Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Friedmanns Test Statisitical Computation
Friedmanns Test Statisitical Computation
Uploaded by
Kristiane Rose LavillaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Vat Receipt: MR Kyle BoydDocument1 pageVat Receipt: MR Kyle BoydNovak Brodsky83% (6)
- Cox-Murray - Apollo The Race of The MoonDocument329 pagesCox-Murray - Apollo The Race of The MoonHipatia50% (2)
- Solution Manual For Differential Equations and Linear Algebra 4th Edition by Goode ISBN 0321964675 9780321964670Document36 pagesSolution Manual For Differential Equations and Linear Algebra 4th Edition by Goode ISBN 0321964675 9780321964670jenniferwatersgbrcixdmzt100% (26)
- Concept Note For Trade FairDocument5 pagesConcept Note For Trade FairRalph Aldrin F. VallesterosNo ratings yet
- Electricians GuideDocument296 pagesElectricians Guidemaeid75% (4)
- StatPro Q3 Week 6 LAS 1Document1 pageStatPro Q3 Week 6 LAS 1jerwinado649No ratings yet
- Q1 WK No.5 LAS GenMath11 FinalDocument8 pagesQ1 WK No.5 LAS GenMath11 FinalBhenryl TanggoyocNo ratings yet
- Correlation: Anton SubarnoDocument17 pagesCorrelation: Anton SubarnoDimas BayuNo ratings yet
- Decision MakingDocument10 pagesDecision Makingrohit chaudharyNo ratings yet
- Sacay, M (LT 3.2)Document7 pagesSacay, M (LT 3.2)Apple ChemNo ratings yet
- Student Name: Zain Asim: Question 1 (Correlation Coefficient and Population Analysis)Document7 pagesStudent Name: Zain Asim: Question 1 (Correlation Coefficient and Population Analysis)Abass GblaNo ratings yet
- Decision Science Mba Assignment Semester2Document7 pagesDecision Science Mba Assignment Semester2Manish JhawarNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Differential Equations and Linear Algebra 4Th Edition by Goode Isbn 0321964675 9780321964670 Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesSolution Manual For Differential Equations and Linear Algebra 4Th Edition by Goode Isbn 0321964675 9780321964670 Full Chapter PDFsandra.montelongo651100% (12)
- Z and T TestsDocument29 pagesZ and T Testscintoy100% (1)
- CORRELATION and RegressionDocument6 pagesCORRELATION and RegressionMikee Jane Mapayo SabilloNo ratings yet
- Department of Mathematics Indian Institute of Technology, GuwahatiDocument3 pagesDepartment of Mathematics Indian Institute of Technology, GuwahatiNaveen GuptaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 18 - CorrelationDocument3 pagesLesson 18 - CorrelationrinnagosakiNo ratings yet
- احصاءDocument3 pagesاحصاءjayomaerNo ratings yet
- Let's ApplyDocument5 pagesLet's ApplyJasmin Dianne RodicolNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4Document14 pagesAssignment 4Mcleo MoonNo ratings yet
- Answers Decision Science Assignment Dec 2022Document10 pagesAnswers Decision Science Assignment Dec 2022Ankita SinghNo ratings yet
- Student ParticularsDocument12 pagesStudent ParticularsSashikala GarnaisonNo ratings yet
- 2a Spearman Rank Correlation Coefficient or Spearman RHODocument6 pages2a Spearman Rank Correlation Coefficient or Spearman RHOJoanna Marie VillamarNo ratings yet
- 4-6 Remediation WorksheetsDocument10 pages4-6 Remediation WorksheetsMary Joy LugaNo ratings yet
- 10 - Exercise On One Way ANOVADocument4 pages10 - Exercise On One Way ANOVAJohn Cedric Vale CruzNo ratings yet
- Z and T TestsDocument30 pagesZ and T TestsMohamed NaeimNo ratings yet
- Chap3 - Determinants and DiagonalizationsDocument52 pagesChap3 - Determinants and DiagonalizationsNguyễn Văn MạnhNo ratings yet
- Chi-Square: Example ProblemDocument7 pagesChi-Square: Example ProblemZsa ChuNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4.1: Solving Linear System by Inverse Matrix: Example1Document7 pagesLecture 4.1: Solving Linear System by Inverse Matrix: Example1YazeedNo ratings yet
- SEM 2 - Decision-Science-Dec 2022Document11 pagesSEM 2 - Decision-Science-Dec 2022lsuryawanshiforcnxNo ratings yet
- Regression and Correlations: Rank CorrelationDocument61 pagesRegression and Correlations: Rank Correlationkaziba stephenNo ratings yet
- MSB Geometry Class 9 bOARD PAPER 1 SolDocument10 pagesMSB Geometry Class 9 bOARD PAPER 1 SolbrijsingNo ratings yet
- Name: - 2K14-EE - Section - Due Date: - Submission DateDocument2 pagesName: - 2K14-EE - Section - Due Date: - Submission DateMuhammadMansoorGoharNo ratings yet
- 1 MinHash-1Document4 pages1 MinHash-1Houssam FoukiNo ratings yet
- Midsem Ee650 Fall2018-Solution IITKDocument8 pagesMidsem Ee650 Fall2018-Solution IITKJivnesh SandhanNo ratings yet
- Decision-Science-Dec 2022Document11 pagesDecision-Science-Dec 2022Rameshwar BhatiNo ratings yet
- Numerical Methods Machine Problem 1Document11 pagesNumerical Methods Machine Problem 1Maria Charlene Caraos TapiaNo ratings yet
- FINAL EXAM IN E-WPS OfficeDocument12 pagesFINAL EXAM IN E-WPS OfficeLorwel ReyesNo ratings yet
- F.Sc-I Math (CH 7) Permutation and CombinationDocument15 pagesF.Sc-I Math (CH 7) Permutation and CombinationMuhammad Hammad HanifNo ratings yet
- 5 Sampling Distribution of The Sample MeanDocument26 pages5 Sampling Distribution of The Sample MeanNathalie NicoleNo ratings yet
- Ala2 SSM PDFDocument96 pagesAla2 SSM PDFVishalkumar BhattNo ratings yet
- Handout 4: The Statistical ModelDocument17 pagesHandout 4: The Statistical ModelYUVISHAIS PAOLA PAYARES BALDIRISNo ratings yet
- Seminar Worksheet. Measures of Dispersion 2Document5 pagesSeminar Worksheet. Measures of Dispersion 2Aruzhan ZhadyrassynNo ratings yet
- Gerak Gempur 2 Gemilang Amanjaya Matematik (Kertas 2) Bahagian ADocument8 pagesGerak Gempur 2 Gemilang Amanjaya Matematik (Kertas 2) Bahagian Anornaz15No ratings yet
- Complex Survey Estimates - PISADocument35 pagesComplex Survey Estimates - PISAAIRTON MOTANo ratings yet
- Understanding Business Statistics 1St Edition Freed Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesUnderstanding Business Statistics 1St Edition Freed Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFcraig.frazier964100% (11)
- Decision Science AssignmentDocument8 pagesDecision Science AssignmentApurv GoelNo ratings yet
- I Parcijalni Ispit Iz Matematike I, EnglishDocument3 pagesI Parcijalni Ispit Iz Matematike I, EnglishErdan SuljicNo ratings yet
- O'Connor - Matrix Chain MultiplicationDocument5 pagesO'Connor - Matrix Chain MultiplicationDerek O'ConnorNo ratings yet
- Measures of VariabilityDocument15 pagesMeasures of VariabilityJonathan Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Pre-Final BSAM 116 (Sampling Theory)Document4 pagesPre-Final BSAM 116 (Sampling Theory)Carl DevinNo ratings yet
- 4th Assignment (Chapter 12)Document2 pages4th Assignment (Chapter 12)Chloe Adrienne DominiqueNo ratings yet
- Correlation and RegressionDocument18 pagesCorrelation and Regressionpromotion sectionNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - Algorithmic Approaches To LayoutingDocument33 pagesLecture 5 - Algorithmic Approaches To LayoutingRazel Justine MendezNo ratings yet
- 300b-l1 2017 CV NotesDocument11 pages300b-l1 2017 CV Notesghania azharNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 4 MatricesDocument49 pagesChapter - 4 MatricesMustafa YılmazNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Quantifying Capsicum Frutescens Lip Plumping EffectDocument8 pagesChapter 3 Quantifying Capsicum Frutescens Lip Plumping EffectMhea Nicole QuilabNo ratings yet
- 3.10 Binomial TheoremDocument4 pages3.10 Binomial TheoremChingad MonkeyNo ratings yet
- Decision Science - NMIMSDocument8 pagesDecision Science - NMIMSlucky.idctechnologiesNo ratings yet
- Business Statistics in Practice 8th Edition Bowerman Solutions Manual DownloadDocument10 pagesBusiness Statistics in Practice 8th Edition Bowerman Solutions Manual DownloadSteven Campbell100% (25)
- Permutation of GroupsDocument55 pagesPermutation of GroupsesylexaNo ratings yet
- Properties of Determinants: Theorem 3: (Row Operations) : Let A Be A Square MatrixDocument24 pagesProperties of Determinants: Theorem 3: (Row Operations) : Let A Be A Square MatrixJahangir AliNo ratings yet
- AHU Air Handling Unit FundamentalsDocument48 pagesAHU Air Handling Unit Fundamentalsniakinezhad50% (2)
- Java Array: Logic Formulation and Intro. To ProgrammingDocument9 pagesJava Array: Logic Formulation and Intro. To ProgrammingklintNo ratings yet
- Connx October 2008Document2 pagesConnx October 2008ScamsIntrernetNo ratings yet
- Project Identification and SelectionDocument8 pagesProject Identification and SelectionSathish Jayakumar50% (6)
- Ebook Prehistoric Life The Definitive Visual History of Life On Earth Low Quality Version DK Publishing Online PDF All ChapterDocument69 pagesEbook Prehistoric Life The Definitive Visual History of Life On Earth Low Quality Version DK Publishing Online PDF All Chapterjoe.simmons244100% (7)
- 2023 Lupong Tagapamayapa Incentives Awards (Ltia) Assessment FormDocument4 pages2023 Lupong Tagapamayapa Incentives Awards (Ltia) Assessment FormNicole Chupungco100% (1)
- Correlation 1Document9 pagesCorrelation 1Bharat ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Parker Valvula Direcional D3W PDFDocument20 pagesParker Valvula Direcional D3W PDFChagas OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Optimisation of Supply Chain of Smart ColoursDocument29 pagesOptimisation of Supply Chain of Smart ColoursPooja ShahNo ratings yet
- Customer LoyaltyDocument10 pagesCustomer LoyaltyCarlos PacaviraNo ratings yet
- Lisa Olle Declaration in SupportDocument5 pagesLisa Olle Declaration in SupportMikey CampbellNo ratings yet
- Courtyard: Unlucky Tabibito ( )Document1 pageCourtyard: Unlucky Tabibito ( )Wraith VoidNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment Techniques (IEC 31010:2019) : Session - 3Document9 pagesRisk Assessment Techniques (IEC 31010:2019) : Session - 3kanchana rameshNo ratings yet
- Formulating Tips For Creams and LotionDocument3 pagesFormulating Tips For Creams and LotionDewi Sekar AyuNo ratings yet
- FFC New Imp FormatDocument1 pageFFC New Imp FormatMalik Zaryab babarNo ratings yet
- Hand-0ut 1 Inres PrelimsDocument7 pagesHand-0ut 1 Inres PrelimsJustin LimboNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Psychology 9th Edition BernsteinDocument45 pagesTest Bank For Psychology 9th Edition BernsteinRamona Fretwell100% (32)
- Invoice: (Your Company Name)Document1 pageInvoice: (Your Company Name)Kemal ZiyadNo ratings yet
- Yanbu: Export Refinery ProjectDocument5 pagesYanbu: Export Refinery ProjectJanakiraman MalligaNo ratings yet
- Sale Deed: ORGANISATION (AWHO), (PAN No. AABTA4251G) A Society Registered UnderDocument26 pagesSale Deed: ORGANISATION (AWHO), (PAN No. AABTA4251G) A Society Registered Undernaveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Ensemble LearningDocument7 pagesEnsemble LearningJavier Garcia RajoyNo ratings yet
- LFL A Comprehensive Guide To EQUIA Forte en PDFDocument16 pagesLFL A Comprehensive Guide To EQUIA Forte en PDFAsus AsusNo ratings yet
- CP7211 Advanced Databases Laboratory ManualDocument63 pagesCP7211 Advanced Databases Laboratory Manualashaheer75% (4)
- Topic 1Document88 pagesTopic 1Funny GuysNo ratings yet
- Ibpm 4Document64 pagesIbpm 4Miguel Angel HernandezNo ratings yet
- Opti Plex 7080Document38 pagesOpti Plex 7080brayerly143No ratings yet
Friedmanns Test Statisitical Computation
Friedmanns Test Statisitical Computation
Uploaded by
Kristiane Rose LavillaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Friedmanns Test Statisitical Computation
Friedmanns Test Statisitical Computation
Uploaded by
Kristiane Rose LavillaCopyright:
Available Formats
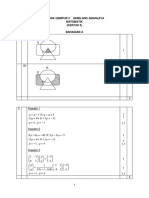
FRIEDMANN’S TEST COMPUTATION
Consider a study involving the determination of the acceptability of bread fortified with Leaf Protein Concentrate
(LPC). Ten (10) panellists are asked to evaluate bread containing 0%, 2%, and 4% LPC. They ranked the samples using a
scale of 1-8 where 1 stands for the least liked and 8 for the most liked sample as presented in the Table 1 below:
Table 1. Obtained data from the panelists in evaluating the bread samples fortified with different leaf protein concentrates.
Block A B C A B C
(Panelist) 0% LPC 2% LPC 4% LPC Rank (Rank)2 Rank (Rank)2 Rank (Rank)2
1 8 7 5 3 9 2 4 1 1
2 7 5 6 3 9 1 1 2 4
3 6 3 4 3 9 1 1 2 4
4 6 4 5 3 9 1 1 3 9
5 5 5 3 2.50 6.25 2.50 6.25 1 1
6 7 5 4 3 9 2 4 1 1
7 8 7 5 3 9 2 4 1 1
8 6 6 6 2 4 2 4 2 4
9 5 8 4 2 4 3 9 1 1
10 7 6 3 3 9 3 9 1 1
Summation Total ∑(RA) = ∑(RA) = ∑(RB) = ∑(RB)2 = ∑(RC) = ∑(RC)2 =
27.50 77.25 19.50 43.25 14.00 27.00
Mean 2.75 1.85 1.40
1. State the Null hypothesis: The samples come from populations with the same distribution.
There is no significant difference between the acceptability of the samples.
2. State the Alternative hypothesis: The samples come from populations with different distributions.
There is a significant difference between the acceptability of the samples.
3. Compute S: Using the values of the Table 1
RTOTAL = RA + RB + Rc S = [ (RA)2 + (RB)2 + (RC)2 ] - [ (RTOTAL)2 ]
= 27.50 + 19.50 + 14.00 3
= 60.00 = [(27.50) + (19.50) + (14.00) ] – [(60.00)2]
2 2 2
3
= [1,294.50] – [3600/3]
= [1,294.50] – [1,200.00]
SCALCULATED = 94.50
4. Find the STABULAR value at α 0.05 and 0.01
The formula is: df = (c-1) (r-1) STABULATED = 28.869 at 0.05 and 34.805 at 0.01 levels of significance.
= (3-1) (10-1)
= (2) (9)
=18
5. Formulate and interpret the conclusion:
Since the S calculated value of 94.50 is greater than its tabular value of 28.869 and 34.805 at 0.05 and 0.01 levels of significance,
respectively, reject the null hypothesis and accept the alternative hypothesis.
The samples come from populations with different distributions. Hence, there is a significant difference between the acceptability
of the samples.
Prepared by:
MIGUEL RAMON M. CALIBJO
Research Teacher
You might also like
- Vat Receipt: MR Kyle BoydDocument1 pageVat Receipt: MR Kyle BoydNovak Brodsky83% (6)
- Cox-Murray - Apollo The Race of The MoonDocument329 pagesCox-Murray - Apollo The Race of The MoonHipatia50% (2)
- Solution Manual For Differential Equations and Linear Algebra 4th Edition by Goode ISBN 0321964675 9780321964670Document36 pagesSolution Manual For Differential Equations and Linear Algebra 4th Edition by Goode ISBN 0321964675 9780321964670jenniferwatersgbrcixdmzt100% (26)
- Concept Note For Trade FairDocument5 pagesConcept Note For Trade FairRalph Aldrin F. VallesterosNo ratings yet
- Electricians GuideDocument296 pagesElectricians Guidemaeid75% (4)
- StatPro Q3 Week 6 LAS 1Document1 pageStatPro Q3 Week 6 LAS 1jerwinado649No ratings yet
- Q1 WK No.5 LAS GenMath11 FinalDocument8 pagesQ1 WK No.5 LAS GenMath11 FinalBhenryl TanggoyocNo ratings yet
- Correlation: Anton SubarnoDocument17 pagesCorrelation: Anton SubarnoDimas BayuNo ratings yet
- Decision MakingDocument10 pagesDecision Makingrohit chaudharyNo ratings yet
- Sacay, M (LT 3.2)Document7 pagesSacay, M (LT 3.2)Apple ChemNo ratings yet
- Student Name: Zain Asim: Question 1 (Correlation Coefficient and Population Analysis)Document7 pagesStudent Name: Zain Asim: Question 1 (Correlation Coefficient and Population Analysis)Abass GblaNo ratings yet
- Decision Science Mba Assignment Semester2Document7 pagesDecision Science Mba Assignment Semester2Manish JhawarNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Differential Equations and Linear Algebra 4Th Edition by Goode Isbn 0321964675 9780321964670 Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesSolution Manual For Differential Equations and Linear Algebra 4Th Edition by Goode Isbn 0321964675 9780321964670 Full Chapter PDFsandra.montelongo651100% (12)
- Z and T TestsDocument29 pagesZ and T Testscintoy100% (1)
- CORRELATION and RegressionDocument6 pagesCORRELATION and RegressionMikee Jane Mapayo SabilloNo ratings yet
- Department of Mathematics Indian Institute of Technology, GuwahatiDocument3 pagesDepartment of Mathematics Indian Institute of Technology, GuwahatiNaveen GuptaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 18 - CorrelationDocument3 pagesLesson 18 - CorrelationrinnagosakiNo ratings yet
- احصاءDocument3 pagesاحصاءjayomaerNo ratings yet
- Let's ApplyDocument5 pagesLet's ApplyJasmin Dianne RodicolNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4Document14 pagesAssignment 4Mcleo MoonNo ratings yet
- Answers Decision Science Assignment Dec 2022Document10 pagesAnswers Decision Science Assignment Dec 2022Ankita SinghNo ratings yet
- Student ParticularsDocument12 pagesStudent ParticularsSashikala GarnaisonNo ratings yet
- 2a Spearman Rank Correlation Coefficient or Spearman RHODocument6 pages2a Spearman Rank Correlation Coefficient or Spearman RHOJoanna Marie VillamarNo ratings yet
- 4-6 Remediation WorksheetsDocument10 pages4-6 Remediation WorksheetsMary Joy LugaNo ratings yet
- 10 - Exercise On One Way ANOVADocument4 pages10 - Exercise On One Way ANOVAJohn Cedric Vale CruzNo ratings yet
- Z and T TestsDocument30 pagesZ and T TestsMohamed NaeimNo ratings yet
- Chap3 - Determinants and DiagonalizationsDocument52 pagesChap3 - Determinants and DiagonalizationsNguyễn Văn MạnhNo ratings yet
- Chi-Square: Example ProblemDocument7 pagesChi-Square: Example ProblemZsa ChuNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4.1: Solving Linear System by Inverse Matrix: Example1Document7 pagesLecture 4.1: Solving Linear System by Inverse Matrix: Example1YazeedNo ratings yet
- SEM 2 - Decision-Science-Dec 2022Document11 pagesSEM 2 - Decision-Science-Dec 2022lsuryawanshiforcnxNo ratings yet
- Regression and Correlations: Rank CorrelationDocument61 pagesRegression and Correlations: Rank Correlationkaziba stephenNo ratings yet
- MSB Geometry Class 9 bOARD PAPER 1 SolDocument10 pagesMSB Geometry Class 9 bOARD PAPER 1 SolbrijsingNo ratings yet
- Name: - 2K14-EE - Section - Due Date: - Submission DateDocument2 pagesName: - 2K14-EE - Section - Due Date: - Submission DateMuhammadMansoorGoharNo ratings yet
- 1 MinHash-1Document4 pages1 MinHash-1Houssam FoukiNo ratings yet
- Midsem Ee650 Fall2018-Solution IITKDocument8 pagesMidsem Ee650 Fall2018-Solution IITKJivnesh SandhanNo ratings yet
- Decision-Science-Dec 2022Document11 pagesDecision-Science-Dec 2022Rameshwar BhatiNo ratings yet
- Numerical Methods Machine Problem 1Document11 pagesNumerical Methods Machine Problem 1Maria Charlene Caraos TapiaNo ratings yet
- FINAL EXAM IN E-WPS OfficeDocument12 pagesFINAL EXAM IN E-WPS OfficeLorwel ReyesNo ratings yet
- F.Sc-I Math (CH 7) Permutation and CombinationDocument15 pagesF.Sc-I Math (CH 7) Permutation and CombinationMuhammad Hammad HanifNo ratings yet
- 5 Sampling Distribution of The Sample MeanDocument26 pages5 Sampling Distribution of The Sample MeanNathalie NicoleNo ratings yet
- Ala2 SSM PDFDocument96 pagesAla2 SSM PDFVishalkumar BhattNo ratings yet
- Handout 4: The Statistical ModelDocument17 pagesHandout 4: The Statistical ModelYUVISHAIS PAOLA PAYARES BALDIRISNo ratings yet
- Seminar Worksheet. Measures of Dispersion 2Document5 pagesSeminar Worksheet. Measures of Dispersion 2Aruzhan ZhadyrassynNo ratings yet
- Gerak Gempur 2 Gemilang Amanjaya Matematik (Kertas 2) Bahagian ADocument8 pagesGerak Gempur 2 Gemilang Amanjaya Matematik (Kertas 2) Bahagian Anornaz15No ratings yet
- Complex Survey Estimates - PISADocument35 pagesComplex Survey Estimates - PISAAIRTON MOTANo ratings yet
- Understanding Business Statistics 1St Edition Freed Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesUnderstanding Business Statistics 1St Edition Freed Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFcraig.frazier964100% (11)
- Decision Science AssignmentDocument8 pagesDecision Science AssignmentApurv GoelNo ratings yet
- I Parcijalni Ispit Iz Matematike I, EnglishDocument3 pagesI Parcijalni Ispit Iz Matematike I, EnglishErdan SuljicNo ratings yet
- O'Connor - Matrix Chain MultiplicationDocument5 pagesO'Connor - Matrix Chain MultiplicationDerek O'ConnorNo ratings yet
- Measures of VariabilityDocument15 pagesMeasures of VariabilityJonathan Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Pre-Final BSAM 116 (Sampling Theory)Document4 pagesPre-Final BSAM 116 (Sampling Theory)Carl DevinNo ratings yet
- 4th Assignment (Chapter 12)Document2 pages4th Assignment (Chapter 12)Chloe Adrienne DominiqueNo ratings yet
- Correlation and RegressionDocument18 pagesCorrelation and Regressionpromotion sectionNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - Algorithmic Approaches To LayoutingDocument33 pagesLecture 5 - Algorithmic Approaches To LayoutingRazel Justine MendezNo ratings yet
- 300b-l1 2017 CV NotesDocument11 pages300b-l1 2017 CV Notesghania azharNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 4 MatricesDocument49 pagesChapter - 4 MatricesMustafa YılmazNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Quantifying Capsicum Frutescens Lip Plumping EffectDocument8 pagesChapter 3 Quantifying Capsicum Frutescens Lip Plumping EffectMhea Nicole QuilabNo ratings yet
- 3.10 Binomial TheoremDocument4 pages3.10 Binomial TheoremChingad MonkeyNo ratings yet
- Decision Science - NMIMSDocument8 pagesDecision Science - NMIMSlucky.idctechnologiesNo ratings yet
- Business Statistics in Practice 8th Edition Bowerman Solutions Manual DownloadDocument10 pagesBusiness Statistics in Practice 8th Edition Bowerman Solutions Manual DownloadSteven Campbell100% (25)
- Permutation of GroupsDocument55 pagesPermutation of GroupsesylexaNo ratings yet
- Properties of Determinants: Theorem 3: (Row Operations) : Let A Be A Square MatrixDocument24 pagesProperties of Determinants: Theorem 3: (Row Operations) : Let A Be A Square MatrixJahangir AliNo ratings yet
- AHU Air Handling Unit FundamentalsDocument48 pagesAHU Air Handling Unit Fundamentalsniakinezhad50% (2)
- Java Array: Logic Formulation and Intro. To ProgrammingDocument9 pagesJava Array: Logic Formulation and Intro. To ProgrammingklintNo ratings yet
- Connx October 2008Document2 pagesConnx October 2008ScamsIntrernetNo ratings yet
- Project Identification and SelectionDocument8 pagesProject Identification and SelectionSathish Jayakumar50% (6)
- Ebook Prehistoric Life The Definitive Visual History of Life On Earth Low Quality Version DK Publishing Online PDF All ChapterDocument69 pagesEbook Prehistoric Life The Definitive Visual History of Life On Earth Low Quality Version DK Publishing Online PDF All Chapterjoe.simmons244100% (7)
- 2023 Lupong Tagapamayapa Incentives Awards (Ltia) Assessment FormDocument4 pages2023 Lupong Tagapamayapa Incentives Awards (Ltia) Assessment FormNicole Chupungco100% (1)
- Correlation 1Document9 pagesCorrelation 1Bharat ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Parker Valvula Direcional D3W PDFDocument20 pagesParker Valvula Direcional D3W PDFChagas OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Optimisation of Supply Chain of Smart ColoursDocument29 pagesOptimisation of Supply Chain of Smart ColoursPooja ShahNo ratings yet
- Customer LoyaltyDocument10 pagesCustomer LoyaltyCarlos PacaviraNo ratings yet
- Lisa Olle Declaration in SupportDocument5 pagesLisa Olle Declaration in SupportMikey CampbellNo ratings yet
- Courtyard: Unlucky Tabibito ( )Document1 pageCourtyard: Unlucky Tabibito ( )Wraith VoidNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment Techniques (IEC 31010:2019) : Session - 3Document9 pagesRisk Assessment Techniques (IEC 31010:2019) : Session - 3kanchana rameshNo ratings yet
- Formulating Tips For Creams and LotionDocument3 pagesFormulating Tips For Creams and LotionDewi Sekar AyuNo ratings yet
- FFC New Imp FormatDocument1 pageFFC New Imp FormatMalik Zaryab babarNo ratings yet
- Hand-0ut 1 Inres PrelimsDocument7 pagesHand-0ut 1 Inres PrelimsJustin LimboNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Psychology 9th Edition BernsteinDocument45 pagesTest Bank For Psychology 9th Edition BernsteinRamona Fretwell100% (32)
- Invoice: (Your Company Name)Document1 pageInvoice: (Your Company Name)Kemal ZiyadNo ratings yet
- Yanbu: Export Refinery ProjectDocument5 pagesYanbu: Export Refinery ProjectJanakiraman MalligaNo ratings yet
- Sale Deed: ORGANISATION (AWHO), (PAN No. AABTA4251G) A Society Registered UnderDocument26 pagesSale Deed: ORGANISATION (AWHO), (PAN No. AABTA4251G) A Society Registered Undernaveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Ensemble LearningDocument7 pagesEnsemble LearningJavier Garcia RajoyNo ratings yet
- LFL A Comprehensive Guide To EQUIA Forte en PDFDocument16 pagesLFL A Comprehensive Guide To EQUIA Forte en PDFAsus AsusNo ratings yet
- CP7211 Advanced Databases Laboratory ManualDocument63 pagesCP7211 Advanced Databases Laboratory Manualashaheer75% (4)
- Topic 1Document88 pagesTopic 1Funny GuysNo ratings yet
- Ibpm 4Document64 pagesIbpm 4Miguel Angel HernandezNo ratings yet
- Opti Plex 7080Document38 pagesOpti Plex 7080brayerly143No ratings yet