Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Vol 3 Ascorbic Acid
Vol 3 Ascorbic Acid
Uploaded by
regdddOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Vol 3 Ascorbic Acid
Vol 3 Ascorbic Acid
Uploaded by
regdddCopyright:
Available Formats
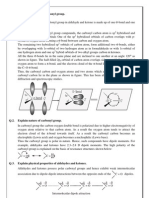
Ascorbic acid is a furan-based lactone of 2-ketogluconic acid.
It contains an
adjacent enediol adjacent to the carbonyl. This -C(OH)=C(OH)-C(=O)- structural
pattern is characteristic of reductones, and increases the acidity of one of the
enol hydroxyl groups. The deprotonated conjugate base is the ascorbate anion, which
is stabilized by electron delocalization that results from resonance between two
forms:
Ascorbate resonance.png
For this reason, ascorbic acid is much more acidic than would be expected if the
compound contained only isolated hydroxyl groups.
Salts
The ascorbate anion forms salts, such as sodium ascorbate, calcium ascorbate, and
potassium ascorbate.
Esters
Ascorbic acid can also react with organic acids as an alcohol forming esters such
as ascorbyl palmitate and ascorbyl stearate.
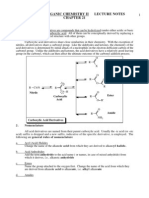
Nucleophilic attack
Nucleophilic attack of ascorbic acid on a proton results in a 1,3-diketone:
Ascorbic diketone.png
You might also like
- Mike MentzerDocument57 pagesMike Mentzerregddd100% (3)
- Creating A Trading Plan EminiMindDocument37 pagesCreating A Trading Plan EminiMindregddd50% (2)
- CH 20Document31 pagesCH 20syedhasnainrazanustNo ratings yet
- Ch20 PDFDocument30 pagesCh20 PDFPilar CaleroNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acid - NotesDocument16 pagesCarboxylic Acid - NotesVANSHIKA GOELNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes For Class 12 Chapter 12 Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsDocument26 pagesChemistry Notes For Class 12 Chapter 12 Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsDipankar YadavNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes and Ketones .NotesDocument32 pagesAldehydes and Ketones .NotesvishalNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic AcidsDocument15 pagesCarboxylic Acidsmadhu bonamNo ratings yet
- Alkyne Chemistry EEEDocument42 pagesAlkyne Chemistry EEEVictor MutugiNo ratings yet
- Vol 4 Ascorbic AcidDocument1 pageVol 4 Ascorbic AcidregdddNo ratings yet
- I Asam KarboksilatDocument40 pagesI Asam KarboksilatArvia SuprafestiNo ratings yet
- Catboxylic Acids and Their DerivativesDocument45 pagesCatboxylic Acids and Their DerivativesAnil Kumar VermaNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic AcidDocument9 pagesCarboxylic AcidjohnsmithprayNo ratings yet
- 4sem U1 Carboxylic AcidDocument20 pages4sem U1 Carboxylic AcidNameirakpam satishNo ratings yet
- Alcohols and Phenols (ROH, Functional GRP - OH.)Document24 pagesAlcohols and Phenols (ROH, Functional GRP - OH.)MadhureemaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 5 Carboxyl CHM413Document40 pagesCHAPTER 5 Carboxyl CHM413Anis NasuhaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20: Carboxylic AcidsDocument3 pagesChapter 20: Carboxylic AcidsRobert GardnerNo ratings yet
- Asam Karboksilat Dan TurunannyaDocument93 pagesAsam Karboksilat Dan TurunannyaUswah HasanahNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acids - 2023Document15 pagesCarboxylic Acids - 2023Sangay ChodenNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic AcidDocument21 pagesCarboxylic Acidelizabeth merzyNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic AcidsDocument3 pagesCarboxylic AcidsDian Agus SetyawatiNo ratings yet
- PDF Carboxylic AcidsDocument45 pagesPDF Carboxylic AcidsRegina Maree BermudezNo ratings yet
- Alcohols 1Document13 pagesAlcohols 1Suresh VedpathakNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic AcidDocument26 pagesCarboxylic AcidDavid ParkNo ratings yet
- Oleh: Prof. Dr. Hj. Maulidiyah, M.Si: Jurusan Kimia FMIPA UHO 2019Document21 pagesOleh: Prof. Dr. Hj. Maulidiyah, M.Si: Jurusan Kimia FMIPA UHO 2019ANDI ELSYA WIDIYA PRASTIKA WEMPI F1C117065No ratings yet
- CH 20Document8 pagesCH 20adafgsdfgNo ratings yet
- Chapter 22: Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution ReactionsDocument4 pagesChapter 22: Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution Reactionsmikec86No ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acid and Their DerivativesDocument13 pagesCarboxylic Acid and Their DerivativesaqidahNo ratings yet
- Al KynesDocument16 pagesAl KynesShivam GuptaNo ratings yet
- Acids&Acid DerivativesDocument5 pagesAcids&Acid DerivativesStephanie Joy EscalaNo ratings yet
- A. Title of Experiment: Carboxylic Acid: Thursday, 10 C. Purpose of ExperimentDocument27 pagesA. Title of Experiment: Carboxylic Acid: Thursday, 10 C. Purpose of ExperimentKeyvir AulinzNo ratings yet
- CH 117 Notes 3Document6 pagesCH 117 Notes 3Benson ShayoNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument42 pagesOrganic ChemistryAlisha KhanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 6 Sem 3 07Document65 pagesChemistry Form 6 Sem 3 07Ng Swee Loong StevenNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acids Class XII NotesDocument43 pagesCarboxylic Acids Class XII NotesAditya BhattNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument15 pagesUntitlednatNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry: Carboxylic Acids & EstersDocument133 pagesOrganic Chemistry: Carboxylic Acids & EstersWai Kwong ChiuNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic AcidDocument2 pagesCarboxylic AciddemNo ratings yet
- CH 05Document31 pagesCH 05nayan159No ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acids PrepaRAtionDocument5 pagesCarboxylic Acids PrepaRAtionJyoti Gaba -ChemistryNo ratings yet
- Notes C16 121Document13 pagesNotes C16 121Amir HussainNo ratings yet
- Car Bani OnDocument29 pagesCar Bani OnPrashant Munnolli100% (1)
- Week 11 AlkunaDocument54 pagesWeek 11 AlkunaNazuwa RosaNo ratings yet
- Alcohol and AldehydeDocument21 pagesAlcohol and AldehydehmtlionNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Acidic Strength of Carboxylic AcidsDocument2 pagesFactors Affecting Acidic Strength of Carboxylic AcidsDildar LakhoNo ratings yet
- 20.3 Aldehydes, Ketones, Carboxylic Acids, and EstersDocument5 pages20.3 Aldehydes, Ketones, Carboxylic Acids, and EstersAcieNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acids ..Document27 pagesCarboxylic Acids ..Mariam HamedNo ratings yet
- Jee-Aldehyde Ketone & Carboxylic Acid Chem XiiDocument72 pagesJee-Aldehyde Ketone & Carboxylic Acid Chem Xiiswastik aroraNo ratings yet
- Notes Class 12 Chemistry Aldehydes Ketones and CarboxylDocument26 pagesNotes Class 12 Chemistry Aldehydes Ketones and CarboxyltcbrihzllmkmkvxfovNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acid and Their DerivatesDocument10 pagesCarboxylic Acid and Their Derivatesvita iftitahiyahNo ratings yet
- Structural Chemistry Organic Chemistry Summary: Alkynes: Structure, Conformations, PropertiesDocument20 pagesStructural Chemistry Organic Chemistry Summary: Alkynes: Structure, Conformations, PropertiesMohanraj ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- I - Asam KarboksilatDocument45 pagesI - Asam KarboksilatAku Big Bos DayuNo ratings yet
- Isomerism in Alkanoic AcidsDocument6 pagesIsomerism in Alkanoic AcidsnelsonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20: Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles: Based On Mcmurry'S Organic Chemistry, 9 EditionDocument48 pagesChapter 20: Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles: Based On Mcmurry'S Organic Chemistry, 9 Edition張湧浩No ratings yet
- Chap 4Document70 pagesChap 4Irfan AzaharNo ratings yet
- L4 - Acids, Esters and Its DerivativesDocument48 pagesL4 - Acids, Esters and Its DerivativesAlexNo ratings yet
- Acidic Basic CharacterDocument29 pagesAcidic Basic Characterkelon scottNo ratings yet
- Ch18.pdf Aldehyde and Ketone PDFDocument43 pagesCh18.pdf Aldehyde and Ketone PDFShakesha HemmingsNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 1Document33 pagesChemistry 1Alvis MwangiNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Question Bank (Subjective)Document16 pagesAldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Question Bank (Subjective)helixvector45411No ratings yet
- Carboxylic AcidDocument9 pagesCarboxylic AcidAbiot DibabaNo ratings yet
- Vol 992growthDocument1 pageVol 992growthregdddNo ratings yet
- Trading StructuresDocument3 pagesTrading StructuresregdddNo ratings yet
- Vol 991 EconDocument2 pagesVol 991 EconregdddNo ratings yet
- Vol 6 Ascorbic AcidDocument1 pageVol 6 Ascorbic AcidregdddNo ratings yet
- RSI CalcDocument2 pagesRSI CalcregdddNo ratings yet
- Vol 2 Ascorbic AcidDocument1 pageVol 2 Ascorbic AcidregdddNo ratings yet