Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MATHLAA DP1 Test 2 - Binomials and Quadratics
MATHLAA DP1 Test 2 - Binomials and Quadratics
Uploaded by
Daniil SHULGAOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MATHLAA DP1 Test 2 - Binomials and Quadratics
MATHLAA DP1 Test 2 - Binomials and Quadratics
Uploaded by
Daniil SHULGACopyright:
Available Formats
NO CALCULATORS ALLOWED FOR THE ENTIRE TEST
1. A room has nine desks arranged in three rows of three desks. Three students sit in the room. If
the students randomly choose a desk find the probability that two out of the front three desks are
chosen.
(Total 5 marks)
IB MAT HLAA: Binomials and Quadratics 1
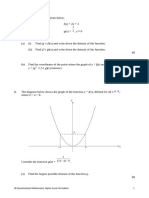
2. The diagram below shows a solid with volume V, obtained from a cube with edge a > 1 when a
1
smaller cube with edge is removed.
a
diagram not to scale
1
Let x = a − .
a
(a) Find V in terms of x.
(4)
1+ 5
(b) Hence or otherwise, show that the only value of a for which V = 4x is a = .
2
(4)
(Total 8 marks)
IB MAT HLAA: Binomials and Quadratics 2
n
x
3. When 1 + , n , is expanded in ascending powers of x, the coefficient of x3 is 70.
2
(a) Find the value of n.
(5)
(b) Hence, find the coefficient of x2.
(1)
(Total 6 marks)
4. (a) Write down the quadratic expression 2x2 + x – 3 as the product of two linear factors.
(1)
(b) Hence, or otherwise, find the coefficient of x in the expansion of (2x2 + x – 3)8.
(4)
(Total 5 marks)
IB MAT HLAA: Binomials and Quadratics 3
5. The diagram shows the graphs of a linear function f and a quadratic function g.
f
On the same axes sketch the graph of . Indicate clearly where the x-intercept and the
g
asymptotes occur.
(Total 5 marks)
6. (a) Express the quadratic 3x2 – 6x + 5 in the form a(x + b)2 + c, where a, b, c .
(3)
(b) Describe a sequence of transformations that transforms the graph of y = x2 to the graph of
y = 3x2 – 6x + 5.
(3)
(Total 6 marks)
IB MAT HLAA: Binomials and Quadratics 4
7.
(1)
(6)
(3)
(3)
(Total 13 marks)
IB MAT HLAA: Binomials and Quadratics 5
You might also like
- Total Pulling Weight of Trolley: 1. Calculation For Pulling ForceDocument5 pagesTotal Pulling Weight of Trolley: 1. Calculation For Pulling ForceNimesh m100% (1)
- Functions Past PapersDocument10 pagesFunctions Past Paperssilagulec9No ratings yet
- Mathematics HL Review Functions GDC 2016: X 2, Giving Your AnswerDocument6 pagesMathematics HL Review Functions GDC 2016: X 2, Giving Your AnswerԱրման ԿարապետյանNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 4. Binomial TheoremDocument1 pageWorksheet 4. Binomial TheoremvalerieNo ratings yet
- Every C2 Question EverDocument52 pagesEvery C2 Question EverRhipz0% (1)
- Section A (45, Marks) Answer All Questions in This Section.: Az y A X Az y A X Z y AxDocument8 pagesSection A (45, Marks) Answer All Questions in This Section.: Az y A X Az y A X Z y Axvoon sjNo ratings yet
- Laws of Logarithms 1Document16 pagesLaws of Logarithms 1savevideos11333333No ratings yet
- AAHLDocument4 pagesAAHLjoseph ronggurNo ratings yet
- p1 Practice Exam Paper B 1.3 2Document10 pagesp1 Practice Exam Paper B 1.3 2Ester MelianaNo ratings yet
- Section A (45, Marks) Answer All Questions in This Section.: Az y A X Az y A X Z y AxDocument8 pagesSection A (45, Marks) Answer All Questions in This Section.: Az y A X Az y A X Z y AxlllNo ratings yet
- IB Math SequencesDocument3 pagesIB Math SequencesSaumyaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Grade 11 June Exam 2019Document9 pagesMathematics Grade 11 June Exam 2019Rowan PhillipsNo ratings yet
- C2 Exponentials & Logs - Laws of Logs PDFDocument16 pagesC2 Exponentials & Logs - Laws of Logs PDFtechang1No ratings yet
- HL Binomial Theorem ProblemsDocument1 pageHL Binomial Theorem Problemsarvindshukla123No ratings yet
- HL Binomial Theorem ProblemsDocument1 pageHL Binomial Theorem Problemsarvindshukla123No ratings yet
- Mathematics Pilot 2Document3 pagesMathematics Pilot 2Kaung Wai HtetNo ratings yet
- Corozal Community College Third Form Mathematics RemedialDocument4 pagesCorozal Community College Third Form Mathematics RemedialAngel ZetinaNo ratings yet
- Integration I HL MathDocument8 pagesIntegration I HL MathRonald McdonaldNo ratings yet
- IB Questionbank Mathematical Studies 3rd Edition 1Document9 pagesIB Questionbank Mathematical Studies 3rd Edition 1KatherineNo ratings yet
- Further Pure Revision: Using IB Higher QuestionsDocument5 pagesFurther Pure Revision: Using IB Higher QuestionsMasimba MhangamiNo ratings yet
- Y12 Chapter 1 To 5 Simultaneous Equations Follow Up WorkDocument6 pagesY12 Chapter 1 To 5 Simultaneous Equations Follow Up Workabdullahkhan.swabi2007No ratings yet
- EB Calc 1 Test Prep 206 Mins With Mark SchemeDocument23 pagesEB Calc 1 Test Prep 206 Mins With Mark SchemeZhang JingkangNo ratings yet
- C3 Exponentials and Logarithms - Laws of LogsDocument11 pagesC3 Exponentials and Logarithms - Laws of LogsFran LeeNo ratings yet
- 5) A Level Further Maths Hyperbolic Functions QPDocument5 pages5) A Level Further Maths Hyperbolic Functions QPNelson BainNo ratings yet
- Garstan Grover Predicted Paper 2 2024Document8 pagesGarstan Grover Predicted Paper 2 2024Daily Quran AhmadNo ratings yet
- Aqa MBP1 W QP Nov04Document4 pagesAqa MBP1 W QP Nov04yanghaoyi1985No ratings yet
- Algebra NonCalc 1Document20 pagesAlgebra NonCalc 1Aden TseNo ratings yet
- 2014 2 HSBM Trial QDocument3 pages2014 2 HSBM Trial QHII SIEW TUNG MoeNo ratings yet
- ch2 & 3 Test MsDocument6 pagesch2 & 3 Test MsAyesha NoumanNo ratings yet
- Math IB Revision CalcusDocument56 pagesMath IB Revision Calcusmykiri79100% (1)
- Aqa MFP1 W QP Jun07Document10 pagesAqa MFP1 W QP Jun07Özgür Oz Yilmaz MehmetNo ratings yet
- Function 2 - Paper 2Document4 pagesFunction 2 - Paper 2Bramantya PribadiNo ratings yet
- MATHLAA DP1 Test 3 - Proofs and PolynomialsDocument2 pagesMATHLAA DP1 Test 3 - Proofs and PolynomialsDaniil SHULGANo ratings yet
- Topic 1 - Algebra Paper 1Document13 pagesTopic 1 - Algebra Paper 1AmalAbdlFattahNo ratings yet
- c1 Test Paper 2Document2 pagesc1 Test Paper 2Hesham MohamedNo ratings yet
- Properties of Curves Worksheet Easy Problems 1Document9 pagesProperties of Curves Worksheet Easy Problems 1V NagarjunaNo ratings yet
- Propertiescurve AAHLDocument10 pagesPropertiescurve AAHLjoseph ronggurNo ratings yet
- RevisionDocument6 pagesRevisionKaran PrabaNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Revision 1Document8 pagesGrade 12 Revision 1ignatia indahNo ratings yet
- Worksheet (4) - Extra Exercises On Integral CalculusDocument19 pagesWorksheet (4) - Extra Exercises On Integral Calculusibrahim fadelNo ratings yet
- C4: Questions From Past Exam Papers - Partial Fractions and Binomial ExpansionDocument23 pagesC4: Questions From Past Exam Papers - Partial Fractions and Binomial Expansionerwin kosasiNo ratings yet
- Algebra and Functions C4Document5 pagesAlgebra and Functions C4Pulkit SharmaNo ratings yet
- 2) Práctica Sucesiones y Series Geométrica USO CALCUDocument3 pages2) Práctica Sucesiones y Series Geométrica USO CALCUAlison Alvarado OtárolaNo ratings yet
- University of Malta: Junior College JUNE 2010Document4 pagesUniversity of Malta: Junior College JUNE 2010Brendon ChiwengaNo ratings yet
- Quadratics Pure 1Document27 pagesQuadratics Pure 1Afnan JaradatNo ratings yet
- Year 12 January Test - Chapter 1-10Document4 pagesYear 12 January Test - Chapter 1-10jayval1426No ratings yet
- University of Malta: Junior College JUNE 2011Document4 pagesUniversity of Malta: Junior College JUNE 2011MargaretNo ratings yet
- Advanced Mathematics 1Document4 pagesAdvanced Mathematics 1james paul100% (1)
- Inverse 3x3 Matrix (A-Level Only)Document23 pagesInverse 3x3 Matrix (A-Level Only)lorylela128No ratings yet
- Linear LawDocument4 pagesLinear LawJoann NgNo ratings yet
- Warming Up Questions - Paper 2 1.: A P R KDocument2 pagesWarming Up Questions - Paper 2 1.: A P R KBramantya PribadiNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 08 Jun 2023Document3 pagesAdobe Scan 08 Jun 2023TeKy FnNo ratings yet
- Test 7 RevisionDocument27 pagesTest 7 RevisionisaacNo ratings yet
- Answer All Questions.: 5 8 Log 2 Log 3Document2 pagesAnswer All Questions.: 5 8 Log 2 Log 3zan2812No ratings yet
- Quadratic SL Q PDFDocument15 pagesQuadratic SL Q PDFSamar GoelNo ratings yet
- Business Mathematics - Model PaperDocument4 pagesBusiness Mathematics - Model PaperUmar AliNo ratings yet
- Business Mathematics - Model PaperDocument4 pagesBusiness Mathematics - Model PaperscamnitinNo ratings yet
- Business Mathematics - Model PaperDocument4 pagesBusiness Mathematics - Model Paperritu mandiya "student"No ratings yet
- Business Mathematics - Model PaperDocument4 pagesBusiness Mathematics - Model PaperTafadzwa KumaniNo ratings yet
- Quadratics PureDocument28 pagesQuadratics PureAfnan JaradatNo ratings yet
- Refraction Through Rectangular Glass SlabDocument3 pagesRefraction Through Rectangular Glass SlabPooja Satheesh100% (1)
- Bolt Preloading and DesignDocument10 pagesBolt Preloading and DesignDianna LambertNo ratings yet
- Double Block and Bleed IsolationDocument24 pagesDouble Block and Bleed Isolationkaizhong1No ratings yet
- Neet 2021Document48 pagesNeet 2021VideoGamesNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2 Ernielle Rae Dela Cruz BSCE-4ADocument9 pagesQuiz 2 Ernielle Rae Dela Cruz BSCE-4AErnielle Rae Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Ebtjr DLPDocument10 pagesEbtjr DLPRomar Brin GramajeNo ratings yet
- Lamina PropertiesDocument7 pagesLamina PropertiesMohd ShahrizanNo ratings yet
- 2 UndeterminedCoefficients SDocument39 pages2 UndeterminedCoefficients SRivalelo HeavymanNo ratings yet
- AISC Live WebinarsDocument25 pagesAISC Live WebinarsHectorNo ratings yet
- Circuit Theory: Report BigprojectDocument10 pagesCircuit Theory: Report BigprojectVũ Hoàng LongNo ratings yet
- Question 1: A Steel Machine Part Is Statically Loaded and Has A YieldDocument9 pagesQuestion 1: A Steel Machine Part Is Statically Loaded and Has A YieldFurkan ŞENNo ratings yet
- Reference Only: I Pus Pond StreetDocument132 pagesReference Only: I Pus Pond StreetJagdish ShindeNo ratings yet
- Allen Chemistry 2Document14 pagesAllen Chemistry 2visitpriyanshujoshi0% (1)
- Lindab AirductsystemsDocument388 pagesLindab AirductsystemsrpufitaNo ratings yet
- First Asia Institute of Technology and Humanities Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics General PhysicsDocument34 pagesFirst Asia Institute of Technology and Humanities Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics General PhysicsAlexandra HerreraNo ratings yet
- Physical Properties of Pumice and Its Behavior As A Coarse Aggregate in ConcreteDocument11 pagesPhysical Properties of Pumice and Its Behavior As A Coarse Aggregate in ConcreteDelicate BantuNo ratings yet
- L3 - Phase Change at Reflection, Stoke's Law, Thin FilmDocument12 pagesL3 - Phase Change at Reflection, Stoke's Law, Thin FilmGaurangi AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Earthquake EngineeringDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Earthquake EngineeringAjay AjaiNo ratings yet
- Evacuation Center (Design of Beam2)Document35 pagesEvacuation Center (Design of Beam2)jerick calingasanNo ratings yet
- Kinematics Olevel Practice QuestionsDocument2 pagesKinematics Olevel Practice Questionstaha zaidi100% (3)
- MV HV Cable ManufacturingDocument33 pagesMV HV Cable ManufacturingAris BudiantoNo ratings yet
- 11 - 30 - 2017 12 - 24 - 11 PM - Final ReportDocument39 pages11 - 30 - 2017 12 - 24 - 11 PM - Final Report2JH19CV015 Mohammedasjadraza MullaNo ratings yet
- 617s 617dDocument1 page617s 617dAri PrasetyoNo ratings yet
- Diagrama Electrico Index 840C - 23469915 - InglesDocument107 pagesDiagrama Electrico Index 840C - 23469915 - InglesJuan QuinteroNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of The Particle Sizes of Four Clay Minerals Tan2016Document12 pagesEvaluation of The Particle Sizes of Four Clay Minerals Tan2016Laura Ximena Giraldo100% (1)
- The Modular Compact Rheometer Series: Product Name MCR EvolutionDocument17 pagesThe Modular Compact Rheometer Series: Product Name MCR EvolutionAbdul MalekNo ratings yet
- Checklist Pavement AnalysisDocument2 pagesChecklist Pavement Analysisp.v.n. lakshmanNo ratings yet
- ACFrOgABF4Wc8jfUCwS1Ot6qBqOF62670WdNhPZLoaDySa0mDDkfqLxE3tNFMDt4USrLqyj VtMwy5YdmnxpqfAti9YVEQnGoloG1QOkL4ZX-etvt7 lM1AhSz1V0OpCCG2YNSXHEGePNBlt-Z3yDocument16 pagesACFrOgABF4Wc8jfUCwS1Ot6qBqOF62670WdNhPZLoaDySa0mDDkfqLxE3tNFMDt4USrLqyj VtMwy5YdmnxpqfAti9YVEQnGoloG1QOkL4ZX-etvt7 lM1AhSz1V0OpCCG2YNSXHEGePNBlt-Z3yNatália Carolina Nascentes MarraNo ratings yet
- ElectrostaticDocument16 pagesElectrostaticDRAG-E-SPORT100% (1)