Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Q3 DLL Sci 8 W3
Q3 DLL Sci 8 W3
Uploaded by
Justin Abad Fernandez0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
46 views6 pagesThis document outlines a science lesson plan for a week-long unit on the particle nature of matter and the water cycle. The lesson objectives are to explain physical changes in terms of the arrangement and motion of atoms and molecules, and to present how water behaves in its different states within the water cycle. Each day focuses on a different topic like condensation, melting, and demonstrating the three states of matter. Activities include experiments, questions, videos and modeling to help students understand these concepts.
Original Description:
Original Title
Q3_DLL_SCI_8_W3
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document outlines a science lesson plan for a week-long unit on the particle nature of matter and the water cycle. The lesson objectives are to explain physical changes in terms of the arrangement and motion of atoms and molecules, and to present how water behaves in its different states within the water cycle. Each day focuses on a different topic like condensation, melting, and demonstrating the three states of matter. Activities include experiments, questions, videos and modeling to help students understand these concepts.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
46 views6 pagesQ3 DLL Sci 8 W3
Q3 DLL Sci 8 W3
Uploaded by
Justin Abad FernandezThis document outlines a science lesson plan for a week-long unit on the particle nature of matter and the water cycle. The lesson objectives are to explain physical changes in terms of the arrangement and motion of atoms and molecules, and to present how water behaves in its different states within the water cycle. Each day focuses on a different topic like condensation, melting, and demonstrating the three states of matter. Activities include experiments, questions, videos and modeling to help students understand these concepts.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 6
School MALLIG NATIONAL HIGH SCHOOL Grade Level 8
DAILY Teacher JUSTIN MARK A. FERNANDEZ Learning Area SCIENCE
Inclusive Dates FEBRUARY 27 – MARCH 03, 2023 Quarter THIRD
Scheduled Time 2:00-3:00 / 4:00-5:00
LESSON
LOG
MONDAY TUESDAY WEDNESDAY THURSDAY FRIDAY
I. OBJECTIVES
A. Content Standard The Learners demonstrate an understanding of: the particle nature of matter as basis for explaining Remediation /
properties, physical changes, and structure of substances and mixtures. Intervention /
B. Performance Standards The Learners shall be able to: present how water behaves in its different states within the water cycle. Enrichment
C. Learning The Learners should be able to: explain physical changes in The Learners should be able to: explain physical Activities
Competencies / terms of the arrangement and motion of atoms and changes in terms of the arrangement and motion of
Objectives (Write the molecules. S8MT-IIIc-d-9 atoms and molecules. S8MT-IIIc-d-9
LC Code)
III. CONTENT INVESTIGATE ABOUT CONDENSATION INVESTIGATE ABOUT MELTING
IV. LEARNING
RESOURCES
A. References
1. Teacher’s Guide
pages
2. Learners’ Materials Learners’ Module pp. 184- Learners’ Module pp. 184- Learners’ Module pp. 187- Learners’ Module pp.
pages 186 186 189 187- 189
3. Textbook pages
4. Additional www.middleschoolchemistr
Materials from y.com
Learning Resources
Portals
B. Other Learning
Resources
V. PROCEDURES
A. Revising previous 1. What do you think may 1. What happens to water What happens when What happens to the
lesson or presenting be the biggest factor which when it is cooled? particles lose their energy kinetic energy of the
the new lesson contributed to the 2. How does the process of and drop their molecules when
evaporation process? condensation take place? temperature? temperature
2. What happened to the 3. Why do droplets form at increases/decreases and
kinetic energy of particles the surface of a covered heat transfer continues?
from liquid to gas/vapor? hot container?
3. How does evaporation
take place?
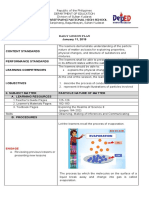
B. Establishing a purpose Ask the students what Show a picture of water Have the students Show a picture or a
for the lesson happens when a cold bottle cycle. imagine eating their short video clip of the
was taken from the fridge own ice cream. melting of polar regions.
and left in an open space. For instance, they are (The teacher may touch
eating outside under a little about the climate
the scorching sun, change.)
how would they eat
their ice cream?
Why is it so?
C. Presenting examples/ (Adapted) Ask the students how clouds Ask the following Ask the following:
instances of the new Prepare a demonstration form. questions: 1. What have you
lesson with the following 1. What will happen to noticed on the
materials: (Note: Should be the ice cream if it is picture/ seen in the
done 5-10 minutes before not eaten video?
the time) immediately? Why? 2. What can you say
2. In what situation will about its effects in
2 clear plastic cups the ice cream melt the environment?
Room temperature water faster and slower? 3. How did this
Ice cubes 3. What might be the happen? (Introduce
Zip lock (gallon size) factors involved in the the melting process)
process?
Procedure:
1. Place water and ice cubes
into two identical cups.
2. Immediately place one of
the cups in a zip lock bag
and get as much air out of
the bag as possible. Close
the bag securely.
3. Allow the cups to sit
undisturbed for about 5-10
minutes.
Ask the students: Why do
you think the cup that is
exposed to more air has
more water on the outside
of it?
D. Discussing new Essential Question: What Essential Question: What Essential Question: What Essential Question: How
concepts and practicing happens when particles lose happens when particles lose happens to the kinetic will you demonstrate
new skills #1 their energy and drop their their energy and drop their energy of the molecules the three states of
temperature? temperature? when temperature matter?
increases/decreases and
heat transfer continues?
E. Discussing concepts Perform activity #5 Part Perform activity #5 Part Perform Activity #6: The teacher may opt to
and practicing new B: Cooling Water page B: Cooling Water page What changes take use the following:
skills #2 186. 186. place when ice turns a. Illustration/Drawing
Answer guide questions Answer guide questions into liquid water? b. Model
#6-9 #6-9 Answer the guide c. Multimedia
questions found on Presentation
pages 187-188. d. Others
With their chosen
materials, students will
create their own particle
model of the following
scenario:
a. solid-liquid
b. gas-liquid
c. liquid-gas
d. liquid-solid
F. Developing mastery
(Leads to Formative
Assessment 3)
G. Finding practical Students will present their Students will present their Students will present their Students will present
applications of findings in class through a findings in class through a findings in class through a their findings in class
concepts and skills in class reporting with the use class reporting with the use class reporting with the through a class reporting
daily living of the table and guide of the table and guide use of the table and guide with the use of the table
questions. (Please refer to questions. (Please refer to questions. (Please refer to and guide questions.
LM for the guide questions) LM for the guide questions) LM for the guide (Please refer to LM for
questions) the guide questions)
H. Making generalizations Key Questions: Key Questions: Key Questions: Key Questions:
and abstractions about 1. What happens to 1. What happens to 1. What do you think 1. What do you think
the lesson water when it is water when it is may be the biggest may be the biggest
cooled? cooled? factor which factor which
2. How does the 2. How does the contributed to the contributed to the
process of process of melting/freezing melting/freezing
condensation take condensation take process? process?
place? place? 2. What happened to the 2. What happened to
3. Why do droplets 3. Why do droplets kinetic energy of the kinetic energy of
form at the surface form at the surface particles from solid to particles from solid
of a covered hot of a covered hot liquid? to liquid?
container? container? 3. What happened to the 3. What happened to
kinetic energy of the kinetic energy of
particles from liquid to particles from liquid
solid? to solid?
4. How does melting take 4. How does melting
place? take place?
5. How does freezing 5. How does freezing
take place? take place?
4. Evaluating learning TRUE or FALSE TRUE or FALSE Identification: The teacher may opt to
Write True if the statement Write True if the statement is 1. It is the process where use the following:
is correct and False if it is correct and False if it is not. liquid turns to solid. e. Illustration/Drawing
not. 1. As the temperature 2. What happens to the f. Model
1. As the temperature increases, the kinetic kinetic energy of g. Multimedia
increases, the kinetic energy increases as well. particles when the Presentation
energy increases as (True) object melts? h. Others
well. (True) 2. When particles lose their 3. If the temperature
2. When particles lose energy, they return to surrounding the object With their chosen
their energy, they their original state. (True) is greater, what materials, students will
return to their original 3. Condensation is a process will take create their own particle
state. (True) process when liquid place? model of the following
3. Condensation is a turns to its gaseous 4. It is the process where scenario:
process when liquid state. (False) solid turns to liquid. a. solid-liquid
turns to its gaseous 4. The gaseous state of When heat is decreased, b. gas-liquid
state. (False) water is called water the object melts/freezes? c. liquid-gas
4. The gaseous state of vapor. (True) d. liquid-solid
water is called water
vapor. (True) Criteria:
40% Accuracy
35% Creativity
15% Resourcefulness
10% Neatness
Total: 100%
5. Additional activities Cite other practical examples Explain to students that
for application or or situations where you there are cases that
remediation could observe the process of some substances can
condensation. change directly from
solid to gas. This process
is called SUBLIMATION.
The opposite of which is
called the DEPOSITION.
VI. REMARKS
VII. REFLECTION
A. No. of learners who
earned 80% in the
evaluation.
B. No. of learners who
require additional
activities for
remediation
C. Did the remedial
lessons work? No. of
learners who have
caught up with the
lesson.
D. No. of learners who
continue to require
remediation.
E. Which of my teaching
strategies worked well?
Why did it work?
F. What difficulties did I
encounter which my
principal or supervisor
can help me solve?
G. What innovation or
localized materials did
I used/discover which I
wish to share with
other learners?
Prepared by: Checked by:
JUSTIN MARK A. FERNANDEZ EUGENE P. SERVITILLO, MA-THM
Subject Teacher Secondary School Principal II
You might also like
- Robert Potter - Tony Binns - Jennifer A. Elliott - Etienne Nel - David W. Smith - Geographies of Development - An Introduction To Development Studies-Routledge (2018)Document662 pagesRobert Potter - Tony Binns - Jennifer A. Elliott - Etienne Nel - David W. Smith - Geographies of Development - An Introduction To Development Studies-Routledge (2018)Andreas100% (1)
- Potential and Kinetic Energy: Grade 8 ScienceDocument21 pagesPotential and Kinetic Energy: Grade 8 ScienceJONATHAN BRIAGASNo ratings yet
- Husserl, Edmund - The Idea of PhenomenologyDocument75 pagesHusserl, Edmund - The Idea of PhenomenologyFelipeMgr100% (7)
- Science 8 - Module 6 - Version 3Document16 pagesScience 8 - Module 6 - Version 3EdcheloNo ratings yet
- Che g8 q3 w4 d4 RevDocument7 pagesChe g8 q3 w4 d4 RevRowena Sta MariaNo ratings yet
- Isotopes WS ANSWERS 1lmscf1Document1 pageIsotopes WS ANSWERS 1lmscf1team TSOTARENo ratings yet
- Science 8 LESSON PLAN - Week 4Document4 pagesScience 8 LESSON PLAN - Week 4Kathryn Decena CentinalesNo ratings yet
- DLL Teenage PregnancyDocument5 pagesDLL Teenage PregnancyCharo Nudo PongasiNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE and TECHNOLOGY 8Document4 pagesSCIENCE and TECHNOLOGY 8ANDJELYN M. ABALOSNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Science 8Document32 pagesLesson 4 Science 8Sir JoshNo ratings yet
- Science 8 q1 w3Document12 pagesScience 8 q1 w3Je-ann AcuNo ratings yet
- Matulatula High School: Multiple Choice DIRECTIONS: Choose The Letter of The Correct Answer. EncircleDocument2 pagesMatulatula High School: Multiple Choice DIRECTIONS: Choose The Letter of The Correct Answer. EncircleANDJELYN M. ABALOSNo ratings yet
- Day 2Document7 pagesDay 2RiC'x CamadoNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Log: (1st Quarter)Document11 pagesDaily Lesson Log: (1st Quarter)Marissa FontanilNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument4 pagesAtomic StructureSherene Supeda100% (1)
- DLP Science 8Document26 pagesDLP Science 8Vianney Camacho100% (1)
- Class A Group 1 CuteDocument3 pagesClass A Group 1 CuteAizelle Taratara100% (1)
- Daily Lesson Log Science 8Document5 pagesDaily Lesson Log Science 8NERISA S. SONIDONo ratings yet
- Science 8 Q3 Week 3 - DLL BausinDocument6 pagesScience 8 Q3 Week 3 - DLL Bausinsheryll BausinNo ratings yet
- DLL Science 8 Q3 WK - 9 - JUDYDocument7 pagesDLL Science 8 Q3 WK - 9 - JUDYAlrei MeaNo ratings yet
- 3 RDDocument5 pages3 RDCAROLYN CAYBOTNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan About MatterDocument4 pagesLesson Plan About MatterglaizaNo ratings yet
- SDO Camarines Norte: Facilitating Dreams, Valuing AspirationsDocument9 pagesSDO Camarines Norte: Facilitating Dreams, Valuing Aspirationsalthea venice baloloyNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in ScienceDocument8 pagesLesson Plan in ScienceBALMACEDA DIANA100% (1)
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 8: ProceduresDocument8 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Science 8: ProceduresMc Laurence Marquez SaligumbaNo ratings yet
- Science 8 Quarter 2 Week 5Document4 pagesScience 8 Quarter 2 Week 5Black Venus100% (2)
- FIRST Summative Test Science 8 THIRD QUARTER MELC 1 AND 2Document4 pagesFIRST Summative Test Science 8 THIRD QUARTER MELC 1 AND 2Juliet VillaruelNo ratings yet
- DLL TemplateDocument2 pagesDLL TemplateJessica Vertudazo CumlaNo ratings yet
- Science 8 Q3 Week 2 - DLL BausinDocument4 pagesScience 8 Q3 Week 2 - DLL Bausinsheryll BausinNo ratings yet
- Group 3 - Development of The Periodic Table Day 2Document3 pagesGroup 3 - Development of The Periodic Table Day 2Lanie Saludares - Po100% (1)
- Final DLL Co1 ZapenDocument3 pagesFinal DLL Co1 ZapenChrisel Luat LopezNo ratings yet
- COT - DLL - 2022 g8 Module 4Document5 pagesCOT - DLL - 2022 g8 Module 4Chrisel Luat LopezNo ratings yet
- Science8 DLLDocument156 pagesScience8 DLLMelanie Trinidad100% (1)
- Bagay, Eurasia A. - DLP - Science 8 - Q3W3Document2 pagesBagay, Eurasia A. - DLP - Science 8 - Q3W3asia bagayNo ratings yet
- 3rd COT DLPDocument5 pages3rd COT DLPCristine roqueroNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Periodic Table Grade NineDocument10 pagesLesson Plan in Periodic Table Grade NineLiezl BallesterosNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Grade 10 Week 7 Quarter 2 February 22 - 26, 2021Document7 pagesDepartment of Education: Grade 10 Week 7 Quarter 2 February 22 - 26, 2021Janeth Miguel SatrainNo ratings yet
- DLL SCIENCE 8 Jan. 30-Feb.3Document53 pagesDLL SCIENCE 8 Jan. 30-Feb.3Raiza Lainah MianoNo ratings yet
- DLL (Motion in 2 Dimension)Document3 pagesDLL (Motion in 2 Dimension)JeanRachoPaynandosNo ratings yet
- DLL Science 10 Week 3 Nov.14-18Document46 pagesDLL Science 10 Week 3 Nov.14-18Raiza Lainah Miano100% (1)
- DLL Grade 8 WorkDocument5 pagesDLL Grade 8 WorkIrish Joy Aguadera - NamuagNo ratings yet
- WHLP 2 Activities EarthquakeDocument6 pagesWHLP 2 Activities EarthquakeAaliyah CarlobosNo ratings yet
- DLL MomentumDocument12 pagesDLL MomentumPrincess AnnNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Log: Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridayDocument3 pagesDaily Lesson Log: Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridayKaren PolinarNo ratings yet
- Sample 7 E'sDocument3 pagesSample 7 E'sEnitsuj Ie-kunNo ratings yet
- LeaP Science G8 Week 6 Q3Document3 pagesLeaP Science G8 Week 6 Q3CriselAlamagNo ratings yet
- Judy Lesson Plan Grade 8Document6 pagesJudy Lesson Plan Grade 8Judy IntervencionNo ratings yet
- Par Cot2 Lesson PlanDocument10 pagesPar Cot2 Lesson PlanJeazel MosendoNo ratings yet
- Electronic ConfigurationDocument4 pagesElectronic ConfigurationkarlNo ratings yet
- Boyles LawDocument3 pagesBoyles LawHeidie BalabboNo ratings yet
- Q3 DLL Sci 8 W7Document5 pagesQ3 DLL Sci 8 W7Justin Abad FernandezNo ratings yet
- G8 Q2 - 2 FINALoct 2018Document27 pagesG8 Q2 - 2 FINALoct 2018sarah joy velascoNo ratings yet
- Grade Level Quarter / Domain Week & Day No. Page No.: Detailed Science Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesGrade Level Quarter / Domain Week & Day No. Page No.: Detailed Science Lesson PlanDenijun Salada AlvarNo ratings yet
- Science 8 Quarter 2 Week 3Document3 pagesScience 8 Quarter 2 Week 3Black Venus100% (2)
- DLL Sci 8 12-12-2022Document4 pagesDLL Sci 8 12-12-2022Lovely Shiena C. AragoncilloNo ratings yet
- Q3 REMEDIATION Final Edited 2Document3 pagesQ3 REMEDIATION Final Edited 2Athena ChoNo ratings yet
- Science 8 Final Summative TestDocument2 pagesScience 8 Final Summative TestEnrick PestilosNo ratings yet
- Science 8 Quarter 2 Week 2Document3 pagesScience 8 Quarter 2 Week 2Black Venus100% (2)
- 1 Mendelian Genetics Preliminary ActivitiesDocument7 pages1 Mendelian Genetics Preliminary ActivitiesJenny PartozaNo ratings yet
- Q3 DLL Sci 8 W5Document4 pagesQ3 DLL Sci 8 W5Justin Abad FernandezNo ratings yet
- What I Need To Know?: QUIZ (Multiple Choice)Document4 pagesWhat I Need To Know?: QUIZ (Multiple Choice)Richard F. TalameraNo ratings yet
- G8 Week 3Document6 pagesG8 Week 3PRIMELYN WAGASNo ratings yet
- Q3 DLL Tle 9 W4Document9 pagesQ3 DLL Tle 9 W4Justin Abad FernandezNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Learning Plan For Inv 2Document3 pagesTutorial Learning Plan For Inv 2Justin Abad FernandezNo ratings yet
- Q3 DLL Sci 8 W7Document5 pagesQ3 DLL Sci 8 W7Justin Abad FernandezNo ratings yet
- Inv 702Document42 pagesInv 702Justin Abad FernandezNo ratings yet
- INV - 702 - Concepts and Models For Innovation ManagementDocument42 pagesINV - 702 - Concepts and Models For Innovation ManagementJustin Abad FernandezNo ratings yet
- LOGODocument10 pagesLOGOJustin Abad FernandezNo ratings yet
- Innovation ManagementDocument15 pagesInnovation ManagementJustin Abad FernandezNo ratings yet
- Innovation in EducationDocument12 pagesInnovation in EducationJustin Abad FernandezNo ratings yet
- LAC On Legal MattersDocument23 pagesLAC On Legal MattersJustin Abad FernandezNo ratings yet
- WLP-Week 6Document15 pagesWLP-Week 6Justin Abad Fernandez100% (1)
- 2022inset - IptDocument29 pages2022inset - IptJustin Abad FernandezNo ratings yet
- WLP-Week 2Document7 pagesWLP-Week 2Justin Abad FernandezNo ratings yet
- WLP-Week 5Document16 pagesWLP-Week 5Justin Abad FernandezNo ratings yet
- WLP-Week 4Document13 pagesWLP-Week 4Justin Abad FernandezNo ratings yet
- Assessing Sleep Quality of Shs StudentsDocument10 pagesAssessing Sleep Quality of Shs StudentsDian HernandezNo ratings yet
- 電容器絕緣油BDV 黏度 - SAS 40EDocument10 pages電容器絕緣油BDV 黏度 - SAS 40EShihlinElectricNo ratings yet
- Yellow Illustrative Digital Education For Children InfographicDocument1 pageYellow Illustrative Digital Education For Children InfographicNur Azimah AzibNo ratings yet
- Solution To Microwave Engineering Pozar Chapter 14 Exercise 17 With MATLABDocument3 pagesSolution To Microwave Engineering Pozar Chapter 14 Exercise 17 With MATLABJohn Bofarull GuixNo ratings yet
- "Twist Off" Type Tension Control Structural Bolt/Nut/Washer Assemblies, Steel, Heat Treated, 120/105 Ksi Minimum Tensile StrengthDocument8 pages"Twist Off" Type Tension Control Structural Bolt/Nut/Washer Assemblies, Steel, Heat Treated, 120/105 Ksi Minimum Tensile StrengthMohammed EldakhakhnyNo ratings yet
- Toyota Corolla A-131L OVERHAULDocument61 pagesToyota Corolla A-131L OVERHAULgerber damian100% (2)
- Client Name: Well, Max Birthdate: AGE: 7 Years, 8 Months School: Grade: 1 Dates of Assessment: July, 2011 Date of Report: Assessed By: FlamesDocument10 pagesClient Name: Well, Max Birthdate: AGE: 7 Years, 8 Months School: Grade: 1 Dates of Assessment: July, 2011 Date of Report: Assessed By: Flamesapi-160674927No ratings yet
- Jetblue Airways: A New BeginningDocument25 pagesJetblue Airways: A New BeginningHesty Tri BudihartiNo ratings yet
- 1st Quarter ToolkitDocument6 pages1st Quarter ToolkitDimple BolotaoloNo ratings yet
- Memory Based Paper Sbi Clerk 11th July 2 266bb4c1Document72 pagesMemory Based Paper Sbi Clerk 11th July 2 266bb4c1SHIVANI chouhanNo ratings yet
- Brkarc-2350 - 2014Document128 pagesBrkarc-2350 - 2014Sarah AnandNo ratings yet
- Selection Post IX Graduation 08-02-2022 EngDocument156 pagesSelection Post IX Graduation 08-02-2022 EngVijay singh TomarNo ratings yet
- The Spirit of Jugaad / Bricolage For Enhanced Corporate EntrepreneurshipDocument20 pagesThe Spirit of Jugaad / Bricolage For Enhanced Corporate EntrepreneurshippanditpreachesNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment On Temperature and Relative Humidity Deviation During On-Going Stability StudiesDocument2 pagesRisk Assessment On Temperature and Relative Humidity Deviation During On-Going Stability StudiesAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA ANo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in ICT ExcelDocument5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in ICT ExcelColleen Vender100% (3)
- LISI AEROSPACE - PULL-STEM™ and PULL-IN™ PinsDocument6 pagesLISI AEROSPACE - PULL-STEM™ and PULL-IN™ PinsLeandro González De CeccoNo ratings yet
- What I Need To KnowDocument16 pagesWhat I Need To Knowgirlie paraisoNo ratings yet
- UPS Technical Data Sheet (MS-DD-SAP01-ELE-DS-0015 - Rev2)Document6 pagesUPS Technical Data Sheet (MS-DD-SAP01-ELE-DS-0015 - Rev2)Muhammad YusufNo ratings yet
- CS198 Programming Assignment 2Document4 pagesCS198 Programming Assignment 2shellnexusNo ratings yet
- Error - Failed To Compute Elastoplastic Strain Variables - 1150 - Knowledge Base PDFDocument3 pagesError - Failed To Compute Elastoplastic Strain Variables - 1150 - Knowledge Base PDFmatinNo ratings yet
- Is Codes ListDocument37 pagesIs Codes Listmoondonoo7No ratings yet
- Aras Innovator Programmers GuideDocument105 pagesAras Innovator Programmers Guidem0de570No ratings yet
- Heater: Hydrate PreventionDocument12 pagesHeater: Hydrate PreventionMahmoud Ahmed Ali AbdelrazikNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management LBdA3TJvQgDocument420 pagesStrategic Management LBdA3TJvQgSazzad HossainNo ratings yet
- CCE Catalogue DetailedDocument28 pagesCCE Catalogue DetailedIshaan SinghNo ratings yet
- Curiculum Vitae JurnalisDocument1 pageCuriculum Vitae JurnalisEh Ada UjankNo ratings yet
- Frampton AntithesispedagogyDocument2 pagesFrampton AntithesispedagogyJohann WieseNo ratings yet
- Statistical Methods For Spatial Data AnalysisDocument3 pagesStatistical Methods For Spatial Data Analysissakali ali0% (1)