Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Phys 14lab Notes
Phys 14lab Notes
Uploaded by
Zymone Eiron DinglasanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Phys 14lab Notes
Phys 14lab Notes
Uploaded by
Zymone Eiron DinglasanCopyright:
Available Formats
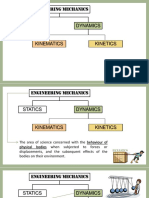
PHYS 14LAB – PHYSICS FOR ENGINEERS
Physics is the branch of science that Law of States that a body at rest will
studies how nature behaves. It Inertia remain at rest or in motion at
relates to all other types of that constant velocity, unless
sciences: chemistry, biology, acted upon by some
geology, astronomy, mechanics, unbalanced, external force
etc. Law of States that the acceleration of a
mechanics oldest branch of Physics which Acceleration body is directly proportional to
deals with the study of the the net force acting on it and
bodies and systems and forces inversely proportional to its
acting on them mass.
dynamics branch of mechanics that deals Law of For every force that acts on one
with bodies in motion Action and body, there is a second force
statics branch of mechanics that deals Reaction equal in magnitude and opposite
with bodies at rest or under in direction
equilibrium condition velocity derivative of position with
kinematics branch of dynamics which respect to time
describes the motion of bodies acceleration derivative of velocity with
without reference to the forces respect to time
that either causes the motion or
are generated as a result of NOTES:
motion
kinetics branch of dynamics which deals *DO NOT LIMIT YOURSELF TO THIS REVIEW
with the study of bodies in MATERIAL AS THERE MAYBE SOME TERMS
motion particularly the force MENTIONED DURING OUR DISCUSSION.
involved in the motion
Force is any interaction that, when *MAKE SURE TO REVIEW THE PRACTICE
unopposed, will change the PROBLEMS WE HAVE ANSWERED DURING
motion of an object. DISCUSSION.
Motion the phenomenon in which an
object changes its position over *GOOD LUCK ON YOUR MIDTERM WEEK!
time
N (newton) / unit of Force in SI
𝑘𝑔 ∙ 𝑚/𝑠 2
inertia is the property of matter that
causes it to resist a change in its
state of motion
scalar is a quantity that has
quantity magnitude only
vector is a quantity that has both a
quantity magnitude and a direction.
motion a progressive change of position
of the body
rectilinear type of motion in which the body
motion moves in a straight line or is
moving in the direction parallel
to its displacement
uniform a motion with constant speed or
motion velocity
uniform a motion with constant change
accelerated in velocity
motion
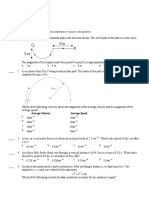
projectile a body, which after being given
an initial velocity (with initial
angle of release), is allowed to
travel under the action of gravity
alone
You might also like
- ME Chapter 2Document1 pageME Chapter 2allovid50% (2)
- Tehnički Engleski Jezik - Vježba Prevoda 3Document1 pageTehnički Engleski Jezik - Vježba Prevoda 3Adnan OmeraševićNo ratings yet
- Newtons Laws of MotionDocument52 pagesNewtons Laws of MotionOluwaferanmi OgunleyeNo ratings yet
- Prepared By: Engr. Lucia V. Ortega 8/28/20 Statics of Rigid BodiesDocument11 pagesPrepared By: Engr. Lucia V. Ortega 8/28/20 Statics of Rigid BodiesJoren JamesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Principles of StaticsDocument9 pagesChapter 1 Principles of StaticsDeniell Kahlil Kyro GabonNo ratings yet
- M1 Introduction To StaticsDocument29 pagesM1 Introduction To StaticsErleNo ratings yet
- Chapter One Hand OutDocument2 pagesChapter One Hand OutFootkball 1No ratings yet
- MODULE 1 UNIT-2 Introduction To Engineering MechanicsDocument44 pagesMODULE 1 UNIT-2 Introduction To Engineering MechanicsMANOJKUMAR MNo ratings yet
- Force and Laws of Motion Class9Document29 pagesForce and Laws of Motion Class9Vedika Gore LSGNo ratings yet
- Motion and Design Word ListDocument6 pagesMotion and Design Word ListCaroline CamonsNo ratings yet
- General Pyhsics 1: Forces Cause MotionDocument1 pageGeneral Pyhsics 1: Forces Cause MotionCris TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Mech 1 NonuDocument20 pagesMech 1 NonuAsnor RandyNo ratings yet
- Introduction Engineering Mechanics 1Document16 pagesIntroduction Engineering Mechanics 1Symoun BontigaoNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics TermsDocument1 pageEngineering Mechanics TermsheheheheheheeNo ratings yet
- Let's Check: Activity 1Document2 pagesLet's Check: Activity 1Melrose LopezNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Rigid Bodies Statics DynamicsDocument5 pagesMechanics of Rigid Bodies Statics DynamicsGianne Karl AlmarinesNo ratings yet
- STATICS OF RIGID BODIES Chapter IDocument23 pagesSTATICS OF RIGID BODIES Chapter IViron LucerianoNo ratings yet
- Triptico. Cinetica de ParticulasDocument2 pagesTriptico. Cinetica de ParticulasMarco GilNo ratings yet
- Laws of Motion 10th SciDocument15 pagesLaws of Motion 10th Scisivadharshan9548No ratings yet
- 68.newton Law eDocument12 pages68.newton Law eMeena rajNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1Document2 pagesGeneral Physics 1Aifah HernandezNo ratings yet
- Objective:: InertiaDocument2 pagesObjective:: InertiaAli AjazNo ratings yet
- Clinical Biomechanics - Mechanical Concepts and TermsDocument30 pagesClinical Biomechanics - Mechanical Concepts and Termsmihaela_moldova9128No ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document22 pagesLecture 1نصرت سعد نصرتNo ratings yet
- Engineering Is The Application of Mathematics, Empirical Evidence and Scientific, EconomicDocument5 pagesEngineering Is The Application of Mathematics, Empirical Evidence and Scientific, EconomicKylle BedisNo ratings yet
- Statics Chapter 1Document14 pagesStatics Chapter 1vladNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics Unit-1Document35 pagesEngineering Mechanics Unit-1M.suresh SureshNo ratings yet
- Matter and Energy. Topic 8-Newton S Laws of MotionDocument2 pagesMatter and Energy. Topic 8-Newton S Laws of MotionAlexa MartínezNo ratings yet
- Emech Module 1Document3 pagesEmech Module 1Mark Joseph BacaniNo ratings yet
- Kinetics Vs KinematicsDocument3 pagesKinetics Vs KinematicsRaj MallickNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Engineering MechanicsDocument11 pagesIntroduction To Engineering MechanicsMyameSirameNo ratings yet
- Investigating Principles Governing MotionDocument16 pagesInvestigating Principles Governing MotionldrnsolanoNo ratings yet
- Engineering MechanicsDocument51 pagesEngineering MechanicsMohan ChandraNo ratings yet
- 2.basic Concepts of Mechanics Lecture 2Document20 pages2.basic Concepts of Mechanics Lecture 2poojaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Slides 1-2Document30 pagesLecture Slides 1-2themarvelbeastNo ratings yet
- LESSON222 Ee 2Document3 pagesLESSON222 Ee 2pollypew333No ratings yet
- Physics Motion MainDocument16 pagesPhysics Motion MainmishrasplparthNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics: Lecture For Top Companies Interviews, TRB, RRB, Tneb, Etc.Document12 pagesEngineering Mechanics: Lecture For Top Companies Interviews, TRB, RRB, Tneb, Etc.sunfaceselvamNo ratings yet
- Lec 01-27-02-2019 - Introductory MechanicsDocument79 pagesLec 01-27-02-2019 - Introductory MechanicsLiviu LucaNo ratings yet
- Mech 2 Module 1 Unit 1 (Introduction)Document8 pagesMech 2 Module 1 Unit 1 (Introduction)Zamantha DomingoNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics: DynamicsDocument8 pagesEngineering Mechanics: DynamicsAnonymous dbtHkdNo ratings yet
- Djj3053 Engineering MechanicsDocument18 pagesDjj3053 Engineering MechanicslyenaNo ratings yet
- Statics of Rigid BodiesDocument2 pagesStatics of Rigid BodiesHazelNoreenSabileManalo100% (1)
- Classical Mechanics Block 1/4Document70 pagesClassical Mechanics Block 1/4Chethan PrathapNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 MotionDocument4 pagesLecture 2 MotionAnne BautistaNo ratings yet
- Statics 101Document4 pagesStatics 101Justine Ejay MoscosaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 TheoryDocument25 pagesUnit 1 TheoryparthibankNo ratings yet
- Force and Newton's Laws: Concise 2-Page Class 10 CBSE NotesDocument2 pagesForce and Newton's Laws: Concise 2-Page Class 10 CBSE Notesamaan 10 BNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Statistics: MechanicsDocument7 pagesIntroduction To Statistics: MechanicsJohn Alexis AncianoNo ratings yet
- تقرير عن توزيع القوى لمادة علم السكونDocument14 pagesتقرير عن توزيع القوى لمادة علم السكونمالك احمدNo ratings yet
- Newton's Second Law of MotionDocument13 pagesNewton's Second Law of MotionStephanie Nichole Anne AquinoNo ratings yet
- Basic Engineering ScienceDocument10 pagesBasic Engineering Scienceஅருண்குமார் அமைப்பியல்No ratings yet
- Untitled Document 1Document6 pagesUntitled Document 1JEROME MICHAEL LAZARONo ratings yet
- Prepared by Dr.A.Vinoth JebarajDocument66 pagesPrepared by Dr.A.Vinoth JebarajMEGHA JAINNo ratings yet
- Affiliated To Central Board of Secondary Education - New DelhiDocument4 pagesAffiliated To Central Board of Secondary Education - New DelhiK.S.SANTHOSH NARAYANANNo ratings yet
- Module-2 Response Spectrum: Introduction To Structural DynamicsDocument58 pagesModule-2 Response Spectrum: Introduction To Structural DynamicsManu P SNo ratings yet
- New Module 1 MechanicsDocument23 pagesNew Module 1 MechanicsGARAY, EUGENIONo ratings yet
- General Physics: Newton Law of MotionDocument4 pagesGeneral Physics: Newton Law of MotionJewel ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Introduction-Forces and Equilibrium: Chapter HighlightsDocument106 pagesIntroduction-Forces and Equilibrium: Chapter HighlightsShanmukh NillaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To DynamicsDocument21 pagesIntroduction To DynamicsDG Deku YTNo ratings yet
- Dynamics SolutionsDocument62 pagesDynamics Solutionsanthony100% (1)
- Rivision 37 Circular Motion With Pass CodeDocument12 pagesRivision 37 Circular Motion With Pass CodeDevin GamageNo ratings yet
- Quarter 2 Part 1Document14 pagesQuarter 2 Part 1yukikyo osamuNo ratings yet
- KinematicsDocument7 pagesKinematicsOrlee Villafañe JrNo ratings yet
- JEE Knockout - Kinematics - 13th MarchDocument94 pagesJEE Knockout - Kinematics - 13th MarchPrinanNo ratings yet
- Kinematics Forces Test 2017Document14 pagesKinematics Forces Test 2017yhhNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1: Quarter 1Document38 pagesGeneral Physics 1: Quarter 1Rizwan OrduñaNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 7: Fluid Motion: AccelerationsDocument13 pagesLecture - 7: Fluid Motion: Accelerationsrohit singhNo ratings yet
- Curvilinear Motion PDFDocument49 pagesCurvilinear Motion PDFDaniel Naoe FestinNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 - Simple Harmonic MotionDocument2 pagesAssignment 1 - Simple Harmonic MotionDr. Pradeep Kumar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Masw Remi Survey GuideDocument10 pagesMasw Remi Survey GuideHoracio RamosNo ratings yet
- E-Book SSC GS (Eng)Document291 pagesE-Book SSC GS (Eng)Shivam SwarnimNo ratings yet
- Final MechanicsDocument94 pagesFinal Mechanicsreyann0% (1)
- Part V: Velocity and Acceleration Analysis of Mechanisms: ME 3610 Course Notes - OutlineDocument35 pagesPart V: Velocity and Acceleration Analysis of Mechanisms: ME 3610 Course Notes - OutlineseekermohanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Kinematics and TranslationDocument11 pagesLesson 3 Kinematics and TranslationAnna kris DulfoNo ratings yet
- Motion of FFBDocument45 pagesMotion of FFBYihun abrahamNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 Newtons LawsDocument54 pagesLesson 5 Newtons Lawss.pcobrado22No ratings yet
- Physics: Principles ofDocument20 pagesPhysics: Principles ofNishan SunarNo ratings yet
- R20 Ce ModelpapersDocument20 pagesR20 Ce ModelpapersprssvrajuNo ratings yet
- Galilean RelativityDocument29 pagesGalilean Relativitysamuel_okenyNo ratings yet
- Pre-Test in MOTIONFinalDocument5 pagesPre-Test in MOTIONFinalElyzza Wye AlbaoNo ratings yet
- Speed, Velocity, and Acceleration: Physics Notes GCE Study BuddyDocument14 pagesSpeed, Velocity, and Acceleration: Physics Notes GCE Study Buddycpika520No ratings yet
- Edexcel Igcse Physics 4ph1 Theory v1Document18 pagesEdexcel Igcse Physics 4ph1 Theory v1farhadmustafa128No ratings yet
- 04 - Rotational Motion - JEE PDFDocument124 pages04 - Rotational Motion - JEE PDFCefas Almeida50% (2)
- 2nd Year Physics Important MCQs Solved - Ratta - PKDocument1 page2nd Year Physics Important MCQs Solved - Ratta - PKEmma SwanNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Principles of Physics A Calculus Based Text 5th Edition Serway Test Bank PDFDocument30 pagesDwnload Full Principles of Physics A Calculus Based Text 5th Edition Serway Test Bank PDFimbreedjejunity.8hi2yz100% (11)
- Science: Third Quarter - Module 1 Describing MotionDocument35 pagesScience: Third Quarter - Module 1 Describing MotionMelanie Tagudin Trinidad94% (17)
- Note: You Are Not Allowed Anymore To Resubmit Your Answer Sheets Once Submitted, It Will Be Considered As Final. Do Not Rush in Answering.Document8 pagesNote: You Are Not Allowed Anymore To Resubmit Your Answer Sheets Once Submitted, It Will Be Considered As Final. Do Not Rush in Answering.REGINA SANTIAGONo ratings yet
- Biomechanics and Muscular-Activity During Sit-to-Stand TransferDocument11 pagesBiomechanics and Muscular-Activity During Sit-to-Stand TransferAh ZhangNo ratings yet