Professional Documents
Culture Documents
HTN Treatment Algorithm
HTN Treatment Algorithm
Uploaded by
Kati GrissomCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Hypertension GuidelinesDocument33 pagesHypertension GuidelinesErlinda NRA100% (1)
- Guidelines Made Simple 2017 HBPDocument29 pagesGuidelines Made Simple 2017 HBPPianNo ratings yet
- New International Society of Hypertension (Ish) Guidelines 2020 - January 17TH 2021Document35 pagesNew International Society of Hypertension (Ish) Guidelines 2020 - January 17TH 2021Rhama Patria100% (1)
- Chapter 43 Drugs Affecting Blood PressureDocument43 pagesChapter 43 Drugs Affecting Blood PressureHannah Lorraine GamayonNo ratings yet
- Water InterviewDocument48 pagesWater InterviewSakuntala DeviNo ratings yet
- NICE CG 127 HypertensionDocument328 pagesNICE CG 127 Hypertensionreiv4xNo ratings yet
- Hipertensi: Dr. Jamaluddin, M.Kes, SP - JPDocument82 pagesHipertensi: Dr. Jamaluddin, M.Kes, SP - JPRahmawati HamudiNo ratings yet
- Blood Pressure Target: Insight From New ACC/AHA Hypertension GuidelineDocument36 pagesBlood Pressure Target: Insight From New ACC/AHA Hypertension GuidelineRetnofNo ratings yet
- Aha Guidelinedriven Management of Hypertension An Evidencebased UpdateDocument56 pagesAha Guidelinedriven Management of Hypertension An Evidencebased UpdateNanda Gopal Reddy AnamNo ratings yet
- 21-3-2022 HTN and DMDocument82 pages21-3-2022 HTN and DMfsvtqsNo ratings yet
- Hypertension Guidelines PDFDocument10 pagesHypertension Guidelines PDFARAVINDANo ratings yet
- Hypertension: Signs and SymptomsDocument22 pagesHypertension: Signs and Symptomschrissanto chandraNo ratings yet
- HypertensionDocument18 pagesHypertensionLeoNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Hypertension: Jai Radhakrishnan, M.D. Division of NephrologyDocument34 pagesTreatment of Hypertension: Jai Radhakrishnan, M.D. Division of NephrologyAndika HNo ratings yet
- Hypertension, Definition, Classification and Initial ManagementDocument24 pagesHypertension, Definition, Classification and Initial ManagementSissiNo ratings yet
- HypertensionDocument37 pagesHypertensionemanmohamed3444No ratings yet
- CPG Hypertension 2018 (Autosaved)Document55 pagesCPG Hypertension 2018 (Autosaved)Navina PurushotmananNo ratings yet
- Beyond Mountains There Are Mountains: (Haitian Proverb)Document47 pagesBeyond Mountains There Are Mountains: (Haitian Proverb)ElvisNo ratings yet
- HTN managment-JNC7Document37 pagesHTN managment-JNC7Vaibhav KaroliyaNo ratings yet
- L1 IM Hypertension (Aug2122)Document7 pagesL1 IM Hypertension (Aug2122)Maria Carmela CastilloNo ratings yet
- Guidelines Made Simple 2017 HBPDocument28 pagesGuidelines Made Simple 2017 HBPThomas EipeNo ratings yet
- Clinical Guidelines For Management of HTNDocument6 pagesClinical Guidelines For Management of HTNChaturangaNSenerath100% (1)
- Presión PediátricaDocument1 pagePresión PediátricadetectiverassingerNo ratings yet
- 2023 Measure 317 MIPSCQMDocument10 pages2023 Measure 317 MIPSCQMramshaltaf2311No ratings yet
- Hypertension BP Diabetes Glycemic Control Targets UHTC 2021Document1 pageHypertension BP Diabetes Glycemic Control Targets UHTC 2021Krishan38No ratings yet
- 6 HypertensionDocument5 pages6 Hypertensionجنى الجنان عقد الجمانNo ratings yet
- Hypertension GuidelinesDocument33 pagesHypertension GuidelinesTika wahyuNo ratings yet
- DR - Antonia Anna Lukito Slide - Webinar 18 April 2020Document34 pagesDR - Antonia Anna Lukito Slide - Webinar 18 April 2020fairuzNo ratings yet
- RJ Protocol CAD50Document2 pagesRJ Protocol CAD50Silvia RoseNo ratings yet
- 2021 BP Guideline From AHADocument1 page2021 BP Guideline From AHAse moNo ratings yet
- An Approach To HTN, Year 4Document52 pagesAn Approach To HTN, Year 4Kholoud KholoudNo ratings yet
- The Seventh Report of The Joint National Committee On Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure (JNC 7)Document33 pagesThe Seventh Report of The Joint National Committee On Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure (JNC 7)billi lisanuddinNo ratings yet
- JNC ViiiDocument45 pagesJNC ViiiNurul F AzzahraNo ratings yet
- A Clinical Classification of HypertensionDocument5 pagesA Clinical Classification of HypertensionGeorge ThomasNo ratings yet
- 7-Treatment of HypertensionDocument4 pages7-Treatment of HypertensionOmnia ElsaftyNo ratings yet
- QR HypertensionDocument8 pagesQR Hypertensionwaniaqilah workNo ratings yet
- Tha Ck1 2021fspptxDocument45 pagesTha Ck1 2021fspptxLinh LeeNo ratings yet
- Tatalaksana Hipertensi Monoterapi Atau Kombinasi-1Document20 pagesTatalaksana Hipertensi Monoterapi Atau Kombinasi-1Vivian VsNo ratings yet
- DentalManagementOfTheHypertensivePatient PDFDocument86 pagesDentalManagementOfTheHypertensivePatient PDFwaleNo ratings yet
- Guias Hta 2022Document8 pagesGuias Hta 2022oriannaocantoNo ratings yet
- HypertensionDocument27 pagesHypertensionshazia kaziNo ratings yet
- Ilmu Penyakit Dalam: BagianDocument48 pagesIlmu Penyakit Dalam: BagianRoberto SoehartonoNo ratings yet
- Hypertension: Blood Pressure Classification in ChildrenDocument4 pagesHypertension: Blood Pressure Classification in ChildrenNdra NuelNo ratings yet
- Referat Hipertensi - Maynaliza Nurul AiniDocument17 pagesReferat Hipertensi - Maynaliza Nurul AiniasiapnikahNo ratings yet
- HT 10 Nop 2020 PDFDocument16 pagesHT 10 Nop 2020 PDFNaura ArtaviaNo ratings yet
- Highlights From The 2017 GuidelineDocument2 pagesHighlights From The 2017 GuidelineRicky ErvindoNo ratings yet
- Blood Pressure ChartDocument9 pagesBlood Pressure Chartver_at_workNo ratings yet
- How To Control BP (BPJS MLG 14 Okt 2014) DR AtmaDocument62 pagesHow To Control BP (BPJS MLG 14 Okt 2014) DR AtmaaceNo ratings yet
- Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Management of High Blood Pressure in AdultsDocument30 pagesPrevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Management of High Blood Pressure in AdultsShazi AliNo ratings yet
- Management of HPDocument54 pagesManagement of HPDaud AbadiNo ratings yet
- Whats New in The ESC 2018 Guidelines For Arterial Hypertension The Ten Most Important MessagesDocument6 pagesWhats New in The ESC 2018 Guidelines For Arterial Hypertension The Ten Most Important MessagesWEnny WidyastutiNo ratings yet
- Hypertension and Its Management: by Dr. UmairDocument20 pagesHypertension and Its Management: by Dr. UmairdockmsNo ratings yet
- Classification Systolic (MM HG) Diastolic (MM HG)Document4 pagesClassification Systolic (MM HG) Diastolic (MM HG)Michelle MartillanoNo ratings yet
- Habits Vs Evidence RAAS ARB Talk FinalDocument45 pagesHabits Vs Evidence RAAS ARB Talk Finalswaleh breik misfirNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis Treatment of Resistant HypertensionDocument68 pagesDiagnosis Treatment of Resistant HypertensionJacob Alexander MarpaungNo ratings yet
- Highlights: 2017 G P, D, e M H B P ADocument2 pagesHighlights: 2017 G P, D, e M H B P AJamie LittleNo ratings yet
- BP MonitorDocument11 pagesBP Monitordrjas007No ratings yet
- Esh-htn 2023 - Nyn - DoctorDocument28 pagesEsh-htn 2023 - Nyn - DoctorShamim KabirNo ratings yet
- Ginjal Dan Hipertensi-1Document132 pagesGinjal Dan Hipertensi-1YERNITA AGUSTINNo ratings yet
- Toxicity and Adverse Effect ManagementDocument2 pagesToxicity and Adverse Effect ManagementMylene MendozaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document3 pagesAssignment 1SaulNo ratings yet
- Current Updates On Management of HypertensionDocument64 pagesCurrent Updates On Management of Hypertensionztt64nmvvpNo ratings yet
- AAFPHypertension GuidelineDocument11 pagesAAFPHypertension GuidelineAbdullrahman AlghamdiNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology QuestionsDocument6 pagesPharmacology Questionsliaqat ahmedNo ratings yet
- Jurnal 3Document9 pagesJurnal 3Eva ParamithaNo ratings yet
- L2 Hypertension in Special GroupsDocument44 pagesL2 Hypertension in Special GroupsMustaquim YusopNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Test Questions: "I Will Observe The Color of My Urine and Stool"Document36 pagesCardiovascular Test Questions: "I Will Observe The Color of My Urine and Stool"Melodia Turqueza GandezaNo ratings yet
- Ambulatory Blood Pressure ReportDocument12 pagesAmbulatory Blood Pressure ReportSundar RamanathanNo ratings yet
- PBL 1 HypertensionDocument11 pagesPBL 1 HypertensionLaughin KowNo ratings yet
- II Mbbs Syllabus MGR Medical UniversityDocument69 pagesII Mbbs Syllabus MGR Medical UniversityRaveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Spotters FinalDocument24 pagesSpotters Finalhpcdhp4wkmNo ratings yet
- Hi Per TensyDocument81 pagesHi Per TensysyahidNo ratings yet
- Benidipine Hydrochloride tab. 8mg「OME」: Brand name:Document2 pagesBenidipine Hydrochloride tab. 8mg「OME」: Brand name:Saurabh RaiNo ratings yet
- WhatsApp Infographic2 PDFDocument1 pageWhatsApp Infographic2 PDFRevanth TNo ratings yet
- An Efficient and Green Synthetic Route To LosartanDocument4 pagesAn Efficient and Green Synthetic Route To LosartandrhgsanganiNo ratings yet
- Stem List CumulativeDocument34 pagesStem List Cumulativeskeebs23No ratings yet
- Nifedipine Drug StudyDocument3 pagesNifedipine Drug StudyCrystal Queen MarquezNo ratings yet
- Rajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences, Bangalore, KarnatakaDocument34 pagesRajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences, Bangalore, KarnatakaYayu AlawiiahNo ratings yet
- Why Worry About: High Blood Pressure?Document8 pagesWhy Worry About: High Blood Pressure?mattvestrandNo ratings yet
- 2011-02-25 FDA Approves EDARBI (Azilsartan Medoxomil) For The Treatment of HypertensionDocument3 pages2011-02-25 FDA Approves EDARBI (Azilsartan Medoxomil) For The Treatment of HypertensionShuona YuanNo ratings yet
- 1 JR IngDocument27 pages1 JR IngDinaNo ratings yet
- Paramedic Inter Facility Transfer TrainingDocument168 pagesParamedic Inter Facility Transfer TrainingnikunjhirparaNo ratings yet
- Health Plus Drug FormularyDocument198 pagesHealth Plus Drug Formularyl84ad8inmiNo ratings yet
- Amlodipine - Drug StudyDocument2 pagesAmlodipine - Drug StudyAcads useNo ratings yet
- Syllabus PharmacologyDocument7 pagesSyllabus PharmacologylouradelNo ratings yet
- Pharmacological and Pharmaceutical Profile of Valsartan: A ReviewDocument8 pagesPharmacological and Pharmaceutical Profile of Valsartan: A ReviewRatna HarefaNo ratings yet
- Aim and ObjectivesDocument3 pagesAim and ObjectivesDevvrat DubeyNo ratings yet
- Interaction Between Amlodipine and Simvastatin in Patients With Hypercholesterolemia and HypertensionDocument5 pagesInteraction Between Amlodipine and Simvastatin in Patients With Hypercholesterolemia and HypertensionSuci Ika PratiwiNo ratings yet
- 6 Hypertension Nursing Care - Arif Setyo UpoyoDocument40 pages6 Hypertension Nursing Care - Arif Setyo UpoyoRizka Nur AgustinNo ratings yet
HTN Treatment Algorithm
HTN Treatment Algorithm
Uploaded by
Kati GrissomOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
HTN Treatment Algorithm
HTN Treatment Algorithm
Uploaded by
Kati GrissomCopyright:
Available Formats
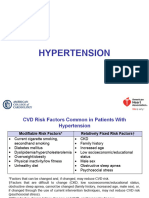
Blood Pressure Categories Hypertension Management
Systolic BP Diastolic BP Based on the 2017 ACC/AHA Guideline for the Prevention, Detection,
BP Category (mmHg) (mmHg) Evaluation, and Management of High Blood Pressure in Adults
Normal Blood Pressure <120 AND <80
Elevated Blood Pressure 120-129 AND <80 Hypertension Treatment Goals
Stage 1 Hypertension 130-139 OR 80-89 Goal for all ages <65 years with hypertension, regardless
of chronic comorbidities, if tolerated is <130/80 mmHg
Stage 2 Hypertension ≥140 OR ≥90
BP goal for ages ≥65 years is <130 mmHg (SBP)
Reasonable to adjust BP goal based on patient factors including: high
Use average of ≥2 BP readings obtained on ≥2 occasions comorbidity burden, life expectancy, clinical judgment, patient preference,
etc.
Hypertension Treatment Algorithm
Normal BP Elevated BP Stage 1 Hypertension Stage 2 Hypertension
<120/<80 mmHg 120-129/<80 mmHg SBP 130-139 or DBP 80-89 mmHg SBP ≥140 or DBP ≥90 mmHg
Promote healthy Nonpharmacological Clinical CVD, estimated Nonpharmacological
No
lifestyle habits interventions 10-year ASCVD risk of ≥10%? interventions
+
Drug treatment for
BP reduction
Nonpharmacological Nonpharmacological • Consider 2 agents from different drug
Reassess Annually Reassess in 3-6 months interventions interventions classes, especially if BP >20/10 mmHg
above goal
+
• Use first-line agents, those preferred
Drug treatment for for existing comorbidities, or based on
BP reduction tolerability
Antihypertensive Medications • Ideally use first-line agents, • Do not combine ACEi, ARB, or aliskiren
otherwise those preferred for Reassess in 3-6 months
existing comorbidities, or
Primary Medications (Generally First-Line) based on tolerability
Thiazide diuretics • Chlorthalidone preferred: long half-life, evidence for CVD benefit
e.g. chlorthalidone, indapamide • HCTZ: may be cheaper, more widely available, more tolerable
hydrochlorothiazide, metolazone • Monitor electrolytes: hyponatremia, hypokalemia, uric acid, calcium
ACE inhibitors • Do not combine with ARBs or aliskiren
e.g. lisinopril, benazepril, • Risk of hyperkalemia, esp. with CKD, K supplements, K-sparing drugs Reassess BP & adherence in
enalapril, ramipril, etc. • Avoid in pregnancy
1 month; assess tolerability
ARBs • Do not combine with ACEis or aliskiren Reassess BP & adherence in sooner as needed
e.g. losartan, valsartan, • Risk of hyperkalemia, esp. with CKD, K supplements, K-sparing drugs
• Avoid in pregnancy
1 month; assess tolerability
olmesartan, etc.
sooner as needed
CCBs, dihydropyridines • Dose-related lower leg edema, more common in females
e.g. amlodipine, felodipine, etc. • Avoid use with HFrEF; use amlodipine or felodipine if required
If BP is above goal
CCBs, non-dihydropyridines* • *Generally less preferred than the dihydropyridine CCBs
e.g. diltiazem, verapamil • Avoid regular use with BBs due to risk of bradycardia and heart block
• Do not use with HFrEF If BP is above goal • Titrate dose as tolerated
• Drug interactions: both are CYP3A4 substrates, moderate inhibitors
• If dosing is optimized then add
Secondary Medications • Titrate dose as tolerated additional drug; first use either
first-line agents, those preferred
Beta-blockers • May be first-line with compelling indication (e.g. IHD, post-MI, HF) • If dosing is optimized then add
for existing comorbidities, or
e.g. atenolol, metoprolol, carvedilol, • HFrEF preferred agents: metoprolol succinate, carvedilol, bisoprolol additional drug; first use either
bisoprolol, labetalol, nebivolol, etc. • Bronchospastic airway disease preferred: atenolol, metoprolol, bisoprolol based on tolerability
• Generally avoid use of BBs with intrinsic sympathomimetic activity first-line agents, those preferred
(e.g. acebutolol, pindolol, penbutolol), especially with IHD or HF for existing comorbidities, or • Do not combine ACEi, ARB, or
• Avoid abrupt cessation: risk of rebound tachycardia based on tolerability aliskiren
Loop diuretics • Preferred diuretics with symptomatic HF • Do not combine ACEi, ARB, or
furosemide, torsemide, bumetanide • Preferred over thiazides with significant CKD (GFR <30 mL/min)
aliskiren
K-sparing diuretics • Minimal antihypertensive effect; used to protect from hypokalemia
triamterene, amiloride • Avoid in patients with significant CKD (GFR <45 mL/min)
Aldosterone antagonists • Preferred add-on with resistant HTN and in primary aldosteronism
spironolactone, eplerenone • K-sparing diuretic effect: avoid with K-sparing diuretics, or CKD
• Spironolactone > risk of gynecomastia, impotence than eplerenone Reference: Whelton PK, Carey RM, Aronow WS, et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/
ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA Guideline for the Prevention,
Alpha-1 blockers • May be considered second-line in those with concomitant BPH Detection, Evaluation, and Management of High Blood Pressure in Adults: A
doxazosin, prazosin, terazosin • Risk for orthostatic hypotension, especially in older adults
Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task
• Use w/ a diuretic and BB: causes fluid retention and reflex tachycardia
Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines [published correction appears in J Am Coll
Direct vasodilators
hydralazine, minoxidil • Hydralazine has risk of drug-induced lupus-like syndrome Cardiol. 2018 May 15;71(19):2275-2279]. J Am Coll Cardiol.
• Minoxidil has risk of hirsutism and requires use with a loop diuretic 2018;71(19):e127-e248. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2017.11.006
Central alpha-2 agonists • Generally last-line due to CNS adverse effects, orthostatic hypotension More clinical pearls at pyrls.com
clonidine, guanfacine, methyldopa • Avoid abrupt cessation: risk of rebound hypertension (esp. clonidine)
® 2021 Cosmas Health, Inc. and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
You might also like
- Hypertension GuidelinesDocument33 pagesHypertension GuidelinesErlinda NRA100% (1)
- Guidelines Made Simple 2017 HBPDocument29 pagesGuidelines Made Simple 2017 HBPPianNo ratings yet
- New International Society of Hypertension (Ish) Guidelines 2020 - January 17TH 2021Document35 pagesNew International Society of Hypertension (Ish) Guidelines 2020 - January 17TH 2021Rhama Patria100% (1)
- Chapter 43 Drugs Affecting Blood PressureDocument43 pagesChapter 43 Drugs Affecting Blood PressureHannah Lorraine GamayonNo ratings yet
- Water InterviewDocument48 pagesWater InterviewSakuntala DeviNo ratings yet
- NICE CG 127 HypertensionDocument328 pagesNICE CG 127 Hypertensionreiv4xNo ratings yet
- Hipertensi: Dr. Jamaluddin, M.Kes, SP - JPDocument82 pagesHipertensi: Dr. Jamaluddin, M.Kes, SP - JPRahmawati HamudiNo ratings yet
- Blood Pressure Target: Insight From New ACC/AHA Hypertension GuidelineDocument36 pagesBlood Pressure Target: Insight From New ACC/AHA Hypertension GuidelineRetnofNo ratings yet
- Aha Guidelinedriven Management of Hypertension An Evidencebased UpdateDocument56 pagesAha Guidelinedriven Management of Hypertension An Evidencebased UpdateNanda Gopal Reddy AnamNo ratings yet
- 21-3-2022 HTN and DMDocument82 pages21-3-2022 HTN and DMfsvtqsNo ratings yet
- Hypertension Guidelines PDFDocument10 pagesHypertension Guidelines PDFARAVINDANo ratings yet
- Hypertension: Signs and SymptomsDocument22 pagesHypertension: Signs and Symptomschrissanto chandraNo ratings yet
- HypertensionDocument18 pagesHypertensionLeoNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Hypertension: Jai Radhakrishnan, M.D. Division of NephrologyDocument34 pagesTreatment of Hypertension: Jai Radhakrishnan, M.D. Division of NephrologyAndika HNo ratings yet
- Hypertension, Definition, Classification and Initial ManagementDocument24 pagesHypertension, Definition, Classification and Initial ManagementSissiNo ratings yet
- HypertensionDocument37 pagesHypertensionemanmohamed3444No ratings yet
- CPG Hypertension 2018 (Autosaved)Document55 pagesCPG Hypertension 2018 (Autosaved)Navina PurushotmananNo ratings yet
- Beyond Mountains There Are Mountains: (Haitian Proverb)Document47 pagesBeyond Mountains There Are Mountains: (Haitian Proverb)ElvisNo ratings yet
- HTN managment-JNC7Document37 pagesHTN managment-JNC7Vaibhav KaroliyaNo ratings yet
- L1 IM Hypertension (Aug2122)Document7 pagesL1 IM Hypertension (Aug2122)Maria Carmela CastilloNo ratings yet
- Guidelines Made Simple 2017 HBPDocument28 pagesGuidelines Made Simple 2017 HBPThomas EipeNo ratings yet
- Clinical Guidelines For Management of HTNDocument6 pagesClinical Guidelines For Management of HTNChaturangaNSenerath100% (1)
- Presión PediátricaDocument1 pagePresión PediátricadetectiverassingerNo ratings yet
- 2023 Measure 317 MIPSCQMDocument10 pages2023 Measure 317 MIPSCQMramshaltaf2311No ratings yet
- Hypertension BP Diabetes Glycemic Control Targets UHTC 2021Document1 pageHypertension BP Diabetes Glycemic Control Targets UHTC 2021Krishan38No ratings yet
- 6 HypertensionDocument5 pages6 Hypertensionجنى الجنان عقد الجمانNo ratings yet
- Hypertension GuidelinesDocument33 pagesHypertension GuidelinesTika wahyuNo ratings yet
- DR - Antonia Anna Lukito Slide - Webinar 18 April 2020Document34 pagesDR - Antonia Anna Lukito Slide - Webinar 18 April 2020fairuzNo ratings yet
- RJ Protocol CAD50Document2 pagesRJ Protocol CAD50Silvia RoseNo ratings yet
- 2021 BP Guideline From AHADocument1 page2021 BP Guideline From AHAse moNo ratings yet
- An Approach To HTN, Year 4Document52 pagesAn Approach To HTN, Year 4Kholoud KholoudNo ratings yet
- The Seventh Report of The Joint National Committee On Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure (JNC 7)Document33 pagesThe Seventh Report of The Joint National Committee On Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure (JNC 7)billi lisanuddinNo ratings yet
- JNC ViiiDocument45 pagesJNC ViiiNurul F AzzahraNo ratings yet
- A Clinical Classification of HypertensionDocument5 pagesA Clinical Classification of HypertensionGeorge ThomasNo ratings yet
- 7-Treatment of HypertensionDocument4 pages7-Treatment of HypertensionOmnia ElsaftyNo ratings yet
- QR HypertensionDocument8 pagesQR Hypertensionwaniaqilah workNo ratings yet
- Tha Ck1 2021fspptxDocument45 pagesTha Ck1 2021fspptxLinh LeeNo ratings yet
- Tatalaksana Hipertensi Monoterapi Atau Kombinasi-1Document20 pagesTatalaksana Hipertensi Monoterapi Atau Kombinasi-1Vivian VsNo ratings yet
- DentalManagementOfTheHypertensivePatient PDFDocument86 pagesDentalManagementOfTheHypertensivePatient PDFwaleNo ratings yet
- Guias Hta 2022Document8 pagesGuias Hta 2022oriannaocantoNo ratings yet
- HypertensionDocument27 pagesHypertensionshazia kaziNo ratings yet
- Ilmu Penyakit Dalam: BagianDocument48 pagesIlmu Penyakit Dalam: BagianRoberto SoehartonoNo ratings yet
- Hypertension: Blood Pressure Classification in ChildrenDocument4 pagesHypertension: Blood Pressure Classification in ChildrenNdra NuelNo ratings yet
- Referat Hipertensi - Maynaliza Nurul AiniDocument17 pagesReferat Hipertensi - Maynaliza Nurul AiniasiapnikahNo ratings yet
- HT 10 Nop 2020 PDFDocument16 pagesHT 10 Nop 2020 PDFNaura ArtaviaNo ratings yet
- Highlights From The 2017 GuidelineDocument2 pagesHighlights From The 2017 GuidelineRicky ErvindoNo ratings yet
- Blood Pressure ChartDocument9 pagesBlood Pressure Chartver_at_workNo ratings yet
- How To Control BP (BPJS MLG 14 Okt 2014) DR AtmaDocument62 pagesHow To Control BP (BPJS MLG 14 Okt 2014) DR AtmaaceNo ratings yet
- Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Management of High Blood Pressure in AdultsDocument30 pagesPrevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Management of High Blood Pressure in AdultsShazi AliNo ratings yet
- Management of HPDocument54 pagesManagement of HPDaud AbadiNo ratings yet
- Whats New in The ESC 2018 Guidelines For Arterial Hypertension The Ten Most Important MessagesDocument6 pagesWhats New in The ESC 2018 Guidelines For Arterial Hypertension The Ten Most Important MessagesWEnny WidyastutiNo ratings yet
- Hypertension and Its Management: by Dr. UmairDocument20 pagesHypertension and Its Management: by Dr. UmairdockmsNo ratings yet
- Classification Systolic (MM HG) Diastolic (MM HG)Document4 pagesClassification Systolic (MM HG) Diastolic (MM HG)Michelle MartillanoNo ratings yet
- Habits Vs Evidence RAAS ARB Talk FinalDocument45 pagesHabits Vs Evidence RAAS ARB Talk Finalswaleh breik misfirNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis Treatment of Resistant HypertensionDocument68 pagesDiagnosis Treatment of Resistant HypertensionJacob Alexander MarpaungNo ratings yet
- Highlights: 2017 G P, D, e M H B P ADocument2 pagesHighlights: 2017 G P, D, e M H B P AJamie LittleNo ratings yet
- BP MonitorDocument11 pagesBP Monitordrjas007No ratings yet
- Esh-htn 2023 - Nyn - DoctorDocument28 pagesEsh-htn 2023 - Nyn - DoctorShamim KabirNo ratings yet
- Ginjal Dan Hipertensi-1Document132 pagesGinjal Dan Hipertensi-1YERNITA AGUSTINNo ratings yet
- Toxicity and Adverse Effect ManagementDocument2 pagesToxicity and Adverse Effect ManagementMylene MendozaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document3 pagesAssignment 1SaulNo ratings yet
- Current Updates On Management of HypertensionDocument64 pagesCurrent Updates On Management of Hypertensionztt64nmvvpNo ratings yet
- AAFPHypertension GuidelineDocument11 pagesAAFPHypertension GuidelineAbdullrahman AlghamdiNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology QuestionsDocument6 pagesPharmacology Questionsliaqat ahmedNo ratings yet
- Jurnal 3Document9 pagesJurnal 3Eva ParamithaNo ratings yet
- L2 Hypertension in Special GroupsDocument44 pagesL2 Hypertension in Special GroupsMustaquim YusopNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Test Questions: "I Will Observe The Color of My Urine and Stool"Document36 pagesCardiovascular Test Questions: "I Will Observe The Color of My Urine and Stool"Melodia Turqueza GandezaNo ratings yet
- Ambulatory Blood Pressure ReportDocument12 pagesAmbulatory Blood Pressure ReportSundar RamanathanNo ratings yet
- PBL 1 HypertensionDocument11 pagesPBL 1 HypertensionLaughin KowNo ratings yet
- II Mbbs Syllabus MGR Medical UniversityDocument69 pagesII Mbbs Syllabus MGR Medical UniversityRaveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Spotters FinalDocument24 pagesSpotters Finalhpcdhp4wkmNo ratings yet
- Hi Per TensyDocument81 pagesHi Per TensysyahidNo ratings yet
- Benidipine Hydrochloride tab. 8mg「OME」: Brand name:Document2 pagesBenidipine Hydrochloride tab. 8mg「OME」: Brand name:Saurabh RaiNo ratings yet
- WhatsApp Infographic2 PDFDocument1 pageWhatsApp Infographic2 PDFRevanth TNo ratings yet
- An Efficient and Green Synthetic Route To LosartanDocument4 pagesAn Efficient and Green Synthetic Route To LosartandrhgsanganiNo ratings yet
- Stem List CumulativeDocument34 pagesStem List Cumulativeskeebs23No ratings yet
- Nifedipine Drug StudyDocument3 pagesNifedipine Drug StudyCrystal Queen MarquezNo ratings yet
- Rajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences, Bangalore, KarnatakaDocument34 pagesRajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences, Bangalore, KarnatakaYayu AlawiiahNo ratings yet
- Why Worry About: High Blood Pressure?Document8 pagesWhy Worry About: High Blood Pressure?mattvestrandNo ratings yet
- 2011-02-25 FDA Approves EDARBI (Azilsartan Medoxomil) For The Treatment of HypertensionDocument3 pages2011-02-25 FDA Approves EDARBI (Azilsartan Medoxomil) For The Treatment of HypertensionShuona YuanNo ratings yet
- 1 JR IngDocument27 pages1 JR IngDinaNo ratings yet
- Paramedic Inter Facility Transfer TrainingDocument168 pagesParamedic Inter Facility Transfer TrainingnikunjhirparaNo ratings yet
- Health Plus Drug FormularyDocument198 pagesHealth Plus Drug Formularyl84ad8inmiNo ratings yet
- Amlodipine - Drug StudyDocument2 pagesAmlodipine - Drug StudyAcads useNo ratings yet
- Syllabus PharmacologyDocument7 pagesSyllabus PharmacologylouradelNo ratings yet
- Pharmacological and Pharmaceutical Profile of Valsartan: A ReviewDocument8 pagesPharmacological and Pharmaceutical Profile of Valsartan: A ReviewRatna HarefaNo ratings yet
- Aim and ObjectivesDocument3 pagesAim and ObjectivesDevvrat DubeyNo ratings yet
- Interaction Between Amlodipine and Simvastatin in Patients With Hypercholesterolemia and HypertensionDocument5 pagesInteraction Between Amlodipine and Simvastatin in Patients With Hypercholesterolemia and HypertensionSuci Ika PratiwiNo ratings yet
- 6 Hypertension Nursing Care - Arif Setyo UpoyoDocument40 pages6 Hypertension Nursing Care - Arif Setyo UpoyoRizka Nur AgustinNo ratings yet