Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Exp 1 and 2
Exp 1 and 2
Uploaded by
imvuuser1Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Exp 1 and 2
Exp 1 and 2
Uploaded by
imvuuser1Copyright:
Available Formats
Analog Circuit Lab (KEC-452)
EXPERIMENT NO.-05
OBJECT: -Application of op-amp:-op- Amp as Summing Amplifier, Difference Amplifier and
Integrator and Diffrentiator.
APPARATUS REQUIRED:-
1. OP- Amp. Designer Kit. (IC-741)
2. Digital Multimeter.
3. Connecting Patch Cords.
THEORY:-An operational amplifier (or an op-amp) is an integrated circuit (IC) that operates
as a voltage amplifier. An op-amp has a differential input. That is, it has two inputs of opposite
polarity. An op-amp has a single output and a very high gain, which means that the output signal
is much higher than input signal. The two input terminals are:
(i) Inverting Terminal (ii) Non- Inverting Terminal
Input at the Inverting terminal is amplified and phase shifted by 180˚ while the input at the non
inverting terminal is amplified without phase shift. OP-Amp basically amplifies difference of
signals at the two terminals.
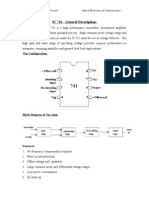
Fig. 5.1 (a) Pin Diagram of IC 741 (b) Symbol of Op-amp
1. SUMMER:-
OP-Amplifier can also function as a summer (addition) amplifier.
The OP-Amp output as summer in inverting mode can be given as-
V0=-R2 (V1 /R1+V2/R2 )
(If R1=R2=R f=R than)
V0= -(V1+V2) i.e. Addition
ECE Department, Prepared By Checked By
SRMCEM, Lko Page 13 of 34
Faculty In-charge Head of Department
Analog Circuit Lab (KEC-452)
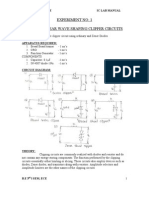
Fig.5.2 SUMMER
PROCEDURE:-
1. The circuit is connected as per the practical circuit shown in the figure.
2. R1=R2=RR is kept at 1K (say).
3. Voltage V1 & V2 are fed at the inverting terminal (<2V)
4. The output voltage is obtained at Pin No. 6 with respect to ground terminal with the help
of a multi meter.
5. The observed value is compared with the theoretical value and the error Calculated.
OBSERVATION TABLE :-
For SUMMER Amplifier:-
S.No. V1 V2 R1 R2 Rf V0 V0 Error %
Theoretical Observed
1
2
3
4
ECE Department, Prepared By Checked By
SRMCEM, Lko Page 14 of 34
Faculty In-charge Head of Department
Analog Circuit Lab (KEC-452)
2. Difference Amplifier:- A Differential amplifier is a type of electronic amplifier that
amplifies the difference between two input voltages but suppresses any voltage common to the
two inputs. It is an analog circuit with two inputs and one output in which the output is ideally
proportional to the difference between the two voltages.
VO = R2 * (V2 – V1)/R1
Fig. 5.3 Op-Amp as Difference Amplifier
PROCEDURE:-
1. The circuit is connected as per the practical circuit shown in the figure.
2. R1=R2 is kept at 1KΩ (say).
3. Voltage V1 & V2 are fed at the inverting terminal and non inverting terminal with respect to
ground.
4. The output voltage is obtained at Pin No. 6 with respect to ground terminal with the help of a
multi meter.
5. The observed value is compared with the theoretical value and the error is calculated.
OBSERVATION TABLE :-
For Difference Amplifier
S.No. V1 V2 R1 R2 V0 = R2*(V2-V1)/R1 V0 Error
Theoretical Observed
ECE Department, Prepared By Checked By
SRMCEM, Lko Page 15 of 34
Faculty In-charge Head of Department
Analog Circuit Lab (KEC-452)
3) INTEGRATOR:- An integrator is a component whose output signal is the
time integral of its input signal. It is the continuous analog of a counter, cumulating the input into
an output.
In this case, current is summer over a period of time and the resultant voltage generated is the
integral of that current as a function of time. This means that if constant voltage is given to the
ramp with a constant slope is generated at the output when the input is positive, the output of the
OP-AMP ramps negative.
In doing so it pulls the inverting terminal negative so as to maintain a virtual earth condition. The
input current (Vin/RI) is being equaled by the current flowing through the capacitor. This
equilibrium is maintained. The equation governing the behavior of a capacitor is C dv/dt =I
where dv/dt is the rate of change of voltage across the capacitor.
Vo = -
So when square wave is applied to the input of circuit, triangular wave from is generated. R 2 help
in providing DC stability. The circuit has low output impedance.
Fig. 5.4 Op-Amp as Integrator
PROCEDURE:-
(i).The circuit is connected as per the integrating circuit.
(ii).Apply square wave input to the integrating circuit.
(iii).Record & trace the output integrated wave form appeared on CRO which is connected to the
output terminal of the circuit
ECE Department, Prepared By Checked By
SRMCEM, Lko Page 16 of 34
Faculty In-charge Head of Department
Analog Circuit Lab (KEC-452)
4) DIFFRENTIATOR:-A differentiator is a circuit that is designed such that the output of
the circuit is approximately directly proportional to the rate of change (the time derivative) of the
input. A true differentiator cannot be physically realized, because it has infinite gain at infinite
frequency. A similar effect can be achieved, however, by limiting the gain above some
frequency.
A differentiator circuit (also known as a differentiating amplifier or inverting differentiator)
consists of an operational amplifier in which a resistor R provides negative feedback and a
capacitor is used at the input side. The circuit is based on the
capacitor's current to voltage relationship
If Vout is the voltage across the resistor and Vin is the voltage across the capacitor, we can
rearrange these two equations to obtain the following equation:
VOUT=-RC dvI/dt
Fig. 5.6 Op-Amp as Diffrentiator
PROCEDURE:-
(i).The circuit is connected as per the Diffrentiator circuit.
(ii).Apply square wave input to the Diffrentiator circuit.
(iii).Record & trace the output differentiated wave form appeared on CRO which is connected to
the output terminal of the circuit.
OBSERVATION: - Trace wave forms on tracing paper.
RESULT:- Summer & integrator both are studied & observations are recorded
PRECAUTION:-
(i).All the connections should be right & tight.
(ii).Connections must be made according to circuit diagram.
(iii).Power must be switched on after checking the connections.
(iv).Tracing must be taken very carefully.
ECE Department, Prepared By Checked By
SRMCEM, Lko Page 17 of 34
Faculty In-charge Head of Department
Analog Circuit Lab (KEC-452)
Related Questions:
Q.1What is BJT differential amplifier?
Q.2 Sketch the dc transfer characteristic of MOSFET differential amplifier.
Q.3 Discuss the principle of Op-Amp as integrator.
Q.4Define slew rate of Op-Amp.
Q.5 Define common mode gain.
ECE Department, Prepared By Checked By
SRMCEM, Lko Page 17 of 34
Faculty In-charge Head of Department
You might also like
- Isolation Work Instruction TemplateDocument5 pagesIsolation Work Instruction TemplateppnNo ratings yet
- Lab 7 (Cascaded Amplifier Design) - Sept 20Document8 pagesLab 7 (Cascaded Amplifier Design) - Sept 20WilfredNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument335 pagesPDFJEFFREY DEE MAURY NORIEGANo ratings yet
- Ica Lab Student MannualDocument88 pagesIca Lab Student MannualprincegirishNo ratings yet
- Kec - 452 - Analog - Circuit - Lab Manual - FinalDocument40 pagesKec - 452 - Analog - Circuit - Lab Manual - FinalAnurag siwachNo ratings yet
- IC Lab MaualDocument59 pagesIC Lab MaualKumar Goud.K100% (2)
- Ic Lab Manual New2Document35 pagesIc Lab Manual New2jietcivilNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual Electronics-II-4Document80 pagesLab Manual Electronics-II-4Naveed SultanNo ratings yet
- EE2003-E03 Operational AmplifierDocument6 pagesEE2003-E03 Operational AmplifierntldvlaiNo ratings yet
- LIC Experiment FINALDocument45 pagesLIC Experiment FINALSantosh PotdarNo ratings yet
- Design An Amplifier With A Gain of - 10 and Input Resistance of 10k . Ri 10k Av - Rf/Ri - 10 - Rf/10k RF 10 X 10 K 100 KDocument21 pagesDesign An Amplifier With A Gain of - 10 and Input Resistance of 10k . Ri 10k Av - Rf/Ri - 10 - Rf/10k RF 10 X 10 K 100 KMangaiyarkarasi VengatachalamNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual: Subject: Integrated Electronics BE 6 Section B Submitted byDocument25 pagesLab Manual: Subject: Integrated Electronics BE 6 Section B Submitted byIqraJahanNo ratings yet
- Expt. No. 8Document5 pagesExpt. No. 8shindevedant60No ratings yet
- LIC Lab ManualDocument57 pagesLIC Lab ManualsfundsNo ratings yet
- Lab 04 Operational Amplifier Applications: Prepared byDocument5 pagesLab 04 Operational Amplifier Applications: Prepared byKhairy Yaakob100% (1)
- Lica Lab ManualDocument53 pagesLica Lab ManualGowtham KannegantiNo ratings yet
- Lica Lab ManualDocument35 pagesLica Lab ManualVallabh JNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuits: Lab Manual Experiment No 8Document6 pagesElectric Circuits: Lab Manual Experiment No 8usamaNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual LicDocument66 pagesLab Manual LicUppum Mulakam FansNo ratings yet
- ECAD2 Complete ManualDocument37 pagesECAD2 Complete ManualJeremy HensleyNo ratings yet
- EC 2 Simulation LabDocument56 pagesEC 2 Simulation LabSadhana SantoorNo ratings yet
- LIC Lab ManualDocument78 pagesLIC Lab ManualPrinthya GudiyaNo ratings yet
- Electronics Lab 2019 G-UmadeviDocument61 pagesElectronics Lab 2019 G-UmadeviGopinathan MNo ratings yet
- Linear Integrated Circuits Lab ManualDocument53 pagesLinear Integrated Circuits Lab Manualsurendrareddy mandati100% (1)
- Ic Lab ManaulDocument73 pagesIc Lab Manaulsreenath1729No ratings yet
- IC Applications Lab ManualDocument42 pagesIC Applications Lab ManualRavikumar ImadabathuniNo ratings yet
- Lab4 OPAMDocument8 pagesLab4 OPAMkhoi26664No ratings yet
- Opamp Lab Assign 1Document9 pagesOpamp Lab Assign 1NareshNo ratings yet
- Lica Lab Manual PDFDocument42 pagesLica Lab Manual PDFKashif AliNo ratings yet
- Silicon Wafer (Substrate) Preparation 2. Epitaxial Growth 3. Oxidation 4. Photolithography 5. Diffusion 6. Ion Implantation 7. Isolation Techniques 8. MetallizationDocument21 pagesSilicon Wafer (Substrate) Preparation 2. Epitaxial Growth 3. Oxidation 4. Photolithography 5. Diffusion 6. Ion Implantation 7. Isolation Techniques 8. MetallizationMangaiyarkarasi VengatachalamNo ratings yet
- LIC Lab ManualDocument79 pagesLIC Lab Manualoniza shaikh100% (1)
- Lab Experiment 5Document3 pagesLab Experiment 5Tasnia YasminNo ratings yet
- Ijret20140304165 PDFDocument4 pagesIjret20140304165 PDFSuyashNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word - Lic LabmanualDocument52 pagesMicrosoft Word - Lic Labmanualaarish-ramesh-5468No ratings yet
- Lab 4 - Properties of The Op-Amp 1 (Buffer Non Inverting Op-Amp)Document9 pagesLab 4 - Properties of The Op-Amp 1 (Buffer Non Inverting Op-Amp)Alia Atikah100% (1)
- Rohini 41410934507Document7 pagesRohini 41410934507funcrusherrNo ratings yet
- IIT BH DNC Lab EE Manual Expt 4Document6 pagesIIT BH DNC Lab EE Manual Expt 4Priyesh PandeyNo ratings yet
- Lic Lab Manual Final - 2017-2018Document36 pagesLic Lab Manual Final - 2017-2018DeepakMishraNo ratings yet
- Lab 7 (Cascaded Amplifier Design) - Sept 20Document8 pagesLab 7 (Cascaded Amplifier Design) - Sept 20WilfredNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes: Department of Electrical & Electronics EngineeringDocument47 pagesLecture Notes: Department of Electrical & Electronics EngineeringSivaranjaniNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Report Cover SheetDocument14 pagesLaboratory Report Cover SheetPreet PatelNo ratings yet
- Lab - 01 (BME-202)Document9 pagesLab - 01 (BME-202)Darakhshan MujtabaNo ratings yet
- Ic Ecad Lab Manual Online PanoramaDocument72 pagesIc Ecad Lab Manual Online PanoramaChaitanya Chakka100% (3)
- Ica Lab (135) Iii-IDocument87 pagesIca Lab (135) Iii-IesesesNo ratings yet
- OPAMP NotesDocument19 pagesOPAMP NotesVenugopal kulkarniNo ratings yet
- Lic Labs PDFDocument41 pagesLic Labs PDFAbdul Subhan AbbasiNo ratings yet
- Eca Lab Manual PDFDocument56 pagesEca Lab Manual PDFrppvch100% (5)
- Analogue EEC436Document46 pagesAnalogue EEC436Akachi OkoroNo ratings yet
- Lic May-June 2017Document15 pagesLic May-June 2017santhosh sekarNo ratings yet
- Mention The Frequency Compensation MethodsDocument10 pagesMention The Frequency Compensation MethodsMadhavan SamNo ratings yet
- Operational Amplifiers NewDocument20 pagesOperational Amplifiers NewLester Garcia100% (1)
- ECE3013 - Linear Integrated Circuits: Module-IiiDocument50 pagesECE3013 - Linear Integrated Circuits: Module-IiiWINORLOSENo ratings yet
- Electronic-Device-lab-2-Operational AmplifiersDocument10 pagesElectronic-Device-lab-2-Operational AmplifiersVy NguyễnNo ratings yet
- ECE321 - 6th EXPDocument4 pagesECE321 - 6th EXPمحمد ابراهيمNo ratings yet
- Linear Integrated CircuitsDocument61 pagesLinear Integrated CircuitsGuruKPO100% (3)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Exercises in Electronics: Operational Amplifier CircuitsFrom EverandExercises in Electronics: Operational Amplifier CircuitsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisFrom EverandElectromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisNo ratings yet
- ABB Battery ChargerDocument56 pagesABB Battery ChargercentralautomacaoNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis Revision Summary SheetDocument1 pageElectrolysis Revision Summary SheetFranklin Parra ArzeNo ratings yet
- Pspice NotesDocument123 pagesPspice NotesKeane Foo100% (1)
- 2BH1510 Fu UsDocument2 pages2BH1510 Fu UsVinoth SenthilNo ratings yet
- KECA 80 C104 KECA 80 C165 Current Sensors: Instructions For Installation, Use and MaintenanceDocument5 pagesKECA 80 C104 KECA 80 C165 Current Sensors: Instructions For Installation, Use and MaintenanceLaurentiu CatalinNo ratings yet
- The Most Friendly Bench Instruments: Appa 200 Series VersameterDocument2 pagesThe Most Friendly Bench Instruments: Appa 200 Series Versametermarcelo zarateNo ratings yet
- Methods of Cable Laying - Electrical RevolutionDocument7 pagesMethods of Cable Laying - Electrical RevolutionjibooryNo ratings yet
- 38-13-10 Rev 2Document128 pages38-13-10 Rev 2Gdb HasseneNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic and Magnetic Suspension: IJEDR1703070 474Document8 pagesElectromagnetic and Magnetic Suspension: IJEDR1703070 474Naani ChowdaryNo ratings yet
- Black and White TV Video Output Applications High-Voltage Switching Applications Driver Stage Audio Amplifier ApplicationsDocument5 pagesBlack and White TV Video Output Applications High-Voltage Switching Applications Driver Stage Audio Amplifier ApplicationsRichard Hernandez RuizNo ratings yet
- BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING MCQsDocument18 pagesBASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING MCQsVimal PalNo ratings yet
- Deh-3900mp Deh-2920mp Deh-2900mp Deh-2900mpb Deh-1920r Deh-1900rDocument8 pagesDeh-3900mp Deh-2920mp Deh-2900mp Deh-2900mpb Deh-1920r Deh-1900rMoldovan GheorgheNo ratings yet
- Two-Phase Half-Wave Pre Driver Fan Motor Driver: DatasheetDocument15 pagesTwo-Phase Half-Wave Pre Driver Fan Motor Driver: DatasheetMOHD RASHIDNo ratings yet
- Kalka Public School: Holiday HomeworkDocument18 pagesKalka Public School: Holiday HomeworkMohammad UmarNo ratings yet
- Ieee Conference Paper - 01Document9 pagesIeee Conference Paper - 01Asha PatilNo ratings yet
- Model BETA 87A User Guide: Application and PlacementDocument12 pagesModel BETA 87A User Guide: Application and PlacementMHEP_DANIELNo ratings yet
- 6AG11346GF007AA1 Datasheet enDocument3 pages6AG11346GF007AA1 Datasheet ensarah.elfishawyNo ratings yet
- Single Phase Series Manual EnglishDocument29 pagesSingle Phase Series Manual EnglishVăn ST QuangNo ratings yet
- Tds 24dp-550 Crown EngDocument2 pagesTds 24dp-550 Crown EngDraganNo ratings yet
- C60N Marine PDFDocument2 pagesC60N Marine PDFViorel CatalinNo ratings yet
- Magneto Optic Current Transformer Technology (MOCT) : Attish JainDocument5 pagesMagneto Optic Current Transformer Technology (MOCT) : Attish JaindiljithNo ratings yet
- JVC TK-C720U Schematics Service ManualDocument52 pagesJVC TK-C720U Schematics Service ManualAntonio CarlosNo ratings yet
- Y Pole PDFDocument11 pagesY Pole PDFZulu Bravo MikeNo ratings yet
- The Fluorescent Lighting System BY - Frank DurdaDocument97 pagesThe Fluorescent Lighting System BY - Frank Durdawas00266No ratings yet
- Rail Motive Power (REGM-6008) : Traction MotorsDocument42 pagesRail Motive Power (REGM-6008) : Traction MotorsMaalmalan KeekiyyaaNo ratings yet
- BomDocument2 pagesBomSơn CaoNo ratings yet
- Amety Gen Protection1Document27 pagesAmety Gen Protection1Lalit KR NeerajNo ratings yet
- RM17TE00 DATASHEET NG en-GBDocument6 pagesRM17TE00 DATASHEET NG en-GBKeerthi Vasan SNo ratings yet