Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Review B2 Organisation
Review B2 Organisation
Uploaded by
Charlotte KnightOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Review B2 Organisation
Review B2 Organisation
Uploaded by
Charlotte KnightCopyright:
Available Formats
Review B2 Organisation
Can you…?
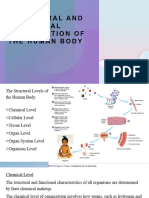
2.1 Principles of organisation
Explain organisational hierarchy.
Define a cell, tissue, organ and organism.
2.2 Animal tissues, organs and organ systems
Know that digestive system is an example of an organ system in which several organs work
together to digest and absorb food.
Relate knowledge of enzymes to Metabolism.
Describe the structure function and optimum conditions for enzymes.
Define denaturation.
Recall the sites of production and the action of amylase, proteases and lipases.
Know that digestive enzymes convert food into small soluble molecules that can be absorbed into
the bloodstream.
State that the products of digestion are used to build new carbohydrates, lipids and proteins.
Some glucose is used in respiration.
Recall where bile is made and stored and its pH and function.
State conditions that increase the rate of fat breakdown by lipase.
Recall the structure and functioning of the human heart and lungs, including how lungs are
adapted for gaseous exchange.
Recall that the heart is an organ that blood around the body in a double circulatory system. The
right ventricle pumps blood to the lungs where gas exchange takes place. The left ventricle pumps
blood around the rest of the body.
Name the major blood vessels.
Describe the structure of the lungs.
Explain natural and artificial pacemakers .
Name the three different types of blood vessel and explain how the structure of these vessels
relates to their functions.
Describe the components of blood and who they are adapted to function.
Describe coronary heart disease: a non-communicable disease.
State that health is the state of physical and mental wellbeing.
Know that defects in the immune system mean that an individual is more likely to suffer from
infectious diseases.
Recall that immune reactions initially caused by a pathogen can trigger allergies such as skin
rashes and asthma.
Know that severe physical ill health can lead to depression and other mental illness.
Explain the effect of lifestyle on some non-communicable diseases and that they can be caused by
and increased by, the interaction of a number of factors.
Recall that benign tumours and malignant tumours result from uncontrolled cell division.
Malignant tumour cells are cancers.
Know lifestyle risk factors for various types of cancer including smoking, obesity, common viruses
and UV exposure. There are also genetic risk factors for some cancers.
2.3 Plant tissues, organs and systems
Know the function of epidermal tissues palisade mesophyll, spongy mesophyll, xylem and
phloem and meristem tissue .
Describe the structures of tissues in the leaf and relate to their functions.
Explain how root hair cells are adapted for the efficient uptake of water and mineral ions.
Know the structure and function of xylem tissue.
Define factors which affect the rate of transpiration.
Explain the role of stomata and guard cells.
Explain the role of phloem tissue and name this process (translocation).
You might also like
- Full Download Solution Manual For Holes Human Anatomy Physiology 16th Edition Charles Welsh Cynthia Prentice Craver PDF Full ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Download Solution Manual For Holes Human Anatomy Physiology 16th Edition Charles Welsh Cynthia Prentice Craver PDF Full Chaptertracikennedyvw3z8d100% (23)
- Holes Human Anatomy and Physiology 15th Edition Shier Solutions ManualDocument4 pagesHoles Human Anatomy and Physiology 15th Edition Shier Solutions ManualKatherineBowenfojib100% (12)
- MCQs in Oral Surgery by Babu SParmarDocument517 pagesMCQs in Oral Surgery by Babu SParmarAmr KhattabNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 A & P Check PointsDocument11 pagesChapter 1 A & P Check PointsRobin Wilfong89% (9)
- Equilibrium The Art of Mastering SelfDocument131 pagesEquilibrium The Art of Mastering SelfSarim Ibn Salahadhin100% (1)
- Webster 2018 Life Science ReviewDocument88 pagesWebster 2018 Life Science Reviewapi-312162583No ratings yet
- Science Form 2 Chapter 1 NotesDocument19 pagesScience Form 2 Chapter 1 NotesAngie Kong Su Mei100% (2)
- Year 11 Jan Mock Revision ListDocument9 pagesYear 11 Jan Mock Revision Listbseddon6969No ratings yet
- 2 Organisation Biology ChecklistDocument3 pages2 Organisation Biology Checklistu19majli0No ratings yet
- Checklist - Digestion & EnzymesDocument1 pageChecklist - Digestion & EnzymesmarinaNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Holes Human Anatomy Physiology 16th Edition Charles Welsh Cynthia Prentice CraverDocument36 pagesSolution Manual For Holes Human Anatomy Physiology 16th Edition Charles Welsh Cynthia Prentice Cravertroul.cubit.nwjkgf100% (44)
- MODULe 1 Ana PhysioDocument10 pagesMODULe 1 Ana Physiojoshua ordenaNo ratings yet
- Local Media8189533475074911973Document21 pagesLocal Media8189533475074911973Jerky JokerNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2Document5 pagesGeneral Biology 2aifs000001No ratings yet
- Grade 6 - SSES - Science - Q2 - Wk3 - GLAKDocument16 pagesGrade 6 - SSES - Science - Q2 - Wk3 - GLAKMelanie TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Answer Key End of Chapter QuestionsDocument102 pagesAnswer Key End of Chapter QuestionsPhoebe Faye LyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 40 and 41 Objectives-1Document5 pagesChapter 40 and 41 Objectives-1Alex KirbyNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Revision List For StudentsDocument3 pagesYear 10 Revision List For StudentsSankarshan DahiyaNo ratings yet
- Module 1 RAWDocument25 pagesModule 1 RAWCordelia TobinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Med Physio (GP)Document9 pagesChapter 1 - Med Physio (GP)Ritch Jerielyn HaliliNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument163 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyColor BlackNo ratings yet
- Human PhysiologyDocument6 pagesHuman Physiologysubu231201No ratings yet
- Basic A&p Booklet Short Version 3Document228 pagesBasic A&p Booklet Short Version 3Hilary Christopher100% (1)
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To The Human Body Study Questions 1 (SQ 1)Document6 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To The Human Body Study Questions 1 (SQ 1)Julie Amor ZantuaNo ratings yet
- ADVANCED PHYSIOLOGY 1st Chapter Short Questions.Document10 pagesADVANCED PHYSIOLOGY 1st Chapter Short Questions.Muhammad Mudassar ChudaryNo ratings yet
- 7.07 Module Review Honors BioDocument4 pages7.07 Module Review Honors BioAbigail MeierNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Body Chemistry: Processes That Characterise LifeDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Body Chemistry: Processes That Characterise LifeLeo OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Holes Human Anatomy and Physiology 15th Edition Shier Solutions Manual PDFDocument35 pagesDwnload Full Holes Human Anatomy and Physiology 15th Edition Shier Solutions Manual PDFbrecciamoodgflo100% (12)
- G2. Human Body Introduction WorksheetDocument4 pagesG2. Human Body Introduction WorksheetMazucatoNo ratings yet
- Biology B1 Characteristics of Living OrganismsDocument28 pagesBiology B1 Characteristics of Living OrganismsShamini Segari GunasakaranNo ratings yet
- Physiology U-1 Introduction TeacherDocument195 pagesPhysiology U-1 Introduction Teachersinte beyuNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To The Human BodyDocument43 pagesAn Introduction To The Human BodySherleen Jane D. Fernandez50% (2)
- How Animals Survive Lesson 5Document30 pagesHow Animals Survive Lesson 5Ellah LaguismaNo ratings yet
- Year 7 Human Biology. All Yellow Answers Lesson 1Document3 pagesYear 7 Human Biology. All Yellow Answers Lesson 1Vinston ÅsénNo ratings yet
- University of Gondar College of Medicine and Health Sciences Department of Medical PhysiologyDocument202 pagesUniversity of Gondar College of Medicine and Health Sciences Department of Medical PhysiologyGifti DemisseNo ratings yet
- OBJECTIVES: Define Anatomy and Physiology, and Explain How They Are RelatedDocument15 pagesOBJECTIVES: Define Anatomy and Physiology, and Explain How They Are RelatedHarpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- Cuadernillo Guia Nutricion 1 y 2 - 2021Document10 pagesCuadernillo Guia Nutricion 1 y 2 - 2021valeinadNo ratings yet
- Introduction To BiochemistryDocument11 pagesIntroduction To BiochemistrySamson Roberto SaballegueNo ratings yet
- The Correlation of Controlling Systems With Homeostasis and Metabolism Alwi ShahabDocument43 pagesThe Correlation of Controlling Systems With Homeostasis and Metabolism Alwi ShahabAnisa Karamina WardaniNo ratings yet
- Assignment No. 1:: Mohammad NumanDocument11 pagesAssignment No. 1:: Mohammad NumanUsama AliNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy ModuleDocument48 pagesHuman Anatomy ModuleCielo CastilloNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument3 pagesUntitled Documentapi-422807575No ratings yet
- Organ SystemDocument36 pagesOrgan SystemsjdvissmarttvNo ratings yet
- B7 Knowledge ChecklistDocument9 pagesB7 Knowledge ChecklisthabuelmagdNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology 1Document6 pagesAnatomy and Physiology 1Dianne LarozaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Course SyllabusDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Course SyllabusDanna ManaloNo ratings yet
- Level Grade 5-6 - Science English - CornellDocument14 pagesLevel Grade 5-6 - Science English - CornellCornell English CenterNo ratings yet
- Life Sciece Module 4 Reporting ContentDocument9 pagesLife Sciece Module 4 Reporting ContentAnthony IlustreNo ratings yet
- Activities 1st EvaluationDocument5 pagesActivities 1st Evaluationvale.alvarovasquezNo ratings yet
- Scie - 10 M 6 Q4Document4 pagesScie - 10 M 6 Q4ainahNo ratings yet
- Modules in Earth ScienceDocument22 pagesModules in Earth ScienceAlpha100% (1)
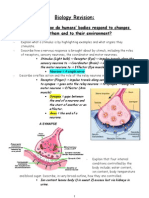
- Biology Revision:: Topic 11.1 - How Do Humans' Bodies Respond To Changes Inside Them and To Their Environment?Document11 pagesBiology Revision:: Topic 11.1 - How Do Humans' Bodies Respond To Changes Inside Them and To Their Environment?lghobrial16No ratings yet
- Module-4-Tissues, Organs, and Organ SystemsDocument19 pagesModule-4-Tissues, Organs, and Organ SystemsMARIA CORAZON CONTANTENo ratings yet
- 1 - Introduction - Into - Human - Body-26730 2Document7 pages1 - Introduction - Into - Human - Body-26730 2Olea MnNo ratings yet
- 2 Structural and Functional Organization, Necessary Life Functions & HomeostasisDocument37 pages2 Structural and Functional Organization, Necessary Life Functions & HomeostasisCamille Marie UrbanoNo ratings yet
- Bio MidtermDocument5 pagesBio MidtermĐặng Thị Hiếu LanNo ratings yet
- Chapter QuestionsDocument8 pagesChapter QuestionsAric DelinaNo ratings yet
- Physiology Chaper 1 NutritionDocument17 pagesPhysiology Chaper 1 NutritionArooj KhanNo ratings yet
- Full Download Holes Human Anatomy and Physiology 15th Edition Shier Solutions ManualDocument35 pagesFull Download Holes Human Anatomy and Physiology 15th Edition Shier Solutions Manualbarovert.o87w100% (33)
- GCSE Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandGCSE Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Review C5 ProgrammingDocument1 pageReview C5 ProgrammingCharlotte KnightNo ratings yet
- Expanding QuestionsDocument7 pagesExpanding QuestionsCharlotte KnightNo ratings yet
- Review C3 IssuesDocument1 pageReview C3 IssuesCharlotte KnightNo ratings yet
- Review B1 CellsDocument1 pageReview B1 CellsCharlotte KnightNo ratings yet
- Review B4 BioenergeticsDocument1 pageReview B4 BioenergeticsCharlotte KnightNo ratings yet
- Form 86 Health Examination Form 1Document2 pagesForm 86 Health Examination Form 1Ryan Paul Nayba100% (1)
- Final Paper Nanomedicine AgentsDocument16 pagesFinal Paper Nanomedicine Agentsapi-610430199No ratings yet
- Cell InjuryDocument92 pagesCell InjuryMariam AlavidzeNo ratings yet
- Retinopathy of PrematurityDocument30 pagesRetinopathy of Prematuritykenikirkucing2No ratings yet
- NexGen Flexion Balancing Instruments Surgical Technique 2897-5967-031-00 Rev1!29!2811 2009 29Document48 pagesNexGen Flexion Balancing Instruments Surgical Technique 2897-5967-031-00 Rev1!29!2811 2009 29flo1987No ratings yet
- Immunology: 'S CompanionsDocument74 pagesImmunology: 'S CompanionsRoahit RajanNo ratings yet
- Lydia HallDocument5 pagesLydia Hallbbasya eihyna100% (5)
- Disseminated Intravascular CoagulationDocument7 pagesDisseminated Intravascular CoagulationSunaina AdhikariNo ratings yet
- GlomerulonephritisDocument58 pagesGlomerulonephritisJosa Anggi Pratama0% (1)
- Ursin, H. (1998) The Psychology in PsychoneuroendocrinologyDocument16 pagesUrsin, H. (1998) The Psychology in PsychoneuroendocrinologyCristian jimènezNo ratings yet
- Production of Platelet CountsDocument9 pagesProduction of Platelet CountsJack KayatNo ratings yet
- Are You Allergic To MorningsDocument2 pagesAre You Allergic To Morningsaeryll1305100% (1)
- Fish Diseases FactsheetDocument2 pagesFish Diseases FactsheetWayneNo ratings yet
- Selina Concise Biology Solutions Class 6 Chapter 3 Cell - The Structure and FunctionsDocument10 pagesSelina Concise Biology Solutions Class 6 Chapter 3 Cell - The Structure and FunctionsFLANTAMOCKNo ratings yet
- Foot Anatomy Tendons and LigamentsDocument3 pagesFoot Anatomy Tendons and Ligamentsanak_kost_aji_baungNo ratings yet
- Case Study 1Document67 pagesCase Study 1Herbie SoNo ratings yet
- Alergi Yang Disebabkan KupuDocument7 pagesAlergi Yang Disebabkan KupuDesi Suryani DewiNo ratings yet
- Electrocytes, Electroplaques or Electroplaxes AreDocument4 pagesElectrocytes, Electroplaques or Electroplaxes Areklauss10No ratings yet
- Membrane TransportDocument25 pagesMembrane TransportvvNo ratings yet
- IPP-LB-HEM-01-01-LH 750 Analyzer and Coulter Gen's SystemDocument13 pagesIPP-LB-HEM-01-01-LH 750 Analyzer and Coulter Gen's SystemMaria Francesca MapaNo ratings yet
- Dr. Huma Fatima AliDocument24 pagesDr. Huma Fatima AliNouman Umar100% (1)
- Unit 3 Gastrointestinal Disorders P3 Nausea and VormitingDocument39 pagesUnit 3 Gastrointestinal Disorders P3 Nausea and VormitingShashidharan MenonNo ratings yet
- Sputum CollectionDocument14 pagesSputum CollectionAira AlaroNo ratings yet
- SilentSoundTechnology DocumentationDocument52 pagesSilentSoundTechnology Documentationlikitha50% (2)
- Biomechanics of Edentulous StateDocument15 pagesBiomechanics of Edentulous StateNadeemNo ratings yet
- Mra CRDocument87 pagesMra CRyailetc3796No ratings yet
- Ekstraksi Anggur Merah - CyntiaDocument11 pagesEkstraksi Anggur Merah - CyntiaAdilah AthtahirahNo ratings yet
- Photoperiodism Powerpoint EduDocument12 pagesPhotoperiodism Powerpoint EduAlabi FauziatBulalaNo ratings yet