Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Smoking Cessation - Overview
Smoking Cessation - Overview
Uploaded by
Kamlesh KumarOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Smoking Cessation - Overview
Smoking Cessation - Overview
Uploaded by
Kamlesh KumarCopyright:
Available Formats
A Practical Guide to Help
Your Patients Quit Using Tobacco
Tobacco dependence is a chronic condition
driven by addiction to nicotine. No amount Key considerations for treating tobacco dependence:
of tobacco use is safe, and treatment of tobacco Behavioral counseling can benefit all patients.
use and dependence often requires multiple
interventions and long-term support. Effective Medication can help patients quit and can be used with
clinical interventions are available to help patients most patients, though special considerations may apply
who use tobacco to quit. for some individuals. See page 3.
Combining behavioral counseling and medication
This guide provides simple steps and suggested
is more effective than either treatment alone.
language that you can use to briefly (3 to 5
minutes) intervene with patients who use tobacco. Follow-up is key to monitoring patients for treatment
These steps can be integrated into the routine adherence, side effects, and efficacy, along with
clinical workflow and can be delivered by the providing support and continued assistance.
entire clinical care team.
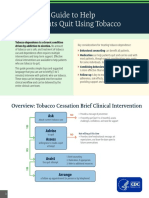
Overview: Tobacco Cessation Brief Clinical Intervention
Provide a message of prevention
Ask NO
If recently quit (last 1 to 12 months), assess
about current tobacco use challenges, confidence, and need for support
YES
Advise
to quit NO Not willing at this time
Provide a brief motivational message, set
Assess expectations, and leave the door open to
willingness to make a quit future conversations
attempt
YES
1. Brief counseling
Assist 2. Medication, if appropriate
the quit attempt 3. Refer to additional resources
YES
Arrange
a follow-up appointment (in person or by telephone)
You might also like
- The RMBC MethodDocument128 pagesThe RMBC MethodFaizan Ahmed100% (2)
- UndergroundG StyleHandgunMainManual PDFDocument46 pagesUndergroundG StyleHandgunMainManual PDFRick Gaines100% (2)
- DBTDocument26 pagesDBTImon Paul100% (3)
- Concept MapDocument1 pageConcept MapLesley Joy T. BaldonadoNo ratings yet
- Counselling in Family MedicineDocument29 pagesCounselling in Family Medicinejaphetnwapi50% (2)
- The Most Important Biblical Discovery of Our TimeDocument21 pagesThe Most Important Biblical Discovery of Our Timececampillo100% (1)
- What Is FashionDocument6 pagesWhat Is FashionArim Arim100% (3)
- HCP Conversation GuideDocument4 pagesHCP Conversation GuidehelfiNo ratings yet
- Relapse PDFDocument4 pagesRelapse PDFShree KudandeNo ratings yet
- Tobacco Cessation ProtocolDocument7 pagesTobacco Cessation ProtocolDavid BriggsNo ratings yet
- Health Promotion: Didik Setiawan, PHD., AptDocument17 pagesHealth Promotion: Didik Setiawan, PHD., AptMisgi Candra DasaNo ratings yet
- Benzodiazepine ProtocolDocument8 pagesBenzodiazepine ProtocolSamuel JeebanNo ratings yet
- Prescriber - 2009 - Edwards - Withdrawing Antidepressants Guide To Patient ManagementDocument5 pagesPrescriber - 2009 - Edwards - Withdrawing Antidepressants Guide To Patient Managementjosipa.vulic108No ratings yet
- Substance DependenceDocument16 pagesSubstance Dependencemardsz94% (18)
- HTP - Supporting The Patient On DialysisDocument8 pagesHTP - Supporting The Patient On DialysisChristine Pialan SalimbagatNo ratings yet
- Counseling Skills: Prof. Datuk Dr. D.M.Thuraiappah MAHSA University CollegeDocument40 pagesCounseling Skills: Prof. Datuk Dr. D.M.Thuraiappah MAHSA University CollegeJason Roy Edward NathanNo ratings yet
- ClinicalDocument5 pagesClinicalMary Hope BacutaNo ratings yet
- Acceptance and Commitment Therapy: Pathways For General PractitionersDocument5 pagesAcceptance and Commitment Therapy: Pathways For General PractitionersAnonymous Ax12P2srNo ratings yet
- Motivational Interviewing: A Brief Guide ToDocument33 pagesMotivational Interviewing: A Brief Guide ToHastin yunita sariNo ratings yet
- Behavioral TherapyDocument10 pagesBehavioral TherapyArshia NadeemNo ratings yet
- Lectura Obligatoria- MET Practical Guide Treasure Ward 1997Document13 pagesLectura Obligatoria- MET Practical Guide Treasure Ward 1997Luis MunitaNo ratings yet
- FACT Kirk Strosahl Presentation PDFDocument11 pagesFACT Kirk Strosahl Presentation PDFAlexander ZelenukhinNo ratings yet
- Altered Thought ProcessDocument17 pagesAltered Thought Processbinteazhar50% (2)
- A Guide To TS Medications - M-313Document14 pagesA Guide To TS Medications - M-313FABRICIO VENTURANo ratings yet
- Choosing AntidepressantDocument4 pagesChoosing AntidepressantJorge Luis Ángeles VelázquezNo ratings yet
- Answer 1Document5 pagesAnswer 1Hezekiah AtindaNo ratings yet
- Antipsychotics Guide Nov-20Document22 pagesAntipsychotics Guide Nov-20luis.parerasNo ratings yet
- Brief Tobacco Intervention Skills (Btis) : Gay B. Ardanas, MDDocument16 pagesBrief Tobacco Intervention Skills (Btis) : Gay B. Ardanas, MDmary grace banaNo ratings yet
- The U&ME-A Programme Sounds Like It Might Be A Fit For My Needs. What Next?Document2 pagesThe U&ME-A Programme Sounds Like It Might Be A Fit For My Needs. What Next?Georgie SNo ratings yet
- Sample NCPDocument3 pagesSample NCPJoedelynne Diane Endaya GarciaNo ratings yet
- Yoga and Counseling ExperienceDocument7 pagesYoga and Counseling ExperienceWilliamArugaNo ratings yet
- Sensate FocusDocument27 pagesSensate FocusMarcelo Da SilvaNo ratings yet
- Polypharmacy: Guidance For Prescribing in Frail AdultsDocument6 pagesPolypharmacy: Guidance For Prescribing in Frail AdultsAgil BredlyNo ratings yet
- Solution-Focused Brief Therapy: Chris IvesonDocument9 pagesSolution-Focused Brief Therapy: Chris IvesonAnonymous 9yIlDrElz7No ratings yet
- Module 12: Problem Solving: ObjectivesDocument8 pagesModule 12: Problem Solving: ObjectivesMaria BagourdiNo ratings yet
- Change Through CounselingDocument13 pagesChange Through CounselingMohamad Saleh Abdul RahmanNo ratings yet
- Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT)Document4 pagesElectroconvulsive Therapy (ECT)Aurea Jasmine DacuycuyNo ratings yet
- Puroc, Liza M.: AssessmentDocument11 pagesPuroc, Liza M.: AssessmentLiza MPNo ratings yet
- The 5as ApproachDocument2 pagesThe 5as ApproachshaimaNo ratings yet
- Table 19-2Document2 pagesTable 19-2Dragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Reward System CircuitDocument4 pagesReward System CircuitMarc Christian SausaNo ratings yet
- Child ManagementDocument42 pagesChild ManagementAlya ElgamriNo ratings yet
- Pharmalogy ZADocument133 pagesPharmalogy ZASamuel KamocheNo ratings yet
- Smoking Cessation Guidelines: For Australian General PracticeDocument26 pagesSmoking Cessation Guidelines: For Australian General PracticequinnNo ratings yet
- Evaluasi Dan Profilaksis Terapi MigrainDocument53 pagesEvaluasi Dan Profilaksis Terapi Migrainnesya_fanniaNo ratings yet
- Motivational Enhancement Therapy (MET)Document4 pagesMotivational Enhancement Therapy (MET)Mani Vannan100% (1)
- Psychiatric MedicationsDocument6 pagesPsychiatric MedicationsMr. Psycho SamNo ratings yet
- 1Document2 pages1comsianNo ratings yet
- Treating PTSD During The COVID-19 Virus OutbreakDocument50 pagesTreating PTSD During The COVID-19 Virus OutbreakmniosoNo ratings yet
- Conducting A Nurse Consultation: ClinicalDocument6 pagesConducting A Nurse Consultation: ClinicalAlif Akbar HasyimiNo ratings yet
- 5 Therapeutic InterventionsDocument2 pages5 Therapeutic InterventionsMentor UstadNo ratings yet
- CCP 606962Document8 pagesCCP 606962Ana MoraisNo ratings yet
- Management of StutteringDocument54 pagesManagement of Stutteringpappu71371% (14)
- My-Visual 58586180Document1 pageMy-Visual 58586180api-608971255No ratings yet
- THE DBT SKILLS WORKBOOK FOR TEENS: Practical DBT Exercises for Mindfulness, Emotion Regulation, and Distress Tolerance (2023 Guide for Beginners)From EverandTHE DBT SKILLS WORKBOOK FOR TEENS: Practical DBT Exercises for Mindfulness, Emotion Regulation, and Distress Tolerance (2023 Guide for Beginners)No ratings yet
- 5219-PRP Support Tool CounsellingDocument10 pages5219-PRP Support Tool CounsellingRodhi AnshariNo ratings yet
- Mental Health and Psychiatric NursingDocument43 pagesMental Health and Psychiatric Nursingalteahmichaella.mintuNo ratings yet
- Denial Related To Previous IneffectiveDocument4 pagesDenial Related To Previous IneffectivePrincess Jovelyn GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Motivational Interviewing - Psychology Today AustraliaDocument9 pagesMotivational Interviewing - Psychology Today Australianicola.gawlikNo ratings yet
- Pharmacotherapy Presented On September 8, 2007 in Nashville, TennesseeDocument7 pagesPharmacotherapy Presented On September 8, 2007 in Nashville, TennesseeTrevaNo ratings yet
- Antidepressant Fact SheetDocument4 pagesAntidepressant Fact Sheetcecile pieNo ratings yet
- Treating Acute Stress Disorder: Asd. AsdDocument48 pagesTreating Acute Stress Disorder: Asd. AsdgianinaNo ratings yet
- Ta Ac Bit English 101316 FinalDocument8 pagesTa Ac Bit English 101316 FinalAnonymous 7rwvZTvMZvNo ratings yet
- 1st Year Chemistry Pairing Scheme 2021 - 11th Class - Ratta - PKDocument2 pages1st Year Chemistry Pairing Scheme 2021 - 11th Class - Ratta - PKazeemNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 Theory of AccidentDocument14 pagesLecture 5 Theory of Accidenthayelom100% (1)
- Reblex AnswersDocument17 pagesReblex AnswersAerol Buenaventura100% (1)
- Full Download 2014 Psychiatric Mental Health Nursing Revised Reprint 5e Test Bank PDF Full ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Download 2014 Psychiatric Mental Health Nursing Revised Reprint 5e Test Bank PDF Full Chapterpassim.pluvialg5ty6100% (17)
- How To Retract BPS Data Back To R3 When There Is No Standard RetractorDocument3 pagesHow To Retract BPS Data Back To R3 When There Is No Standard Retractorraphavega2010No ratings yet
- Group Number, Grade and Section, Subjec and Name of The TeacherDocument4 pagesGroup Number, Grade and Section, Subjec and Name of The TeacherSalvador GaldámezNo ratings yet
- Draft Local Budget Circular Re Grant of Honorarium To SK Officials - v1Document4 pagesDraft Local Budget Circular Re Grant of Honorarium To SK Officials - v1rodysseusNo ratings yet
- Ms. Rossana Hoyos DíazDocument19 pagesMs. Rossana Hoyos DíazMaryNo ratings yet
- Quotation - ABS 2020-21 - E203 - Mr. K Ramesh ReddyDocument1 pageQuotation - ABS 2020-21 - E203 - Mr. K Ramesh ReddyairblisssolutionsNo ratings yet
- Third Party Logistics: A Literature Review and Research AgendaDocument26 pagesThird Party Logistics: A Literature Review and Research AgendaRuxandra Radus100% (1)
- Naet Basic 15 GuideDocument6 pagesNaet Basic 15 Guidesissicarranza100% (1)
- Lesson 9. Phylum Mollusca PDFDocument44 pagesLesson 9. Phylum Mollusca PDFJonard PedrosaNo ratings yet
- Sample Thesis 2Document127 pagesSample Thesis 2Carlo Troy AcelottNo ratings yet
- A Shoe Story: Look at Manny's Shoes. Where Do You Think They Have Been?Document8 pagesA Shoe Story: Look at Manny's Shoes. Where Do You Think They Have Been?Renier John BambaNo ratings yet
- Collections and Recollections by Russell, George William Erskine, 1853-1919Document202 pagesCollections and Recollections by Russell, George William Erskine, 1853-1919Gutenberg.org100% (1)
- ModulationDocument7 pagesModulationSyeda MiznaNo ratings yet
- Full Download Art of Leadership 5th Edition Manning Test Bank PDF Full ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Download Art of Leadership 5th Edition Manning Test Bank PDF Full Chaptermasqueedenized8a43l100% (19)
- Cracking The Consulting Interview: Select Experiences of Kearney HiresDocument28 pagesCracking The Consulting Interview: Select Experiences of Kearney HiresLuqman HakimNo ratings yet
- EPM-1183 Ethics, Code of Conduct & Professional PracticeDocument41 pagesEPM-1183 Ethics, Code of Conduct & Professional PracticeDev ThackerNo ratings yet
- The Stolen Party ThesisDocument8 pagesThe Stolen Party Thesisfexschhld100% (2)
- Literary Devices DefinitionsDocument2 pagesLiterary Devices DefinitionsAlanna BryantNo ratings yet
- Onomasiology (From GreekDocument4 pagesOnomasiology (From GreekAnonymous hcACjq8No ratings yet
- Characteristics of LDCsDocument22 pagesCharacteristics of LDCstinsaeres100% (2)
- Rmit PHD Thesis GuidelinesDocument7 pagesRmit PHD Thesis Guidelinesdwnt5e3k100% (2)
- (GOLD) The Examples of Final Semester TestDocument8 pages(GOLD) The Examples of Final Semester TestMetiska MunzilaNo ratings yet