Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Properties of Matter
Properties of Matter
Uploaded by
Jenie Rose C. PeningOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Properties of Matter
Properties of Matter
Uploaded by
Jenie Rose C. PeningCopyright:
Available Formats
Properties of Matter
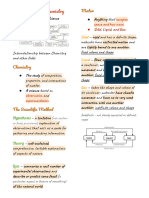
Physical Property
- can be measured without changing the chemical composition of that matter
- can be further subdivided into extensive and intensive properties.
Extensive Properties
- are those that depend on the amount of matter being measured.
- classic examples of extensive physical properties are the mass, volume, and number of moles
- decreasing the amount of matter being weighed will decrease the mass of that matter.
Intensive properties
- are independent of the amount of matter being considered.
- examples of intensive properties are color, melting point, boiling point, and density.
Chemical Properties
- describe the characteristic ability of a substance to react to form new substances.
- classic examples of chemical properties include flammability and susceptibility to corrosion.
Types of Matter
Pure Substance
A substance is a form of matter with a definite composition and distinct properties. A
pure substance can be further classified into two categories: elements and compounds.
Element
- a substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances using any chemical.
Compound
- two or more types of elements are used in fixed proportion with one another to form a single
substance
You might also like
- Properties of Matter Notes Grade 8Document1 pageProperties of Matter Notes Grade 8Maristela Paraan MacaranasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 OutlineDocument4 pagesChapter 1 Outlinedill1233No ratings yet
- Chemistry 11: Lesson 1 - Matter and Its PropertiesDocument4 pagesChemistry 11: Lesson 1 - Matter and Its PropertiesMary Roselen MonayaNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRYDocument1 pageCHEMISTRYwella wellaNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1Document4 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1Jelou LumakinNo ratings yet
- 3rd MASTERY - CHEM 1Document3 pages3rd MASTERY - CHEM 1Rhasher YbañezNo ratings yet
- Basic ChemistryDocument3 pagesBasic ChemistryAngelou HernandezNo ratings yet
- Concept MapDocument5 pagesConcept MapMar YaNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Mathematics, Science, and TechnologyDocument3 pagesModule 5 Mathematics, Science, and TechnologyMarianne Bag-aoNo ratings yet
- Particle Nature of MatterDocument22 pagesParticle Nature of MatterEve JoyceNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1Document21 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1mariayvankaNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1Document4 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1yoonsjwlNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer MATTERDocument3 pagesScience Reviewer MATTERRACHELL SATSATINNo ratings yet
- MatterDocument2 pagesMatterBilledo ClarkNo ratings yet
- Matter and Its PropertiesDocument10 pagesMatter and Its PropertiesGerald CatiponNo ratings yet
- Teacher-Made Learner's Home Task: S7MT-ib-c-3 S7MT-id-e-2Document4 pagesTeacher-Made Learner's Home Task: S7MT-ib-c-3 S7MT-id-e-2Carissa Mae CañeteNo ratings yet
- MatterDocument29 pagesMatterJeNo ratings yet
- Physical and Chemical Properties of MatterDocument6 pagesPhysical and Chemical Properties of MatterRampotz Ü EchizenNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Unit 2 Chemistry (Matter)Document40 pagesLesson 4 Unit 2 Chemistry (Matter)Evelyn Battuac de AustriaNo ratings yet
- Physical and Chemical Properties and ChangesDocument12 pagesPhysical and Chemical Properties and ChangesAaron JadeNo ratings yet
- GENERAL CHEMISTRY 1 REVIEWER Lesson 1Document3 pagesGENERAL CHEMISTRY 1 REVIEWER Lesson 1jjjangchunNo ratings yet
- My Chemistry NotesDocument6 pagesMy Chemistry Notess2023100462No ratings yet
- Matter and Its NatureDocument5 pagesMatter and Its NatureYogendra VarmaNo ratings yet
- Topic Outline:: Salcedo, Eastern Samar 6807 Eastern Samar, PhilippinesDocument3 pagesTopic Outline:: Salcedo, Eastern Samar 6807 Eastern Samar, PhilippinesMegan AldeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Classification of MatterDocument7 pagesChapter 2 Classification of MatterPatrice Francisco100% (1)
- Unit 2 - Matter and Energy Characteristics of Matter and CALCULATION IN ChemistryDocument4 pagesUnit 2 - Matter and Energy Characteristics of Matter and CALCULATION IN ChemistryTwice OnceNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1.3 - Matter. Classification, Physical States, and PropertiesDocument30 pagesLesson 1.3 - Matter. Classification, Physical States, and PropertiesLovely Joy GareNo ratings yet
- Prelim ChemDocument6 pagesPrelim ChemMim MimNo ratings yet
- Week 2Document3 pagesWeek 2Prima LebananNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Chapter 1Document17 pagesChemistry Chapter 1Joyce EstrevencionNo ratings yet
- Properties of MatterDocument34 pagesProperties of MatterElmas ChiongNo ratings yet
- Week - q1 State of MatterDocument21 pagesWeek - q1 State of Matterjustine alinaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Physical and Chemical Properties of MatterDocument3 pagesLesson 2 Physical and Chemical Properties of MatterAndrea MurielNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Matter and Its PropertiesDocument29 pagesChapter 1 Matter and Its PropertiesLexter CastilloNo ratings yet
- PS Lesson 3Document2 pagesPS Lesson 3euginNo ratings yet
- Colorful and Fun Science Safety Rules PresentationDocument21 pagesColorful and Fun Science Safety Rules Presentationkimallison shinNo ratings yet
- MatterDocument34 pagesMatterJimarie CarilNo ratings yet
- What Are Subatomic Particles Made Of?: Examples of Chemical PropertiesDocument2 pagesWhat Are Subatomic Particles Made Of?: Examples of Chemical PropertiesValerie AriesVirgoNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1 - Module 1 (Ryah Lyn Revale 12 Stem Pasteur)Document4 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1 - Module 1 (Ryah Lyn Revale 12 Stem Pasteur)Ryah Lyn RevaleNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Topic 1 ReviewerDocument3 pagesGeneral Chemistry Topic 1 ReviewerNishka CarabeoNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem 1 W1Document7 pagesGen Chem 1 W1Kenken GenotivaNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument7 pagesChemistryLouie Joice MartinezNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Concepts Classification and States of MatterDocument40 pagesUnit 2 Concepts Classification and States of Matterapi-327076063No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Chem IDocument11 pagesChapter 1 Chem IStudy LionNo ratings yet
- Properties of A MaterialsDocument13 pagesProperties of A Materialsgracemin doncilloNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 and 2: Properties of Matter: Rbi Script: General Chemistry 1 Prepared By: Donnafe M. AganonDocument2 pagesLesson 1 and 2: Properties of Matter: Rbi Script: General Chemistry 1 Prepared By: Donnafe M. Aganonbenjie panlicanNo ratings yet
- Science 7 ReviewerDocument8 pagesScience 7 ReviewerClarice PalattaoNo ratings yet
- Local Media7711445783592677217Document33 pagesLocal Media7711445783592677217katNo ratings yet
- Science 6 Physical and Chemical Properties of MatterDocument17 pagesScience 6 Physical and Chemical Properties of MatterLharize CastroNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Chapter 2 "Matter and Change" Outline: Section 2.1 Properties of Matter I. Describing MatterDocument2 pagesChemistry - Chapter 2 "Matter and Change" Outline: Section 2.1 Properties of Matter I. Describing Matterapi-529187592No ratings yet
- Lesson 1 C1Document6 pagesLesson 1 C1alex beltran songNo ratings yet
- 1 - Describing & Classifying MatterDocument9 pages1 - Describing & Classifying MatterizzyNo ratings yet
- Gen ChemDocument2 pagesGen Chembrie calixtroNo ratings yet
- Gen Chemistry 1-Task 1Document4 pagesGen Chemistry 1-Task 1khlneNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2 - Matter-and-EnergyDocument26 pagesChapter-2 - Matter-and-EnergyJam BermejoNo ratings yet
- Mark Ace Lardera - (Template) Learning Activity Sheet Grade 12 STEM General Chemistry 1 Week 1Document8 pagesMark Ace Lardera - (Template) Learning Activity Sheet Grade 12 STEM General Chemistry 1 Week 1Zyrus Dizon MondiaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry First SemDocument8 pagesChemistry First SemceeNo ratings yet
- Physical Properties of MatterDocument14 pagesPhysical Properties of MatterSoso Anoos100% (1)
- MatterDocument3 pagesMatterCUIZON, GEORDETTE DIVINENo ratings yet
- What You Need to Know About Beautiful Nails: A Better Understanding of Nail ChemistryFrom EverandWhat You Need to Know About Beautiful Nails: A Better Understanding of Nail ChemistryNo ratings yet