Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cell Structure and Function
Cell Structure and Function
Uploaded by
KukuPaladCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Asterion Practical Handbook of Anatomy-2eDocument265 pagesAsterion Practical Handbook of Anatomy-2eMohammad AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Sop For Hemoglobin Determination by HPLCDocument13 pagesSop For Hemoglobin Determination by HPLCUMMID WashimNo ratings yet
- Bio f4 1Document1 pageBio f4 1afrina farihaNo ratings yet
- 1cell Structure and Taxonomy 1Document90 pages1cell Structure and Taxonomy 1Jezebhel ArestaNo ratings yet
- Microbial Morphology and ClassificationDocument95 pagesMicrobial Morphology and ClassificationAskYahGirl ChannelNo ratings yet
- 1cell Structure and TaxonomyDocument103 pages1cell Structure and TaxonomyJericho LastimosaNo ratings yet
- Introduction and Pioneers in Microbiology and ParasitologyDocument4 pagesIntroduction and Pioneers in Microbiology and ParasitologyJasmin Pearl AndayaNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 Parts of Cell and Function Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic CellsDocument2 pagesActivity 1 Parts of Cell and Function Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic CellsRIVERA, BRENNAN L.No ratings yet
- Notes Cells (Slides by Slidesgo)Document38 pagesNotes Cells (Slides by Slidesgo)salinaNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelle CardsDocument6 pagesCell Organelle CardsVienne MonroidNo ratings yet
- Activity 1Document4 pagesActivity 1sharksiedNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Ultrastructure of Cells (Main)Document46 pages1.2 Ultrastructure of Cells (Main)MeryemNo ratings yet
- Biology I For Non-Majors: Module 4: Prokaryotes and EukaryotesDocument23 pagesBiology I For Non-Majors: Module 4: Prokaryotes and EukaryotesEmma RiftyanNo ratings yet
- Activity 1Document4 pagesActivity 1sharksiedNo ratings yet
- The Biological CellDocument23 pagesThe Biological CellVivaMapwaNo ratings yet
- CellDocument75 pagesCellJustin SilviaNo ratings yet
- Cells F05Document31 pagesCells F05Fetro Dola SyamsuNo ratings yet
- Prokaryote Vs EukaryoteDocument48 pagesProkaryote Vs Eukaryotesunifeb128075No ratings yet
- General Biology-1: Senior High School Grade 12 GDocument6 pagesGeneral Biology-1: Senior High School Grade 12 GJackylyn Evangelista100% (2)
- Activity 1 Gen Bio 1Document3 pagesActivity 1 Gen Bio 1Villanueva, Liv Harlet A.No ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips - Cell Structure Functions Introduction Eucaryotic Cell StructureDocument31 pagesDokumen - Tips - Cell Structure Functions Introduction Eucaryotic Cell StructureJairra Jae LunaNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 9 Science Chap 5 - The Fundamental Unit of Life - Revision NotesDocument6 pagesCBSE Class 9 Science Chap 5 - The Fundamental Unit of Life - Revision NotesRahul ManhasNo ratings yet
- NeucleDocument25 pagesNeucleUjala SinghNo ratings yet
- Biology CellDocument25 pagesBiology CellcamumendoNo ratings yet
- Biochem Lecture 2Document3 pagesBiochem Lecture 2Samier AlihuddinNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Cell OrganisationDocument27 pagesCell Structure and Cell OrganisationAzmaniza AdnanNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument19 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsjhabNo ratings yet
- 3b-Bspsy-Gen-Zoo-Format-Doc (Human Cell)Document2 pages3b-Bspsy-Gen-Zoo-Format-Doc (Human Cell)JohnCaesar P SobrevegaNo ratings yet
- The Cellular Basis of LifeDocument50 pagesThe Cellular Basis of LifeSteve EstebanNo ratings yet
- Cell CompiledDocument7 pagesCell CompiledRizza Mae Telebrico CantereNo ratings yet
- IB Biology Notes - 23 Eukaryotic CellsDocument3 pagesIB Biology Notes - 23 Eukaryotic CellsJohn Philip D. NapalNo ratings yet
- Cell Grade 7Document65 pagesCell Grade 7SUDARAT THONGPHAYONGNo ratings yet
- Assignment in General Biology 1Document3 pagesAssignment in General Biology 1neil aldwin garciaNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio Module 3Document7 pagesGen Bio Module 3Jann Ranniel PanlilioNo ratings yet
- GNBIO1 Summary For Cell Structures and ClassificationsDocument6 pagesGNBIO1 Summary For Cell Structures and ClassificationsGgggnek OhculNo ratings yet
- KIFAYAT Tahisli Biology - First Edition V3Document135 pagesKIFAYAT Tahisli Biology - First Edition V3Ahmad Al FadelNo ratings yet
- Cell and Molecular BiologyDocument17 pagesCell and Molecular BiologyHizzei Caballero100% (4)
- Prokaryotic Cell Vs Eukaryotic CellDocument23 pagesProkaryotic Cell Vs Eukaryotic CellEleonor DistrajoNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles - Structure and FunctionDocument6 pagesCell Organelles - Structure and FunctionKaryl Marie Rodas JaminNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and EukaryotcG7Document41 pagesProkaryotic and EukaryotcG7Nes ConstanteNo ratings yet
- Chap 5 FullDocument130 pagesChap 5 Fullgaelle tannous100% (1)
- Prokaryotic VS. EukaryoticDocument49 pagesProkaryotic VS. EukaryoticusernameNo ratings yet
- CellDocument17 pagesCellAaliyah Quesha LadjamatliNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Cell WorksheetsDocument28 pagesPlant and Animal Cell WorksheetsMarisol Leal PradoNo ratings yet
- Cell Parts and Their FunctionsDocument3 pagesCell Parts and Their FunctionsChristine Suizo SebucaoNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument15 pagesBiologyChit su su zawNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Cells Digital PacketDocument22 pagesUnit 2 Cells Digital PacketTevin KimNo ratings yet
- ISE Bio Mod1 1Document19 pagesISE Bio Mod1 1Shubham YadavNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and FunctionsDocument23 pagesCell Structure and FunctionsAngel OrodioNo ratings yet
- Prok A Ryo Tic Eukaryotic CellsDocument31 pagesProk A Ryo Tic Eukaryotic CellsAMADO JR BANAWANo ratings yet
- Ana CellsDocument4 pagesAna CellsDCRUZNo ratings yet
- Sel PDFDocument32 pagesSel PDFJeje DengiNo ratings yet
- The Cell 1: Group 2Document37 pagesThe Cell 1: Group 2Vỹ KhangNo ratings yet
- Bio Notes (ZNotes) MYPDocument65 pagesBio Notes (ZNotes) MYPkimaaya vermaNo ratings yet
- Bio 103 L1-2 - NiaDocument33 pagesBio 103 L1-2 - Niasubrotoghosh2001No ratings yet
- Cell Bio Quiz 1Document3 pagesCell Bio Quiz 1raphaelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document100 pagesChapter 2AQEESHA NUWAIRA BINTI USMAN BN21110154No ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - The Cell - The Basic Unit of LifeDocument10 pagesLecture 2 - The Cell - The Basic Unit of LifeKaye EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles LectureDocument54 pagesCell Organelles LectureAlthea Aubrey AgbayaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Cell As The Basic Unit of LifeDocument3 pagesChapter 2 Cell As The Basic Unit of LifeKay TangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 BiologyDocument14 pagesChapter 1 BiologyMarina ArvanitopoulouNo ratings yet
- The Animal Cell and Division Biology for Kids | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandThe Animal Cell and Division Biology for Kids | Children's Biology BooksNo ratings yet
- Obstetric Nursing Normal AbnormalDocument20 pagesObstetric Nursing Normal Abnormalkim torinoNo ratings yet
- Stem LeavesDocument20 pagesStem LeavesMerrylFranciscoNo ratings yet
- Midterm 1 Review Psych 1102Document66 pagesMidterm 1 Review Psych 1102Roham RazaviNo ratings yet
- Hodgkins Lymphoma by Dr. Anum UsmanDocument48 pagesHodgkins Lymphoma by Dr. Anum UsmanHumar Haider100% (1)
- Laporan Kasus Hipertensi Pulmonal-Ridha MardhatillahDocument3 pagesLaporan Kasus Hipertensi Pulmonal-Ridha MardhatillahAtunNo ratings yet
- Horner Syndrome: A Clinical Review: Timothy J. MartinDocument10 pagesHorner Syndrome: A Clinical Review: Timothy J. Martinpresentator dadakanNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerve Examination 231109 191528Document43 pagesCranial Nerve Examination 231109 191528najlaxd2002No ratings yet
- VS TLN 27547 2208 3Document12 pagesVS TLN 27547 2208 3Deni ArdianNo ratings yet
- Wildlife EcologyDocument12 pagesWildlife Ecologysamarth.kumar2021No ratings yet
- COG PSYC ReviewerDocument6 pagesCOG PSYC ReviewerKyla JuantaNo ratings yet
- 200 Level Module 2 Histology QuestionsDocument8 pages200 Level Module 2 Histology QuestionsPrecious Julius100% (1)
- Thesis Topics Clinical BiochemistryDocument4 pagesThesis Topics Clinical Biochemistryafknoaabc100% (1)
- Harrisons Principles of Internal Medicine, 19th EditionDocument22 pagesHarrisons Principles of Internal Medicine, 19th EditionTALBIYAH SABDAH RIZAN TAUPIQ -No ratings yet
- Apoptosis LectureDocument103 pagesApoptosis LectureGajanan SaykhedkarNo ratings yet
- NematologyLaboratoryInvestigations PDFDocument195 pagesNematologyLaboratoryInvestigations PDFyenniffer VicenteNo ratings yet
- (P2 Esei) Compare Between Fish and HumanDocument2 pages(P2 Esei) Compare Between Fish and HumanKar Ru100% (3)
- Tissues: Biology Le.6Document41 pagesTissues: Biology Le.69B 36 Raghuram VedantamNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System SheetDocument11 pagesCardiovascular System SheetBetsy Brown ByersmithNo ratings yet
- College of Human Kinetics: Cagayan State UniversityDocument9 pagesCollege of Human Kinetics: Cagayan State UniversityVan Errl Nicolai SantosNo ratings yet
- Dopamine in ParkinsonsDocument2 pagesDopamine in ParkinsonsRanjitNo ratings yet
- MCH 402 Medicinal Chemistry (Chapter II)Document84 pagesMCH 402 Medicinal Chemistry (Chapter II)PARVATHY ANILNo ratings yet
- Chest X-Ray (CXR) Interpretation 2Document30 pagesChest X-Ray (CXR) Interpretation 2NaveedNo ratings yet
- Barriers of Protein and Peptide Drug DeliveryDocument12 pagesBarriers of Protein and Peptide Drug DeliveryAashish chaudhari100% (2)
- Linkage of Diabetic Retinopathy With Blood Antioxidants and Gut Microbiota in Type Two Diabetes Mellitus Saudi PatientsDocument11 pagesLinkage of Diabetic Retinopathy With Blood Antioxidants and Gut Microbiota in Type Two Diabetes Mellitus Saudi PatientsAthenaeum Scientific PublishersNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of OsteoarthritisDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of OsteoarthritisHajar ToharNo ratings yet
- STEM Fair Reaserch Paper SY 2023-2024Document7 pagesSTEM Fair Reaserch Paper SY 2023-2024ngumemagaliNo ratings yet
- 2018 - Alshammari The Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia and It's AetiologiesDocument6 pages2018 - Alshammari The Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia and It's AetiologieskanaNo ratings yet
- fMRI Analysis of Situational and Behavior Description Interview QuestionsDocument12 pagesfMRI Analysis of Situational and Behavior Description Interview QuestionsEszter SzerencsiNo ratings yet
Cell Structure and Function
Cell Structure and Function
Uploaded by
KukuPaladOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cell Structure and Function
Cell Structure and Function
Uploaded by
KukuPaladCopyright:
Available Formats
5/16/23, 8:29 PM Cell Structure and Function
Cell Structure and Cell Function
2.1 Cell Structure and Cell Function
Cell organelles Functions
Plasma membrane Regulates the movement of substances across the cell
Separates the contents of the cell from the external environment
Cell wall Maintains the shape of plant cells
Protects the plant cells from burst
Provides strength and support to the plant cell
Cytoplasm Acts as a medium for biochemical reactions of most living processes in the cell
Nucleus Carries genetic information in the form of DNA
Vacuole Stores nutrients, wastes and metabolic by-product
Ribosome Synthesises proteins
Mitochondrion Synthesises ATP
Site of cellular respiration
Rough endoplasmic reticulum Transports proteins made by the ribosomes throughout the cell
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum Synthesises lipids and carries detoxification of drugs
Golgi apparatus Modifies, transports, sort and package the proteins and carbohydrates
Lysosome Digests old and worn organelles
Breakdown complex organic molecules
Centriole Form spindle fibres during cell division
Chloroplast Site of photosynthesis
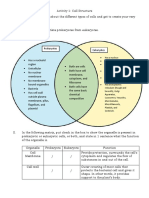
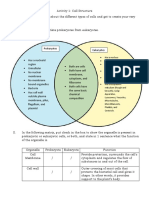
Similarities between plant cell and animal cell:
Both cells contain a nucleus, cytoplasm, plasma membrane, Golgi apparatus, mitochondrion, endoplasmic reticulum and ribosomes.
Differences between plant cell and animal cell:
Plant Cells Animal Cells
Has a fixed shape Does not have a fixed shape
Has a cell wall Does not have a cell wall
Has chloroplasts Does not have a chloroplasts
Has a large vacuole No vacuole
Stores carbohydrates in the form of starch Stores carbohydrates in the form of glycogen
Does not have a centriole Has centrioles
© 2023 Pandai.org All Rights Reserved Made with in Malaysia
https://question.pandai.org/note/read/kssm-bg-10-02-01/KSSM-F4-BG-02-01 1/1
You might also like
- Asterion Practical Handbook of Anatomy-2eDocument265 pagesAsterion Practical Handbook of Anatomy-2eMohammad AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Sop For Hemoglobin Determination by HPLCDocument13 pagesSop For Hemoglobin Determination by HPLCUMMID WashimNo ratings yet
- Bio f4 1Document1 pageBio f4 1afrina farihaNo ratings yet
- 1cell Structure and Taxonomy 1Document90 pages1cell Structure and Taxonomy 1Jezebhel ArestaNo ratings yet
- Microbial Morphology and ClassificationDocument95 pagesMicrobial Morphology and ClassificationAskYahGirl ChannelNo ratings yet
- 1cell Structure and TaxonomyDocument103 pages1cell Structure and TaxonomyJericho LastimosaNo ratings yet
- Introduction and Pioneers in Microbiology and ParasitologyDocument4 pagesIntroduction and Pioneers in Microbiology and ParasitologyJasmin Pearl AndayaNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 Parts of Cell and Function Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic CellsDocument2 pagesActivity 1 Parts of Cell and Function Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic CellsRIVERA, BRENNAN L.No ratings yet
- Notes Cells (Slides by Slidesgo)Document38 pagesNotes Cells (Slides by Slidesgo)salinaNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelle CardsDocument6 pagesCell Organelle CardsVienne MonroidNo ratings yet
- Activity 1Document4 pagesActivity 1sharksiedNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Ultrastructure of Cells (Main)Document46 pages1.2 Ultrastructure of Cells (Main)MeryemNo ratings yet
- Biology I For Non-Majors: Module 4: Prokaryotes and EukaryotesDocument23 pagesBiology I For Non-Majors: Module 4: Prokaryotes and EukaryotesEmma RiftyanNo ratings yet
- Activity 1Document4 pagesActivity 1sharksiedNo ratings yet
- The Biological CellDocument23 pagesThe Biological CellVivaMapwaNo ratings yet
- CellDocument75 pagesCellJustin SilviaNo ratings yet
- Cells F05Document31 pagesCells F05Fetro Dola SyamsuNo ratings yet
- Prokaryote Vs EukaryoteDocument48 pagesProkaryote Vs Eukaryotesunifeb128075No ratings yet
- General Biology-1: Senior High School Grade 12 GDocument6 pagesGeneral Biology-1: Senior High School Grade 12 GJackylyn Evangelista100% (2)
- Activity 1 Gen Bio 1Document3 pagesActivity 1 Gen Bio 1Villanueva, Liv Harlet A.No ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips - Cell Structure Functions Introduction Eucaryotic Cell StructureDocument31 pagesDokumen - Tips - Cell Structure Functions Introduction Eucaryotic Cell StructureJairra Jae LunaNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 9 Science Chap 5 - The Fundamental Unit of Life - Revision NotesDocument6 pagesCBSE Class 9 Science Chap 5 - The Fundamental Unit of Life - Revision NotesRahul ManhasNo ratings yet
- NeucleDocument25 pagesNeucleUjala SinghNo ratings yet
- Biology CellDocument25 pagesBiology CellcamumendoNo ratings yet
- Biochem Lecture 2Document3 pagesBiochem Lecture 2Samier AlihuddinNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Cell OrganisationDocument27 pagesCell Structure and Cell OrganisationAzmaniza AdnanNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument19 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsjhabNo ratings yet
- 3b-Bspsy-Gen-Zoo-Format-Doc (Human Cell)Document2 pages3b-Bspsy-Gen-Zoo-Format-Doc (Human Cell)JohnCaesar P SobrevegaNo ratings yet
- The Cellular Basis of LifeDocument50 pagesThe Cellular Basis of LifeSteve EstebanNo ratings yet
- Cell CompiledDocument7 pagesCell CompiledRizza Mae Telebrico CantereNo ratings yet
- IB Biology Notes - 23 Eukaryotic CellsDocument3 pagesIB Biology Notes - 23 Eukaryotic CellsJohn Philip D. NapalNo ratings yet
- Cell Grade 7Document65 pagesCell Grade 7SUDARAT THONGPHAYONGNo ratings yet
- Assignment in General Biology 1Document3 pagesAssignment in General Biology 1neil aldwin garciaNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio Module 3Document7 pagesGen Bio Module 3Jann Ranniel PanlilioNo ratings yet
- GNBIO1 Summary For Cell Structures and ClassificationsDocument6 pagesGNBIO1 Summary For Cell Structures and ClassificationsGgggnek OhculNo ratings yet
- KIFAYAT Tahisli Biology - First Edition V3Document135 pagesKIFAYAT Tahisli Biology - First Edition V3Ahmad Al FadelNo ratings yet
- Cell and Molecular BiologyDocument17 pagesCell and Molecular BiologyHizzei Caballero100% (4)
- Prokaryotic Cell Vs Eukaryotic CellDocument23 pagesProkaryotic Cell Vs Eukaryotic CellEleonor DistrajoNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles - Structure and FunctionDocument6 pagesCell Organelles - Structure and FunctionKaryl Marie Rodas JaminNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and EukaryotcG7Document41 pagesProkaryotic and EukaryotcG7Nes ConstanteNo ratings yet
- Chap 5 FullDocument130 pagesChap 5 Fullgaelle tannous100% (1)
- Prokaryotic VS. EukaryoticDocument49 pagesProkaryotic VS. EukaryoticusernameNo ratings yet
- CellDocument17 pagesCellAaliyah Quesha LadjamatliNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Cell WorksheetsDocument28 pagesPlant and Animal Cell WorksheetsMarisol Leal PradoNo ratings yet
- Cell Parts and Their FunctionsDocument3 pagesCell Parts and Their FunctionsChristine Suizo SebucaoNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument15 pagesBiologyChit su su zawNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Cells Digital PacketDocument22 pagesUnit 2 Cells Digital PacketTevin KimNo ratings yet
- ISE Bio Mod1 1Document19 pagesISE Bio Mod1 1Shubham YadavNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and FunctionsDocument23 pagesCell Structure and FunctionsAngel OrodioNo ratings yet
- Prok A Ryo Tic Eukaryotic CellsDocument31 pagesProk A Ryo Tic Eukaryotic CellsAMADO JR BANAWANo ratings yet
- Ana CellsDocument4 pagesAna CellsDCRUZNo ratings yet
- Sel PDFDocument32 pagesSel PDFJeje DengiNo ratings yet
- The Cell 1: Group 2Document37 pagesThe Cell 1: Group 2Vỹ KhangNo ratings yet
- Bio Notes (ZNotes) MYPDocument65 pagesBio Notes (ZNotes) MYPkimaaya vermaNo ratings yet
- Bio 103 L1-2 - NiaDocument33 pagesBio 103 L1-2 - Niasubrotoghosh2001No ratings yet
- Cell Bio Quiz 1Document3 pagesCell Bio Quiz 1raphaelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document100 pagesChapter 2AQEESHA NUWAIRA BINTI USMAN BN21110154No ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - The Cell - The Basic Unit of LifeDocument10 pagesLecture 2 - The Cell - The Basic Unit of LifeKaye EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles LectureDocument54 pagesCell Organelles LectureAlthea Aubrey AgbayaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Cell As The Basic Unit of LifeDocument3 pagesChapter 2 Cell As The Basic Unit of LifeKay TangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 BiologyDocument14 pagesChapter 1 BiologyMarina ArvanitopoulouNo ratings yet
- The Animal Cell and Division Biology for Kids | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandThe Animal Cell and Division Biology for Kids | Children's Biology BooksNo ratings yet
- Obstetric Nursing Normal AbnormalDocument20 pagesObstetric Nursing Normal Abnormalkim torinoNo ratings yet
- Stem LeavesDocument20 pagesStem LeavesMerrylFranciscoNo ratings yet
- Midterm 1 Review Psych 1102Document66 pagesMidterm 1 Review Psych 1102Roham RazaviNo ratings yet
- Hodgkins Lymphoma by Dr. Anum UsmanDocument48 pagesHodgkins Lymphoma by Dr. Anum UsmanHumar Haider100% (1)
- Laporan Kasus Hipertensi Pulmonal-Ridha MardhatillahDocument3 pagesLaporan Kasus Hipertensi Pulmonal-Ridha MardhatillahAtunNo ratings yet
- Horner Syndrome: A Clinical Review: Timothy J. MartinDocument10 pagesHorner Syndrome: A Clinical Review: Timothy J. Martinpresentator dadakanNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerve Examination 231109 191528Document43 pagesCranial Nerve Examination 231109 191528najlaxd2002No ratings yet
- VS TLN 27547 2208 3Document12 pagesVS TLN 27547 2208 3Deni ArdianNo ratings yet
- Wildlife EcologyDocument12 pagesWildlife Ecologysamarth.kumar2021No ratings yet
- COG PSYC ReviewerDocument6 pagesCOG PSYC ReviewerKyla JuantaNo ratings yet
- 200 Level Module 2 Histology QuestionsDocument8 pages200 Level Module 2 Histology QuestionsPrecious Julius100% (1)
- Thesis Topics Clinical BiochemistryDocument4 pagesThesis Topics Clinical Biochemistryafknoaabc100% (1)
- Harrisons Principles of Internal Medicine, 19th EditionDocument22 pagesHarrisons Principles of Internal Medicine, 19th EditionTALBIYAH SABDAH RIZAN TAUPIQ -No ratings yet
- Apoptosis LectureDocument103 pagesApoptosis LectureGajanan SaykhedkarNo ratings yet
- NematologyLaboratoryInvestigations PDFDocument195 pagesNematologyLaboratoryInvestigations PDFyenniffer VicenteNo ratings yet
- (P2 Esei) Compare Between Fish and HumanDocument2 pages(P2 Esei) Compare Between Fish and HumanKar Ru100% (3)
- Tissues: Biology Le.6Document41 pagesTissues: Biology Le.69B 36 Raghuram VedantamNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System SheetDocument11 pagesCardiovascular System SheetBetsy Brown ByersmithNo ratings yet
- College of Human Kinetics: Cagayan State UniversityDocument9 pagesCollege of Human Kinetics: Cagayan State UniversityVan Errl Nicolai SantosNo ratings yet
- Dopamine in ParkinsonsDocument2 pagesDopamine in ParkinsonsRanjitNo ratings yet
- MCH 402 Medicinal Chemistry (Chapter II)Document84 pagesMCH 402 Medicinal Chemistry (Chapter II)PARVATHY ANILNo ratings yet
- Chest X-Ray (CXR) Interpretation 2Document30 pagesChest X-Ray (CXR) Interpretation 2NaveedNo ratings yet
- Barriers of Protein and Peptide Drug DeliveryDocument12 pagesBarriers of Protein and Peptide Drug DeliveryAashish chaudhari100% (2)
- Linkage of Diabetic Retinopathy With Blood Antioxidants and Gut Microbiota in Type Two Diabetes Mellitus Saudi PatientsDocument11 pagesLinkage of Diabetic Retinopathy With Blood Antioxidants and Gut Microbiota in Type Two Diabetes Mellitus Saudi PatientsAthenaeum Scientific PublishersNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of OsteoarthritisDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of OsteoarthritisHajar ToharNo ratings yet
- STEM Fair Reaserch Paper SY 2023-2024Document7 pagesSTEM Fair Reaserch Paper SY 2023-2024ngumemagaliNo ratings yet
- 2018 - Alshammari The Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia and It's AetiologiesDocument6 pages2018 - Alshammari The Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia and It's AetiologieskanaNo ratings yet
- fMRI Analysis of Situational and Behavior Description Interview QuestionsDocument12 pagesfMRI Analysis of Situational and Behavior Description Interview QuestionsEszter SzerencsiNo ratings yet