Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Role of Aggregate Demand in Reducing Unemploy
The Role of Aggregate Demand in Reducing Unemploy
Uploaded by
Fajyan KhanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Role of Aggregate Demand in Reducing Unemploy
The Role of Aggregate Demand in Reducing Unemploy
Uploaded by
Fajyan KhanCopyright:
Available Formats
Menu
The Role of Aggregate
Demand in Reducing
unemployment
14 November 2007 by Tejvan Pettinger
Evaluate the importance of
managing aggregate demand
(AD) to bring about a
sustained reduction in the
rate of unemployment in the
UK economy.
In 1992 Unemployment in the UK rose
to 3 million. A signiBcant part of this
unemployment this was due to the
recession of 1992.
In a recession, demand deBcient
unemployment will increase. This is
because as Brms close down they have
to lay oI workers. Other Brms, may
stay in business by not hiring new
workers or laying oI some existing
workers. In a recession, we get a rise in
unemployment due to deBciency of
aggregate demand.
Increasing AD to increase
employment
Therefore, in this case, it is important
for the government to try and boost
Aggregate Demand (AD) and increase
the rate of economic growth. For
example, the government could pursue
expansionary Bscal policy; e.g – lower
taxes and higher government spending.
This will lead to an increase in AD and
therefore, higher growth and jobs will
be created reducing unemployment.
Governments may be reluctant to
pursue expansionary Bscal policy
because it will lead to higher
borrowing.
Also, if AD increases too quickly it will
cause inUation. Therefore, the growth
may be unsustainable and the boom
may lead to a bust. In this case, the job
creation will only be temporary.
Therefore, it is important to manage
AD, so as to maintain stable, low
inUationary growth. This will allow a
sustained reduction in unemployment.
To a large extent, this is what has
happened in the UK since 1992. The
MPC used monetary policy (changing
interest rates) to enable low inUation
and stable growth from 1992-2007. In
2009, the rise in unemployment caused
the MPC to cut interest rates to 0.5% –
in a bid to boost aggregate demand
and create jobs.
AD is very important. However, there
are many other types of
unemployment which will not be
reduced through demand
management.
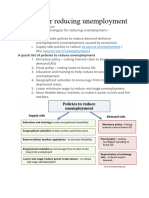
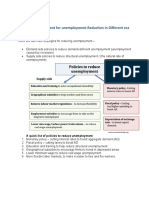
These include:
Frictional unemployment
(looking between jobs)
Structural unemployment. –
People without the right skills for
the labour market
Geographical unemployment – a
mismatch of skills throughout
the country.
Real wage unemployment –
caused by wages being above
equilibrium levels.
disguised unemployment – when
people are put on sickness
beneBts. (not counted in o_cial
JSA measure) See true level of
unemployment in the UK
Voluntary unemployment – when
beneBts are too high they
encourage people to remain on
beneBts rather than work.
E.g. It is argued that if the EU
experienced faster growth,
unemployment will still remain a
problem because of structural supply-
side factors. Often know as the natural
of unemployment. To achieve full
employment it is necessary to use
supply-side policies as well. Supply-side
policies can include
More Uexible labour markets
Retraining for the long-term
unemployed
Improved geographical mobility.
Related Essays:
Natural Rate of Unemployment
Causes of unemployment
Policies to reduce
unemployment
unemployment
Chinese Yuan Dollar Forecast 2008
Preparing for Economics Interview at
Oxford
5 thoughts on “The Role of
Aggregate Demand in Reducing
unemployment”
Pingback: Unemployment Spain - How
to Reduce | Economics Blog
Pingback: Unemployment Levels and
InUation — Economics Blog
NIKOLAI NIkolaev
12 January 2009 at 9:45 pm
Hey i believe that
unemployemtn can be
decreased with subsidies. If we
all followed Senator Judis’
plans, this mess wouldn’t have
occured.
CONNOR BARNES
26 March 2009 at 9:38 pm
I BELIEVE THAT
UNEMPLOYMENT CAN BE
DECREASED THRU GOV
SPENDIN
CONNOR BARNES
26 March 2009 at 9:40 pm
also unemployment could be
lower if we provided more tax
incentives too work
Comments are closed.
View: all Revision Guides
A-Level revision AS-Level Revision
guide £8.95 guide £5.00
A-Level Model GCSE Revision
Essays £9.00 Guide £8.49
Get new posts by email:
Enter your email
Subscribe
Recent Posts
Will House Price Falls in 2023 be like
Crashes of 2007 and 1991?
Could the UK could rejoin the EU?
Videos about economic collapse on
Youtube
Why Landlords are Facing A Tougher
Economic Situation
How Bank Failures can destroy the
economy
Selected Posts
Causes of Wall Street Crash 1929
Causes of Great Depression
UK economy in 1920s
Keynesian Economics
The problem of printing money
The importance of economics
Understanding exchange rates
10 reasons for studying economics
Impact of immigration on UK economy
Random Glossary term
Carbon Tax- Advantages and
Disadvantages
UK economy stats
Ask an economics question
You are welcome to ask any questions on
Economics.
Ask a question
About
Tejvan Pettinger studied PPE at LMH,
Oxford University. Find out more
Terms & Conditions | Privacy Policy | Contact
| © -
Economicshelp.org 2023
You might also like
- Unemployment EssayDocument5 pagesUnemployment EssayKevin Nguyen100% (1)
- Unemployment Essay PlanDocument3 pagesUnemployment Essay PlanEren SevinceNo ratings yet
- Policies For Reducing UnemploymentDocument14 pagesPolicies For Reducing UnemploymentAnushkaa DattaNo ratings yet
- Policies For Reducing UnemploymentDocument6 pagesPolicies For Reducing UnemploymentAnushkaa DattaNo ratings yet
- UnemploymentDocument43 pagesUnemploymentdestinyebeku01No ratings yet
- Unemployment EssayDocument9 pagesUnemployment EssayJenney TatNo ratings yet
- What Can Be Done at The Macro Level To Control Unemployment?Document3 pagesWhat Can Be Done at The Macro Level To Control Unemployment?Mohammed AshroffNo ratings yet
- Longest Recession Since Great Depression: How To Deal With Very Large DebtDocument31 pagesLongest Recession Since Great Depression: How To Deal With Very Large DebtAkshay ShahNo ratings yet
- Explain How The UK National Minimum Wage Can Distort The Operation of A Competitive Labour Market?Document7 pagesExplain How The UK National Minimum Wage Can Distort The Operation of A Competitive Labour Market?MatthewNo ratings yet
- Policies To Control InflationDocument5 pagesPolicies To Control InflationMohsin ManzoorNo ratings yet
- Jobs Market Faces Slow Painful Contraction: Economics Data ResponseDocument2 pagesJobs Market Faces Slow Painful Contraction: Economics Data ResponseaaravNo ratings yet
- Unemp Rate Pol EffectivenessDocument3 pagesUnemp Rate Pol EffectivenessEren SevinceNo ratings yet
- Ma AssignmentDocument6 pagesMa AssignmentHusien JaletoNo ratings yet
- Krugwellsecps3e Macro Ch06Document6 pagesKrugwellsecps3e Macro Ch06webizerNo ratings yet
- 10.1 Cost of Unemployment: - Individuals Suffer From Losing Their JobsDocument10 pages10.1 Cost of Unemployment: - Individuals Suffer From Losing Their JobsVinny HungweNo ratings yet
- Business Eceonomics ProjectDocument9 pagesBusiness Eceonomics ProjectMuhammad Waleed ArsalNo ratings yet
- Demand Deficient UnemploymentDocument3 pagesDemand Deficient UnemploymentRosmarie Derimais100% (1)
- Strategies To Reduce UnemploymentDocument12 pagesStrategies To Reduce Unemploymentsnijay100% (1)
- Economic Fluctuations: QuestionsDocument11 pagesEconomic Fluctuations: Questionsyolanda argi utamiNo ratings yet
- Week 12 - Tutorial QuestionsDocument9 pagesWeek 12 - Tutorial Questionsqueeen of the kingdomNo ratings yet
- Economic Cycle PRELIMDocument6 pagesEconomic Cycle PRELIMNichaiNo ratings yet
- Case Study MacroeconomicsDocument14 pagesCase Study MacroeconomicsjeylaNo ratings yet
- Essay On Causes of RecessionDocument2 pagesEssay On Causes of Recessionnickey.123No ratings yet
- Unemployment: Témakör 3 Téma 4 1Document3 pagesUnemployment: Témakör 3 Téma 4 1Mark MatyasNo ratings yet
- Assignment BBA 1 POM by Shubhankar Mridha Student Id - 211001101252 1 Sem. 1. What Is Government Expenditure Multiplier ? AnsDocument6 pagesAssignment BBA 1 POM by Shubhankar Mridha Student Id - 211001101252 1 Sem. 1. What Is Government Expenditure Multiplier ? AnsBAPPA PRODUCTIONNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomic - UlangkajiDocument12 pagesMacroeconomic - UlangkajiAnanthi BaluNo ratings yet
- Eco Mid 104Document9 pagesEco Mid 104Tasmim AhmedNo ratings yet
- Strategies To Reduce UnemploymentDocument23 pagesStrategies To Reduce UnemploymentprashantgoruleNo ratings yet
- The Failure of Supply-Side EconomicsDocument5 pagesThe Failure of Supply-Side EconomicsCenter for American ProgressNo ratings yet
- Unemeployment and Policies To Reduce ItDocument2 pagesUnemeployment and Policies To Reduce Itmandeep.agarwalNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics EssayDocument7 pagesMacroeconomics EssayAchim EduardNo ratings yet
- 4.3.4 Macro PracticeDocument6 pages4.3.4 Macro Practicebuiclara07No ratings yet
- EconDocument19 pagesEconkajan thevNo ratings yet
- Principles of Economics Ii Assignment QuestionDocument8 pagesPrinciples of Economics Ii Assignment QuestionChristianJerryNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument113 pagesIlovepdf MergedSaket ShankarNo ratings yet
- Revision For Mid Exam Beeb3023 Intmd Macro A191 1Document18 pagesRevision For Mid Exam Beeb3023 Intmd Macro A191 1Amirul AimanNo ratings yet
- 6 Ultimate Evaluation TechniquesDocument2 pages6 Ultimate Evaluation TechniquesHow Xin YiNo ratings yet
- UK Economy HND AssignmentDocument11 pagesUK Economy HND AssignmentShakirAhamedNo ratings yet
- Recovering For A Recession and Some Possible ProblemsDocument10 pagesRecovering For A Recession and Some Possible ProblemsAbdoukadirr SambouNo ratings yet
- 02 (Sidra Liaqat)Document17 pages02 (Sidra Liaqat)John FriehNo ratings yet
- Poverty Income Inequality and Economic GrowthDocument5 pagesPoverty Income Inequality and Economic GrowthThankachan CJNo ratings yet
- SolutionsManual Ch30Document16 pagesSolutionsManual Ch30Thiba SathivelNo ratings yet
- Unemployment: MacroeconomicsDocument41 pagesUnemployment: MacroeconomicsChevalier ChevalierNo ratings yet
- GROUP 10 Micro ProjectDocument13 pagesGROUP 10 Micro Projectnhiuyen147No ratings yet
- Case 12Document5 pagesCase 12Hussain ZakiNo ratings yet
- MWR in UKDocument17 pagesMWR in UKAy KaNo ratings yet
- PS5 - F10 KZ v3Document7 pagesPS5 - F10 KZ v3Vaid RamNo ratings yet
- ECON 318/2 Fall 2017 - ASSIGNMENT 1: Answer Key Question #1.inflation Targeting and Unemployment (15 Marks)Document5 pagesECON 318/2 Fall 2017 - ASSIGNMENT 1: Answer Key Question #1.inflation Targeting and Unemployment (15 Marks)Vin HNo ratings yet
- Assignment: ECO161: Fundamentals of Macro Economics Homework-IIIDocument4 pagesAssignment: ECO161: Fundamentals of Macro Economics Homework-IIIBhagwant SinghNo ratings yet
- Unemployment Q2a Ans (Pg26)Document3 pagesUnemployment Q2a Ans (Pg26)HuYimingNo ratings yet
- Advanced Economics QuestionsDocument5 pagesAdvanced Economics QuestionsIainNo ratings yet
- Macro1 - Essay - Muhammad Zaim Ilyasa Bin KasimDocument2 pagesMacro1 - Essay - Muhammad Zaim Ilyasa Bin KasimMUHAMMAD ZAIM ILYASA KASIMNo ratings yet
- AEUNEMPLOYMENTDocument6 pagesAEUNEMPLOYMENTReniel RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Case Study Group 2-2Document5 pagesCase Study Group 2-2Fatima AliyevaNo ratings yet
- MacroeconomicsDocument4 pagesMacroeconomicsBurhan barchaNo ratings yet
- Econ Unemployment P1b HWDocument3 pagesEcon Unemployment P1b HWmichellec24No ratings yet
- EC1009 May ExamDocument10 pagesEC1009 May ExamFabioNo ratings yet
- Answer Tutorial MacroeconomicsDocument6 pagesAnswer Tutorial MacroeconomicsAinaasyahirah RosidanNo ratings yet
- Active Aging in Economy and Society: Carl Bertelsmann Prize 2006From EverandActive Aging in Economy and Society: Carl Bertelsmann Prize 2006No ratings yet
- Key Differences Between Sole Proprietorship and Joint Hindu Family Firm - A Comparison ChartDocument6 pagesKey Differences Between Sole Proprietorship and Joint Hindu Family Firm - A Comparison ChartVarun KocharNo ratings yet
- Pile Cutting / Hacking (Sub-Structure Work)Document2 pagesPile Cutting / Hacking (Sub-Structure Work)Rahmat HariNo ratings yet
- Markov ChainDocument37 pagesMarkov ChainNyoman Arto SupraptoNo ratings yet
- Ce Nov 19 R17Document18 pagesCe Nov 19 R17Anonymous yO7rcec6vuNo ratings yet
- Virtual Reality and Artificial Intelligence in Motion SimulatorsDocument18 pagesVirtual Reality and Artificial Intelligence in Motion SimulatorsSyed RazviNo ratings yet
- Law of Contracts IDocument29 pagesLaw of Contracts IAlok BhattNo ratings yet
- Example ReportDocument4 pagesExample ReportFirzanNo ratings yet
- General Income TaxDocument3 pagesGeneral Income TaxFlorean SoniaNo ratings yet
- PATANJALIDocument16 pagesPATANJALIAbhishek PandeyNo ratings yet
- MKTG 5th Canadian EditionDocument418 pagesMKTG 5th Canadian EditionArturo VeranoNo ratings yet
- Oil-Degassing:: 1-SeparationDocument34 pagesOil-Degassing:: 1-SeparationAhmed AbdullaNo ratings yet
- 17 March 2011 Case Study DiamondDocument7 pages17 March 2011 Case Study DiamondIonita AlexandruNo ratings yet
- Balance Sheet SampleDocument1 pageBalance Sheet Samplewaqas akramNo ratings yet
- Presented By: Ujjwal Jaryal RF17E1A05Document9 pagesPresented By: Ujjwal Jaryal RF17E1A05Ujjwal JaryalNo ratings yet
- Aviatin PowerpointDocument21 pagesAviatin PowerpointBeyanka CruickshankNo ratings yet
- Diagnostico Parte 1 MalibuDocument161 pagesDiagnostico Parte 1 MalibuHugo Armando Escamilla LozanoNo ratings yet
- Born To WinDocument23 pagesBorn To WinSuvra PattanaikNo ratings yet
- C1 UseDocument4 pagesC1 UseMichał JanickiNo ratings yet
- Rittal Technical System Catalogue Ri4Power x201lm PDFDocument92 pagesRittal Technical System Catalogue Ri4Power x201lm PDFRatilal M JadavNo ratings yet
- Article 19 (A) Freedom of Speech and ExpressionDocument4 pagesArticle 19 (A) Freedom of Speech and ExpressionEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Service & Maintenance Manual High Speed Separator: Product No. 881039-12-01/1 Book No. 568854-02 Rev. 2Document133 pagesService & Maintenance Manual High Speed Separator: Product No. 881039-12-01/1 Book No. 568854-02 Rev. 2امير الموسوي100% (1)
- User - S - Manual Thermometer PDFDocument22 pagesUser - S - Manual Thermometer PDFjuanNo ratings yet
- Square and Square Root (6th Grade)Document18 pagesSquare and Square Root (6th Grade)Rishabh Vasudev Kapatkar100% (2)
- Complex AnalysisDocument144 pagesComplex AnalysisMiliyon Tilahun100% (4)
- S11 1321 01aDocument20 pagesS11 1321 01aMarsKwokNo ratings yet
- UPDATE YANG BELUM Mengerjakan Sertifikasi TCO Maret Update 0804 Jam 08.00 WIBDocument2 pagesUPDATE YANG BELUM Mengerjakan Sertifikasi TCO Maret Update 0804 Jam 08.00 WIBWendi ArtheaNo ratings yet
- Roof Mounted Fans HCTB - HCTT Series, Axial Flow Fans: Applications Description Air ExtractionDocument9 pagesRoof Mounted Fans HCTB - HCTT Series, Axial Flow Fans: Applications Description Air ExtractionmarckalhiNo ratings yet
- Canon in C (Fingerstyle) PDFDocument3 pagesCanon in C (Fingerstyle) PDFXavier VergaraNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan On An AtomDocument6 pagesLesson Plan On An AtomAnonymous ZsTY4mkysTNo ratings yet
- Toyota Vios Manual Book DownloadDocument24 pagesToyota Vios Manual Book DownloadVidi EfendiNo ratings yet