Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Diff Salts
Diff Salts
Uploaded by
Arnav GuptaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- MetalsDocument12 pagesMetalsdela2No ratings yet
- Metals NotesDocument19 pagesMetals NotesELIJAH MUPETANo ratings yet
- Thermal DecompositionDocument4 pagesThermal DecompositionDiddled_skittlesNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Week 2 4Document6 pagesChemistry Week 2 4nkweguedward1No ratings yet
- Reactivity Series of Metals: Reactions of Metals Effect of Heat On Metal CarbonatesDocument24 pagesReactivity Series of Metals: Reactions of Metals Effect of Heat On Metal CarbonatesCarl Agape DavisNo ratings yet
- Reactivity SeriesDocument5 pagesReactivity SeriesTAKUNDA MARIMENo ratings yet
- S Block ElementsDocument4 pagesS Block ElementssubkitsNo ratings yet
- Metals NotesDocument4 pagesMetals NotesXGC Ahssn YtNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non-MetalDocument6 pagesMetals and Non-MetalAansh ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Mainly in Group I, Group II, and The Transition Block - Those The Staircase LineDocument14 pagesMainly in Group I, Group II, and The Transition Block - Those The Staircase LineOrderPlace AccountNo ratings yet
- CH 3Document12 pagesCH 3charanNo ratings yet
- Importance of MetalsDocument0 pagesImportance of MetalsAdnan Chowdhury100% (1)
- Metal ReactivityDocument30 pagesMetal ReactivityMin Nyo SinNo ratings yet
- Ch3 METALS AND NON METALS PART2Document6 pagesCh3 METALS AND NON METALS PART2Varsha IX-ANo ratings yet
- Chemistry NotesDocument3 pagesChemistry NotesIngrid ChanNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non MetalsDocument57 pagesMetals and Non MetalsLOLBOINo ratings yet
- Importance of MetalsDocument22 pagesImportance of MetalsLucas RebornNo ratings yet
- Alkali Metals and Alkaline Earth MetalsDocument16 pagesAlkali Metals and Alkaline Earth MetalsPrashantNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non-MetalsDocument23 pagesMetals and Non-MetalsAnonymous ufMAGXcskMNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non Metals - NotesDocument13 pagesMetals and Non Metals - NotesmittalshivamNo ratings yet
- Re Activity Series & Corrosion of MetalsDocument8 pagesRe Activity Series & Corrosion of MetalsAli MahadNo ratings yet
- DownloadedDocument12 pagesDownloadedAniket shuklaNo ratings yet
- Actions of Heat On:: Metals Oxides Metals Hydroxides Carbonates NitratesDocument1 pageActions of Heat On:: Metals Oxides Metals Hydroxides Carbonates NitratesKeyur KadiwarNo ratings yet
- Chap 9Document17 pagesChap 9Tun Lin AungNo ratings yet
- Metals Updated - 240327 - 155648Document19 pagesMetals Updated - 240327 - 155648jhkxt22n9sNo ratings yet
- Metals OlevleDocument9 pagesMetals OlevleaayannisarNo ratings yet
- Properties of MetalsDocument17 pagesProperties of MetalsDavies MasumbaNo ratings yet
- Extraction (提煉) of Metal s from Metal Ores (礦石)Document53 pagesExtraction (提煉) of Metal s from Metal Ores (礦石)manish932No ratings yet
- 10th Metals and Non-Metals Test Paper Solved - 01 PDFDocument3 pages10th Metals and Non-Metals Test Paper Solved - 01 PDFRamachandranPerumalNo ratings yet
- MetalsDocument14 pagesMetalsnayyabNo ratings yet
- METALSDocument12 pagesMETALSjpkaomeNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Metals and Non MetalsDocument10 pagesNCERT Solutions For CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Metals and Non MetalsHari PrasadNo ratings yet
- Ref: Corrosion: AlloysDocument7 pagesRef: Corrosion: AlloysAhmed shakilNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry - Redox, Reactivity Series and AnalysisDocument20 pagesIGCSE Chemistry - Redox, Reactivity Series and AnalysisChemistryKlipz93% (14)
- 3 NOV Class 10 Metals and Non-Metals ChemDocument40 pages3 NOV Class 10 Metals and Non-Metals Chemgourav kaliaNo ratings yet
- 3 Metals and Non MetalsDocument23 pages3 Metals and Non Metalsmazharpunjabi67% (3)
- CSEC Chem Metals Chemistry of Gardening EtcDocument25 pagesCSEC Chem Metals Chemistry of Gardening Etcdela2100% (2)
- Metals - PropertiesDocument66 pagesMetals - Propertiesrheanna.bartonNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non-Metals - Chemical Properties NotesDocument13 pagesMetals and Non-Metals - Chemical Properties NotesDhyan ShahNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non MetalsDocument15 pagesMetals and Non Metals2erwr100% (2)
- Metals and Non MetalsDocument10 pagesMetals and Non MetalsKaran MahajanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13, 14 - Metals PDFDocument9 pagesChapter 13, 14 - Metals PDFAarush SharmaNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non-MetalsDocument14 pagesMetals and Non-MetalsKunal HazarikaNo ratings yet
- 1 Characteristics of MetalsDocument2 pages1 Characteristics of MetalsMatthew BeekhooNo ratings yet
- MetallurgyDocument5 pagesMetallurgyrishikeshsunbeamianNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non Metals - Shobhit NirwanDocument17 pagesMetals and Non Metals - Shobhit NirwanBhaskar 8287No ratings yet
- Metals and Non Metals-1Document20 pagesMetals and Non Metals-1aditiaryaa.23No ratings yet
- Metals and Metallurgy NotesDocument6 pagesMetals and Metallurgy Notesgaziahmad100% (2)
- MetalsDocument22 pagesMetalsWalu BNNo ratings yet
- 4.4. Revision Checklist: Chemical Changes: Reactivity of MetalsDocument6 pages4.4. Revision Checklist: Chemical Changes: Reactivity of MetalsJadyn Mc SweenNo ratings yet
- 4.4. Revision Checklist: Chemical Changes: Reactivity of MetalsDocument6 pages4.4. Revision Checklist: Chemical Changes: Reactivity of MetalsJadyn Mc SweenNo ratings yet
- D 4-4-Chemical-Changes-TrilogyDocument5 pagesD 4-4-Chemical-Changes-Trilogyishikagajjar123No ratings yet
- DR Khin Maung Toe: ChemistryDocument25 pagesDR Khin Maung Toe: ChemistryHan Zin OoNo ratings yet
- 4.4 Chemical ChangesDocument6 pages4.4 Chemical Changesdynamiccosmic7No ratings yet
- Lecture04b Main-Group Elements-PART2 - PenDocument40 pagesLecture04b Main-Group Elements-PART2 - PenAaf AbdRashidNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Class - VIII Topic-MetallurgyDocument46 pagesChemistry Class - VIII Topic-Metallurgyrajesh duaNo ratings yet
- 8th Metal and Non MetalDocument8 pages8th Metal and Non MetalsubrotokumarmohantaNo ratings yet
- The Working of Steel: Annealing, Heat Treating and Hardening of Carbon and Alloy SteelFrom EverandThe Working of Steel: Annealing, Heat Treating and Hardening of Carbon and Alloy SteelNo ratings yet
- Extractive Metallurgy 2: Metallurgical Reaction ProcessesFrom EverandExtractive Metallurgy 2: Metallurgical Reaction ProcessesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Oxy-Acetylene Welding and Cutting: Electric, Forge and Thermit Welding together with related methods and materials used in metal working and the oxygen process for removal of carbonFrom EverandOxy-Acetylene Welding and Cutting: Electric, Forge and Thermit Welding together with related methods and materials used in metal working and the oxygen process for removal of carbonRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Chaoter5notesphysics - MayankDocument6 pagesChaoter5notesphysics - MayankArnav GuptaNo ratings yet
- Bio Linking QuestionsDocument102 pagesBio Linking QuestionsArnav GuptaNo ratings yet
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Fuel CellsDocument1 pageAdvantages and Disadvantages of Fuel CellsArnav GuptaNo ratings yet
- Paper 6 Final RevisionDocument28 pagesPaper 6 Final RevisionArnav GuptaNo ratings yet
- ColoursDocument1 pageColoursArnav GuptaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chem ReactionsDocument1 pageOrganic Chem ReactionsArnav GuptaNo ratings yet
- Enemy 0620.62 NotesDocument21 pagesEnemy 0620.62 NotesArnav GuptaNo ratings yet
Diff Salts
Diff Salts
Uploaded by
Arnav GuptaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Diff Salts
Diff Salts
Uploaded by
Arnav GuptaCopyright:
Available Formats
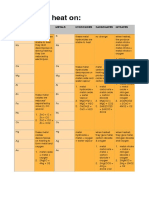
More reactive metals are more difficult to decompose(they have a greater thermal
stability). For example potassium and sodium carbonates are heat stable. Carbonates
below Na in the reactivity series decompose to the oxides of the metal + CO2.
Metals decompose more easily as it goes down the reactivity series.
CARBONATES
Metal carbonates such as: calcium carbonate, magnesium carbonate, zinc carbonate,
lead carbonate, iron(III) carbonate, copper(II) carbonate --> decompose on heating
to give metal oxide + CO2
Silver carbonate:
1. Decomposes on heating to give silver oxide + Co2
2. Silver oxide is thermally unstable
3. Silver oxide further decomposes to silver
2Ag2O(s) ---> 4Ag(s) + O2(g)
NITRATES
1. Potassium and sodium nitrates decompose into metal nitrite + O2
for example: 2NaNO3(s) ---> 2NaNO2(s) + O2(g)
2. Calcium nitrate, magnesium nitrate, aluminum nitrate, zinc nitrate, lead nitrate
and copper nitrate decompose into metal oxide + NO2 + O2
for example: 2Mg(NO3)2(s) ---> 2MgO(s) + 4NO2(g) + O2(g)
3. Gold nitrate and silver nitrate decompose into metal + NO2 + O2
for example: 2AgNO3(s) ---> 2Ag(s) + 2NO2(g) + O2(g)
HYDROXIDES
1. Calcium hydroxide, magnesium hydroxide, aluminum hydroxide, zinc hydroxide, iron
hydroxide, lead hydroxide and copper hydroxide decompose to form metal oxide + H2O
for example: Ca(OH)2(aq) ---> CaO(s) + H2O(l)
You might also like
- MetalsDocument12 pagesMetalsdela2No ratings yet
- Metals NotesDocument19 pagesMetals NotesELIJAH MUPETANo ratings yet
- Thermal DecompositionDocument4 pagesThermal DecompositionDiddled_skittlesNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Week 2 4Document6 pagesChemistry Week 2 4nkweguedward1No ratings yet
- Reactivity Series of Metals: Reactions of Metals Effect of Heat On Metal CarbonatesDocument24 pagesReactivity Series of Metals: Reactions of Metals Effect of Heat On Metal CarbonatesCarl Agape DavisNo ratings yet
- Reactivity SeriesDocument5 pagesReactivity SeriesTAKUNDA MARIMENo ratings yet
- S Block ElementsDocument4 pagesS Block ElementssubkitsNo ratings yet
- Metals NotesDocument4 pagesMetals NotesXGC Ahssn YtNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non-MetalDocument6 pagesMetals and Non-MetalAansh ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Mainly in Group I, Group II, and The Transition Block - Those The Staircase LineDocument14 pagesMainly in Group I, Group II, and The Transition Block - Those The Staircase LineOrderPlace AccountNo ratings yet
- CH 3Document12 pagesCH 3charanNo ratings yet
- Importance of MetalsDocument0 pagesImportance of MetalsAdnan Chowdhury100% (1)
- Metal ReactivityDocument30 pagesMetal ReactivityMin Nyo SinNo ratings yet
- Ch3 METALS AND NON METALS PART2Document6 pagesCh3 METALS AND NON METALS PART2Varsha IX-ANo ratings yet
- Chemistry NotesDocument3 pagesChemistry NotesIngrid ChanNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non MetalsDocument57 pagesMetals and Non MetalsLOLBOINo ratings yet
- Importance of MetalsDocument22 pagesImportance of MetalsLucas RebornNo ratings yet
- Alkali Metals and Alkaline Earth MetalsDocument16 pagesAlkali Metals and Alkaline Earth MetalsPrashantNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non-MetalsDocument23 pagesMetals and Non-MetalsAnonymous ufMAGXcskMNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non Metals - NotesDocument13 pagesMetals and Non Metals - NotesmittalshivamNo ratings yet
- Re Activity Series & Corrosion of MetalsDocument8 pagesRe Activity Series & Corrosion of MetalsAli MahadNo ratings yet
- DownloadedDocument12 pagesDownloadedAniket shuklaNo ratings yet
- Actions of Heat On:: Metals Oxides Metals Hydroxides Carbonates NitratesDocument1 pageActions of Heat On:: Metals Oxides Metals Hydroxides Carbonates NitratesKeyur KadiwarNo ratings yet
- Chap 9Document17 pagesChap 9Tun Lin AungNo ratings yet
- Metals Updated - 240327 - 155648Document19 pagesMetals Updated - 240327 - 155648jhkxt22n9sNo ratings yet
- Metals OlevleDocument9 pagesMetals OlevleaayannisarNo ratings yet
- Properties of MetalsDocument17 pagesProperties of MetalsDavies MasumbaNo ratings yet
- Extraction (提煉) of Metal s from Metal Ores (礦石)Document53 pagesExtraction (提煉) of Metal s from Metal Ores (礦石)manish932No ratings yet
- 10th Metals and Non-Metals Test Paper Solved - 01 PDFDocument3 pages10th Metals and Non-Metals Test Paper Solved - 01 PDFRamachandranPerumalNo ratings yet
- MetalsDocument14 pagesMetalsnayyabNo ratings yet
- METALSDocument12 pagesMETALSjpkaomeNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Metals and Non MetalsDocument10 pagesNCERT Solutions For CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Metals and Non MetalsHari PrasadNo ratings yet
- Ref: Corrosion: AlloysDocument7 pagesRef: Corrosion: AlloysAhmed shakilNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry - Redox, Reactivity Series and AnalysisDocument20 pagesIGCSE Chemistry - Redox, Reactivity Series and AnalysisChemistryKlipz93% (14)
- 3 NOV Class 10 Metals and Non-Metals ChemDocument40 pages3 NOV Class 10 Metals and Non-Metals Chemgourav kaliaNo ratings yet
- 3 Metals and Non MetalsDocument23 pages3 Metals and Non Metalsmazharpunjabi67% (3)
- CSEC Chem Metals Chemistry of Gardening EtcDocument25 pagesCSEC Chem Metals Chemistry of Gardening Etcdela2100% (2)
- Metals - PropertiesDocument66 pagesMetals - Propertiesrheanna.bartonNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non-Metals - Chemical Properties NotesDocument13 pagesMetals and Non-Metals - Chemical Properties NotesDhyan ShahNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non MetalsDocument15 pagesMetals and Non Metals2erwr100% (2)
- Metals and Non MetalsDocument10 pagesMetals and Non MetalsKaran MahajanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13, 14 - Metals PDFDocument9 pagesChapter 13, 14 - Metals PDFAarush SharmaNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non-MetalsDocument14 pagesMetals and Non-MetalsKunal HazarikaNo ratings yet
- 1 Characteristics of MetalsDocument2 pages1 Characteristics of MetalsMatthew BeekhooNo ratings yet
- MetallurgyDocument5 pagesMetallurgyrishikeshsunbeamianNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non Metals - Shobhit NirwanDocument17 pagesMetals and Non Metals - Shobhit NirwanBhaskar 8287No ratings yet
- Metals and Non Metals-1Document20 pagesMetals and Non Metals-1aditiaryaa.23No ratings yet
- Metals and Metallurgy NotesDocument6 pagesMetals and Metallurgy Notesgaziahmad100% (2)
- MetalsDocument22 pagesMetalsWalu BNNo ratings yet
- 4.4. Revision Checklist: Chemical Changes: Reactivity of MetalsDocument6 pages4.4. Revision Checklist: Chemical Changes: Reactivity of MetalsJadyn Mc SweenNo ratings yet
- 4.4. Revision Checklist: Chemical Changes: Reactivity of MetalsDocument6 pages4.4. Revision Checklist: Chemical Changes: Reactivity of MetalsJadyn Mc SweenNo ratings yet
- D 4-4-Chemical-Changes-TrilogyDocument5 pagesD 4-4-Chemical-Changes-Trilogyishikagajjar123No ratings yet
- DR Khin Maung Toe: ChemistryDocument25 pagesDR Khin Maung Toe: ChemistryHan Zin OoNo ratings yet
- 4.4 Chemical ChangesDocument6 pages4.4 Chemical Changesdynamiccosmic7No ratings yet
- Lecture04b Main-Group Elements-PART2 - PenDocument40 pagesLecture04b Main-Group Elements-PART2 - PenAaf AbdRashidNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Class - VIII Topic-MetallurgyDocument46 pagesChemistry Class - VIII Topic-Metallurgyrajesh duaNo ratings yet
- 8th Metal and Non MetalDocument8 pages8th Metal and Non MetalsubrotokumarmohantaNo ratings yet
- The Working of Steel: Annealing, Heat Treating and Hardening of Carbon and Alloy SteelFrom EverandThe Working of Steel: Annealing, Heat Treating and Hardening of Carbon and Alloy SteelNo ratings yet
- Extractive Metallurgy 2: Metallurgical Reaction ProcessesFrom EverandExtractive Metallurgy 2: Metallurgical Reaction ProcessesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Oxy-Acetylene Welding and Cutting: Electric, Forge and Thermit Welding together with related methods and materials used in metal working and the oxygen process for removal of carbonFrom EverandOxy-Acetylene Welding and Cutting: Electric, Forge and Thermit Welding together with related methods and materials used in metal working and the oxygen process for removal of carbonRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Chaoter5notesphysics - MayankDocument6 pagesChaoter5notesphysics - MayankArnav GuptaNo ratings yet
- Bio Linking QuestionsDocument102 pagesBio Linking QuestionsArnav GuptaNo ratings yet
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Fuel CellsDocument1 pageAdvantages and Disadvantages of Fuel CellsArnav GuptaNo ratings yet
- Paper 6 Final RevisionDocument28 pagesPaper 6 Final RevisionArnav GuptaNo ratings yet
- ColoursDocument1 pageColoursArnav GuptaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chem ReactionsDocument1 pageOrganic Chem ReactionsArnav GuptaNo ratings yet
- Enemy 0620.62 NotesDocument21 pagesEnemy 0620.62 NotesArnav GuptaNo ratings yet