Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lo 3 Ok
Lo 3 Ok
Uploaded by
Edgar BatistianaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- PassThru API 1Document83 pagesPassThru API 1andaposa9No ratings yet
- COC 2 Module 2.1Document5 pagesCOC 2 Module 2.1sanpascualmikyla14No ratings yet
- 5the Sem Computer Network Lab ManualDocument68 pages5the Sem Computer Network Lab ManualVishal Sharma0% (1)
- 1KW-61433-0 Increasing ProductivityNetworking Instruments AppsBrief 070518Document14 pages1KW-61433-0 Increasing ProductivityNetworking Instruments AppsBrief 070518termmmNo ratings yet
- 657ac38c7eb2clab9 CCN 2023Document13 pages657ac38c7eb2clab9 CCN 2023Muhammad Ali RajarNo ratings yet
- Content Standards: LO 3. Set Router/wi-Fi/wireless Access Point/repeater ConfigurationDocument9 pagesContent Standards: LO 3. Set Router/wi-Fi/wireless Access Point/repeater ConfigurationRusty Ugay LumbresNo ratings yet
- Lab9 CCN 2023Document18 pagesLab9 CCN 2023Muhammad Ali RajarNo ratings yet
- 5707e9cc972d3 Wwb6 Quickstart Guide EnglishDocument8 pages5707e9cc972d3 Wwb6 Quickstart Guide EnglishRosalino Castillejos PinedaNo ratings yet
- Ensure The Configuration Conforms To The Manufacturer's Instructions/manualDocument19 pagesEnsure The Configuration Conforms To The Manufacturer's Instructions/manualSau Jr Sy CairasNo ratings yet
- How To Configure Your PC To A Local Area Network: StepsDocument13 pagesHow To Configure Your PC To A Local Area Network: StepsEliad RMndemeNo ratings yet
- Networking/Port Forwarding/DDNS Overview GuideDocument13 pagesNetworking/Port Forwarding/DDNS Overview GuideBeqir CubolliNo ratings yet
- Mwnapr-1 QigDocument6 pagesMwnapr-1 QigmikeNo ratings yet
- -Repeater: 展开 尺 寸: 3 6 0 x 2 4 0 mm 成品 尺 寸: 1 2 0 x 9 0 mmDocument2 pages-Repeater: 展开 尺 寸: 3 6 0 x 2 4 0 mm 成品 尺 寸: 1 2 0 x 9 0 mmhelmoz100% (1)
- DONETLE ICT 10 Q4 Week 1 8 Additional Topics - RemovedDocument10 pagesDONETLE ICT 10 Q4 Week 1 8 Additional Topics - Removedallenformentera9No ratings yet
- WirelessinstallationDocument26 pagesWirelessinstallationFuad IsmailNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks-2 Practical-1Document6 pagesComputer Networks-2 Practical-1vaibhav vermaNo ratings yet
- LO 2 OkDocument14 pagesLO 2 OkEdgar BatistianaNo ratings yet
- Lab9 CCN 2023Document17 pagesLab9 CCN 2023Muhammad Ali RajarNo ratings yet
- C46 Exp4Document10 pagesC46 Exp4pravintp123No ratings yet
- Module 12-13 Css34 q2 FinalDocument4 pagesModule 12-13 Css34 q2 Finaljonathan labajoNo ratings yet
- 7.5.1 LabDocument6 pages7.5.1 LabLHNo ratings yet
- Ict 4Document16 pagesIct 4jerry.mejiaNo ratings yet
- Guided Learning Activity Kit: Sptve-Computer System ServicingDocument25 pagesGuided Learning Activity Kit: Sptve-Computer System ServicingSam PaglingayenNo ratings yet
- TLE-CSS Grade9 Module Q4W7Document4 pagesTLE-CSS Grade9 Module Q4W7gela vynxNo ratings yet
- Airlink101 Access Point - Ap431wDocument42 pagesAirlink101 Access Point - Ap431wJim ParentNo ratings yet
- LESSON 4 Peer To Peer NetworkDocument4 pagesLESSON 4 Peer To Peer NetworkReign Jay FerrerNo ratings yet
- Q2 MODULE6 G12 CSS NCII Luciano Millan NHSDocument11 pagesQ2 MODULE6 G12 CSS NCII Luciano Millan NHSALBERT ALGONESNo ratings yet
- Qig Di-604Document12 pagesQig Di-604Dark _No ratings yet
- Jignesh VarmaDocument25 pagesJignesh VarmaNarappaNo ratings yet
- User Manual: MAN-525503/525534-UM-0413-01Document26 pagesUser Manual: MAN-525503/525534-UM-0413-01Anthony DavisNo ratings yet
- WS-WN523: Wireless Extender&RouterDocument21 pagesWS-WN523: Wireless Extender&RouterAlka389No ratings yet
- Nov. 7 G10Document56 pagesNov. 7 G10Honey Diana MejiaNo ratings yet
- 9IS44077 LanAdapter GB 4-07 - 2Document11 pages9IS44077 LanAdapter GB 4-07 - 2MARIVEL BASANo ratings yet
- Experiment 16Document3 pagesExperiment 16rapraptapayoonNo ratings yet
- p310 v3.50 QuickStartGuideDocument5 pagesp310 v3.50 QuickStartGuideTomaž BajželjNo ratings yet
- BR-6428nS V5: Quick Installation GuideDocument19 pagesBR-6428nS V5: Quick Installation GuideAggeliki KosteliNo ratings yet
- 11n USB Dongle ManualDocument20 pages11n USB Dongle ManualgroovychickNo ratings yet
- Lab - Configure Firewall SettingsDocument3 pagesLab - Configure Firewall SettingsSgr Eka 13No ratings yet
- Q4 Module1-2 CSS 12Document10 pagesQ4 Module1-2 CSS 12Ched Augustus AranNo ratings yet
- Wireless Adapter Quick Installation Guide: 1.software and Driver SetupDocument2 pagesWireless Adapter Quick Installation Guide: 1.software and Driver SetupnitinfutaneNo ratings yet
- 1.3.6 Packet Tracer Build A Home Network Answer KeyDocument9 pages1.3.6 Packet Tracer Build A Home Network Answer KeySasha MarianchukNo ratings yet
- Manual de Usuario (Airlink) PDFDocument41 pagesManual de Usuario (Airlink) PDFLic Rick JohnsonNo ratings yet
- 6.1.4.8 Lab - Configure Firewall SettingsDocument3 pages6.1.4.8 Lab - Configure Firewall SettingsMaria Jiminian0% (1)
- Troubleshooting Network and CommunicationDocument14 pagesTroubleshooting Network and CommunicationnetpazNo ratings yet
- Las Fourth Q Wireless Config 2023 2024Document22 pagesLas Fourth Q Wireless Config 2023 2024Nia Kristel Salas AdralesNo ratings yet
- SP912G ManualDocument11 pagesSP912G ManualesilvaopNo ratings yet
- (WR Net 018 CC) Manual For DHCPDocument8 pages(WR Net 018 CC) Manual For DHCPKhyle Laurenz DuroNo ratings yet
- DI-804HV: Check Your Package ContentsDocument12 pagesDI-804HV: Check Your Package ContentsJorge Manuel Ramirez GianellaNo ratings yet
- InstructionsDocument10 pagesInstructionsapi-247087458No ratings yet
- Configuring Network Connections For Windows 10Document32 pagesConfiguring Network Connections For Windows 10Joseph ButawanNo ratings yet
- Ap411w ManualDocument32 pagesAp411w ManualrogercomNo ratings yet
- Lab 7 - Create A Simple NetworkDocument14 pagesLab 7 - Create A Simple NetworkNurul afiqah MansorNo ratings yet
- Wireless Communication FileDocument38 pagesWireless Communication FilerishabhNo ratings yet
- Computer Systems Servicing 10 Week3-4Document10 pagesComputer Systems Servicing 10 Week3-4jf2ralba100% (1)
- Wireless Configuration: Connect The Router On A Wired LAN EnvironmentDocument16 pagesWireless Configuration: Connect The Router On A Wired LAN Environmentjun arvie100% (1)
- Configure Wide Area Network (Access Point)Document8 pagesConfigure Wide Area Network (Access Point)Lady Christianne BucsitNo ratings yet
- Hacking : A Comprehensive, Step-By-Step Guide to Techniques and Strategies to Learn Ethical Hacking with Practical Examples to Computer Hacking, Wireless Network, Cybersecurity and Penetration TestingFrom EverandHacking : A Comprehensive, Step-By-Step Guide to Techniques and Strategies to Learn Ethical Hacking with Practical Examples to Computer Hacking, Wireless Network, Cybersecurity and Penetration TestingNo ratings yet
- LO 1 CSS OkDocument46 pagesLO 1 CSS OkEdgar BatistianaNo ratings yet
- Lo 5 CSS OkDocument17 pagesLo 5 CSS OkEdgar BatistianaNo ratings yet
- Comp. Programming Week 1&2Document23 pagesComp. Programming Week 1&2Edgar BatistianaNo ratings yet
- Comp. Programming Week 5&6Document11 pagesComp. Programming Week 5&6Edgar BatistianaNo ratings yet
- Comp. Programming Week 3&4Document19 pagesComp. Programming Week 3&4Edgar BatistianaNo ratings yet
- Comp. Programming Week 7&8Document13 pagesComp. Programming Week 7&8Edgar BatistianaNo ratings yet
- OAW Stellar AP Quick Start Guide R3.0Document2 pagesOAW Stellar AP Quick Start Guide R3.0kirinVAGNo ratings yet
- 01 - Overview of Satellite Systems PDFDocument21 pages01 - Overview of Satellite Systems PDFAhmed RiyadNo ratings yet
- CMSE LG v2 PDFDocument222 pagesCMSE LG v2 PDFRakesh KumarNo ratings yet
- 4214514-02 - Technical Information - TopTronic E GW Modbus TCP-RS485Document24 pages4214514-02 - Technical Information - TopTronic E GW Modbus TCP-RS485Sima Catalin-IonutNo ratings yet
- Alepo AAA Server Selected To Launch 4G Wireless Broadband in AngolaDocument2 pagesAlepo AAA Server Selected To Launch 4G Wireless Broadband in AngolaAlepoNo ratings yet
- Compal LA-9241PDocument56 pagesCompal LA-9241Pn nnNo ratings yet
- p188 BluetoothDocument12 pagesp188 Bluetoothjnanesh582No ratings yet
- SD WAN Over HSM 5.0.cleanedDocument12 pagesSD WAN Over HSM 5.0.cleanedHugo GarciaNo ratings yet
- Consul Tutorial PDFDocument53 pagesConsul Tutorial PDFvvNo ratings yet
- FormaxDocument3 pagesFormaxajabsinghchauhan760No ratings yet
- Media Platform User GuideDocument207 pagesMedia Platform User Guidefrangky.rengkungNo ratings yet
- Peachpit Press Managing Apple Devices 3rd Edition 0134301854 PDFDocument737 pagesPeachpit Press Managing Apple Devices 3rd Edition 0134301854 PDFMiguel LopezNo ratings yet
- Apxverr20x CDocument2 pagesApxverr20x CJCARLOS COLQUENo ratings yet
- Fast - Lane F5 NETWORKS - CONFIGURING BIG IP ADVANCED WAFDocument5 pagesFast - Lane F5 NETWORKS - CONFIGURING BIG IP ADVANCED WAFGuido BaroncelliNo ratings yet
- Pegasus Spyware AnalysisDocument35 pagesPegasus Spyware AnalysisRIJU GHOSHNo ratings yet
- Simatic S5 318-3UA11 Central Controller Interface Module: ManualDocument37 pagesSimatic S5 318-3UA11 Central Controller Interface Module: ManualAutomacao16No ratings yet
- Cnav Man 017.9 (C Nav3050 User Guide)Document186 pagesCnav Man 017.9 (C Nav3050 User Guide)Mohammed HassanNo ratings yet
- SEL-3010 Event Messenger: Features, Benefits, and ApplicationsDocument20 pagesSEL-3010 Event Messenger: Features, Benefits, and ApplicationsEmmanuel EntzanaNo ratings yet
- FortiOS 7.0 PortsDocument6 pagesFortiOS 7.0 Portsvedant vedNo ratings yet
- VodafoneDocument62 pagesVodafoneAbdul Manaf P MNo ratings yet
- Complete Umts Call FlowDocument4 pagesComplete Umts Call FlowRahim KhanNo ratings yet
- FirstAlert FA168CPS v7 Programming ManualDocument40 pagesFirstAlert FA168CPS v7 Programming ManualjsbatchNo ratings yet
- Angle Modulation SystemsDocument35 pagesAngle Modulation SystemsseenudesignNo ratings yet
- M80 User ManualDocument1 pageM80 User ManualabcNo ratings yet
- Running Head: Security Attack On Systems and Web Servers 1Document8 pagesRunning Head: Security Attack On Systems and Web Servers 1kim kimNo ratings yet
- A Design of Triangular Sierpinski Gasket Fractal AntennaDocument3 pagesA Design of Triangular Sierpinski Gasket Fractal Antennasuman uppalaNo ratings yet
- GSM Repair / Maint Policy-Telecom / Allied EqptDocument9 pagesGSM Repair / Maint Policy-Telecom / Allied EqptImran AzizNo ratings yet
- What Is Cybersecurity and NetworkingDocument4 pagesWhat Is Cybersecurity and NetworkingFilipa MirandaNo ratings yet
Lo 3 Ok
Lo 3 Ok
Uploaded by
Edgar BatistianaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lo 3 Ok
Lo 3 Ok
Uploaded by
Edgar BatistianaCopyright:
Available Formats
Pre-Test: What Do You Already Know?
Pre-Test LO 2
I. DIRECTIONS: Arrange the following procedures. Label your answer in ascending order.
A. Configuring a Router.
______ Assign the router a new username and password.
______ Connect your router to your computer and your modem.
______ Enter in your router’s address.
______ Enter in your username and password.
______ Open a web browser.
______ Reset your router if you can’t access it.
B. Setting up Wireless Network.
______ Assign the router a new username and password.
______ Connect your router to your computer and your modem.
______ Enter in your router’s address.
______ Enter in your username and password.
______ Open a web browser.
______ Reset your router if you can’t access it.
II. IDENTIFICATION: Identify what is being asked. Choose your answer in the box provided.
1. Computers for which the rule is applied.
2. It “Allow” or “Block” based on what the rule is supposed to do.
3. Rule that controls the connections performed by a specific Windows service or feature.
4. Rule that controls the connections performed by a specific Windows service or feature.
5. Shares the network protocols for which the rule is applied.
6. Tells the user whether that rule overrides an existing block rule. By default, all rules should
have the value “No” for this parameter.
7. Tells the user whether the rule is applied for connections made on specific local ports or
not.
8. Tells the user whether the rule is applied for connections made on specific remote ports or
not.
9. Tells the user whether the rule is applied only when devices with specific IP addresses are
connected or not.
COMPUTER SYSTEMS SERVICING
K to 12 Technology and Livelihood Education
10. Tells the user whether the rule is applied only when your computer has a specific IP
address or not.
11. tells the user whether the rule is enabled and applied by Windows Firewall or not.
12. The network location/profile the rule is applied to: private, public, or domain (for business
networks with network domains).
13. The rule applies to a specific program.
14. The rule applies to the network traffic that is performed through a specific port.
15. The rule is applied only when the computer is connected to a network domain.
16. The rule is applied only when the computer is connected to trusted private networks.
17. The rule is applied only when the computer is connected to untrusted public networks.
18. The user account which is set as the owner/creator of the rule.
19. The user accounts for which the rule is applied (for inbound rules only).
20. This applies only to apps from the Windows Store and it shares the package name of the
app the rule applies to.
Action Application package Authorized computers Authorized users
Domain Enabled Local address Local port
Local user owner Override Port Predefined
Predefined Private Profile Program
Protocol Public Remote address Remote port
COMPUTER SYSTEMS SERVICING
K to 12 Technology and Livelihood Education
DISCUSSION: INFORMATION SHEET
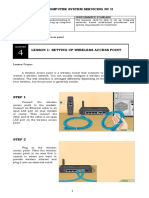
LO3: Set Router/Wi-fi/Wireless access point/Repeater Configuration
Learning Code: TLE_IACSS912SUCN-If-j-IIae-35
Objectives:
3.1 Configure client device systems settings in accordance with manufacturer’s instructions
and end user preference
3.2 Configure LAN in accordance with manufacturer’s instructions and network design
3.3 Configure WAN in accordance with manufacturer’s instructions and network design
3.4 Configure wireless settings in accordance with manufacturer’s instructions, network
design, and end-user preferences
3.5 Configure security/firewall/advanced settings in accordance with manufacturers
instruction and end-user preference
How to Configure Local Network Area
Step 1: Attach the RJ-45 connector to the Ethernet network port on
your PC.
Step 2: Right click on ‘My Network Places’ icons
located on the desktop and in the popup
menu. Click on Properties
Alternatively, click ‘Start’ from the
taskbar and right click on ‘My Network
Places’ option from the popup menu.
In the menu that appears select
‘Properties’
COMPUTER SYSTEMS SERVICING
K to 12 Technology and Livelihood Education
Step 3:
Right-click on ‘Local Area Connection’ in the
new Window that appears (under the LAN or
High-Speed internet section).
Step 4: Click Properties in the popup menu that appears.
Step 5: Scroll down and select ‘Internet Protocol
(TCP/IP) and click on ‘Properties' in the Local Area
Connection dialog box that appears under the
connection box.
COMPUTER SYSTEMS SERVICING
K to 12 Technology and Livelihood Education
Step 6: Opt for obtaining the configuration
settings automatically or manually. To obtain
the settings automatically, select ‘Obtain an IP
Address Automatically’. However, to use this
option, you will need to have a DHCP server
that will function in allocating and managing IP
address to ensure that there are no conflicts.
Step 7:
Configure your PC to the network manually, if you modem isn't
connected that with the options mentioned above.
Click the option ‘Use the following IP Address’.
Enter the IP address to use. It is important
that you consult your network administrator on the
IP to use so as to avoid conflicts occurring in the
network, i.e. a situation where two PCs have similar
IP addresses.
COMPUTER SYSTEMS SERVICING
K to 12 Technology and Livelihood Education
Enter the Subnet Mask and Default gateway. The subnet
mask is used to identify the network level you are in while
the default gateway identifies the router connection.
Step 8: Check the option ‘Show
icon in notification area when
connected.
Step 9: Click ‘OK”. This will enable you to know if the local area
connection is connected or disconnected.
COMPUTER SYSTEMS SERVICING
K to 12 Technology and Livelihood Education
How to Configure a Router
Configuring router is divided into several parts, namely;
Part 1: Connecting to the Router
Part 2: Setting up a Wireless Network
Part 3: Forwarding Ports
Part 4: Blocking Websites
Part 1: Connecting to the Router
Step 1: Connect your router to your computer and your
modem. Use Ethernet cables to connect your modem to the
WAN/WLAN/Internet port on your router, and connect your
computer to the “1”, “2”, “3”, or “4” port on the router.
Step 2: Open a web browser. Your router’s configuration page
can be accessed by any computer that is connected to the same
network. When configuring your router, you will have the best
results if you connect with a computer that is wired to the router
with an Ethernet cable.
Part 3: Enter in your router’s address. Routers are
accessed through your web browser by entering
the IP address into the address bar. The IP address
varies a bit by manufacturer, but most are the
same or very close. These are some of the more
popular manufacturers and the associated
addresses:[1]
Linksys - http://192.168.1.1
3Com - http://192.168.1.1
D-Link - http://192.168.0.1
Belkin - http://192.168.2.1
Netgear - http://192.168.1.1
Most routers have their default address printed in the documentation or on a sticker on
the router itself. You can also look it up online on the manufacturer’s website.
COMPUTER SYSTEMS SERVICING
K to 12 Technology and Livelihood Education
Step 4: Enter in your username and password. Before
you access the configuration page, you’ll be asked for a
username and password. Most routers will come with a
default username/password combo, while some allow
you to proceed without entering anything.
Your router’s documentation will tell you the
default username and password required. They
may also be printed on the router itself.
”admin” is one of the most common default
usernames.
”admin” or “password” are two of the most common passwords.
Step 5: Reset your router if you can’t access it. If you’ve
looked up your default address and username/password
combo and you still can’t access your router, you can
reset it to factory defaults to clear out any changes that
may have been made. This is useful for secondhand
routers or old changes that you can’t remember.
You can reset your router by pressing the Reset
button on it. This button is usually small and recessed, and can only be reached by a
paper clip. Some routers have a button that can be pressed more easily.
After pressing the reset button, wait 30-60 seconds and then try entering the router’s
address and username/password combination again.
Step 6: Assign the router a new username and
password. Leaving your router with the default username and
password is very insecure, and you should change it immediately
after setting it up. You can usually find this in the Administration
section of the router configuration.
Choose a username and password that can’t be easily
guessed. Include numbers and symbols in the password
to make sure that it is hard to crack.
COMPUTER SYSTEMS SERVICING
K to 12 Technology and Livelihood Education
Part 2: Setting up a Wireless Network
Step 1: Check your Internet settings. In the
Internet, Setup, or Home menu of your router,
check that your Internet IP address, DCHP, and
DNS settings are all set. These should typically
be set to automatic unless your service provider
informs you otherwise.
Many routers will provide a test button
on the Internet menu page. Click it to
check if your internet settings are
configured correctly.
Step 2: Open the Wireless settings. This menu may be
called Wireless, Wireless Settings, Basic Setup, or
something similar. This page will display your wireless
SSID, channel, encryption, and other settings.
Step 3: Name your network. Find the field labeled
SSID. This is the name of your network, and it will
appear in the list of available networks for your
wireless devices. Be sure to not put any personal
information in your network name, as the name will
be public.
Make sure that the “Enable SSID Broadcast”
box is checked.
The Channel should be set to Auto. If you
have a lot of wireless networks in your
area, your router will automatically move the network to a clean channel.
COMPUTER SYSTEMS SERVICING
K to 12 Technology and Livelihood Education
Step 4: Choose your wireless encryption. This can
also be called the Security Options. Here you’ll be
able to choose which method you want to use to
encrypt your network traffic. The options for most
routers are WEP, WPA-PSK, and WPA2-PSK.
WPA2 is the most secure mode of
encryption, and you should use it if all of
your devices support it. Only older
devices do not support WPA2.
Step 5: Choose a passphrase. The
passphrase is what you enter when a
device connects to your network. A
strong passphrase will help protect
your network from unwanted
intruders. You should always have a
passphrase for your network.
Step 6: Apply your settings. Once you have
chosen your SSID, encryption type, and
passphrase, click the Apply or Save button to
start your wireless network. Your router will
process for a few seconds, and then your
wireless network will be detectable by your
wireless devices.
COMPUTER SYSTEMS SERVICING
K to 12 Technology and Livelihood Education
Part 3: Forwarding Ports
Step 1: Open the Port Forwarding menu. This
can usually be found in the Advanced section
of the router’s configuration page.
Step 2: Add a new service or rule. Click the
button to add a custom service. This will
open a form where you can enter the port
forwarding information.
Name/Service Name – This is the
name of the program you are port
forwarding for. The name is only for
you to easily recognize it in a list.
Protocol – Your options are TCP,
UDP, and TCP/UDP. Refer to the
program you are forwarding the
port for to see what option you should choose.
External Starting Port – This is the first port in the range of ports that you want to open.
External Ending Port – This is the last port in the range of ports that you want to open. If
you are only opening one port, enter the same port into this field.
Check the box that uses the same port range for the Internal ports, or fill out the same
information for the Internal port fields.
Internal IP address – This is the IP address for the computer that you want to open the
port for. To find out the IP address for the device, follow this guide for PC or this
guide for Mac OS X.
Step 3: Save or Apply the rule. Your router will process for a few
moments, and then the changes will be applied. Your program will
now be able to access the open port for the computer you
specified.
COMPUTER SYSTEMS SERVICING
K to 12 Technology and Livelihood Education
Part 4: Blocking Websites
Step 1: Open the Block Sites menu. This can be
found in the Security or Parental Controls section of
the configuration menu. You can block sites from
being accessed by any device on your network,
though you can allow specific devices to access
them. You can also set a schedule for the blocks,
which is especially useful for homework time or
when you need to focus on work.
Step 2: Add a site to the block list. Your
options will change depending on the
router you are using. Some routers allow
you to block keywords as well as specific
sites. Add what you want to block to the
list.
Step 3: Allow trusted computers to view
blocked sites. You can check a box to
allow trusted IP addresses to view
blocked sites. This can be useful for
parents who still want access to the sites
that they’ve blocked for their kids.
Once you’ve checked the box,
add it the IP addresses you want
to bypass the blocks. This
guide will tell you how to find
your IP address.
COMPUTER SYSTEMS SERVICING
K to 12 Technology and Livelihood Education
Step 4: Set your block schedule. This
may be in a separate menu from the
block list. You can select which days of
the week you want the block to take
effect, as well as the time of day that it
is implemented. Once you are done,
click the Apply button.
Using Windows Firewall with Advanced Security
Windows Firewall with
Advanced Security
Windows
Firewall with Advanced
Security is a
management snap-in
for the Windows
Firewall from which you
COMPUTER SYSTEMS SERVICING
K to 12 Technology and Livelihood Education
can control in a very detailed way, all the rules and exceptions that govern how the Windows
Firewall works.
In order to access it, you need to open the Windows Firewall as shown in the previous
lesson and then click or tap the “Advanced settings” link on the column on the left.
“Windows Firewall with
Advanced Security” is now
open. This snap-in looks
big and scary at first, and
for good reason. This is
where Windows Firewall
stores all its rules at a very
detailed level. What we
have seen in the previous
lesson is only a limited but
user-friendly view of the
rules that govern its
functioning. This is where
you get dirty and edit any
parameter, no matter how
small, for any rule and
exception
Understanding Inbound, Outbound & Connection Security Rules
In Windows Firewall with Advanced Security you will encounter three important types
of rules:
Inbound rules – they apply to traffic that is coming from the network or the Internet to your
Windows computer or device. For example, if you are downloading a file through BitTorrent,
the download of that file is filtered through an inbound rule.
Outbound rules – these rules apply to traffic that is originating from your computer and going
to the network and the Internet. For example, your request to load the How-To Geek website
in your web browser is outbound traffic and it is filtered through an outbound rule. When the
website is downloaded and loaded by your browser, this is inbound traffic.
Connection security rules –less common rules that are used to secure the traffic between two
specific computers while it crosses the network. This type of rule is used in very controlled
environments with special security requirements. Unlike inbound and outbound rules which
are applied only to your computer or device, connection security rules require both computers
involved in the communication to have the same rules applied.
All the rules can be configured so that they are specific to certain computers, user
accounts, programs, apps, services, ports, protocols, or network adapters.
COMPUTER SYSTEMS SERVICING
K to 12 Technology and Livelihood Education
You can display the rules of a certain type by selecting the appropriate category in the
column on the left.
You
will see lots of inbound and outbound rules. Some rules will have a green checkmark near their
name while others will have a gray one. The rules with the green checkmark are enabled,
meaning that they are used by Windows Firewall. Those with a gray checkmark are disabled
and they are not used by Windows Firewall.
Windows Firewall rules have the following parameters that can be edited:
Name – the name of the rule you are viewing.
Group – the group the rule belongs to. Generally, the group describes the app or the Windows
feature the rule belongs to. For example, rules that apply to a specific app or program will have
the app/program name as the group. Rules that are related to the same networking feature,
e.g. File and Printer Sharing, will have as a group name the feature they relate to.
Profile – the network location/profile the rule is applied to: private, public, or domain (for
business networks with network domains).
Enabled – it tells you whether the rule is enabled and applied by Windows Firewall or not.
Action – the action can “Allow” or “Block” based on what the rule is supposed to do.
Override – tells you whether that rule overrides an existing block rule. By default, all rules
should have the value “No” for this parameter.
Program – the desktop program the rule applies to.
Local address – tells you whether the rule is applied only when your computer has a specific IP
address or not.
Remote address – tells you whether the rule is applied only when devices with specific IP
addresses are connected or not.
Protocol – shares the network protocols for which the rule is applied.
COMPUTER SYSTEMS SERVICING
K to 12 Technology and Livelihood Education
Local port – tells you whether the rule is applied for connections made on specific local ports
or not.
Remote port – tells you whether the rule is applied for connections made on specific remote
ports or not.
Authorized users – the user accounts for which the rule is applied (for inbound rules only).
Authorized computers – computers for which the rule is applied.
Authorized local principals – the user accounts for which the rule is applied (for outbound
rules only).
Local user owner – the user account which is set as the owner/creator of the rule.
Application package – this applies only to apps from the Windows Store and it shares the
package name of the app the rule applies to.
What Can Be Monitored from the Windows Firewall with Advanced Security
Beneath the three types of rules mentioned earlier, you will find a section named
“Monitoring.” If you expand it, you can view the active firewall rules, the active connection
security rules, and view the active security associations.
COMPUTER SYSTEMS SERVICING
K to 12 Technology and Livelihood Education
A security association is something that most of us will never use. This is the information
maintained about a secure encrypted channel on the local computer or device, so that this
information can be used for future network traffic to a specific remote computer or device.
Here you can view which peers are currently connected to your computer and which protection
suite was used by Windows to form the security association.
How to Manage Existing Windows Firewall Rules
The first thing you should keep in mind when working with the rules that are built into
the Windows Firewall is that it is better to disable a rule than delete it. In case you do
something ill-advised, then it is very easy to repair everything by re-enabling disabled rules.
Rules which get deleted cannot be recovered unless you restore all the Windows Firewall
settings to their defaults.
To disable a rule, first select it and then press “Disable Rule” on the column on the right.
COMPUTER SYSTEMS SERVICING
K to 12 Technology and Livelihood Education
Alternatively, you can also right click on a rule and select “Disable Rule.”
If you want to edit a rule and the way it works, you can do so by double-clicking on it,
selecting it, and then pressing “Properties” in the column on the right or right-clicking on it and
selecting “Properties.”
All the parameters we have mentioned earlier in this lesson can be modified in the
“Properties” window of that rule.
COMPUTER SYSTEMS SERVICING
K to 12 Technology and Livelihood Education
When you are done making your changes, don’t forget to press “OK,” so that they are
applied.
How to Create an Outbound Rule for the Windows Firewall
Creating rules in Windows Firewall with Advanced Security is easier than you
would think and it involves using a friendly wizard. To illustrate, let’s create an
outbound rule that blocks access to the network and the Internet for Skype, only
when you are connected to untrusted public networks.
To do this, go to “Outbound Rules” and press “New Rule” in the column on
the right.
COMPUTER SYSTEMS SERVICING
K to 12 Technology and Livelihood Education
This opens the “New Outbound Rule Wizard,” where you will create the new
rule in just a couple of steps. First, you are asked to select the type of rule you want
to create.
Your choices are:
Program – the rule applies to a specific program
Port – the rule applies to the network traffic that is performed through a specific
port
Predefined – rule that controls the connections performed by a specific Windows
service or feature
Custom – a custom rule that can block both programs and ports or a specific
combination of both.
For our example, we have selected “Program” and pressed “Next.”
Depending on what you have chosen at the previous step, you are now asked
to select the program or the ports that you want to add to the rule.
For our example, we have selected the executable of the program that we
want to block – Skype.exe. When you’ve finished setting things up, press “Next.”
COMPUTER SYSTEMS SERVICING
K to 12 Technology and Livelihood Education
Next, you specify the action that should be taken:
Allow the connection – this includes both secure and insecure connections
Allow the connection if it is secure – the connection is allowed only if it is made
through a secure channel. You can specify the kind of authentication and
encryption you want applied by pressing “Customize”
Block the connection – blocks the connection, whether it is secure or not
For our example we have selected “Block the connection” and pressed “Next.”
COMPUTER SYSTEMS SERVICING
K to 12 Technology and Livelihood Education
Now you are asked to select when the rule applies. This means the network
location when the rule is applied:
Domain – the rule is applied only when the computer is connected to a network
domain
Private – the rule is applied only when the computer is connected to trusted
private networks
Public – the rule is applied only when the computer is connected to untrusted
public networks
For our example we have chosen “Public” because we wanted to block access only
when the computer is connected to untrusted public networks.
When done making your choice, press “Next.”
You are asked to
enter a name and a description for the newly created rule. Please don’t take the
easy way out when you do this. Write something that is very descriptive so that you
can understand what’s up with this rule later, when you need to edit the Windows
Firewall rules.
Press “Finish” and the rule is created and used by the Windows Firewall.
COMPUTER SYSTEMS SERVICING
K to 12 Technology and Livelihood Education
How to Create an Inbound Rule for the Windows Firewall
In Windows Firewall with Advanced Security, go to “Inbound Rules” and press
“New Rule” in the column on the right.
COMPUTER SYSTEMS SERVICING
K to 12 Technology and Livelihood Education
The “New Inbound Rule Wizard” is started. The options it displays are almost
the same as the “New Outbound Rule Wizard” so we won’t explain everything again.
We will provide more detail only where it makes sense.
To explain, we have created a rule which blocks all inbound traffic made using the
TCP protocol on the port 30770. At the first step we selected “Program” and pressed
“Next.”
Now we are asked to select the protocol for which the rule applies and the
port. The choices for protocols are TCP and UDP. If you want a rule that applies to
both, you need to create two rules, one for each protocol.
Then, we had the choice to block all ports or only specific ones. We selected
“Specific local ports”, entered “30770,” and pressed “Next.”
COMPUTER SYSTEMS SERVICING
K to 12 Technology and Livelihood Education
Now you are asked to select what action to take when a connection matches the
conditions specified earlier. For our example, we have chosen “Block the connection” and
pressed “Next.”
COMPUTER SYSTEMS SERVICING
K to 12 Technology and Livelihood Education
Now you have to select the network locations for which the rule applies.
Since we wanted to block all TCP traffic on port 30770, we selected all three
locations and pressed “Next.”
Finally, enter the name and the description for the newly created rule and press
“Finish.”
The rule has been created and it is now used by the Windows Firewall.
COMPUTER SYSTEMS SERVICING
K to 12 Technology and Livelihood Education
How to Restore Windows Firewall to its Defaults
If you have fiddled too much with the rules in Windows Firewall and things have started
to work incorrectly, you can easily undo all your settings and restore Windows Firewall to its
defaults. This can be done only for an administrator account.
To do this, open the Windows Firewall and from the left column, click or tap “Restore defaults.”
You are now informed of what this resetting will do, when you’re ready, press “Reset
defaults.”
COMPUTER SYSTEMS SERVICING
K to 12 Technology and Livelihood Education
You are asked to confirm that you are okay to go ahead with the reset.
You are back to the “Windows Firewall” window. All its settings have been reset to the
defaults as if your Windows installation were brand new. You can now reconfigure its settings
from scratch and hopefully solve your problems.
COMPUTER SYSTEMS SERVICING
K to 12 Technology and Livelihood Education
Congratulations!
You did a great job! Rest and relax while then
move on to the next lesson. Good Luck!
REFERENCES
https://www.deped.gov.ph/wp-content/uploads/2019/01/Computer-Systems-Se
rvicing-NC-II-CG.pdf
https://tesda.gov.ph/Download/Training_Regulations?Searchcat=Training%20Re
gulations
https://pyramidsolutions.com/network-connectivity/blog-nc/what-is-network-connectiv
ity/
https://www.wikihow.com/Configure-Local-Network-Area
https://www.wikihow.com/Configure-a-Router
https://www.howtogeek.com/school/windows-network-security/lesson5/
COMPUTER SYSTEMS SERVICING
K to 12 Technology and Livelihood Education
Post-Test: How Much Have You Learned?
POST-TEST
I. DIRECTIONS: Arrange the following procedures. Label your answer in ascending order.
A. Configuring a Router.
______ Assign the router a new username and password.
______ Connect your router to your computer and your modem.
______ Enter in your router’s address.
______ Enter in your username and password.
______ Open a web browser.
______ Reset your router if you can’t access it.
B. Setting up Wireless Network.
______ Assign the router a new username and password.
______ Connect your router to your computer and your modem.
______ Enter in your router’s address.
______ Enter in your username and password.
______ Open a web browser.
______ Reset your router if you can’t access it.
II. IDENTIFICATION: Identify what is being asked. Choose your answer in the box provided.
1. Computers for which the rule is applied.
2. It “Allow” or “Block” based on what the rule is supposed to do.
3. Rule that controls the connections performed by a specific Windows service or feature.
4. Rule that controls the connections performed by a specific Windows service or feature.
5. Shares the network protocols for which the rule is applied.
6. Tells the user whether that rule overrides an existing block rule. By default, all rules should
have the value “No” for this parameter.
7. Tells the user whether the rule is applied for connections made on specific local ports or
not.
8. Tells the user whether the rule is applied for connections made on specific remote ports or
not.
COMPUTER SYSTEMS SERVICING
K to 12 Technology and Livelihood Education
9. Tells the user whether the rule is applied only when devices with specific IP addresses are
connected or not.
10. Tells the user whether the rule is applied only when your computer has a specific IP
address or not.
11. tells the user whether the rule is enabled and applied by Windows Firewall or not.
12. The network location/profile the rule is applied to: private, public, or domain (for business
networks with network domains).
13. The rule applies to a specific program.
14. The rule applies to the network traffic that is performed through a specific port.
15. The rule is applied only when the computer is connected to a network domain.
16. The rule is applied only when the computer is connected to trusted private networks.
17. The rule is applied only when the computer is connected to untrusted public networks.
18. The user account which is set as the owner/creator of the rule.
19. The user accounts for which the rule is applied (for inbound rules only).
20. This applies only to apps from the Windows Store and it shares the package name of the
app the rule applies to.
Action Application package Authorized computers Authorized users
Domain Enabled Local address Local port
Local user owner Override Port Predefined
Predefined Private Profile Program
Protocol Public Remote address Remote port
COMPUTER SYSTEMS SERVICING
K to 12 Technology and Livelihood Education
You might also like
- PassThru API 1Document83 pagesPassThru API 1andaposa9No ratings yet
- COC 2 Module 2.1Document5 pagesCOC 2 Module 2.1sanpascualmikyla14No ratings yet
- 5the Sem Computer Network Lab ManualDocument68 pages5the Sem Computer Network Lab ManualVishal Sharma0% (1)
- 1KW-61433-0 Increasing ProductivityNetworking Instruments AppsBrief 070518Document14 pages1KW-61433-0 Increasing ProductivityNetworking Instruments AppsBrief 070518termmmNo ratings yet
- 657ac38c7eb2clab9 CCN 2023Document13 pages657ac38c7eb2clab9 CCN 2023Muhammad Ali RajarNo ratings yet
- Content Standards: LO 3. Set Router/wi-Fi/wireless Access Point/repeater ConfigurationDocument9 pagesContent Standards: LO 3. Set Router/wi-Fi/wireless Access Point/repeater ConfigurationRusty Ugay LumbresNo ratings yet
- Lab9 CCN 2023Document18 pagesLab9 CCN 2023Muhammad Ali RajarNo ratings yet
- 5707e9cc972d3 Wwb6 Quickstart Guide EnglishDocument8 pages5707e9cc972d3 Wwb6 Quickstart Guide EnglishRosalino Castillejos PinedaNo ratings yet
- Ensure The Configuration Conforms To The Manufacturer's Instructions/manualDocument19 pagesEnsure The Configuration Conforms To The Manufacturer's Instructions/manualSau Jr Sy CairasNo ratings yet
- How To Configure Your PC To A Local Area Network: StepsDocument13 pagesHow To Configure Your PC To A Local Area Network: StepsEliad RMndemeNo ratings yet
- Networking/Port Forwarding/DDNS Overview GuideDocument13 pagesNetworking/Port Forwarding/DDNS Overview GuideBeqir CubolliNo ratings yet
- Mwnapr-1 QigDocument6 pagesMwnapr-1 QigmikeNo ratings yet
- -Repeater: 展开 尺 寸: 3 6 0 x 2 4 0 mm 成品 尺 寸: 1 2 0 x 9 0 mmDocument2 pages-Repeater: 展开 尺 寸: 3 6 0 x 2 4 0 mm 成品 尺 寸: 1 2 0 x 9 0 mmhelmoz100% (1)
- DONETLE ICT 10 Q4 Week 1 8 Additional Topics - RemovedDocument10 pagesDONETLE ICT 10 Q4 Week 1 8 Additional Topics - Removedallenformentera9No ratings yet
- WirelessinstallationDocument26 pagesWirelessinstallationFuad IsmailNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks-2 Practical-1Document6 pagesComputer Networks-2 Practical-1vaibhav vermaNo ratings yet
- LO 2 OkDocument14 pagesLO 2 OkEdgar BatistianaNo ratings yet
- Lab9 CCN 2023Document17 pagesLab9 CCN 2023Muhammad Ali RajarNo ratings yet
- C46 Exp4Document10 pagesC46 Exp4pravintp123No ratings yet
- Module 12-13 Css34 q2 FinalDocument4 pagesModule 12-13 Css34 q2 Finaljonathan labajoNo ratings yet
- 7.5.1 LabDocument6 pages7.5.1 LabLHNo ratings yet
- Ict 4Document16 pagesIct 4jerry.mejiaNo ratings yet
- Guided Learning Activity Kit: Sptve-Computer System ServicingDocument25 pagesGuided Learning Activity Kit: Sptve-Computer System ServicingSam PaglingayenNo ratings yet
- TLE-CSS Grade9 Module Q4W7Document4 pagesTLE-CSS Grade9 Module Q4W7gela vynxNo ratings yet
- Airlink101 Access Point - Ap431wDocument42 pagesAirlink101 Access Point - Ap431wJim ParentNo ratings yet
- LESSON 4 Peer To Peer NetworkDocument4 pagesLESSON 4 Peer To Peer NetworkReign Jay FerrerNo ratings yet
- Q2 MODULE6 G12 CSS NCII Luciano Millan NHSDocument11 pagesQ2 MODULE6 G12 CSS NCII Luciano Millan NHSALBERT ALGONESNo ratings yet
- Qig Di-604Document12 pagesQig Di-604Dark _No ratings yet
- Jignesh VarmaDocument25 pagesJignesh VarmaNarappaNo ratings yet
- User Manual: MAN-525503/525534-UM-0413-01Document26 pagesUser Manual: MAN-525503/525534-UM-0413-01Anthony DavisNo ratings yet
- WS-WN523: Wireless Extender&RouterDocument21 pagesWS-WN523: Wireless Extender&RouterAlka389No ratings yet
- Nov. 7 G10Document56 pagesNov. 7 G10Honey Diana MejiaNo ratings yet
- 9IS44077 LanAdapter GB 4-07 - 2Document11 pages9IS44077 LanAdapter GB 4-07 - 2MARIVEL BASANo ratings yet
- Experiment 16Document3 pagesExperiment 16rapraptapayoonNo ratings yet
- p310 v3.50 QuickStartGuideDocument5 pagesp310 v3.50 QuickStartGuideTomaž BajželjNo ratings yet
- BR-6428nS V5: Quick Installation GuideDocument19 pagesBR-6428nS V5: Quick Installation GuideAggeliki KosteliNo ratings yet
- 11n USB Dongle ManualDocument20 pages11n USB Dongle ManualgroovychickNo ratings yet
- Lab - Configure Firewall SettingsDocument3 pagesLab - Configure Firewall SettingsSgr Eka 13No ratings yet
- Q4 Module1-2 CSS 12Document10 pagesQ4 Module1-2 CSS 12Ched Augustus AranNo ratings yet
- Wireless Adapter Quick Installation Guide: 1.software and Driver SetupDocument2 pagesWireless Adapter Quick Installation Guide: 1.software and Driver SetupnitinfutaneNo ratings yet
- 1.3.6 Packet Tracer Build A Home Network Answer KeyDocument9 pages1.3.6 Packet Tracer Build A Home Network Answer KeySasha MarianchukNo ratings yet
- Manual de Usuario (Airlink) PDFDocument41 pagesManual de Usuario (Airlink) PDFLic Rick JohnsonNo ratings yet
- 6.1.4.8 Lab - Configure Firewall SettingsDocument3 pages6.1.4.8 Lab - Configure Firewall SettingsMaria Jiminian0% (1)
- Troubleshooting Network and CommunicationDocument14 pagesTroubleshooting Network and CommunicationnetpazNo ratings yet
- Las Fourth Q Wireless Config 2023 2024Document22 pagesLas Fourth Q Wireless Config 2023 2024Nia Kristel Salas AdralesNo ratings yet
- SP912G ManualDocument11 pagesSP912G ManualesilvaopNo ratings yet
- (WR Net 018 CC) Manual For DHCPDocument8 pages(WR Net 018 CC) Manual For DHCPKhyle Laurenz DuroNo ratings yet
- DI-804HV: Check Your Package ContentsDocument12 pagesDI-804HV: Check Your Package ContentsJorge Manuel Ramirez GianellaNo ratings yet
- InstructionsDocument10 pagesInstructionsapi-247087458No ratings yet
- Configuring Network Connections For Windows 10Document32 pagesConfiguring Network Connections For Windows 10Joseph ButawanNo ratings yet
- Ap411w ManualDocument32 pagesAp411w ManualrogercomNo ratings yet
- Lab 7 - Create A Simple NetworkDocument14 pagesLab 7 - Create A Simple NetworkNurul afiqah MansorNo ratings yet
- Wireless Communication FileDocument38 pagesWireless Communication FilerishabhNo ratings yet
- Computer Systems Servicing 10 Week3-4Document10 pagesComputer Systems Servicing 10 Week3-4jf2ralba100% (1)
- Wireless Configuration: Connect The Router On A Wired LAN EnvironmentDocument16 pagesWireless Configuration: Connect The Router On A Wired LAN Environmentjun arvie100% (1)
- Configure Wide Area Network (Access Point)Document8 pagesConfigure Wide Area Network (Access Point)Lady Christianne BucsitNo ratings yet
- Hacking : A Comprehensive, Step-By-Step Guide to Techniques and Strategies to Learn Ethical Hacking with Practical Examples to Computer Hacking, Wireless Network, Cybersecurity and Penetration TestingFrom EverandHacking : A Comprehensive, Step-By-Step Guide to Techniques and Strategies to Learn Ethical Hacking with Practical Examples to Computer Hacking, Wireless Network, Cybersecurity and Penetration TestingNo ratings yet
- LO 1 CSS OkDocument46 pagesLO 1 CSS OkEdgar BatistianaNo ratings yet
- Lo 5 CSS OkDocument17 pagesLo 5 CSS OkEdgar BatistianaNo ratings yet
- Comp. Programming Week 1&2Document23 pagesComp. Programming Week 1&2Edgar BatistianaNo ratings yet
- Comp. Programming Week 5&6Document11 pagesComp. Programming Week 5&6Edgar BatistianaNo ratings yet
- Comp. Programming Week 3&4Document19 pagesComp. Programming Week 3&4Edgar BatistianaNo ratings yet
- Comp. Programming Week 7&8Document13 pagesComp. Programming Week 7&8Edgar BatistianaNo ratings yet
- OAW Stellar AP Quick Start Guide R3.0Document2 pagesOAW Stellar AP Quick Start Guide R3.0kirinVAGNo ratings yet
- 01 - Overview of Satellite Systems PDFDocument21 pages01 - Overview of Satellite Systems PDFAhmed RiyadNo ratings yet
- CMSE LG v2 PDFDocument222 pagesCMSE LG v2 PDFRakesh KumarNo ratings yet
- 4214514-02 - Technical Information - TopTronic E GW Modbus TCP-RS485Document24 pages4214514-02 - Technical Information - TopTronic E GW Modbus TCP-RS485Sima Catalin-IonutNo ratings yet
- Alepo AAA Server Selected To Launch 4G Wireless Broadband in AngolaDocument2 pagesAlepo AAA Server Selected To Launch 4G Wireless Broadband in AngolaAlepoNo ratings yet
- Compal LA-9241PDocument56 pagesCompal LA-9241Pn nnNo ratings yet
- p188 BluetoothDocument12 pagesp188 Bluetoothjnanesh582No ratings yet
- SD WAN Over HSM 5.0.cleanedDocument12 pagesSD WAN Over HSM 5.0.cleanedHugo GarciaNo ratings yet
- Consul Tutorial PDFDocument53 pagesConsul Tutorial PDFvvNo ratings yet
- FormaxDocument3 pagesFormaxajabsinghchauhan760No ratings yet
- Media Platform User GuideDocument207 pagesMedia Platform User Guidefrangky.rengkungNo ratings yet
- Peachpit Press Managing Apple Devices 3rd Edition 0134301854 PDFDocument737 pagesPeachpit Press Managing Apple Devices 3rd Edition 0134301854 PDFMiguel LopezNo ratings yet
- Apxverr20x CDocument2 pagesApxverr20x CJCARLOS COLQUENo ratings yet
- Fast - Lane F5 NETWORKS - CONFIGURING BIG IP ADVANCED WAFDocument5 pagesFast - Lane F5 NETWORKS - CONFIGURING BIG IP ADVANCED WAFGuido BaroncelliNo ratings yet
- Pegasus Spyware AnalysisDocument35 pagesPegasus Spyware AnalysisRIJU GHOSHNo ratings yet
- Simatic S5 318-3UA11 Central Controller Interface Module: ManualDocument37 pagesSimatic S5 318-3UA11 Central Controller Interface Module: ManualAutomacao16No ratings yet
- Cnav Man 017.9 (C Nav3050 User Guide)Document186 pagesCnav Man 017.9 (C Nav3050 User Guide)Mohammed HassanNo ratings yet
- SEL-3010 Event Messenger: Features, Benefits, and ApplicationsDocument20 pagesSEL-3010 Event Messenger: Features, Benefits, and ApplicationsEmmanuel EntzanaNo ratings yet
- FortiOS 7.0 PortsDocument6 pagesFortiOS 7.0 Portsvedant vedNo ratings yet
- VodafoneDocument62 pagesVodafoneAbdul Manaf P MNo ratings yet
- Complete Umts Call FlowDocument4 pagesComplete Umts Call FlowRahim KhanNo ratings yet
- FirstAlert FA168CPS v7 Programming ManualDocument40 pagesFirstAlert FA168CPS v7 Programming ManualjsbatchNo ratings yet
- Angle Modulation SystemsDocument35 pagesAngle Modulation SystemsseenudesignNo ratings yet
- M80 User ManualDocument1 pageM80 User ManualabcNo ratings yet
- Running Head: Security Attack On Systems and Web Servers 1Document8 pagesRunning Head: Security Attack On Systems and Web Servers 1kim kimNo ratings yet
- A Design of Triangular Sierpinski Gasket Fractal AntennaDocument3 pagesA Design of Triangular Sierpinski Gasket Fractal Antennasuman uppalaNo ratings yet
- GSM Repair / Maint Policy-Telecom / Allied EqptDocument9 pagesGSM Repair / Maint Policy-Telecom / Allied EqptImran AzizNo ratings yet
- What Is Cybersecurity and NetworkingDocument4 pagesWhat Is Cybersecurity and NetworkingFilipa MirandaNo ratings yet