalsayhigaurav07No ratings yet
- Test 1 SolDocument5 pagesTest 1 Solken20050324No ratings yet
- Sequence of Functions Counterexamples - Lecture Note - by SA 2021Document3 pagesSequence of Functions Counterexamples - Lecture Note - by SA 2021Fazal KarimNo ratings yet
- Block 1 MEC 003 Unit 2Document20 pagesBlock 1 MEC 003 Unit 2Abhishek PatraNo ratings yet
- MA 101 (Mathematics - I) : Differentiability: Exercise Set 1Document1 pageMA 101 (Mathematics - I) : Differentiability: Exercise Set 1AdityaNo ratings yet
- Function PDFDocument3 pagesFunction PDFDany DwNo ratings yet
- Soal UTS Madas BilingualDocument1 pageSoal UTS Madas BilingualJuwita PardedeNo ratings yet
- ECON6067 Problem Set 1 SolutionDocument2 pagesECON6067 Problem Set 1 SolutionMingtao ChenNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Analysis of Functions Increasing and Decreasing FunctionsDocument7 pages4.1 Analysis of Functions Increasing and Decreasing FunctionsAnemesh BaruaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10 Local Extrema and Points of InflectionDocument4 pagesLecture 10 Local Extrema and Points of InflectionShresth SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two-MATH122Document21 pagesChapter Two-MATH122Josiah GyanNo ratings yet
- CBSE I Succeed Math 12th SP11Document10 pagesCBSE I Succeed Math 12th SP11vk7820066No ratings yet
- Calc 1 Chapter 4Document11 pagesCalc 1 Chapter 4freakysnatchNo ratings yet
- Solutions Problem Set 1 (Diff)Document4 pagesSolutions Problem Set 1 (Diff)AdityaNo ratings yet
- Https App - Oswaalbooks.com Download Sample-Qp Subsolution 350SAP-3 SolDocument11 pagesHttps App - Oswaalbooks.com Download Sample-Qp Subsolution 350SAP-3 Sol3107aloksinghNo ratings yet
- Lec.9 DifferentiationDocument13 pagesLec.9 DifferentiationNajiba HamadNo ratings yet
- Revision Test 2Document39 pagesRevision Test 2Thabo InnocentNo ratings yet
- Exercises MEF - 4 - 2018 - SolutionDocument7 pagesExercises MEF - 4 - 2018 - SolutionrtchuidjangnanaNo ratings yet
- Continuity WSDocument11 pagesContinuity WSNarendra GaddamNo ratings yet
- Limits of FunctionsDocument31 pagesLimits of FunctionsMustafaNo ratings yet
- MA 101 (Mathematics - I) : Differentiation: Exercise Set 2Document1 pageMA 101 (Mathematics - I) : Differentiation: Exercise Set 2AdityaNo ratings yet
- Functional Operators (AM-22), Volume 2: The Geometry of Orthogonal Spaces. (AM-22)From EverandFunctional Operators (AM-22), Volume 2: The Geometry of Orthogonal Spaces. (AM-22)No ratings yet
- Transformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandTransformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)