Professional Documents
Culture Documents
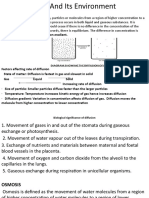
Osmosis and Diffusion
Osmosis and Diffusion
Uploaded by
sidra ahmadOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Osmosis and Diffusion
Osmosis and Diffusion
Uploaded by
sidra ahmadCopyright:
Available Formats
MOVEME
NTPAST
IMP IN PAPER
AND
CONCEPTS AND QS
1. Examples of diffusion (in living org.)
Oxygen molecules moving into the red blood cells
Carbon dio molecules moving out of the red blood cells
C and o move in and out of the mesophyll cells
C/O/W.V moving in or out of the stomata
2. What increases the rate of diffusion?
Increase in concentration gradient
Decrease in thickness of membrane
Increasing the surface are of the membrane
Increasing the temp
3. What happens to an animal cell when placed in concentrated and
dilute solution?
Concentrated: water will leave the cell causing the cell to shrink.
Dilute/pure: water will enter the cell causing the cell to swell up and
burst
4. What happens to a plant cell when placed in a concentrated and
dilute solution?
Concentrated: water will leave the cell making it flaccid, if more water
leaves the cell, it will become plasmolysed
Dilute: water enters the cell causing the cell to be turgid.
5. what happens to a plant cell when it is boiled?
The cell’s membrane dies
Only diffusion takes place, no osmosis
When put in a solution, diffusion takes from solution to the cell.
Enzymes denatured.
6. Diffusion and osmosis.
Only osmosis requires a partially permeable membrane
Both require a concentration gradient
No energy required
down the concentration gradient
Osmosis is diffusion, diffusion is not osmosis
Diffusion: any molecule, osmosis: only water molecules
7. Examples of active transport.
Reabsorption of glucose by kidney tubules
Uptake of glucose by villi/ glucose molecules into the epithelium lines of
small intestine.
Uptake of ions by roots.
8. Define the term osmosis/ active transport?
Osmosis: the net movement of water molecules from a region of high
water potential to a region of low water potential through a partially
permeable membrane.
Active transport: the movement of molecules or ions through a cell
membrane from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher
concentration (against/up the concentration gradient) using energy from
respiration.
9. Three factors that affect the rate of diffusion.
Surface area/ thickness/ thinness
Temperature
Concentration gradient
10. Function of cell components.
Cell wall: withstands the internal turgor pressure, prevents the cell from
bursting.
Cell membrane: partially permeable, controls movement of substances in
and out of the cell.
Cell sap/ vacuole: storage, exerts the turgor pressure to maintain the
shape.
Chloroplasts: photosynthesis
Nucleus: controls the activities of a cell, hereditary material
Cytoplasm: metabolic reactions.
You might also like
- The Cell and Its Environment: Biology, Ss 1Document3 pagesThe Cell and Its Environment: Biology, Ss 1AJAYI PETER100% (1)
- 12-2103471 Heat Transfer in EngineDocument12 pages12-2103471 Heat Transfer in EngineRamasamikannan RamasamikannanNo ratings yet
- Movement in and Out of CellsDocument25 pagesMovement in and Out of Cellsmajanga johnNo ratings yet
- Cell PhysiologyDocument12 pagesCell PhysiologyJaseme OtoyoNo ratings yet
- Cell Transport NotesDocument10 pagesCell Transport NotesReyad BarbarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Movement in and Out of CellsDocument6 pagesChapter 3 Movement in and Out of CellsWezu heavenNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane: Function and Structure Grade 11 BiologyDocument51 pagesCell Membrane: Function and Structure Grade 11 BiologyChester WengerNo ratings yet
- Movement in and Out of Cells NotesDocument9 pagesMovement in and Out of Cells Notesmanarehab35No ratings yet
- Cells and Its Environment Ss1 NoteDocument14 pagesCells and Its Environment Ss1 NoteEllaNo ratings yet
- O Level Biology Notes With SpecDocument66 pagesO Level Biology Notes With Specshaayaa71% (7)
- Movement Across The Cell MembraneDocument3 pagesMovement Across The Cell MembraneUmi Zaheera AzharNo ratings yet
- Bio OL Chapter 3 & 4Document9 pagesBio OL Chapter 3 & 4zuhra123coolNo ratings yet
- Cell Physiology: Definition:Is The Study of The Functions of Cell StructureDocument92 pagesCell Physiology: Definition:Is The Study of The Functions of Cell StructureRichard NestorNo ratings yet
- Chap 10 Diffusion, Osmosis and Transport - TeacherDocument20 pagesChap 10 Diffusion, Osmosis and Transport - TeacherSulochana Devi PalanisamyNo ratings yet
- Movement Into and Out of CellsDocument9 pagesMovement Into and Out of CellsMuhammad Ahmad NoorNo ratings yet
- Cell Classix Notes Session2 Made by Purnima SharmaDocument4 pagesCell Classix Notes Session2 Made by Purnima Sharmajeetjyoti787No ratings yet
- CellsDocument5 pagesCellsCaroleNo ratings yet
- Movement of Subtances Across Plasma MembraneDocument414 pagesMovement of Subtances Across Plasma MembranezazaNo ratings yet
- AkdogDocument10 pagesAkdognorhain4.aNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes Class 9Document5 pagesBiology Notes Class 9lalitha muraliNo ratings yet
- The Fundamental Unit of Life Comprehensive Notes PDFDocument13 pagesThe Fundamental Unit of Life Comprehensive Notes PDFMuhammad SaadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Biology Form 4Document37 pagesChapter 3 Biology Form 4CuteOnion Furmon100% (1)
- Movement in and Out of CellsDocument30 pagesMovement in and Out of CellsEmy AnkrahNo ratings yet
- Ch.4 - Absorption by Roots - Class 10 IcseDocument3 pagesCh.4 - Absorption by Roots - Class 10 IcseIshita BhavnaniNo ratings yet
- 04 NotesDocument6 pages04 NotesAirus SamaNo ratings yet
- 2 D Movement in and Out of CellsDocument39 pages2 D Movement in and Out of Cellsyippee.ndi13No ratings yet
- CellDocument5 pagesCellMyrene CeblanoNo ratings yet
- $RVFRK1HDocument43 pages$RVFRK1HRAKIB AL MAHDINo ratings yet
- General Biology 1Document15 pagesGeneral Biology 1Beejae ApalisNo ratings yet
- Year 9 Science Revision BookletDocument25 pagesYear 9 Science Revision BookletLabeenaNo ratings yet
- Absorption by RootsDocument7 pagesAbsorption by RootsSaswatNo ratings yet
- CELL PHYSIOLOGY@starDocument6 pagesCELL PHYSIOLOGY@starDENIS KIPKOSGEINo ratings yet
- Membrane Integrity Under Osmosis: LaboratoryDocument13 pagesMembrane Integrity Under Osmosis: LaboratoryLiana Macdonald-KainoaNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life ScienceDocument30 pagesEarth and Life ScienceChristian VitalesNo ratings yet
- Diffusion: AlveoliDocument5 pagesDiffusion: Alveoliaby251188No ratings yet
- Cell Membrane & HomeostasisDocument50 pagesCell Membrane & Homeostasisapi-233187566No ratings yet
- Transport of Materials in Plants and AnimalsDocument62 pagesTransport of Materials in Plants and AnimalsMugenyi IshmaelNo ratings yet
- Senior High School: Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics (Stem) Specialized SubjectDocument53 pagesSenior High School: Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics (Stem) Specialized Subjectpotato macchiatoNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Biology Notes Updated April 2016Document94 pagesIGCSE Biology Notes Updated April 2016Adi101010101010101100% (1)
- Transport Across Cell Membrane.: DR Nilesh Kate MBBS, MD Associate ProfDocument67 pagesTransport Across Cell Membrane.: DR Nilesh Kate MBBS, MD Associate ProfAspireNo ratings yet
- The Fundamental Unit of Life Comprehensive NotesDocument12 pagesThe Fundamental Unit of Life Comprehensive NotesMuhammad SaadNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio - Q2Document20 pagesGen Bio - Q2Mary Angel DimasacatNo ratings yet
- Movement Into and Out of Cells Objectives:3.1Document12 pagesMovement Into and Out of Cells Objectives:3.1Army ForeverNo ratings yet
- Movement in and Out of CellsDocument48 pagesMovement in and Out of CellsmadzivirejayNo ratings yet
- Honors Biology The Osmosis Lab ReportDocument18 pagesHonors Biology The Osmosis Lab Reportapi-388790167No ratings yet
- Absorption by RootsDocument6 pagesAbsorption by RootsbirendraNo ratings yet
- Movement in and Out of CellsDocument10 pagesMovement in and Out of CellsMoni VillalbaNo ratings yet
- Cell and Its Environment: Week 4Document10 pagesCell and Its Environment: Week 4ogochukwuezenekwe762No ratings yet
- Cell Boundaries Module 2Document17 pagesCell Boundaries Module 2Vedha SinghNo ratings yet
- Gavin Hagerty - Notes - 8.3 Cell TransportDocument6 pagesGavin Hagerty - Notes - 8.3 Cell Transportgavinhagerty709No ratings yet
- Movement in and Out of CellsDocument18 pagesMovement in and Out of CellsEmy AnkrahNo ratings yet
- Plant Physiology: Chapter - 1: Absorption by RootsDocument17 pagesPlant Physiology: Chapter - 1: Absorption by RootsSaad ZulfiqarNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument212 pagesNotesmaatlabatshabileNo ratings yet
- Ch3 OL RevisionDocument11 pagesCh3 OL Revisionzuhra123coolNo ratings yet
- The Movement of Substances Across The Plasma MembraneDocument30 pagesThe Movement of Substances Across The Plasma MembraneNorizan HusainNo ratings yet
- Plasma Membranes Sheet AnswersDocument3 pagesPlasma Membranes Sheet Answerskim szymanskiNo ratings yet
- Act2 Bio SciDocument4 pagesAct2 Bio SciPamaran, Kristel DenishNo ratings yet
- Cell Physiology and Cellular MetabolismDocument25 pagesCell Physiology and Cellular MetabolismCla NuvalNo ratings yet
- Activity 3 Diffusion and OsmosisDocument6 pagesActivity 3 Diffusion and OsmosisThea Calyn WalicanNo ratings yet
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers Movement of substancesFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers Movement of substancesNo ratings yet
- Koch I. Analysis of Multivariate and High-Dimensional Data 2013Document532 pagesKoch I. Analysis of Multivariate and High-Dimensional Data 2013rciani100% (15)
- One Time Registration For TNPSCDocument2 pagesOne Time Registration For TNPSCtrismaheshNo ratings yet
- Carte Fantome PDFDocument390 pagesCarte Fantome PDFbinzegger100% (1)
- CTDI Phantom User's GuideDocument18 pagesCTDI Phantom User's GuideAida Cristiana SanduNo ratings yet
- PreliminariesDocument11 pagesPreliminariesGhabbFloresPalNo ratings yet
- Os Lab Manual AimlDocument107 pagesOs Lab Manual Aimlpooja ppNo ratings yet
- Facility Preventive Maintenance ChecklistDocument5 pagesFacility Preventive Maintenance ChecklistFaisalNo ratings yet
- 1953-File Utama Naskah-6037-2-10-20200429Document20 pages1953-File Utama Naskah-6037-2-10-20200429taufik hidayatNo ratings yet
- Ethics QuizDocument2 pagesEthics QuizLegogie Moses AnoghenaNo ratings yet
- KFC225 Operating HandbookDocument25 pagesKFC225 Operating HandbooksunaryaNo ratings yet
- Report 5817-BDocument6 pagesReport 5817-BAll Weld Inspection Training ServicesNo ratings yet
- Final Health EducDocument139 pagesFinal Health EducsprrwgoldenNo ratings yet
- Lección 11 - How MuchDocument4 pagesLección 11 - How Muchyo no fuiNo ratings yet
- 2023 Grade 7 - 9 EMS ATP MediationDocument19 pages2023 Grade 7 - 9 EMS ATP MediationtmshuqwanaNo ratings yet
- Umbilical Catheterization in ServiceDocument11 pagesUmbilical Catheterization in ServiceLucian CaelumNo ratings yet
- Product Catalogue-IoT PT. MSIDocument30 pagesProduct Catalogue-IoT PT. MSIMaz ZildaneNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four: The Cost of Capital 4.1. The Concept of Cost of CapitalDocument9 pagesChapter Four: The Cost of Capital 4.1. The Concept of Cost of Capitalmelat felekeNo ratings yet
- SMART VTS Wireless Solutions: Features SVTS-500 SVTS-600 SVTS-700 SVTS-900 SVTS-1200Document6 pagesSMART VTS Wireless Solutions: Features SVTS-500 SVTS-600 SVTS-700 SVTS-900 SVTS-1200Sri KanthNo ratings yet
- Environmental Systems and Societies Paper 3 SLDocument15 pagesEnvironmental Systems and Societies Paper 3 SLAfra LamisaNo ratings yet
- A8Ponetics: Series SystemsDocument86 pagesA8Ponetics: Series SystemsdmitroivanenkoNo ratings yet
- Covumaiphuongthionline Cacthituonglai 1Document2 pagesCovumaiphuongthionline Cacthituonglai 1Ngọc ThảoNo ratings yet
- Archaeological Landmarks in TurkeyDocument2 pagesArchaeological Landmarks in TurkeyMoustafa Ben AmorNo ratings yet
- Certificate: Internal External PrincipalDocument36 pagesCertificate: Internal External PrincipalNitesh kuraheNo ratings yet
- The Unstoppable Human Species The Emergence of Homo Sapiens in Prehistory John J Shea 2 All ChapterDocument52 pagesThe Unstoppable Human Species The Emergence of Homo Sapiens in Prehistory John J Shea 2 All Chapterfrieda.jaimes821100% (9)
- Chemistry 10th Edition Whitten Test BankDocument12 pagesChemistry 10th Edition Whitten Test BankEdwinMyersbnztx100% (64)
- Blueprint Q1 Grade 6 - in ScienceDocument20 pagesBlueprint Q1 Grade 6 - in ScienceJheng A NignigakNo ratings yet
- Cicol NT Slurry: Constructive SolutionsDocument3 pagesCicol NT Slurry: Constructive SolutionstalatzahoorNo ratings yet
- International Approved ProtocolsDocument27 pagesInternational Approved Protocolscyril ochieng wangaNo ratings yet
- NB Private Equity Partners Ltd.Document68 pagesNB Private Equity Partners Ltd.ArvinLedesmaChiong100% (1)