Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Science
Science
Uploaded by
Gutierrez, Patricia MaeCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Srednicki qft2 PDFDocument109 pagesSrednicki qft2 PDFCharlie HultgreenNo ratings yet
- Of An Atom . .......................... 2Document12 pagesOf An Atom . .......................... 2amyjanecelestialNo ratings yet
- Solid State Historical ContextDocument11 pagesSolid State Historical ContextbookregtestNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3. Atomic Structure and Periodic LawDocument32 pagesLecture 3. Atomic Structure and Periodic LawВалентина ЮзьковаNo ratings yet
- Atoms MoleculesDocument78 pagesAtoms MoleculesShanenely minNo ratings yet
- Sci9 Q2 Lesson 1 Atomic Model, Sub Atomic ParticlesDocument29 pagesSci9 Q2 Lesson 1 Atomic Model, Sub Atomic ParticlesFlorenze GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Structure of An Atom: AtomsDocument8 pagesIntroduction To The Structure of An Atom: Atomsshowmytv12No ratings yet
- Unit 2. The AtomDocument26 pagesUnit 2. The Atomgarciaortegajulia5No ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument6 pagesAtomic StructureDileep KumarNo ratings yet
- Atomicstructurepresentation 170510013215Document16 pagesAtomicstructurepresentation 170510013215Nilimoy Choudhury100% (1)
- Science-Q2-Notes BanzonDocument3 pagesScience-Q2-Notes BanzonfeytNo ratings yet
- 3 Discovery of The Subatomic Particles - Atomic ModelsDocument41 pages3 Discovery of The Subatomic Particles - Atomic ModelsFranchesca De los SantosNo ratings yet
- SCI Q2 ReviewerDocument14 pagesSCI Q2 ReviewerJonash Miguel LorzanoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Atomic Theory and Periodic TableDocument9 pagesChapter 2 Atomic Theory and Periodic TableArth LubayNo ratings yet
- 2.intro To Electrical TechnologyDocument117 pages2.intro To Electrical TechnologyRichard del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Atomic ModelDocument46 pagesAtomic ModelShannelle Anne CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document16 pagesChapter 1aregawi weleabezgiNo ratings yet
- Psma PrelimsDocument42 pagesPsma PrelimsPrincess Rose GamboaNo ratings yet
- Esp Answer KeyDocument2 pagesEsp Answer KeyAslan MorgadoNo ratings yet
- Atomic Theory CH-1Document64 pagesAtomic Theory CH-1tazebNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Atomic Structure - Notes...Document7 pagesGrade 8 Atomic Structure - Notes...Antonita100% (1)
- Atomic ST 8 IIT Class ...Document7 pagesAtomic ST 8 IIT Class ...Venugopal RNo ratings yet
- Unit Iv-VDocument18 pagesUnit Iv-VIvy Marie ToyonganNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 Atomic Structure: 2.1 The Nuclear AtomDocument45 pagesTopic 2 Atomic Structure: 2.1 The Nuclear AtomIan SembadaNo ratings yet
- PhysicalScienceQ1 ReviewerDocument3 pagesPhysicalScienceQ1 Reviewerrlyalns1128No ratings yet
- Electronic ConfigurationDocument10 pagesElectronic ConfigurationNicole ChangNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2Document8 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2Almira MejoradaNo ratings yet
- Atomic PhysicsDocument5 pagesAtomic Physicslove meNo ratings yet
- Structure of An AtomDocument4 pagesStructure of An Atomsompriya007No ratings yet
- YT Structure of The AtomDocument72 pagesYT Structure of The AtomAbhishek Kumar100% (1)
- CBSE Class 9 Science Revision Notes Chapter - 4 Structure of AtomDocument7 pagesCBSE Class 9 Science Revision Notes Chapter - 4 Structure of AtomShweta ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Physis 2nd and 3rd Term ss3Document38 pagesPhysis 2nd and 3rd Term ss3Dada RasheedNo ratings yet
- Atomic Scale StructuresDocument3 pagesAtomic Scale StructuresErish Brylle G. MañalacNo ratings yet
- Intro To Electrical Technology EditedDocument60 pagesIntro To Electrical Technology Editedmae OrgayaNo ratings yet
- Atomic ModelDocument14 pagesAtomic Modellanyasdeq112No ratings yet
- Atomic Theory: A Brief HistoryDocument61 pagesAtomic Theory: A Brief HistoryAbid Al RezaNo ratings yet
- REVIEWER OF GEN CHEM ^0 RWS 2ND SUMMATIVE TESTDocument8 pagesREVIEWER OF GEN CHEM ^0 RWS 2ND SUMMATIVE TEST11boyle.locsinjanilleNo ratings yet
- Leaving Cert Chemistry NotesDocument116 pagesLeaving Cert Chemistry NotesSnivySerpentNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure: By: Chynna B. Piclet 12 - ST AugustineDocument23 pagesAtomic Structure: By: Chynna B. Piclet 12 - ST AugustineZhel TomoroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02 Atomic StructureDocument62 pagesChapter 02 Atomic StructureJishen ZhuNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Chem 1Document64 pagesInorganic Chem 1Habtamu mullu BiadgoNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Chem 1Document2 pagesReviewer in Chem 1MARY ZIANNE GABRIELLE QUINTONo ratings yet
- Molecule by Shayan Ahmad KhattakDocument19 pagesMolecule by Shayan Ahmad KhattakShayan Ahmad Khattak, BS Physics Student, UoPNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument6 pagesAtomic StructureAl MubarakNo ratings yet
- PDF 20221114 080033 0000Document2 pagesPDF 20221114 080033 0000John Marithe PutunganNo ratings yet
- Models of The AtomDocument38 pagesModels of The AtomKC TorresNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry PresentationDocument45 pagesGeneral Chemistry PresentationJohn Adrian MalunesNo ratings yet
- Atomic ModelsDocument10 pagesAtomic ModelsMuhammad SamyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Atomic Structure & Interatomic Bonding: Issues To Address..Document52 pagesChapter 2: Atomic Structure & Interatomic Bonding: Issues To Address..ÖmerNo ratings yet
- Ass Mahfuz Sir Byb SiamDocument10 pagesAss Mahfuz Sir Byb SiamNowfal Hasan SiamNo ratings yet
- Phy1204 Atoms PresentationDocument6 pagesPhy1204 Atoms PresentationAnuradha ItwaruNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument6 pagesChemistryMANASI AHIRE [SOUS-EO054]No ratings yet
- Structure of AtomsDocument26 pagesStructure of AtomsdhruvindharmendraNo ratings yet
- Atomic Theories Quatum ModelDocument31 pagesAtomic Theories Quatum Modelerinallyson20No ratings yet
- Atomic Structure and Electronic Structure of The Atom Rz29fmDocument17 pagesAtomic Structure and Electronic Structure of The Atom Rz29fmkerri “Kerri” samNo ratings yet
- CH 1Document58 pagesCH 1smohammedadenNo ratings yet
- Electronic Structure of AtomDocument78 pagesElectronic Structure of AtomJC MalinaoNo ratings yet
- Science (Quarter 2)Document2 pagesScience (Quarter 2)Around Josef Ezekiel Villa Del ReyNo ratings yet
- Lesson - Atomic Structure: Scientist DiscoveryDocument4 pagesLesson - Atomic Structure: Scientist DiscoveryKokkilaa ParameswaranNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding: Model of An AtomDocument9 pagesAtomic Structure and Chemical Bonding: Model of An AtomSoumya Ranjan SahooNo ratings yet
- PANI Coupled Hierarchical Bi2S3 Nanoflowers BasedDocument13 pagesPANI Coupled Hierarchical Bi2S3 Nanoflowers Basedanmol sharmaNo ratings yet
- 12 Physics Notes Ch05 Magnetism and MatterDocument2 pages12 Physics Notes Ch05 Magnetism and MatterRishabhNo ratings yet
- Nano Dimensional MaterialsDocument151 pagesNano Dimensional MaterialsCHEM22028 NidhiNo ratings yet
- Thin Film Research PapersDocument7 pagesThin Film Research Papersozbvtcvkg100% (1)
- Intermolecular Forces of Attraction Properties of LiquidDocument38 pagesIntermolecular Forces of Attraction Properties of LiquidJa FloresNo ratings yet
- 03 Quantum-Dot-Based Solar Cells - Recent Advances, Strategies, and ChallengesDocument15 pages03 Quantum-Dot-Based Solar Cells - Recent Advances, Strategies, and ChallengesBiancaBeloNo ratings yet
- Heusler AlloysDocument12 pagesHeusler Alloysrebid.burlier-0hNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 9 Coordination CompoundsDocument23 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 9 Coordination CompoundsFEARLESS NETWORKx fanNo ratings yet
- GPL 212 Determination of Surface Tension of A LiquidDocument28 pagesGPL 212 Determination of Surface Tension of A LiquidyasintharaNo ratings yet
- 36 Modern-Energy LevelsDocument6 pages36 Modern-Energy LevelseltytanNo ratings yet
- SlaterDocument16 pagesSlaterprivate3737No ratings yet
- Booklet 1 Methods For in Vivo Dosimetry in External RadiotherapyDocument87 pagesBooklet 1 Methods For in Vivo Dosimetry in External RadiotherapyNesly M. MateoNo ratings yet
- Crystal Field TheoryDocument39 pagesCrystal Field TheoryRahmi HayatunnufusNo ratings yet
- Studies On Structural and Magnetic Properties of Ternary CobaltDocument8 pagesStudies On Structural and Magnetic Properties of Ternary CobaltKamenriderNo ratings yet
- Laser DiodeDocument41 pagesLaser DiodeSaurabh SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- XRD (X - Ray Diffraction)Document7 pagesXRD (X - Ray Diffraction)summi64No ratings yet
- Semiconductors Basics1 2013Document30 pagesSemiconductors Basics1 2013SriHariKalyanBNo ratings yet
- DLVO Theory (And Other Stuffs)Document34 pagesDLVO Theory (And Other Stuffs)AFZBNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document3 pagesTutorial 1doldolzzNo ratings yet
- JFET Operation & CharacteristicsDocument5 pagesJFET Operation & CharacteristicsAnusooya VNo ratings yet
- Ingaas/Gaassb Heterojunction Tfet: January 2015Document6 pagesIngaas/Gaassb Heterojunction Tfet: January 2015Anonymous jxm0WNS7QaNo ratings yet
- Dielectrics and FerroelectricsDocument47 pagesDielectrics and FerroelectricsibrahimNo ratings yet
- Mech 340-HW4Document4 pagesMech 340-HW4sridndNo ratings yet
- 277705-Article Text-380138-1-10-20140620Document6 pages277705-Article Text-380138-1-10-20140620Omkar BharankarNo ratings yet
- 45 Ex2 PracticeDocument5 pages45 Ex2 PracticeJules BrunoNo ratings yet
- Electron and Hole Mobilities in Si As A Function of Concentration and Temperature PDFDocument4 pagesElectron and Hole Mobilities in Si As A Function of Concentration and Temperature PDFFrancisco EstradaNo ratings yet
- Unit 01Document21 pagesUnit 01mathanstar77No ratings yet
- Physics 262: Problem Set 3: Due: Oct 22Document2 pagesPhysics 262: Problem Set 3: Due: Oct 22romanberens2No ratings yet
- Review On Nanomaterials: Synthesis and Applications: ArticleDocument10 pagesReview On Nanomaterials: Synthesis and Applications: ArticleDhanunjayaNo ratings yet
Science
Science
Uploaded by
Gutierrez, Patricia MaeOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Science
Science
Uploaded by
Gutierrez, Patricia MaeCopyright:
Available Formats
SCIENCE
LONG TEST REVIEWER
ERNEST RUTHERFORD
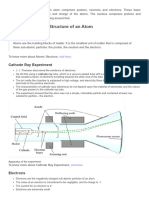
ATOM He discovered the nucleus in the year 1911,
through the Gold Foil Experiment.
The basic unit of matter and the smallest particle that
make up elements. It is composed of three QUANTUM (QUANTA)
subatomic particles.
It is the smallest amount of energy that can be
SUBATOMIC PARTS OF AN ATOM measured. Quantum comes from Latin, meaning
● Neutrons - has no charge / uncharged "an amount" or "how much?"
● Protons - positively charged
● Electrons - negatively charged QUANTUM MECHANICAL MODEL OF AN ATOM
THE NUCLEUS
It is the center part of the atom, also the densest part It is the most advanced and accurate model of the
as the mass is concentrated here, it contains the atom used by chemists & physicists — proposed by
neutrons and protons which makes it positively Erwin Schrodinger. In this model, electrons
charged. surround the nucleus in a form resembling a cloud
called, “electron cloud.”
SCIENTISTS THAT STUDIED THE ATOM THE ELECTRON CLOUD
The region around the nucleus where an electron is
DEMOCRITUS most likely to be found is called the electron cloud. A
He is an ancient Greek philosopher who is viewed by high density is where the electrons are most likely to
many as being the “Father of Modern Science.” He be and a low density is where the electrons are least
was the first person to use the word ‘atom,’ which likely to be.
means indivisible. He also called the smallest unit
of matter, ‘atomus.’
ARISTOTLE LOUIS DE BROGLIE
He believed that matter came from the four He introduced the idea that particles, such as
elements, namely, Fire, Air, Earth, and Water. electrons, could be described not only as particles
but also as waves. (Wave Particle Duality Theory)
JOHN DALTON
He adapted Democritus’ theory and discovered the WERNER KARL HEISENBERG
atom. Dalton believed that the atom is a solid He believed that we cannot know both the
sphere. (Billiard Ball Model) position and speed of a particle, such as a photon
or electron, with perfect accuracy. (Heisenberg
Uncertainty Principle)
JOSEPH JOHN THOMSON (JJ)
He discovered the electrons in the year 1897,
which he called corpuscles, through the Cathode ERWIN SCHRODINGER
Ray Experiment. Thomson believed that the He used the wave-particle duality of the electron to
negatively charged electrons are embedded in a develop and solve a complex mathematical equation
positively charged soup/fluid. (Plum Pudding that accurately describes the behavior of the electron
Model) in a hydrogen atom. (Electron Cloud Model)
NEILS BOHR BOHR’S MODEL VS THE QUANTUM MODEL
He created the Planetary Model of an Atom. Bohr Bohr's model postulates the electrons to revolve in
believed that the negatively charged electrons circular orbits while the quantum mechanical model
revolve around the positively charged nucleus in removes the possibility of a definite electronic
definite circular paths called ‘orbits’ or ‘shells,’ each pathway.
of which has their own fixed energy.
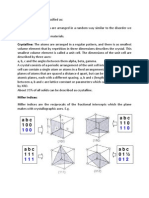
TYPES OF COMPOUNDS
** The Quantum Mechanical Model rejects the idea
that the electron travels on fixed orbits.
IONIC COMPOUNDS
WHAT DESCRIBES THE PROBABLE LOCATION OF It has an ionic bond, the elements involved are
“metal + non-metal.” In this type of compound, the
THE ELECTRONS electrons are transferred.
PRINCIPAL ENERGY LEVELS The valence electrons of the metal elements are
It indicates the relative size and energy of atomic transferred to the non-metal elements as a chemical
orbitals. N = Integers. “N = 1, N = 2, N = 3, N = 4” reaction — metals lose e, non-metals gain e.
As N increases, the orbital becomes larger, the Other properties of Ionic Compounds:
electrons spend more time farther away from the ● Soluble in Water
nucleus, and the energy of the atom level increases. ● Conducts Electricity
● High Melting and Boiling Point
To know an element’s principal energy level, you can ● Solid
look at the rows of the PTE called the periods.
COVALENT COMPOUNDS
ENERGY SUBLEVELS It has a covalent bond, the elements involved are
Principal Energy Levels are broken down into “non-metal + non-metal,” or, “metalloid +
sublevels. non-metal.” In this type of compound, the electrons
are shared.
Sublevels define the orbital shape (s, p, d, f):
N = 1, 1 sublevel (s) The valence electrons of both elements are shared
N = 2, 2 sublevel (s, p) as a chemical reaction. It becomes neutral, no
N = 3, 3 sublevel (s,p, d) charge.
N = 4, 4 sublevel (s, p, d, f)
Other properties of Covalent Compounds:
● Insoluble in Water
ORBITALS
● Does Not Conduct Electricity
Each sublevel has a different number of orbitals. ● Low Melting and Boiling Point
● Solid, Liquid, or Gas
s orbital: 1 x 2 e = 2e
p orbital: 3 x 2 e = 6e
d orbital: 5 x 2 e = 10e OTHER TERMINOLOGIES
f orbital: 7 x 2 e = 2e Neutral Atom - protons = electrons
ELECTRON SPINS Valence Electrons - electrons that are found in the
Each orbital of an atom can have two electrons, they outermost shell of an atom, electrons that can be
have to be in opposite spins. gained or lost as a chemical reaction
Cations - positively charged ions, this can be formed
COMPOUNDS when an atom loses an electron
Pure substances made up of 2 or more different Cations - negatively charged ions, this can be
elements. It has a definite proportion and is formed when an atom gains an electron
chemically combined. The elements lose their
individual properties and produce new substances. Ion - acquired a charge by gaining or losing and
electron, it forms when atoms of different elements
It can be broken down into smaller type of matter. combine by transferring electrons (the chemical
reaction)
All compounds are molecules, but not all molecules
are compounds.
** Molecules - 2 or more atoms connected through
chemical bonds.
You might also like
- Srednicki qft2 PDFDocument109 pagesSrednicki qft2 PDFCharlie HultgreenNo ratings yet
- Of An Atom . .......................... 2Document12 pagesOf An Atom . .......................... 2amyjanecelestialNo ratings yet
- Solid State Historical ContextDocument11 pagesSolid State Historical ContextbookregtestNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3. Atomic Structure and Periodic LawDocument32 pagesLecture 3. Atomic Structure and Periodic LawВалентина ЮзьковаNo ratings yet
- Atoms MoleculesDocument78 pagesAtoms MoleculesShanenely minNo ratings yet
- Sci9 Q2 Lesson 1 Atomic Model, Sub Atomic ParticlesDocument29 pagesSci9 Q2 Lesson 1 Atomic Model, Sub Atomic ParticlesFlorenze GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Structure of An Atom: AtomsDocument8 pagesIntroduction To The Structure of An Atom: Atomsshowmytv12No ratings yet
- Unit 2. The AtomDocument26 pagesUnit 2. The Atomgarciaortegajulia5No ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument6 pagesAtomic StructureDileep KumarNo ratings yet
- Atomicstructurepresentation 170510013215Document16 pagesAtomicstructurepresentation 170510013215Nilimoy Choudhury100% (1)
- Science-Q2-Notes BanzonDocument3 pagesScience-Q2-Notes BanzonfeytNo ratings yet
- 3 Discovery of The Subatomic Particles - Atomic ModelsDocument41 pages3 Discovery of The Subatomic Particles - Atomic ModelsFranchesca De los SantosNo ratings yet
- SCI Q2 ReviewerDocument14 pagesSCI Q2 ReviewerJonash Miguel LorzanoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Atomic Theory and Periodic TableDocument9 pagesChapter 2 Atomic Theory and Periodic TableArth LubayNo ratings yet
- 2.intro To Electrical TechnologyDocument117 pages2.intro To Electrical TechnologyRichard del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Atomic ModelDocument46 pagesAtomic ModelShannelle Anne CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document16 pagesChapter 1aregawi weleabezgiNo ratings yet
- Psma PrelimsDocument42 pagesPsma PrelimsPrincess Rose GamboaNo ratings yet
- Esp Answer KeyDocument2 pagesEsp Answer KeyAslan MorgadoNo ratings yet
- Atomic Theory CH-1Document64 pagesAtomic Theory CH-1tazebNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Atomic Structure - Notes...Document7 pagesGrade 8 Atomic Structure - Notes...Antonita100% (1)
- Atomic ST 8 IIT Class ...Document7 pagesAtomic ST 8 IIT Class ...Venugopal RNo ratings yet
- Unit Iv-VDocument18 pagesUnit Iv-VIvy Marie ToyonganNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 Atomic Structure: 2.1 The Nuclear AtomDocument45 pagesTopic 2 Atomic Structure: 2.1 The Nuclear AtomIan SembadaNo ratings yet
- PhysicalScienceQ1 ReviewerDocument3 pagesPhysicalScienceQ1 Reviewerrlyalns1128No ratings yet
- Electronic ConfigurationDocument10 pagesElectronic ConfigurationNicole ChangNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2Document8 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2Almira MejoradaNo ratings yet
- Atomic PhysicsDocument5 pagesAtomic Physicslove meNo ratings yet
- Structure of An AtomDocument4 pagesStructure of An Atomsompriya007No ratings yet
- YT Structure of The AtomDocument72 pagesYT Structure of The AtomAbhishek Kumar100% (1)
- CBSE Class 9 Science Revision Notes Chapter - 4 Structure of AtomDocument7 pagesCBSE Class 9 Science Revision Notes Chapter - 4 Structure of AtomShweta ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Physis 2nd and 3rd Term ss3Document38 pagesPhysis 2nd and 3rd Term ss3Dada RasheedNo ratings yet
- Atomic Scale StructuresDocument3 pagesAtomic Scale StructuresErish Brylle G. MañalacNo ratings yet
- Intro To Electrical Technology EditedDocument60 pagesIntro To Electrical Technology Editedmae OrgayaNo ratings yet
- Atomic ModelDocument14 pagesAtomic Modellanyasdeq112No ratings yet
- Atomic Theory: A Brief HistoryDocument61 pagesAtomic Theory: A Brief HistoryAbid Al RezaNo ratings yet
- REVIEWER OF GEN CHEM ^0 RWS 2ND SUMMATIVE TESTDocument8 pagesREVIEWER OF GEN CHEM ^0 RWS 2ND SUMMATIVE TEST11boyle.locsinjanilleNo ratings yet
- Leaving Cert Chemistry NotesDocument116 pagesLeaving Cert Chemistry NotesSnivySerpentNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure: By: Chynna B. Piclet 12 - ST AugustineDocument23 pagesAtomic Structure: By: Chynna B. Piclet 12 - ST AugustineZhel TomoroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02 Atomic StructureDocument62 pagesChapter 02 Atomic StructureJishen ZhuNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Chem 1Document64 pagesInorganic Chem 1Habtamu mullu BiadgoNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Chem 1Document2 pagesReviewer in Chem 1MARY ZIANNE GABRIELLE QUINTONo ratings yet
- Molecule by Shayan Ahmad KhattakDocument19 pagesMolecule by Shayan Ahmad KhattakShayan Ahmad Khattak, BS Physics Student, UoPNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument6 pagesAtomic StructureAl MubarakNo ratings yet
- PDF 20221114 080033 0000Document2 pagesPDF 20221114 080033 0000John Marithe PutunganNo ratings yet
- Models of The AtomDocument38 pagesModels of The AtomKC TorresNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry PresentationDocument45 pagesGeneral Chemistry PresentationJohn Adrian MalunesNo ratings yet
- Atomic ModelsDocument10 pagesAtomic ModelsMuhammad SamyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Atomic Structure & Interatomic Bonding: Issues To Address..Document52 pagesChapter 2: Atomic Structure & Interatomic Bonding: Issues To Address..ÖmerNo ratings yet
- Ass Mahfuz Sir Byb SiamDocument10 pagesAss Mahfuz Sir Byb SiamNowfal Hasan SiamNo ratings yet
- Phy1204 Atoms PresentationDocument6 pagesPhy1204 Atoms PresentationAnuradha ItwaruNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument6 pagesChemistryMANASI AHIRE [SOUS-EO054]No ratings yet
- Structure of AtomsDocument26 pagesStructure of AtomsdhruvindharmendraNo ratings yet
- Atomic Theories Quatum ModelDocument31 pagesAtomic Theories Quatum Modelerinallyson20No ratings yet
- Atomic Structure and Electronic Structure of The Atom Rz29fmDocument17 pagesAtomic Structure and Electronic Structure of The Atom Rz29fmkerri “Kerri” samNo ratings yet
- CH 1Document58 pagesCH 1smohammedadenNo ratings yet
- Electronic Structure of AtomDocument78 pagesElectronic Structure of AtomJC MalinaoNo ratings yet
- Science (Quarter 2)Document2 pagesScience (Quarter 2)Around Josef Ezekiel Villa Del ReyNo ratings yet
- Lesson - Atomic Structure: Scientist DiscoveryDocument4 pagesLesson - Atomic Structure: Scientist DiscoveryKokkilaa ParameswaranNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding: Model of An AtomDocument9 pagesAtomic Structure and Chemical Bonding: Model of An AtomSoumya Ranjan SahooNo ratings yet
- PANI Coupled Hierarchical Bi2S3 Nanoflowers BasedDocument13 pagesPANI Coupled Hierarchical Bi2S3 Nanoflowers Basedanmol sharmaNo ratings yet
- 12 Physics Notes Ch05 Magnetism and MatterDocument2 pages12 Physics Notes Ch05 Magnetism and MatterRishabhNo ratings yet
- Nano Dimensional MaterialsDocument151 pagesNano Dimensional MaterialsCHEM22028 NidhiNo ratings yet
- Thin Film Research PapersDocument7 pagesThin Film Research Papersozbvtcvkg100% (1)
- Intermolecular Forces of Attraction Properties of LiquidDocument38 pagesIntermolecular Forces of Attraction Properties of LiquidJa FloresNo ratings yet
- 03 Quantum-Dot-Based Solar Cells - Recent Advances, Strategies, and ChallengesDocument15 pages03 Quantum-Dot-Based Solar Cells - Recent Advances, Strategies, and ChallengesBiancaBeloNo ratings yet
- Heusler AlloysDocument12 pagesHeusler Alloysrebid.burlier-0hNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 9 Coordination CompoundsDocument23 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 9 Coordination CompoundsFEARLESS NETWORKx fanNo ratings yet
- GPL 212 Determination of Surface Tension of A LiquidDocument28 pagesGPL 212 Determination of Surface Tension of A LiquidyasintharaNo ratings yet
- 36 Modern-Energy LevelsDocument6 pages36 Modern-Energy LevelseltytanNo ratings yet
- SlaterDocument16 pagesSlaterprivate3737No ratings yet
- Booklet 1 Methods For in Vivo Dosimetry in External RadiotherapyDocument87 pagesBooklet 1 Methods For in Vivo Dosimetry in External RadiotherapyNesly M. MateoNo ratings yet
- Crystal Field TheoryDocument39 pagesCrystal Field TheoryRahmi HayatunnufusNo ratings yet
- Studies On Structural and Magnetic Properties of Ternary CobaltDocument8 pagesStudies On Structural and Magnetic Properties of Ternary CobaltKamenriderNo ratings yet
- Laser DiodeDocument41 pagesLaser DiodeSaurabh SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- XRD (X - Ray Diffraction)Document7 pagesXRD (X - Ray Diffraction)summi64No ratings yet
- Semiconductors Basics1 2013Document30 pagesSemiconductors Basics1 2013SriHariKalyanBNo ratings yet
- DLVO Theory (And Other Stuffs)Document34 pagesDLVO Theory (And Other Stuffs)AFZBNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document3 pagesTutorial 1doldolzzNo ratings yet
- JFET Operation & CharacteristicsDocument5 pagesJFET Operation & CharacteristicsAnusooya VNo ratings yet
- Ingaas/Gaassb Heterojunction Tfet: January 2015Document6 pagesIngaas/Gaassb Heterojunction Tfet: January 2015Anonymous jxm0WNS7QaNo ratings yet
- Dielectrics and FerroelectricsDocument47 pagesDielectrics and FerroelectricsibrahimNo ratings yet
- Mech 340-HW4Document4 pagesMech 340-HW4sridndNo ratings yet
- 277705-Article Text-380138-1-10-20140620Document6 pages277705-Article Text-380138-1-10-20140620Omkar BharankarNo ratings yet
- 45 Ex2 PracticeDocument5 pages45 Ex2 PracticeJules BrunoNo ratings yet
- Electron and Hole Mobilities in Si As A Function of Concentration and Temperature PDFDocument4 pagesElectron and Hole Mobilities in Si As A Function of Concentration and Temperature PDFFrancisco EstradaNo ratings yet
- Unit 01Document21 pagesUnit 01mathanstar77No ratings yet
- Physics 262: Problem Set 3: Due: Oct 22Document2 pagesPhysics 262: Problem Set 3: Due: Oct 22romanberens2No ratings yet
- Review On Nanomaterials: Synthesis and Applications: ArticleDocument10 pagesReview On Nanomaterials: Synthesis and Applications: ArticleDhanunjayaNo ratings yet