Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 viewsDam Engineering CIE 522 - Lecture 5
Dam Engineering CIE 522 - Lecture 5
Uploaded by
Emmanuel MwabaThis document discusses energy dissipation in dam engineering. It explains that water flowing through spillways and discharge structures acquires high kinetic energy that must be dissipated to prevent erosion and damage. Common methods of energy dissipation mentioned are stepped spillways, stilling basins, and plunge pools. Stepped spillways help dissipate energy through turbulence on the steps. Stilling basins and plunge pools dissipate energy as the high velocity water hits the basin/pool and mixes with the slower moving water. Proper energy dissipation is crucial for dam safety.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Bund Wall Calculation Capacity CHK (Consider 2 New Tanks)Document2 pagesBund Wall Calculation Capacity CHK (Consider 2 New Tanks)Tu Tu Dar33% (3)
- Comparison of BOQ Quantities With IFC/ Shop Drawings: (Including LLO)Document2 pagesComparison of BOQ Quantities With IFC/ Shop Drawings: (Including LLO)Arshad MahmoodNo ratings yet
- A-Guide-to-Safe-and-Cost-Effective-Spillways - Peter Mason PDFDocument8 pagesA-Guide-to-Safe-and-Cost-Effective-Spillways - Peter Mason PDFFacundoNo ratings yet
- Program - Proposed Construction of The Earth Dam Chikuni - MonzeDocument1 pageProgram - Proposed Construction of The Earth Dam Chikuni - MonzeWoodlock Limited0% (1)
- Jatigede DAMDocument51 pagesJatigede DAMGhozali Mahmud100% (3)
- Example On Design of Gravity DamDocument7 pagesExample On Design of Gravity DamKinfe Mehari100% (46)
- Dam Engineering CIE 522 - Lecture 8Document7 pagesDam Engineering CIE 522 - Lecture 8Emmanuel MwabaNo ratings yet
- 01 SmallCanals enDocument10 pages01 SmallCanals enErika Pariona ColosNo ratings yet
- A Guide To Safe and Cost Effective SpillwaysDocument8 pagesA Guide To Safe and Cost Effective SpillwaysdjajadjajaNo ratings yet
- Regulating Structures For Canal FlowsDocument13 pagesRegulating Structures For Canal FlowsRenz Ryan DolorNo ratings yet
- Energy DissipatersDocument8 pagesEnergy DissipatersLeticia Karine Sanches BritoNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Design of Stilling Basins and Energy Dissipators 1Document4 pagesHydraulic Design of Stilling Basins and Energy Dissipators 1ناهض عهد عبد المحسن ناهضNo ratings yet
- Ater Upply: Nfiltration Alleries AND EllsDocument32 pagesAter Upply: Nfiltration Alleries AND EllsvictorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Energy DissipatersDocument15 pagesChapter 3 Energy DissipatersKaseye AmareNo ratings yet
- Detail Study of Hydroelectric Power PlantDocument139 pagesDetail Study of Hydroelectric Power PlantDivyansh Singh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Energy Dissipation: Irrigation EngineeringDocument47 pagesEnergy Dissipation: Irrigation EngineeringMd Raihan AliNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 Hydro Power PlantDocument12 pagesTopic 6 Hydro Power PlantILEENVIRUSNo ratings yet
- Lecture-7 Canal FallDocument24 pagesLecture-7 Canal FallqasimhassanietNo ratings yet
- Lecture-8 Canal FallDocument24 pagesLecture-8 Canal FallSameer SaleemNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Jump1Document16 pagesHydraulic Jump1Gvganesh BabuNo ratings yet
- Dams, Reservoir, Spillways & Energy Dissipators-1 PDFDocument21 pagesDams, Reservoir, Spillways & Energy Dissipators-1 PDFRakesh ManralNo ratings yet
- Course: Waterworks. Theme: Overchutes. DATE: 14/5/18 WorkgroupDocument10 pagesCourse: Waterworks. Theme: Overchutes. DATE: 14/5/18 WorkgroupRONALNo ratings yet
- Water Resources HandoutsDocument5 pagesWater Resources HandoutsPaulo BurceNo ratings yet
- Selection of Spillways: 5.5 Energy Dissipation Below SpillwaysDocument4 pagesSelection of Spillways: 5.5 Energy Dissipation Below SpillwayshanoseNo ratings yet
- Why Check Valves SlamDocument2 pagesWhy Check Valves SlamBramJanssen76No ratings yet
- Morning Glory Spillway - Hungry Horse DamDocument32 pagesMorning Glory Spillway - Hungry Horse DamPierre LacosteNo ratings yet
- Ajit HydroDocument48 pagesAjit HydroSrihariKyatam100% (1)
- Hydropower NotesDocument20 pagesHydropower Notesanish.bhandariNo ratings yet
- Canal FallsDocument10 pagesCanal Fallsnizamaniza80% (5)
- CE Lecture 9 (Hydraulic Structures)Document32 pagesCE Lecture 9 (Hydraulic Structures)Hammad AmjadNo ratings yet
- Energy Dissipation Devices - S.K. Mazumder PDFDocument10 pagesEnergy Dissipation Devices - S.K. Mazumder PDFtsksingh100% (2)
- Chap 4-3-4 Spillways-Energy Dissipators RR ST VersDocument12 pagesChap 4-3-4 Spillways-Energy Dissipators RR ST VersCivil EngineeringNo ratings yet
- H. BibliographyDocument50 pagesH. BibliographyClaudio Figueroa RoaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 20 - Spillways 03.04.2021Document5 pagesLecture 20 - Spillways 03.04.2021Morio MosoroNo ratings yet
- Class Notes SpillwayDocument7 pagesClass Notes SpillwayIcegroup Coaching100% (1)
- Energy Dissipators-1Document8 pagesEnergy Dissipators-1Mūssā Mūhābā ZēĒthiopiāNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Energy Potential Energy: Tidal Power Advantages and DisadvantagesDocument2 pagesKinetic Energy Potential Energy: Tidal Power Advantages and Disadvantagessatendra_gangwarNo ratings yet
- Module 5 - Hydroelectric Power Plant - DR - JosephDocument70 pagesModule 5 - Hydroelectric Power Plant - DR - JosephHariom KumarNo ratings yet
- DHS Module1Document27 pagesDHS Module1Sajed AbdulrahmanZaiNo ratings yet
- Module 7 Irrigation StructureDocument20 pagesModule 7 Irrigation StructureSrivvass ReddyNo ratings yet
- CH 3-Renewable Energy Resources Class NotesDocument7 pagesCH 3-Renewable Energy Resources Class Notesmerooney desanchesNo ratings yet
- 21 - Spillways Energy Dissipators and Spillway GatesDocument56 pages21 - Spillways Energy Dissipators and Spillway GatesBilal MzhrNo ratings yet
- 02 - 2 Design of Weir - Surface AnalysisDocument84 pages02 - 2 Design of Weir - Surface AnalysisMohammed JemalNo ratings yet
- Literature Review and Objectives of StudyDocument34 pagesLiterature Review and Objectives of Studyyaseen90azizNo ratings yet
- LundDocument1 pageLundnkmkm05No ratings yet
- Energy Dissipation StructuresDocument3 pagesEnergy Dissipation StructuresSaad ShauketNo ratings yet
- Mebruk HS1 Chapter 1aDocument5 pagesMebruk HS1 Chapter 1aRefisa JiruNo ratings yet
- HS1 Chapter 1Document5 pagesHS1 Chapter 1hanoseNo ratings yet
- Site Selection For Dams & Reservoirs (Original)Document62 pagesSite Selection For Dams & Reservoirs (Original)Venu Manikanta84% (19)
- Che190-Hydroelectric PowerDocument74 pagesChe190-Hydroelectric PowerJohn Patrick DagleNo ratings yet
- 4.0 Spillway and LocationDocument46 pages4.0 Spillway and LocationMuletaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11Document35 pagesLecture 11Ismail SakrNo ratings yet
- PDM University: AssignmentDocument5 pagesPDM University: AssignmentVikas SharmaNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 Canal&drainage MergedDocument35 pagesUnit-1 Canal&drainage Mergedsushanth kumarNo ratings yet
- Power Plant Engineering 2Document29 pagesPower Plant Engineering 2Anushree GhoshNo ratings yet
- Vaults & Domes: Construction Technique /failures: Definition of A VaultDocument2 pagesVaults & Domes: Construction Technique /failures: Definition of A VaultDivya VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Detention Ponds Outlets Including Risers, Orifices, and WeirsDocument15 pagesDetention Ponds Outlets Including Risers, Orifices, and WeirsBoos yousufNo ratings yet
- Critical Review of Stilling Basin Models For Pipe Outlet WorksDocument4 pagesCritical Review of Stilling Basin Models For Pipe Outlet WorksInternational Journal of Research in Engineering and TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Spilways Unit - IVDocument49 pagesSpilways Unit - IVvixivi6780100% (1)
- Plunge Pools Vischer HagerDocument2 pagesPlunge Pools Vischer HagerJuanFernandoEscobarNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Analysis of Gravity Dams - CE 309-CE22S2 - Fluid MechanicsDocument6 pages5.1 Analysis of Gravity Dams - CE 309-CE22S2 - Fluid MechanicsRUSSELNo ratings yet
- Irrigation Works: The Principles on Which Their Design and Working Should Be Based, with Special Details Relating to Indian Canals and Some Proposed ImprovementsFrom EverandIrrigation Works: The Principles on Which Their Design and Working Should Be Based, with Special Details Relating to Indian Canals and Some Proposed ImprovementsNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 6 MarketingDocument38 pagesLECTURE 6 MarketingEmmanuel MwabaNo ratings yet
- Dam Engineering CIE 522 - Course - 03032023Document7 pagesDam Engineering CIE 522 - Course - 03032023Emmanuel MwabaNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 4 StaffingDocument33 pagesLECTURE 4 StaffingEmmanuel MwabaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 - 2021 - 2022Document2 pagesAssignment 2 - 2021 - 2022Emmanuel MwabaNo ratings yet
- Austin ChilufyaDocument9 pagesAustin ChilufyaEmmanuel MwabaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Cie 412 Reinf ConcDocument1 pageAssignment 1 Cie 412 Reinf ConcEmmanuel MwabaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 - CIE 531 - EGM 501 - 2021Document26 pagesLecture 9 - CIE 531 - EGM 501 - 2021Emmanuel MwabaNo ratings yet
- Design Calculations TemplateDocument20 pagesDesign Calculations TemplateEmmanuel MwabaNo ratings yet
- Dam Inspection Check ListDocument3 pagesDam Inspection Check ListEmmanuel MwabaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 - CIE 531 - EGM 501 - 2021Document52 pagesLecture 8 - CIE 531 - EGM 501 - 2021Emmanuel MwabaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12 - CIE 531 - EGM - 501 - 2021 - 2022Document66 pagesLecture 12 - CIE 531 - EGM - 501 - 2021 - 2022Emmanuel MwabaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - CIE 531 - EGM 501 - 2021Document48 pagesLecture 5 - CIE 531 - EGM 501 - 2021Emmanuel MwabaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 - CIE 562Document88 pagesLecture 6 - CIE 562Emmanuel MwabaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - CIE 531-EGM 501 - 2021Document41 pagesLecture 2 - CIE 531-EGM 501 - 2021Emmanuel MwabaNo ratings yet
- Dam Engineering CIE 522 - Lecture 6 - Brainer - Assignment 5Document9 pagesDam Engineering CIE 522 - Lecture 6 - Brainer - Assignment 5Emmanuel MwabaNo ratings yet
- Dam Engineering CIE 522 - Lecture 1 - Chapter 9 - 03032023Document23 pagesDam Engineering CIE 522 - Lecture 1 - Chapter 9 - 03032023Emmanuel MwabaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 - CIE 531-EGM 501 - 2021 - 2022Document48 pagesLecture 7 - CIE 531-EGM 501 - 2021 - 2022Emmanuel MwabaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10 - CIE 531 - EGM 501 - 2021Document31 pagesLecture 10 - CIE 531 - EGM 501 - 2021Emmanuel MwabaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - CIE 551 - Part 4Document25 pagesLecture 5 - CIE 551 - Part 4Emmanuel MwabaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - CIE 551 - Part 3Document32 pagesLecture 3 - CIE 551 - Part 3Emmanuel MwabaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 - CIE 551 - Part 1Document19 pagesLecture 7 - CIE 551 - Part 1Emmanuel MwabaNo ratings yet
- Driver Pedestrian, and Vehicle CharacteristicsDocument15 pagesDriver Pedestrian, and Vehicle CharacteristicsEmmanuel MwabaNo ratings yet
- Overview of The Transportation Sector in ZambiaDocument41 pagesOverview of The Transportation Sector in ZambiaEmmanuel MwabaNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument8 pagesIntroductionEmmanuel MwabaNo ratings yet
- Introduction Classification Advantages and Disadvantages Site Selection Selection of Type of DamDocument30 pagesIntroduction Classification Advantages and Disadvantages Site Selection Selection of Type of DamKubaNo ratings yet
- Government of Andhra Pradesh Government of Andhra Pradesh: Subject SubjectDocument21 pagesGovernment of Andhra Pradesh Government of Andhra Pradesh: Subject SubjectseshuNo ratings yet
- Classification of DamDocument14 pagesClassification of DamflywithkenNo ratings yet
- Design of Spillways 2.0 #Document40 pagesDesign of Spillways 2.0 #SahanNo ratings yet
- Fuse Gates PDFDocument9 pagesFuse Gates PDFmasanegraNo ratings yet
- Evaluasi Stabilitas Mercu Bendung Batang Toru, Kabupaten Tapanuli UtaraDocument7 pagesEvaluasi Stabilitas Mercu Bendung Batang Toru, Kabupaten Tapanuli UtaraWindafriskazalukhuNo ratings yet
- Jawai-Map-CATCHMENT AREASDocument1 pageJawai-Map-CATCHMENT AREASRituparna NathNo ratings yet
- Spillways 130820165335 Phpapp02 PDFDocument12 pagesSpillways 130820165335 Phpapp02 PDFpradeepbmahajanNo ratings yet
- D D' E E' B C: Plan SpillwayDocument1 pageD D' E E' B C: Plan SpillwayFirmansyah MardwionoNo ratings yet
- 1.dam HydDocument35 pages1.dam Hydshiva kamraniNo ratings yet
- Pakistan Studies - Affairs - Most Important MCQs (Set III) For CSS, PMS, PCS, NTSDocument9 pagesPakistan Studies - Affairs - Most Important MCQs (Set III) For CSS, PMS, PCS, NTSJatoi AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Corumana Dam Emergancy Spillway-Design Case 1 - Labyrinth WeirDocument1 pageCorumana Dam Emergancy Spillway-Design Case 1 - Labyrinth WeirguildkeyNo ratings yet
- Dam FailureDocument16 pagesDam FailureFlorentina SuduNo ratings yet
- Data of Dams R1Document16 pagesData of Dams R1Tejasri PinnapareddyNo ratings yet
- Spesifikasi Teknis Bendungan Karian, Banten.Document8 pagesSpesifikasi Teknis Bendungan Karian, Banten.Ronald Hidayat100% (1)
- Design Consideration of R.C.C. DamDocument3 pagesDesign Consideration of R.C.C. Damdeadlyman8372100% (1)
- Spillway NotesDocument15 pagesSpillway Notesvinod choudhariNo ratings yet
- Rivers and DamsDocument6 pagesRivers and DamsYashwant SinghNo ratings yet
- Btcol 08Document255 pagesBtcol 08Aishwarya SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Budget and Work Program For Excavation For DamDocument1 pageBudget and Work Program For Excavation For DamBernie QuepNo ratings yet
- Lec #19 (Permeability Thru Stratified Soils)Document24 pagesLec #19 (Permeability Thru Stratified Soils)Muhammad Irfan100% (1)
- A Glossary - of Words and Phrases - Rela Ted To Dams - IcoldDocument70 pagesA Glossary - of Words and Phrases - Rela Ted To Dams - IcoldTansel YılmazNo ratings yet
- Daily Bulletin in Excel For 05092020Document1 pageDaily Bulletin in Excel For 05092020Moran RajNo ratings yet
- Irrigation System of Pakistan GK by G.K KingdomDocument10 pagesIrrigation System of Pakistan GK by G.K KingdomAsad AliNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Design of Stepped SpillwaysDocument12 pagesHydraulic Design of Stepped SpillwaysCristian Hadad100% (1)
Dam Engineering CIE 522 - Lecture 5
Dam Engineering CIE 522 - Lecture 5
Uploaded by
Emmanuel Mwaba0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views8 pagesThis document discusses energy dissipation in dam engineering. It explains that water flowing through spillways and discharge structures acquires high kinetic energy that must be dissipated to prevent erosion and damage. Common methods of energy dissipation mentioned are stepped spillways, stilling basins, and plunge pools. Stepped spillways help dissipate energy through turbulence on the steps. Stilling basins and plunge pools dissipate energy as the high velocity water hits the basin/pool and mixes with the slower moving water. Proper energy dissipation is crucial for dam safety.
Original Description:
dam engineering
Original Title
Dam Engineering CIE 522_Lecture 5
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses energy dissipation in dam engineering. It explains that water flowing through spillways and discharge structures acquires high kinetic energy that must be dissipated to prevent erosion and damage. Common methods of energy dissipation mentioned are stepped spillways, stilling basins, and plunge pools. Stepped spillways help dissipate energy through turbulence on the steps. Stilling basins and plunge pools dissipate energy as the high velocity water hits the basin/pool and mixes with the slower moving water. Proper energy dissipation is crucial for dam safety.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views8 pagesDam Engineering CIE 522 - Lecture 5
Dam Engineering CIE 522 - Lecture 5
Uploaded by
Emmanuel MwabaThis document discusses energy dissipation in dam engineering. It explains that water flowing through spillways and discharge structures acquires high kinetic energy that must be dissipated to prevent erosion and damage. Common methods of energy dissipation mentioned are stepped spillways, stilling basins, and plunge pools. Stepped spillways help dissipate energy through turbulence on the steps. Stilling basins and plunge pools dissipate energy as the high velocity water hits the basin/pool and mixes with the slower moving water. Proper energy dissipation is crucial for dam safety.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 8
Dam Engineering CIE 522
Lecturer: Chanda Chisha
MSc. Water Mgt; BEng; PGD. Env.Mgt
5.0 Energy Dissipation
5.0 Energy Dissipation
5.1 General - Water Flows with high pressure and forces
5.2 Energy Dissipation on Spillways which could lead to distraction of any
5.3 Stepped Spillway object. – It has High Energy.
5.4 Stilling basins - This Energy has to be well managed or
5.5 Plunge pools contained.
- Energy dissipation is termed the process by
which Energy is “Wasted”.
- Spillways and stilling basins are structures
designed to dissipate the energy which
could be of considerable magnitude.
- Water that flows over any spillway acquires
a lot of Kinetic Energy due to its conversion
from Potential Energy into Kinetic Energy.
- This High Flow of the water when
discharged into the river has the ability to
scour the riverbed and in certain cases
undermine the downstream lower layers of
the dam, thus compromising the dam
safety.
5.0 Energy Dissipation
5.0 Energy Dissipation
5.1 General - Uncontrolled scouring may lead to the
5.2 Energy Dissipation on Spillways backward extension and damaging of the
5.3 Stepped Spillway spillway & the dam.
5.4 Stilling basins
5.5 Plunge pools - This Can be controlled by dissipating the kinetic
energy before it is discharged downstream the
river channel.
- Energy Dissipation is attained by inclusion in any
dam the following;
1. Stepped Spillways
2. Stilling Basins
3. Plunge Pools
5.0 Energy Dissipation
5.0 Energy Dissipation
5.1 General 1. Stepped Spillways
5.2 Energy Dissipation on Spillways
5.3 Stepped Spillway - The importance of a well sized spillway
5.4 Stilling basins cannot be over emphasized. Spillway
5.5 Plunge pools selection and design forms a very
important aspect in the dam design
process.
- A stepped spillway is a spillway with steps
on the spillway chute to assist in the
dissipation of the kinetic energy of the
descending water. This eliminates or
reduces the need for an additional
energy dissipater, such as a body of
water, at the end of the spillway
downstream.
- The stepped spillway could either be
incorporated in an over-flow spillway or
non-overflow spillway.
5.0 Energy Dissipation
5.0 Energy Dissipation
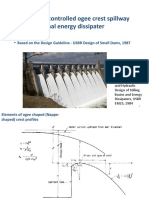
5.1 General - 2. Plunge Pool
5.2 Energy Dissipation on Spillways
5.3 Stepped Spillway - This is a structure constructed below the water
5.4 Stilling basins fall or rapids to dissipate energy.
5.5 Plunge pools - Others define it as an energy dissipater which
is located downstream or at an outlet of a
spillway.
- The mechanism is to dissipate the energy of
the water as the water is discharged into the
plunge pool.
5.0 Energy Dissipation
5.0 Energy Dissipation
5.1 General - 2. Plunge Pool
5.2 Energy Dissipation on Spillways - Typical Schematic Case of the Plunge Pool At
5.3 Stepped Spillway Kariba Dams
5.4 Stilling basins
5.5 Plunge pools
5.0 Energy Dissipation
5.0 Energy Dissipation
5.1 General - 3. Stilling Basin
5.2 Energy Dissipation on Spillways
5.3 Stepped Spillway - This is an energy dissipating structure constructed
5.4 Stilling basins downstream. This is more or less an apron at the downstream
of the dam.
5.5 Plunge pools
- Others term this as a basin-like structure where energy is
dissipated.
- The stilling basin makes it possible for the kinetic to cause the
turbulence and in the process, it is lost as heat energy.
- Special appurtenances such as chute blocks, sills and baffles
piers are provided in the stilling basins.
(i) The chute blocks furrows the incoming jet & and lift a
portion of it from the floor producing a shorter length of
jump than would be possible without them. This is used to
form a serated device at the entrance to the stilling
basin.
(ii) The sill has the function of additional function of diffusing the
residual portion of high velocity jet that may reach the end
of the basin. It is provided at the end of the stilling basin and
reduces the length of the jump & controls the scour.
(iii) Baffle Piers are blocks that are placed in the intermediate
position across the basin floor. It dissipates energy by the
impact action. They are useful in small structures with low
incoming velocities, but are however, unsuitable where high
velocities make cavitation possible
5.0 Energy Dissipation
Resource Material
https://www.usbr.gov/tsc/techreferences/hydraulics_lab/pubs/PAP/PAP-0951.pdf
https://www.usbr.gov/tsc/techreferences/hydraulics_lab/pubs/HL/HL-2015-06.pdf
https://espace.library.uq.edu.au/view/UQ:13560/Art233d.pdf
https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/pdf/10.4296/cwrj147
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/303565276_Guidelines_for_Hydraulic_Desig
n_of_Stepped_Spillways
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/245297351_Hydraulic_Design_of_Stepped_
Spillways
https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/media/60338aaf8fa8f5432bc23dbe/_Guidanc
e_for_the_Design_and_Maintenance_of_Stepped_Masonry_Spillways.pdf
https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/00221680209499889
https://www.nrcs.usda.gov/Internet/FSE_DOCUMENTS/nrcs142p2_007673.xls
https://www.usbr.gov/tsc/techreferences/hydraulics_lab/pubs/EM/EM25.pdf
You might also like
- Bund Wall Calculation Capacity CHK (Consider 2 New Tanks)Document2 pagesBund Wall Calculation Capacity CHK (Consider 2 New Tanks)Tu Tu Dar33% (3)
- Comparison of BOQ Quantities With IFC/ Shop Drawings: (Including LLO)Document2 pagesComparison of BOQ Quantities With IFC/ Shop Drawings: (Including LLO)Arshad MahmoodNo ratings yet
- A-Guide-to-Safe-and-Cost-Effective-Spillways - Peter Mason PDFDocument8 pagesA-Guide-to-Safe-and-Cost-Effective-Spillways - Peter Mason PDFFacundoNo ratings yet
- Program - Proposed Construction of The Earth Dam Chikuni - MonzeDocument1 pageProgram - Proposed Construction of The Earth Dam Chikuni - MonzeWoodlock Limited0% (1)
- Jatigede DAMDocument51 pagesJatigede DAMGhozali Mahmud100% (3)
- Example On Design of Gravity DamDocument7 pagesExample On Design of Gravity DamKinfe Mehari100% (46)
- Dam Engineering CIE 522 - Lecture 8Document7 pagesDam Engineering CIE 522 - Lecture 8Emmanuel MwabaNo ratings yet
- 01 SmallCanals enDocument10 pages01 SmallCanals enErika Pariona ColosNo ratings yet
- A Guide To Safe and Cost Effective SpillwaysDocument8 pagesA Guide To Safe and Cost Effective SpillwaysdjajadjajaNo ratings yet
- Regulating Structures For Canal FlowsDocument13 pagesRegulating Structures For Canal FlowsRenz Ryan DolorNo ratings yet
- Energy DissipatersDocument8 pagesEnergy DissipatersLeticia Karine Sanches BritoNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Design of Stilling Basins and Energy Dissipators 1Document4 pagesHydraulic Design of Stilling Basins and Energy Dissipators 1ناهض عهد عبد المحسن ناهضNo ratings yet
- Ater Upply: Nfiltration Alleries AND EllsDocument32 pagesAter Upply: Nfiltration Alleries AND EllsvictorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Energy DissipatersDocument15 pagesChapter 3 Energy DissipatersKaseye AmareNo ratings yet
- Detail Study of Hydroelectric Power PlantDocument139 pagesDetail Study of Hydroelectric Power PlantDivyansh Singh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Energy Dissipation: Irrigation EngineeringDocument47 pagesEnergy Dissipation: Irrigation EngineeringMd Raihan AliNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 Hydro Power PlantDocument12 pagesTopic 6 Hydro Power PlantILEENVIRUSNo ratings yet
- Lecture-7 Canal FallDocument24 pagesLecture-7 Canal FallqasimhassanietNo ratings yet
- Lecture-8 Canal FallDocument24 pagesLecture-8 Canal FallSameer SaleemNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Jump1Document16 pagesHydraulic Jump1Gvganesh BabuNo ratings yet
- Dams, Reservoir, Spillways & Energy Dissipators-1 PDFDocument21 pagesDams, Reservoir, Spillways & Energy Dissipators-1 PDFRakesh ManralNo ratings yet
- Course: Waterworks. Theme: Overchutes. DATE: 14/5/18 WorkgroupDocument10 pagesCourse: Waterworks. Theme: Overchutes. DATE: 14/5/18 WorkgroupRONALNo ratings yet
- Water Resources HandoutsDocument5 pagesWater Resources HandoutsPaulo BurceNo ratings yet
- Selection of Spillways: 5.5 Energy Dissipation Below SpillwaysDocument4 pagesSelection of Spillways: 5.5 Energy Dissipation Below SpillwayshanoseNo ratings yet
- Why Check Valves SlamDocument2 pagesWhy Check Valves SlamBramJanssen76No ratings yet
- Morning Glory Spillway - Hungry Horse DamDocument32 pagesMorning Glory Spillway - Hungry Horse DamPierre LacosteNo ratings yet
- Ajit HydroDocument48 pagesAjit HydroSrihariKyatam100% (1)
- Hydropower NotesDocument20 pagesHydropower Notesanish.bhandariNo ratings yet
- Canal FallsDocument10 pagesCanal Fallsnizamaniza80% (5)
- CE Lecture 9 (Hydraulic Structures)Document32 pagesCE Lecture 9 (Hydraulic Structures)Hammad AmjadNo ratings yet
- Energy Dissipation Devices - S.K. Mazumder PDFDocument10 pagesEnergy Dissipation Devices - S.K. Mazumder PDFtsksingh100% (2)
- Chap 4-3-4 Spillways-Energy Dissipators RR ST VersDocument12 pagesChap 4-3-4 Spillways-Energy Dissipators RR ST VersCivil EngineeringNo ratings yet
- H. BibliographyDocument50 pagesH. BibliographyClaudio Figueroa RoaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 20 - Spillways 03.04.2021Document5 pagesLecture 20 - Spillways 03.04.2021Morio MosoroNo ratings yet
- Class Notes SpillwayDocument7 pagesClass Notes SpillwayIcegroup Coaching100% (1)
- Energy Dissipators-1Document8 pagesEnergy Dissipators-1Mūssā Mūhābā ZēĒthiopiāNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Energy Potential Energy: Tidal Power Advantages and DisadvantagesDocument2 pagesKinetic Energy Potential Energy: Tidal Power Advantages and Disadvantagessatendra_gangwarNo ratings yet
- Module 5 - Hydroelectric Power Plant - DR - JosephDocument70 pagesModule 5 - Hydroelectric Power Plant - DR - JosephHariom KumarNo ratings yet
- DHS Module1Document27 pagesDHS Module1Sajed AbdulrahmanZaiNo ratings yet
- Module 7 Irrigation StructureDocument20 pagesModule 7 Irrigation StructureSrivvass ReddyNo ratings yet
- CH 3-Renewable Energy Resources Class NotesDocument7 pagesCH 3-Renewable Energy Resources Class Notesmerooney desanchesNo ratings yet
- 21 - Spillways Energy Dissipators and Spillway GatesDocument56 pages21 - Spillways Energy Dissipators and Spillway GatesBilal MzhrNo ratings yet
- 02 - 2 Design of Weir - Surface AnalysisDocument84 pages02 - 2 Design of Weir - Surface AnalysisMohammed JemalNo ratings yet
- Literature Review and Objectives of StudyDocument34 pagesLiterature Review and Objectives of Studyyaseen90azizNo ratings yet
- LundDocument1 pageLundnkmkm05No ratings yet
- Energy Dissipation StructuresDocument3 pagesEnergy Dissipation StructuresSaad ShauketNo ratings yet
- Mebruk HS1 Chapter 1aDocument5 pagesMebruk HS1 Chapter 1aRefisa JiruNo ratings yet
- HS1 Chapter 1Document5 pagesHS1 Chapter 1hanoseNo ratings yet
- Site Selection For Dams & Reservoirs (Original)Document62 pagesSite Selection For Dams & Reservoirs (Original)Venu Manikanta84% (19)
- Che190-Hydroelectric PowerDocument74 pagesChe190-Hydroelectric PowerJohn Patrick DagleNo ratings yet
- 4.0 Spillway and LocationDocument46 pages4.0 Spillway and LocationMuletaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11Document35 pagesLecture 11Ismail SakrNo ratings yet
- PDM University: AssignmentDocument5 pagesPDM University: AssignmentVikas SharmaNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 Canal&drainage MergedDocument35 pagesUnit-1 Canal&drainage Mergedsushanth kumarNo ratings yet
- Power Plant Engineering 2Document29 pagesPower Plant Engineering 2Anushree GhoshNo ratings yet
- Vaults & Domes: Construction Technique /failures: Definition of A VaultDocument2 pagesVaults & Domes: Construction Technique /failures: Definition of A VaultDivya VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Detention Ponds Outlets Including Risers, Orifices, and WeirsDocument15 pagesDetention Ponds Outlets Including Risers, Orifices, and WeirsBoos yousufNo ratings yet
- Critical Review of Stilling Basin Models For Pipe Outlet WorksDocument4 pagesCritical Review of Stilling Basin Models For Pipe Outlet WorksInternational Journal of Research in Engineering and TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Spilways Unit - IVDocument49 pagesSpilways Unit - IVvixivi6780100% (1)
- Plunge Pools Vischer HagerDocument2 pagesPlunge Pools Vischer HagerJuanFernandoEscobarNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Analysis of Gravity Dams - CE 309-CE22S2 - Fluid MechanicsDocument6 pages5.1 Analysis of Gravity Dams - CE 309-CE22S2 - Fluid MechanicsRUSSELNo ratings yet
- Irrigation Works: The Principles on Which Their Design and Working Should Be Based, with Special Details Relating to Indian Canals and Some Proposed ImprovementsFrom EverandIrrigation Works: The Principles on Which Their Design and Working Should Be Based, with Special Details Relating to Indian Canals and Some Proposed ImprovementsNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 6 MarketingDocument38 pagesLECTURE 6 MarketingEmmanuel MwabaNo ratings yet
- Dam Engineering CIE 522 - Course - 03032023Document7 pagesDam Engineering CIE 522 - Course - 03032023Emmanuel MwabaNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 4 StaffingDocument33 pagesLECTURE 4 StaffingEmmanuel MwabaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 - 2021 - 2022Document2 pagesAssignment 2 - 2021 - 2022Emmanuel MwabaNo ratings yet
- Austin ChilufyaDocument9 pagesAustin ChilufyaEmmanuel MwabaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Cie 412 Reinf ConcDocument1 pageAssignment 1 Cie 412 Reinf ConcEmmanuel MwabaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 - CIE 531 - EGM 501 - 2021Document26 pagesLecture 9 - CIE 531 - EGM 501 - 2021Emmanuel MwabaNo ratings yet
- Design Calculations TemplateDocument20 pagesDesign Calculations TemplateEmmanuel MwabaNo ratings yet
- Dam Inspection Check ListDocument3 pagesDam Inspection Check ListEmmanuel MwabaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 - CIE 531 - EGM 501 - 2021Document52 pagesLecture 8 - CIE 531 - EGM 501 - 2021Emmanuel MwabaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12 - CIE 531 - EGM - 501 - 2021 - 2022Document66 pagesLecture 12 - CIE 531 - EGM - 501 - 2021 - 2022Emmanuel MwabaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - CIE 531 - EGM 501 - 2021Document48 pagesLecture 5 - CIE 531 - EGM 501 - 2021Emmanuel MwabaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 - CIE 562Document88 pagesLecture 6 - CIE 562Emmanuel MwabaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - CIE 531-EGM 501 - 2021Document41 pagesLecture 2 - CIE 531-EGM 501 - 2021Emmanuel MwabaNo ratings yet
- Dam Engineering CIE 522 - Lecture 6 - Brainer - Assignment 5Document9 pagesDam Engineering CIE 522 - Lecture 6 - Brainer - Assignment 5Emmanuel MwabaNo ratings yet
- Dam Engineering CIE 522 - Lecture 1 - Chapter 9 - 03032023Document23 pagesDam Engineering CIE 522 - Lecture 1 - Chapter 9 - 03032023Emmanuel MwabaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 - CIE 531-EGM 501 - 2021 - 2022Document48 pagesLecture 7 - CIE 531-EGM 501 - 2021 - 2022Emmanuel MwabaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10 - CIE 531 - EGM 501 - 2021Document31 pagesLecture 10 - CIE 531 - EGM 501 - 2021Emmanuel MwabaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - CIE 551 - Part 4Document25 pagesLecture 5 - CIE 551 - Part 4Emmanuel MwabaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - CIE 551 - Part 3Document32 pagesLecture 3 - CIE 551 - Part 3Emmanuel MwabaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 - CIE 551 - Part 1Document19 pagesLecture 7 - CIE 551 - Part 1Emmanuel MwabaNo ratings yet
- Driver Pedestrian, and Vehicle CharacteristicsDocument15 pagesDriver Pedestrian, and Vehicle CharacteristicsEmmanuel MwabaNo ratings yet
- Overview of The Transportation Sector in ZambiaDocument41 pagesOverview of The Transportation Sector in ZambiaEmmanuel MwabaNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument8 pagesIntroductionEmmanuel MwabaNo ratings yet
- Introduction Classification Advantages and Disadvantages Site Selection Selection of Type of DamDocument30 pagesIntroduction Classification Advantages and Disadvantages Site Selection Selection of Type of DamKubaNo ratings yet
- Government of Andhra Pradesh Government of Andhra Pradesh: Subject SubjectDocument21 pagesGovernment of Andhra Pradesh Government of Andhra Pradesh: Subject SubjectseshuNo ratings yet
- Classification of DamDocument14 pagesClassification of DamflywithkenNo ratings yet
- Design of Spillways 2.0 #Document40 pagesDesign of Spillways 2.0 #SahanNo ratings yet
- Fuse Gates PDFDocument9 pagesFuse Gates PDFmasanegraNo ratings yet
- Evaluasi Stabilitas Mercu Bendung Batang Toru, Kabupaten Tapanuli UtaraDocument7 pagesEvaluasi Stabilitas Mercu Bendung Batang Toru, Kabupaten Tapanuli UtaraWindafriskazalukhuNo ratings yet
- Jawai-Map-CATCHMENT AREASDocument1 pageJawai-Map-CATCHMENT AREASRituparna NathNo ratings yet
- Spillways 130820165335 Phpapp02 PDFDocument12 pagesSpillways 130820165335 Phpapp02 PDFpradeepbmahajanNo ratings yet
- D D' E E' B C: Plan SpillwayDocument1 pageD D' E E' B C: Plan SpillwayFirmansyah MardwionoNo ratings yet
- 1.dam HydDocument35 pages1.dam Hydshiva kamraniNo ratings yet
- Pakistan Studies - Affairs - Most Important MCQs (Set III) For CSS, PMS, PCS, NTSDocument9 pagesPakistan Studies - Affairs - Most Important MCQs (Set III) For CSS, PMS, PCS, NTSJatoi AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Corumana Dam Emergancy Spillway-Design Case 1 - Labyrinth WeirDocument1 pageCorumana Dam Emergancy Spillway-Design Case 1 - Labyrinth WeirguildkeyNo ratings yet
- Dam FailureDocument16 pagesDam FailureFlorentina SuduNo ratings yet
- Data of Dams R1Document16 pagesData of Dams R1Tejasri PinnapareddyNo ratings yet
- Spesifikasi Teknis Bendungan Karian, Banten.Document8 pagesSpesifikasi Teknis Bendungan Karian, Banten.Ronald Hidayat100% (1)
- Design Consideration of R.C.C. DamDocument3 pagesDesign Consideration of R.C.C. Damdeadlyman8372100% (1)
- Spillway NotesDocument15 pagesSpillway Notesvinod choudhariNo ratings yet
- Rivers and DamsDocument6 pagesRivers and DamsYashwant SinghNo ratings yet
- Btcol 08Document255 pagesBtcol 08Aishwarya SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Budget and Work Program For Excavation For DamDocument1 pageBudget and Work Program For Excavation For DamBernie QuepNo ratings yet
- Lec #19 (Permeability Thru Stratified Soils)Document24 pagesLec #19 (Permeability Thru Stratified Soils)Muhammad Irfan100% (1)
- A Glossary - of Words and Phrases - Rela Ted To Dams - IcoldDocument70 pagesA Glossary - of Words and Phrases - Rela Ted To Dams - IcoldTansel YılmazNo ratings yet
- Daily Bulletin in Excel For 05092020Document1 pageDaily Bulletin in Excel For 05092020Moran RajNo ratings yet
- Irrigation System of Pakistan GK by G.K KingdomDocument10 pagesIrrigation System of Pakistan GK by G.K KingdomAsad AliNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Design of Stepped SpillwaysDocument12 pagesHydraulic Design of Stepped SpillwaysCristian Hadad100% (1)