Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bks MaiHL 1302 Gdc05 XXTNSP
Bks MaiHL 1302 Gdc05 XXTNSP
Uploaded by
Sun Xi Yao0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views2 pagesThis document discusses solving binomial probability problems using a TI-Nspire CX calculator. It provides examples of finding the probability of getting exactly 3 girls out of 6 children and the probability of getting 3 consecutive girls. It also shows how to calculate the minimum sample size needed from a population of over 4 million so that the probability of the sample having no carriers of a virus is less than 0.4.
Original Description:
Original Title
Bks MaiHL 1302 Gdc05 Xxtnsp
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses solving binomial probability problems using a TI-Nspire CX calculator. It provides examples of finding the probability of getting exactly 3 girls out of 6 children and the probability of getting 3 consecutive girls. It also shows how to calculate the minimum sample size needed from a population of over 4 million so that the probability of the sample having no carriers of a virus is less than 0.4.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views2 pagesBks MaiHL 1302 Gdc05 XXTNSP
Bks MaiHL 1302 Gdc05 XXTNSP
Uploaded by
Sun Xi YaoThis document discusses solving binomial probability problems using a TI-Nspire CX calculator. It provides examples of finding the probability of getting exactly 3 girls out of 6 children and the probability of getting 3 consecutive girls. It also shows how to calculate the minimum sample size needed from a population of over 4 million so that the probability of the sample having no carriers of a virus is less than 0.4.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
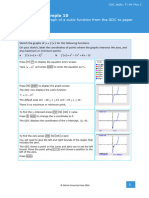
GDC skills: TI-Nspire CX
Chapter 13 / Example 5
Binomial probabilities
a In a family of six children, find
i the probability that there are exactly three girls
ii the probability that exactly three consecutive girls are born.
b A study shows that 0.9% of a population of over 4 000 000 carries a virus. Find the
smallest size of sample from the population required in order that the probability
of the sample having no carriers is less than 0.4.
G B 6, 0.5 . Find P G 3 .
Open a new document and add a Calculator page.
Press b 5:Probability | 5:Distributions | A:Binomial Pdf…
Enter 6 as the number of trials, 0.5 as the probability of success
and 3 as the X value.
Press · or click OK with the touchpad.
The GDC displays the solution P G 3 0.3125 .
6
1
P(3 consecutive girls) = 4 0.0625 .
2
Type f1(x) and press / t Ï.
Press b 5:Probability | 5:Distributions | B:Binomial Cdf…
Enter x as the number of trials, 0.009 as the probability of
success and 0 as the Lower Bound and 0 as the Upper Bound.
Press · or click OK with the touchpad.
The function f1(x) is defined.
Display this function in a table.
Press / ~ (¿) and add a Lists & Spreadsheet page.
© Oxford University Press 2019 1
GDC skills: TI-Nspire CX
Chapter 13 / Example 5
Binomial probabilities
Press / T to change from a spreadsheet to a table.
Press ·.
The GDC displays a table of f1(x).
Scroll down the table using ¤.
From the table, you can see that n = 102 is the first value for
which P C 0 0.4 .
Hence n = 102 is the minimum value required.
© Oxford University Press 2019 2
You might also like
- Biostat FinalDocument11 pagesBiostat FinalIashdip iashdipNo ratings yet
- Additional QuestionsDocument10 pagesAdditional QuestionsAhmad RazaNo ratings yet
- HW3/621/BSUDocument3 pagesHW3/621/BSUGamma.SigmaNo ratings yet
- Session 3 DistribtionDocument46 pagesSession 3 DistribtionChaitu Un PrediCtbleNo ratings yet
- Bks MaiHL 1406 gdc19 XXTNSPDocument2 pagesBks MaiHL 1406 gdc19 XXTNSPlillieNo ratings yet
- Finding Binomial Probabilities: Chapter 7 / Example 22Document2 pagesFinding Binomial Probabilities: Chapter 7 / Example 22Ariane CarbajalNo ratings yet
- Bks MaiHL 1402 gdc03 XXTNSPDocument2 pagesBks MaiHL 1402 gdc03 XXTNSPlillieNo ratings yet
- Stats NotesDocument18 pagesStats NotesJinal RajgorNo ratings yet
- Weeks 1 and 2 Math381Document37 pagesWeeks 1 and 2 Math381Saeed KhawamNo ratings yet
- Bks MaiHL 1406 gdc18 XXTNSPDocument2 pagesBks MaiHL 1406 gdc18 XXTNSPlillieNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Probability - Binomial and Normal DistributionsDocument64 pagesIntroduction To Probability - Binomial and Normal DistributionsFadel DeebNo ratings yet
- Binomial Distributions: The Basic Practice of StatisticsDocument13 pagesBinomial Distributions: The Basic Practice of StatisticsUsernamefireNo ratings yet
- GMP - QTMD) - End TermDocument7 pagesGMP - QTMD) - End TermRahul RathodNo ratings yet
- Section 6.2Document24 pagesSection 6.2PunchedASnail klo.No ratings yet
- Chi-Square Test For For Goodness-of-Fit: AnnouncementsDocument4 pagesChi-Square Test For For Goodness-of-Fit: AnnouncementsNellson NichioustNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument28 pagesUntitledAlp ÇelikNo ratings yet
- Finding The Number of Terms in A Geometric Sequence: Chapter 1 / Example 15Document8 pagesFinding The Number of Terms in A Geometric Sequence: Chapter 1 / Example 15Diandra Satria AdhitamaNo ratings yet
- Bks MaiHL 1403 gdc05 XXTNSPDocument2 pagesBks MaiHL 1403 gdc05 XXTNSPlillieNo ratings yet
- GCD HL CH6 Example11Document4 pagesGCD HL CH6 Example11Mark ChangNo ratings yet
- Bks MaiHL 1306 gdc18 XXTNSPDocument1 pageBks MaiHL 1306 gdc18 XXTNSPlillieNo ratings yet
- Statistical Methods in Quality ManagementDocument71 pagesStatistical Methods in Quality ManagementKurtNo ratings yet
- Kode B: Final Exam Second Semester 2019/2020Document12 pagesKode B: Final Exam Second Semester 2019/2020reviandiramadhan100% (1)
- 8.1 Power PointDocument19 pages8.1 Power PointkrothrocNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Business Statistics 5th Edition Bowerman Test Bank 1Document36 pagesEssentials of Business Statistics 5th Edition Bowerman Test Bank 1brittneybyrdocsxdfgkyq100% (33)
- MDAE FC 2022-23 Stats Problem&SolutionsDocument17 pagesMDAE FC 2022-23 Stats Problem&SolutionsPranil ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- M130 Tutorial - 5 Some Discrete Probability Distributions-V.2Document23 pagesM130 Tutorial - 5 Some Discrete Probability Distributions-V.2Frederic FarahNo ratings yet
- Section 1: Introducing The Binomial DistributionDocument6 pagesSection 1: Introducing The Binomial DistributionVarul SinhaNo ratings yet
- Bks MaiSL 0903 gdc10 Xxti84Document5 pagesBks MaiSL 0903 gdc10 Xxti84W SNo ratings yet
- Binomial DistributionDocument12 pagesBinomial DistributionHarika KalluriNo ratings yet
- Examples of Discrete Probability Distributions: Binomial PoissonDocument17 pagesExamples of Discrete Probability Distributions: Binomial PoissonDionesa Joy D RizalteNo ratings yet
- A Review of Basic Statistical Concepts: Answers To Problems and Cases 1Document94 pagesA Review of Basic Statistical Concepts: Answers To Problems and Cases 1Terry ReynaldoNo ratings yet
- Minitab Activity 4 - LatozaDocument6 pagesMinitab Activity 4 - LatozaAngel LatozaNo ratings yet
- Bks MaaHL 0502 gdc05 Xxti84Document4 pagesBks MaaHL 0502 gdc05 Xxti845546152rishabh9No ratings yet
- Module 4 - Fundamentals of ProbabilityDocument50 pagesModule 4 - Fundamentals of ProbabilitybindewaNo ratings yet
- Rvrlecture 1Document20 pagesRvrlecture 1Kezia PrabhakarNo ratings yet
- Viva Que 1Document43 pagesViva Que 1MD Imamur RahmanNo ratings yet
- SQQS1013-Chapter 5Document52 pagesSQQS1013-Chapter 5Anis anisyaNo ratings yet
- Curriculum VitaeDocument101 pagesCurriculum VitaeKholid BaldanNo ratings yet
- ECE 313, Section F: Hour Exam I: Monday March 5, 2012 7:00 P.M. - 8:15 P.M. 163 EverittDocument9 pagesECE 313, Section F: Hour Exam I: Monday March 5, 2012 7:00 P.M. - 8:15 P.M. 163 EverittspitzersglareNo ratings yet
- Lesson 9 - Binomial Distributions: Return To Cover PageDocument6 pagesLesson 9 - Binomial Distributions: Return To Cover PagezaenalkmiNo ratings yet
- Hyp 8384Document3 pagesHyp 8384Mert YeşilbursaNo ratings yet
- Discrete Random Variables Excel PDFDocument11 pagesDiscrete Random Variables Excel PDFdosorioa2No ratings yet
- Modelling With Power Functions: Chapter 6 / Example 11Document4 pagesModelling With Power Functions: Chapter 6 / Example 11Sophie HoltusNo ratings yet
- Statistical Methods in Quality ManagementDocument71 pagesStatistical Methods in Quality ManagementKurtNo ratings yet
- Statistical Experiment: 5.1 Random Variables and Probability DistributionsDocument23 pagesStatistical Experiment: 5.1 Random Variables and Probability DistributionsDan VenencianoNo ratings yet
- Sampling Distributions: Probabilities For Sample MeansDocument3 pagesSampling Distributions: Probabilities For Sample Meanslucifer angelNo ratings yet
- Summer 578 Assignment 2 SolutionsDocument13 pagesSummer 578 Assignment 2 SolutionsGradu8tedOne100% (1)
- The Binomial DistributionDocument19 pagesThe Binomial DistributionK Kunal RajNo ratings yet
- Inference About A Population: - Population Mean - Population ProportionDocument29 pagesInference About A Population: - Population Mean - Population ProportionAhmed HadadNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 & 8 Brief Lecture Notes On Probability Distributions: Binomial, Poisson and Normal DistributionDocument17 pagesLecture 7 & 8 Brief Lecture Notes On Probability Distributions: Binomial, Poisson and Normal DistributionNazmul HudaNo ratings yet
- Intro To Probability (Pattern Recognition)Document94 pagesIntro To Probability (Pattern Recognition)Asish SorahiaNo ratings yet
- Probability ExamplesDocument2 pagesProbability ExamplesSajjadNo ratings yet
- Bks MaiSL 1301 gdc07 XXTNSPDocument3 pagesBks MaiSL 1301 gdc07 XXTNSPengabd345No ratings yet
- 12 ProbabilityDocument38 pages12 ProbabilityKin Lok ChanNo ratings yet
- A Probability Is A Number Between 0 and 1, InclusiveDocument13 pagesA Probability Is A Number Between 0 and 1, InclusiveLeopold LasetNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03Document22 pagesChapter 03Osama SamhaNo ratings yet
- Normal Approximation of The Binomial DistributionDocument18 pagesNormal Approximation of The Binomial Distributionmahmoud fuqahaNo ratings yet
- Assignment #3 Hypothesis TestingDocument10 pagesAssignment #3 Hypothesis TestingJihen SmariNo ratings yet
- Section 5.5Document32 pagesSection 5.5PunchedASnail klo.No ratings yet