Professional Documents
Culture Documents
5constant Current
5constant Current
Uploaded by
arihant122Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Power Supplies & RegulatorsDocument15 pagesPower Supplies & RegulatorsNarasimha Murthy YayavaramNo ratings yet
- Active Power Factor Correction Technique For Single Phase Full Bridge RectifierDocument6 pagesActive Power Factor Correction Technique For Single Phase Full Bridge RectifierAnand KumarNo ratings yet
- VGScienta Pressure MeasurementDocument16 pagesVGScienta Pressure Measurementarihant122No ratings yet
- Chapter 6-Voltage RegulatorDocument36 pagesChapter 6-Voltage RegulatorSumaya ShinosNo ratings yet
- Potentiometers: Nstrument Ransformers ANDDocument26 pagesPotentiometers: Nstrument Ransformers ANDDIVYA PRASOONA CNo ratings yet
- List of ComponentsDocument13 pagesList of ComponentsBenita AgbagwaraNo ratings yet
- Ntroduction: Unregulated Power Supply - DiagramDocument12 pagesNtroduction: Unregulated Power Supply - DiagramMadhu Mathi ErNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - Power Supply, DC Voltmeter, DC Ammeter SASTRA UniversityDocument25 pagesUnit 4 - Power Supply, DC Voltmeter, DC Ammeter SASTRA UniversitystarNo ratings yet
- HALIDDocument23 pagesHALIDBUKENYA BEEE-2026No ratings yet
- IE Mod 01 PowerSupplyDocument25 pagesIE Mod 01 PowerSupplyRy AnNo ratings yet
- DC Regulated Power SupplyDocument14 pagesDC Regulated Power SupplyMegha Projects100% (2)
- What Is Power Supply?Document11 pagesWhat Is Power Supply?Hlmy HlmyNo ratings yet
- DC Power Supply CircuitDocument7 pagesDC Power Supply CircuitEhtasham Ul HassanNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3 Eng NaderDocument7 pagesExperiment 3 Eng Naderياسر العويطيNo ratings yet
- Switch Mode Power Supply and Switching RegulatorsDocument10 pagesSwitch Mode Power Supply and Switching Regulatorsmarcoms75No ratings yet
- Power SupplyDocument91 pagesPower SupplyshreekadapaNo ratings yet
- Voltage Regulator:: 1. Load Current (IL)Document2 pagesVoltage Regulator:: 1. Load Current (IL)Madhu Bilugali MahadevaswamyNo ratings yet
- Slup 075Document12 pagesSlup 075Gowtham SanampalliNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Switched-Mode Power Supply (SMPS) CircuitsDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Switched-Mode Power Supply (SMPS) Circuits9chand3100% (1)
- 02A Lesson Proper For Week 7Document9 pages02A Lesson Proper For Week 7Maxela CastroNo ratings yet
- Voltage Regulator: Analog ElectronicsDocument46 pagesVoltage Regulator: Analog ElectronicsAkshat SinghNo ratings yet
- ANE 620S Course Notes 2015Document177 pagesANE 620S Course Notes 2015TimothyShapamNo ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between A Current TransformerDocument9 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between A Current TransformerVenkata Suresh MandavaNo ratings yet
- Regulated DC Power SupplyDocument15 pagesRegulated DC Power SupplynalumilanimeNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document18 pagesUnit 4H. ShekharNo ratings yet
- Project On InverterDocument22 pagesProject On InverterSaikat Mitra43% (7)
- Theory of Switched Mode Power SupplyDocument21 pagesTheory of Switched Mode Power Supplyseahate100% (1)
- New Techniques For Measuring Feedback Loop Transfer Functions in Current Mode ConvertersDocument15 pagesNew Techniques For Measuring Feedback Loop Transfer Functions in Current Mode Convertersvikaspawar2012No ratings yet
- First Quadrant Single Phase Ac To DC Converter Semiconverter Separately Excited DC MotorDocument9 pagesFirst Quadrant Single Phase Ac To DC Converter Semiconverter Separately Excited DC MotorzaidNo ratings yet
- Basic Switching CircuitsDocument19 pagesBasic Switching Circuitsash1968No ratings yet
- DocuDocument49 pagesDocutechmindzNo ratings yet
- Question BankDocument11 pagesQuestion BankRohini MukunthanNo ratings yet
- One Cycle ControlDocument9 pagesOne Cycle ControlNithin SebastianNo ratings yet
- EEEN40197 Lecture Notes AJF PDFDocument46 pagesEEEN40197 Lecture Notes AJF PDFAnonymous gVhwdk9ui9No ratings yet
- Arc Welding Power SourcesDocument34 pagesArc Welding Power SourcesNatasa ZdravkovskaNo ratings yet
- Lab 2 Buck ConverterDocument3 pagesLab 2 Buck ConverterShah VinodNo ratings yet
- Sem ReportDocument38 pagesSem ReportSafalsha BabuNo ratings yet
- Power SupplyDocument48 pagesPower Supplyayam burritoNo ratings yet
- Power Pack: Constant Power Supply Kartik Kumar 1887021Document14 pagesPower Pack: Constant Power Supply Kartik Kumar 1887021Lakshay BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Converter 4 20maDocument19 pagesConverter 4 20mabnurkholis100% (1)
- Basic Electrical Engineering Interview Questions and AnswersDocument14 pagesBasic Electrical Engineering Interview Questions and AnswersDanish AliNo ratings yet
- KMT#4Document5 pagesKMT#4RomanHerreraNo ratings yet
- How An Smps Works: Rectifier StageDocument7 pagesHow An Smps Works: Rectifier StageImran AshrafNo ratings yet
- How An SMPS WorksDocument7 pagesHow An SMPS WorksĐorđe PopovićNo ratings yet
- Report On Power SupplyDocument14 pagesReport On Power SupplyBhavesh MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Topic - Voltage RegulatorDocument43 pagesTopic - Voltage RegulatorAryan Singh JadaunNo ratings yet
- Power Factor Correction Using Boost ConverterDocument24 pagesPower Factor Correction Using Boost Converterফারহানা আক্তার গল্পNo ratings yet
- Half Wave and Full Wave RectifierDocument10 pagesHalf Wave and Full Wave RectifiersunilsathishNo ratings yet
- Study and Design, Simulation of PWM Based Buck Converter For Low Power ApplicationDocument17 pagesStudy and Design, Simulation of PWM Based Buck Converter For Low Power ApplicationIOSRjournalNo ratings yet
- Power Supplies: Transducers AC and DC Diodes CapacitorsDocument10 pagesPower Supplies: Transducers AC and DC Diodes CapacitorsJose C. Lita JrNo ratings yet
- KTVR Knowledge Park For: Engineering and TechnologyDocument23 pagesKTVR Knowledge Park For: Engineering and Technologyshiva shakthyNo ratings yet
- DC TransformerDocument25 pagesDC TransformerUmair100% (1)
- 7.13 Power Supply Control Input Voltage and Duty Ratio.: Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 07Document12 pages7.13 Power Supply Control Input Voltage and Duty Ratio.: Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 07Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Pdemarco 4Document4 pagesPdemarco 4Paul DeMarcoNo ratings yet
- Industrial Electronics 1st ExamDocument34 pagesIndustrial Electronics 1st ExamJomar Bonje100% (1)
- SMPS:-: Switched-Mode Power Supply (Switching-Mode Power Supply, SMPS, or Simplyswitcher) Is An ElectronicDocument4 pagesSMPS:-: Switched-Mode Power Supply (Switching-Mode Power Supply, SMPS, or Simplyswitcher) Is An ElectronicSumit SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Instrument TransformersDocument30 pagesChapter 2 Instrument TransformersBharat ThapaNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- STEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10From EverandSTEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10No ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Matlab For Engineers Applications in Control Electrical Engineering It and Robotics 7526Document524 pagesMatlab For Engineers Applications in Control Electrical Engineering It and Robotics 7526hpnguyenthanh007100% (1)
- Instrumentation Engineers HandbookDocument314 pagesInstrumentation Engineers HandbookMaresdaSatria100% (1)
- LV FundamentalsDocument165 pagesLV Fundamentalsmacarong272No ratings yet
- EE271 ProjectDocument29 pagesEE271 ProjectQuang MạnhNo ratings yet
- Sony Vaio PCG-K13 Quanta JE2Document38 pagesSony Vaio PCG-K13 Quanta JE2luckyman7No ratings yet
- Data Sheet: BC237 BC237BDocument8 pagesData Sheet: BC237 BC237Be178anangNo ratings yet
- Datasheet LTC1286 FsDocument25 pagesDatasheet LTC1286 FsRamonNo ratings yet
- Ultra-Dense Storage Server Increased VersatilityDocument2 pagesUltra-Dense Storage Server Increased VersatilityBa VuVanNo ratings yet
- PLE-1ME Mixer Amplifier DatasheetDocument4 pagesPLE-1ME Mixer Amplifier DatasheetNiladri GhoshNo ratings yet
- Maxim Integrated - AutomotiveDocument32 pagesMaxim Integrated - AutomotivepHysiXNo ratings yet
- Specs Lenovo ThinkCentre M82Document27 pagesSpecs Lenovo ThinkCentre M82nur fuadNo ratings yet
- Remote Power ControllerDocument2 pagesRemote Power Controllerdavid reyesNo ratings yet
- Sams8 5388 LG 32LC7DCDocument12 pagesSams8 5388 LG 32LC7DCsvctechNo ratings yet
- Fir Filter DesignDocument4 pagesFir Filter DesignRamanathan SunderNo ratings yet
- Fire Fighting Robot Using Arduino UNODocument6 pagesFire Fighting Robot Using Arduino UNODarshan ParmarNo ratings yet
- At Mega 8535Document321 pagesAt Mega 8535nanggrianaNo ratings yet
- DEVICE Exp 4 StudentDocument4 pagesDEVICE Exp 4 StudentTouhid AlamNo ratings yet
- X12D - X15D: 1,000 Watt Active LoudspeakerDocument16 pagesX12D - X15D: 1,000 Watt Active LoudspeakerHanafy GarengNo ratings yet
- Samsung LA40C550 ManualDocument44 pagesSamsung LA40C550 ManualOmer MehdiNo ratings yet
- 7576xxx Rev 0909Document1 page7576xxx Rev 0909pandavision76No ratings yet
- 03 Electrical NotesDocument27 pages03 Electrical NotesizzazackNo ratings yet
- Vb-Audio Cable: Configuring Vb-Cable System Settings Hifi-Cable & Asio BridgeDocument8 pagesVb-Audio Cable: Configuring Vb-Cable System Settings Hifi-Cable & Asio BridgeNatanael ManriqueNo ratings yet
- TASK SHEET Study GuideDocument10 pagesTASK SHEET Study GuideJohn Raymund MabansayNo ratings yet
- Obe Curriculum For The Course: RGPV (Diploma Wing) BhopalDocument22 pagesObe Curriculum For The Course: RGPV (Diploma Wing) BhopalHarshit Sahu CS-26No ratings yet
- Engineering Mini ProjectDocument8 pagesEngineering Mini ProjectnkniteshNo ratings yet
- TL 3845Document12 pagesTL 3845sarad43No ratings yet
- Non-Linear Junction Detector: User ManualDocument35 pagesNon-Linear Junction Detector: User Manualarnes_88No ratings yet
- Manual Sony Vaio Fit SOSVF15213CBWDocument450 pagesManual Sony Vaio Fit SOSVF15213CBWramenzoniNo ratings yet
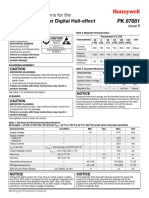
- Honeywell Sensing Bipolar Digital Hall Effect Sensor Ic Installation Instructions Ss41 Pk87881 6 enDocument3 pagesHoneywell Sensing Bipolar Digital Hall Effect Sensor Ic Installation Instructions Ss41 Pk87881 6 enMeghamala MandalNo ratings yet
- Installation Manual: VPN BoxDocument4 pagesInstallation Manual: VPN BoxilhgsygbNo ratings yet
- M.Tech (Microwave & Communication Engineering) PVP17Document2 pagesM.Tech (Microwave & Communication Engineering) PVP17kprk414No ratings yet
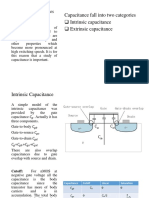
- Capacitance Fall Into Two Categories Intrinsic Capacitance Extrinsic CapacitanceDocument10 pagesCapacitance Fall Into Two Categories Intrinsic Capacitance Extrinsic Capacitancewajid aliNo ratings yet
5constant Current
5constant Current
Uploaded by
arihant122Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
5constant Current
5constant Current
Uploaded by
arihant122Copyright:
Available Formats
Constant Current Power Supplies
Theory
A constant current supply functions as a regulated current source. It requires a change in thinking, to look at a supply that puts out a constant flow (current) regardless of the pressure (voltage). A Few Basics A theoretically perfect voltage generator would have zero internal impedance. A perfect current equivalent would have infinite internal impedance. If the source internal resistance, Rg, is very low when compared to the load, then it is said to be stiff and approximates a pure voltage source. Voltage drop across Rg is negligible underload . If Rg is very large compared to the load resistance RL, and the source voltage is increased, a changing load resistance will have very little effect on load current. This is because the load current is mainly determined by the source voltage Eb and the internal resistance Rg and is independent of load resistance. Practically, the situation is valid for RL < Rg/10, where RL is the load resistance in series with Rg. Achieving useful outputs with sources like batteries and resistors is not very practical, but does illustrate which parameters must be controlled in order to build true constant current (and constant voltage) supplies. Practical Supply A constant current power supply can be represented as a four terminal active device. The input represents a DC voltage source for basic current regulators, and it represents AC line voltage for those supplies which are complete with rectifiers and filters. To characterize the supply, definitions must be established. In a practical system, a transformer, rectifier and filter is included in each case in order to produce DC power. The power controller is added after this stage. A constant current power supply consists of a DC power source that drives a series pass transistor which is controlled by a high gain op amp. The feedback signal is obtained from a shunt resistor Rs. In constant voltage the feedback comes from a voltage driver. The pass transistor operates as an emitter follower with a voltage gain of unity. Both the DC power source and transistor can be replaced by a single op amp which has a DC output capability equal to the combination. The resulting circuit can be redrawn in the form of a simple non-inverting op amp. The op amp is considered an ideal amplifier with infinite gain, and infinite input impedance, and amplifies the input voltage er, by the ratio of the feedback and gain resistors. In a constant current supply, the load resistance is the feedback resistor for the op amp. Since the supplies are isolated or floating, the output common can be any point desired. In a constant current supply, the output common is at a slightly different potential than the DC power source negative terminal because of the voltage drop across the shunt, Rs.
K1G1 (s) = K1/sT1 + 1 K2G2 (s) = K2/sT2 + 1 G3 (s) = 1 (for resistive load) H(s) = 1 FIGURE 2.
A constant current supply is a relatively simple loop. The load is part of the loop and loop stability can be affected by the load. The time constant of the power amplifier T2, is very short for fast response. The amplifier transfer function is chosen to provide the dominant pole of the system (T1 is made large), because it is the easiest to control. Open loop gains on the order of 10,000 are necessary to achieve 0.01 percent regulation. Loop stability is a problem. Care must be taken by power supply designers so that the unit meets stability requirements under all normal conditions of line, load and external environment. Linear Scaling Easy
Constant current is a convenient way to build linear scaled systems using potentiometric transducers or position indicators. In a simple example, a 10 turn 1k potentiometer is supplied with a constant 10 mA of current which results in a ten volt output with one volt per turn. This can be read out directly on a DVM (digital voltmeter). By simply changing the current level the calibration can be easily adjusted to any value. This allows voltages directly proportional to degrees, pressure, acceleration, and so on, to be scaled and read directly on meters.
eo = RL + RS er RS iL = eL e e = S = r RL RS RS
Another advantage of constant current is when the transducer is remotely located requiring long leads. Normally, with constant voltage, changes in line resistance would directly affect the
FIGURE 1.
2401 Stanwell Drive Concord, California 94520 Ph: 925/687-4411 or 800/542-3355 Fax: 925/687-3333 www.calex.com Email: sales@calex.com
4/2001
Constant Current Power Supplies
accuracy of the measurement. The voltage across the potentiometer Rp is reduced by the sum of iR1 + iR2 and this will change as the temperature changes. The value of i = Ep/ (R1 +R2) changes as R1 and R2 change, further complicating the problem. Constant current eliminates all of these error components since current through the potentiometer remains constant. Fluctuations in lead resistance between the supply and potentiometer do not affect the results.
For Ei : Ep = Ei - i (R1 + R2) For Ii : EL = iRp FIGURE 3.
Performance Characteristics Output Compliance Output Impedance Automatic Crossover Output Ripple Temperature Coefficient Slew Rate Transient Response Regulator Stability
Constant Current Constant current (adj.) Maximum output voltage High Adjustable voltage limiting RMS current Ripple Change in output current versus temperature Maximum rate of change of output current Current response to step function change in load or reference Subject to loop oscillations if load is too inductive
Constant Voltage Constant voltage (adj.) Maximum output current Low Adjustable current limiting RMS voltage ripple Change in output voltage versus temperature Maximum rate of change of output voltage Voltage response to step function change in load or reference Subject to loop oscillations if load is too capacitive
2401 Stanwell Drive Concord, California 94520 Ph: 925/687-4411 or 800/542-3355 Fax: 925/687-3333 www.calex.com Email: sales@calex.com
4/2001
You might also like
- Power Supplies & RegulatorsDocument15 pagesPower Supplies & RegulatorsNarasimha Murthy YayavaramNo ratings yet
- Active Power Factor Correction Technique For Single Phase Full Bridge RectifierDocument6 pagesActive Power Factor Correction Technique For Single Phase Full Bridge RectifierAnand KumarNo ratings yet
- VGScienta Pressure MeasurementDocument16 pagesVGScienta Pressure Measurementarihant122No ratings yet
- Chapter 6-Voltage RegulatorDocument36 pagesChapter 6-Voltage RegulatorSumaya ShinosNo ratings yet
- Potentiometers: Nstrument Ransformers ANDDocument26 pagesPotentiometers: Nstrument Ransformers ANDDIVYA PRASOONA CNo ratings yet
- List of ComponentsDocument13 pagesList of ComponentsBenita AgbagwaraNo ratings yet
- Ntroduction: Unregulated Power Supply - DiagramDocument12 pagesNtroduction: Unregulated Power Supply - DiagramMadhu Mathi ErNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - Power Supply, DC Voltmeter, DC Ammeter SASTRA UniversityDocument25 pagesUnit 4 - Power Supply, DC Voltmeter, DC Ammeter SASTRA UniversitystarNo ratings yet
- HALIDDocument23 pagesHALIDBUKENYA BEEE-2026No ratings yet
- IE Mod 01 PowerSupplyDocument25 pagesIE Mod 01 PowerSupplyRy AnNo ratings yet
- DC Regulated Power SupplyDocument14 pagesDC Regulated Power SupplyMegha Projects100% (2)
- What Is Power Supply?Document11 pagesWhat Is Power Supply?Hlmy HlmyNo ratings yet
- DC Power Supply CircuitDocument7 pagesDC Power Supply CircuitEhtasham Ul HassanNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3 Eng NaderDocument7 pagesExperiment 3 Eng Naderياسر العويطيNo ratings yet
- Switch Mode Power Supply and Switching RegulatorsDocument10 pagesSwitch Mode Power Supply and Switching Regulatorsmarcoms75No ratings yet
- Power SupplyDocument91 pagesPower SupplyshreekadapaNo ratings yet
- Voltage Regulator:: 1. Load Current (IL)Document2 pagesVoltage Regulator:: 1. Load Current (IL)Madhu Bilugali MahadevaswamyNo ratings yet
- Slup 075Document12 pagesSlup 075Gowtham SanampalliNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Switched-Mode Power Supply (SMPS) CircuitsDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Switched-Mode Power Supply (SMPS) Circuits9chand3100% (1)
- 02A Lesson Proper For Week 7Document9 pages02A Lesson Proper For Week 7Maxela CastroNo ratings yet
- Voltage Regulator: Analog ElectronicsDocument46 pagesVoltage Regulator: Analog ElectronicsAkshat SinghNo ratings yet
- ANE 620S Course Notes 2015Document177 pagesANE 620S Course Notes 2015TimothyShapamNo ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between A Current TransformerDocument9 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between A Current TransformerVenkata Suresh MandavaNo ratings yet
- Regulated DC Power SupplyDocument15 pagesRegulated DC Power SupplynalumilanimeNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document18 pagesUnit 4H. ShekharNo ratings yet
- Project On InverterDocument22 pagesProject On InverterSaikat Mitra43% (7)
- Theory of Switched Mode Power SupplyDocument21 pagesTheory of Switched Mode Power Supplyseahate100% (1)
- New Techniques For Measuring Feedback Loop Transfer Functions in Current Mode ConvertersDocument15 pagesNew Techniques For Measuring Feedback Loop Transfer Functions in Current Mode Convertersvikaspawar2012No ratings yet
- First Quadrant Single Phase Ac To DC Converter Semiconverter Separately Excited DC MotorDocument9 pagesFirst Quadrant Single Phase Ac To DC Converter Semiconverter Separately Excited DC MotorzaidNo ratings yet
- Basic Switching CircuitsDocument19 pagesBasic Switching Circuitsash1968No ratings yet
- DocuDocument49 pagesDocutechmindzNo ratings yet
- Question BankDocument11 pagesQuestion BankRohini MukunthanNo ratings yet
- One Cycle ControlDocument9 pagesOne Cycle ControlNithin SebastianNo ratings yet
- EEEN40197 Lecture Notes AJF PDFDocument46 pagesEEEN40197 Lecture Notes AJF PDFAnonymous gVhwdk9ui9No ratings yet
- Arc Welding Power SourcesDocument34 pagesArc Welding Power SourcesNatasa ZdravkovskaNo ratings yet
- Lab 2 Buck ConverterDocument3 pagesLab 2 Buck ConverterShah VinodNo ratings yet
- Sem ReportDocument38 pagesSem ReportSafalsha BabuNo ratings yet
- Power SupplyDocument48 pagesPower Supplyayam burritoNo ratings yet
- Power Pack: Constant Power Supply Kartik Kumar 1887021Document14 pagesPower Pack: Constant Power Supply Kartik Kumar 1887021Lakshay BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Converter 4 20maDocument19 pagesConverter 4 20mabnurkholis100% (1)
- Basic Electrical Engineering Interview Questions and AnswersDocument14 pagesBasic Electrical Engineering Interview Questions and AnswersDanish AliNo ratings yet
- KMT#4Document5 pagesKMT#4RomanHerreraNo ratings yet
- How An Smps Works: Rectifier StageDocument7 pagesHow An Smps Works: Rectifier StageImran AshrafNo ratings yet
- How An SMPS WorksDocument7 pagesHow An SMPS WorksĐorđe PopovićNo ratings yet
- Report On Power SupplyDocument14 pagesReport On Power SupplyBhavesh MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Topic - Voltage RegulatorDocument43 pagesTopic - Voltage RegulatorAryan Singh JadaunNo ratings yet
- Power Factor Correction Using Boost ConverterDocument24 pagesPower Factor Correction Using Boost Converterফারহানা আক্তার গল্পNo ratings yet
- Half Wave and Full Wave RectifierDocument10 pagesHalf Wave and Full Wave RectifiersunilsathishNo ratings yet
- Study and Design, Simulation of PWM Based Buck Converter For Low Power ApplicationDocument17 pagesStudy and Design, Simulation of PWM Based Buck Converter For Low Power ApplicationIOSRjournalNo ratings yet
- Power Supplies: Transducers AC and DC Diodes CapacitorsDocument10 pagesPower Supplies: Transducers AC and DC Diodes CapacitorsJose C. Lita JrNo ratings yet
- KTVR Knowledge Park For: Engineering and TechnologyDocument23 pagesKTVR Knowledge Park For: Engineering and Technologyshiva shakthyNo ratings yet
- DC TransformerDocument25 pagesDC TransformerUmair100% (1)
- 7.13 Power Supply Control Input Voltage and Duty Ratio.: Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 07Document12 pages7.13 Power Supply Control Input Voltage and Duty Ratio.: Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 07Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Pdemarco 4Document4 pagesPdemarco 4Paul DeMarcoNo ratings yet
- Industrial Electronics 1st ExamDocument34 pagesIndustrial Electronics 1st ExamJomar Bonje100% (1)
- SMPS:-: Switched-Mode Power Supply (Switching-Mode Power Supply, SMPS, or Simplyswitcher) Is An ElectronicDocument4 pagesSMPS:-: Switched-Mode Power Supply (Switching-Mode Power Supply, SMPS, or Simplyswitcher) Is An ElectronicSumit SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Instrument TransformersDocument30 pagesChapter 2 Instrument TransformersBharat ThapaNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- STEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10From EverandSTEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10No ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Matlab For Engineers Applications in Control Electrical Engineering It and Robotics 7526Document524 pagesMatlab For Engineers Applications in Control Electrical Engineering It and Robotics 7526hpnguyenthanh007100% (1)
- Instrumentation Engineers HandbookDocument314 pagesInstrumentation Engineers HandbookMaresdaSatria100% (1)
- LV FundamentalsDocument165 pagesLV Fundamentalsmacarong272No ratings yet
- EE271 ProjectDocument29 pagesEE271 ProjectQuang MạnhNo ratings yet
- Sony Vaio PCG-K13 Quanta JE2Document38 pagesSony Vaio PCG-K13 Quanta JE2luckyman7No ratings yet
- Data Sheet: BC237 BC237BDocument8 pagesData Sheet: BC237 BC237Be178anangNo ratings yet
- Datasheet LTC1286 FsDocument25 pagesDatasheet LTC1286 FsRamonNo ratings yet
- Ultra-Dense Storage Server Increased VersatilityDocument2 pagesUltra-Dense Storage Server Increased VersatilityBa VuVanNo ratings yet
- PLE-1ME Mixer Amplifier DatasheetDocument4 pagesPLE-1ME Mixer Amplifier DatasheetNiladri GhoshNo ratings yet
- Maxim Integrated - AutomotiveDocument32 pagesMaxim Integrated - AutomotivepHysiXNo ratings yet
- Specs Lenovo ThinkCentre M82Document27 pagesSpecs Lenovo ThinkCentre M82nur fuadNo ratings yet
- Remote Power ControllerDocument2 pagesRemote Power Controllerdavid reyesNo ratings yet
- Sams8 5388 LG 32LC7DCDocument12 pagesSams8 5388 LG 32LC7DCsvctechNo ratings yet
- Fir Filter DesignDocument4 pagesFir Filter DesignRamanathan SunderNo ratings yet
- Fire Fighting Robot Using Arduino UNODocument6 pagesFire Fighting Robot Using Arduino UNODarshan ParmarNo ratings yet
- At Mega 8535Document321 pagesAt Mega 8535nanggrianaNo ratings yet
- DEVICE Exp 4 StudentDocument4 pagesDEVICE Exp 4 StudentTouhid AlamNo ratings yet
- X12D - X15D: 1,000 Watt Active LoudspeakerDocument16 pagesX12D - X15D: 1,000 Watt Active LoudspeakerHanafy GarengNo ratings yet
- Samsung LA40C550 ManualDocument44 pagesSamsung LA40C550 ManualOmer MehdiNo ratings yet
- 7576xxx Rev 0909Document1 page7576xxx Rev 0909pandavision76No ratings yet
- 03 Electrical NotesDocument27 pages03 Electrical NotesizzazackNo ratings yet
- Vb-Audio Cable: Configuring Vb-Cable System Settings Hifi-Cable & Asio BridgeDocument8 pagesVb-Audio Cable: Configuring Vb-Cable System Settings Hifi-Cable & Asio BridgeNatanael ManriqueNo ratings yet
- TASK SHEET Study GuideDocument10 pagesTASK SHEET Study GuideJohn Raymund MabansayNo ratings yet
- Obe Curriculum For The Course: RGPV (Diploma Wing) BhopalDocument22 pagesObe Curriculum For The Course: RGPV (Diploma Wing) BhopalHarshit Sahu CS-26No ratings yet
- Engineering Mini ProjectDocument8 pagesEngineering Mini ProjectnkniteshNo ratings yet
- TL 3845Document12 pagesTL 3845sarad43No ratings yet
- Non-Linear Junction Detector: User ManualDocument35 pagesNon-Linear Junction Detector: User Manualarnes_88No ratings yet
- Manual Sony Vaio Fit SOSVF15213CBWDocument450 pagesManual Sony Vaio Fit SOSVF15213CBWramenzoniNo ratings yet
- Honeywell Sensing Bipolar Digital Hall Effect Sensor Ic Installation Instructions Ss41 Pk87881 6 enDocument3 pagesHoneywell Sensing Bipolar Digital Hall Effect Sensor Ic Installation Instructions Ss41 Pk87881 6 enMeghamala MandalNo ratings yet
- Installation Manual: VPN BoxDocument4 pagesInstallation Manual: VPN BoxilhgsygbNo ratings yet
- M.Tech (Microwave & Communication Engineering) PVP17Document2 pagesM.Tech (Microwave & Communication Engineering) PVP17kprk414No ratings yet
- Capacitance Fall Into Two Categories Intrinsic Capacitance Extrinsic CapacitanceDocument10 pagesCapacitance Fall Into Two Categories Intrinsic Capacitance Extrinsic Capacitancewajid aliNo ratings yet