Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Acfrogbd Sdxinp0mtk2gcuyb-Aktoxoi5yge0qmcajqwgu2wgajquml Jfzfxsqk3x5fuakcja3adjjlzddkuio7wh1lhnu65aneq0k Htid v8 Ac8cyh2xtxgozuwrfgruozl-Kl5d1o2p3c3
Acfrogbd Sdxinp0mtk2gcuyb-Aktoxoi5yge0qmcajqwgu2wgajquml Jfzfxsqk3x5fuakcja3adjjlzddkuio7wh1lhnu65aneq0k Htid v8 Ac8cyh2xtxgozuwrfgruozl-Kl5d1o2p3c3
Uploaded by
marcOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Acfrogbd Sdxinp0mtk2gcuyb-Aktoxoi5yge0qmcajqwgu2wgajquml Jfzfxsqk3x5fuakcja3adjjlzddkuio7wh1lhnu65aneq0k Htid v8 Ac8cyh2xtxgozuwrfgruozl-Kl5d1o2p3c3
Acfrogbd Sdxinp0mtk2gcuyb-Aktoxoi5yge0qmcajqwgu2wgajquml Jfzfxsqk3x5fuakcja3adjjlzddkuio7wh1lhnu65aneq0k Htid v8 Ac8cyh2xtxgozuwrfgruozl-Kl5d1o2p3c3
Uploaded by
marcCopyright:
Available Formats
Module 6- Adult Teaching and Learning
Adult definition
Psychological : “ A person is a n adult to the extend that he or she perceives himself or
herself to be essentially responsible for his or her own life.”
Sociological:” An individual is a person who has come to the stage of his life in which
he or she has assumed full responsibility for himself and usually for others, who has
concomitantly accepted functionally productive in his community.”
Andragogy – the art and science of helping adult learners
- used originally by Alexander Knapp, a German, in 1833
- developed as adult education theory by Max Knowles, an American
- Built upon two central, difining attributes:
Learners are self-directed and autonomous
The teacher is a facilitator of learning rather than a presenter
of content.
Pedagogy – the art and science of teaching children
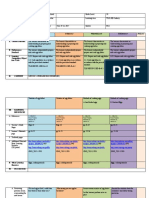
Comparison between” Andragogy and Pedagogy
As Regards to Andragogy Pedagogy
Orientation to Learners seeks to acquire Learning is subject-orientedwith
Learning competence to cope with enphasis on content, mostof
demands of their world; they which they may forget because it
seek personal development and has no immediate relevance
acgienvement of potential; they (principle of deferred gratification)
also seek immediate
gratification; learning must be
relevant and immediately
applicable
Concept of the Role of the learners is Role of the learner is dependent
Learners essentially self-directing
Role of a teacher is to Teacher takes responsibility for
encourage and nurture this self- the whoke learning process
directed need
Learners experience Learners bring little experience to
accumulated over a lifetime is a the learning situation
great resource for learning both
Role of for self and others
Learner;s Learners attach greater Learners dependent on expert
Experience significance to what they input
experience rather thsn they sre
told
Main techniques are Main techniques are transmittal
experimental techniques techniques
Learners learn when they feel a Learners learn what they are
need to learn conditioned to learn to obtain
parental, societal approval
Learning should meet their Fear of failure is a great
Readiness to needs to help them cope with motivator
learn the demands of their world-
home, work, etc.
Learning should be organized to Learning is standardized and
meet learner needs and progressive because it is aimed at
sequenced according to the same age group is similar in
individual’s ability and readiness its learning needs and its
to learn readiness to learn.
General Conditions of the Client of Extension
1. Resource-poor
2. Most neglected in terms of basic services such extension, health, roads, markets
3. Poor access to information and technology options
4. Inappropriate farming/fishery practices
5. Typically individualistic (not interested to join organizationd)
6. Dole-out oriented ( due to experiences in past programs/project appraoches)
7. Rural remote and exposed to peace and order problems
8. Have varied land tenure/arrangements issue
9. Have varied experiences in projects that have come and gone without
sustaining(thus, might be cynical, pessimestic or distrusting)
Principles of Adult Learning
1. The need to know
- Adult need to know what and why need to learn before undertaking to
learn it. Adults are more afraid to fail and want to make sure the
undertaking is worthwhile.
2. The learners self-concept and self-direction
- Adult have a self-concept of being responsible for their oown decisions
and for their own lives. They resent and resist ideas “imposed” on them.
3. The role of the learner’s experiences
- Adult possess varying quantity and quality of experineces. This implies a
wider divergence and difference within groups, or a high degree of
heterogeneity; different biases that may influence their openness to
incoming information/ideas, and the rate of adoption of the same. It is
important for the learning fcilitator to draw from the participants
experiences when starting a topc or discussion.
4. Readiness to learn
- Adult become ready to learn those things they neeed to know and be
able to do in order to cope effectively with their real-life situations. Adult
question the truth or usefulness of the information they receive.
5. Orientation to learning
- Adults are life-centered or task-centered in the orientation to learning.
Adults learn to assist in performing tasks and dealing with problems.
6. Motivation
- Adults are more responsive on internal pressures (e.g. self-esteem,
quality of life); then external motivations (better production, higher
income_. It is necessary for the facilitator to raise their self-confidence.
7. Participation in learning is vountary
- Not all learning methods can be equally effective to all adult
learners.Facilitator need to know to be innovative to design appropriate
methods and approaches.
Adult learns best when………..
They have strong desire to learn
They put an effort to learn
They have clear goal
They have receive satisfaction
Principles of Adult Teaching and Learning
1. Self Activity or active response
To effectively change the behavior of people, we should make them
actively participate in doing what is to be learned
2. Repetition or Practice
A leraning activity experienced many times tends to be remenbered longer
and to be recalled easier.
3. Timing
Learning takes place more readily when a fact or skill is taught at the
same time or just before the time when it can be used in some serviceable
way
4. Association
Experiences that happen together tend to recur together hence we learn
once by associating it with the other.
5. Satisfaction
Anything that is satisfying will promote learning.
6. Reward
Reward promotes learning
7. Motivation
The ease of learning varies directly with the meaningfulness of the
materials presented
8. Aperception
Learners perceive the new in terms of the old
9. Transfer
A person learns through transfer to the extent that the abilities acquired in
one situation help in the other.
10. Readiness
The more fully a person is in readiness to act in a certain way the more
satisfying it will be for him to act in that way and the more annoying it will
be if prevented.
11. Mindset
Past experienes keep individuals from using objeects in different ways.
12. Use and Disuse
When something is learned and used, it is remebered but when it is not
used, it is forgetten.
13. Individual differences
No two people are exactly alike. People vary in their ability to benefit from
one taeching method or techniques.
14. Contrast
We tend to remember those things which are in sharp contrast to one
another.
15. Recency
The more recent an experience, the more readily it can be recalled.
Reference:
Green Empire PH (www.facebook.com/green empireph)
You might also like
- Ebook PDF The Inclusive Classroom Strategies For Effective Differentiated Instruction 6th Edition PDFDocument41 pagesEbook PDF The Inclusive Classroom Strategies For Effective Differentiated Instruction 6th Edition PDFscott.stokley449100% (39)
- Pedagogy and Andragogy PPT Bec Bagalkot MbaDocument29 pagesPedagogy and Andragogy PPT Bec Bagalkot MbaBabasab Patil (Karrisatte)100% (1)
- LESSON PLAN DIASS Week 3Document5 pagesLESSON PLAN DIASS Week 3VIRGILIO JR FABINo ratings yet
- LESSON PLAN MATHEMATICS FORM 1 (Edu)Document6 pagesLESSON PLAN MATHEMATICS FORM 1 (Edu)fiezah_halim100% (2)
- Adult LearningDocument19 pagesAdult LearningMaurisMilzaamANo ratings yet
- Background On The Concept and The Educator: Knowles' 5 Assumptions of Adult LearnersDocument3 pagesBackground On The Concept and The Educator: Knowles' 5 Assumptions of Adult LearnersShiVani KoLashNo ratings yet
- Andragogy and Learning TheoryDocument36 pagesAndragogy and Learning TheoryAyu AmbarwatiNo ratings yet
- Principles of Adult Learning: Unit 2.3Document14 pagesPrinciples of Adult Learning: Unit 2.3Ronnie RicardelNo ratings yet
- The Adult Learner Dr. Radhika KapurDocument6 pagesThe Adult Learner Dr. Radhika KapurRenata SephiaNo ratings yet
- KnowlesDocument6 pagesKnowlesMericar EsmedioNo ratings yet
- AndragogyDocument21 pagesAndragogyrezky wijayantoNo ratings yet
- AndragogyDocument21 pagesAndragogyteloletNo ratings yet
- Pembelajar Dewasa Dan MandiriDocument19 pagesPembelajar Dewasa Dan MandiriingeNo ratings yet
- Nature of LearningDocument2 pagesNature of LearningFlorens Genoves BagatNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3.2 Knowles Adult Learning TheoryDocument4 pagesLesson 3.2 Knowles Adult Learning Theoryjaydee tiukinhoyNo ratings yet
- Methodology of Human Rights EducationDocument33 pagesMethodology of Human Rights EducationRoberto Iñigo SanchezNo ratings yet
- PED 12 - Facilitating Learning in Diverse Contexts - Unit 1Document18 pagesPED 12 - Facilitating Learning in Diverse Contexts - Unit 1Mary Antonette JalosjosNo ratings yet
- Adult Learning and Learning StylesDocument52 pagesAdult Learning and Learning StylesLino MacalintalNo ratings yet
- The Learning CycleDocument19 pagesThe Learning Cyclehaddi awanNo ratings yet
- St. Louis College of Bulanao: Purok 6, Bulanao, Tabuk City, Kalinga 3800Document5 pagesSt. Louis College of Bulanao: Purok 6, Bulanao, Tabuk City, Kalinga 3800Cath TacisNo ratings yet
- Adult Learning and Learning NeedsDocument42 pagesAdult Learning and Learning NeedskrishnasreeNo ratings yet
- Strategies in Teaching Social Studies Inductive and Deductive Andragogy vs. PedagogyDocument31 pagesStrategies in Teaching Social Studies Inductive and Deductive Andragogy vs. PedagogyArvie VillegasNo ratings yet
- 3 - Learning TheoriesDocument22 pages3 - Learning Theoriesاسامة محمد السيد رمضانNo ratings yet
- 30 Things We Know For Sure About Adult LearningDocument3 pages30 Things We Know For Sure About Adult LearningAndre Henrique Torres RibeiroNo ratings yet
- Tep 2 Unit 1Document7 pagesTep 2 Unit 1Carol Santiago CarpioNo ratings yet
- Facilitating Adult Learning Dr. Radhika KapurDocument7 pagesFacilitating Adult Learning Dr. Radhika KapurCaroline AquenNo ratings yet
- Facilitating: Learner-Centered TeachingDocument8 pagesFacilitating: Learner-Centered TeachingShe Na - mNo ratings yet
- Principles of LearningDocument16 pagesPrinciples of LearningBernard BanalNo ratings yet
- Working With Adults As Learners:: Theory and PracticeDocument31 pagesWorking With Adults As Learners:: Theory and PracticeLei Anne Kate DimailigNo ratings yet
- What Does Andragogy Mean?: Malcolm Shepherd KnowlesDocument34 pagesWhat Does Andragogy Mean?: Malcolm Shepherd Knowlesjezarie delosreyesNo ratings yet
- Adult EducationDocument3 pagesAdult Educationsclry16No ratings yet
- Principles of TeachingDocument89 pagesPrinciples of TeachingAnne Anne Cabeltis-MañaboNo ratings yet
- 0 Training TechniquesDocument22 pages0 Training TechniquesHani BoudiafNo ratings yet
- Carl Rogers Humanistic Learning PrinciplesDocument2 pagesCarl Rogers Humanistic Learning PrinciplesSAZALI BIN MOHAMED MOKHTARUDINNo ratings yet
- Principles of Learning: UNIT II - Chapter 1Document63 pagesPrinciples of Learning: UNIT II - Chapter 1Juodie Lee VaelNo ratings yet
- Ag ExDocument22 pagesAg ExMaria Reina Mae CapuyanNo ratings yet
- Group 8 NSG103Document26 pagesGroup 8 NSG103Nashebah A. BatuganNo ratings yet
- Principles of Teaching Prelim Exam NotesDocument2 pagesPrinciples of Teaching Prelim Exam NotesMaybza ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Child, Adolescent, AND Adult LearningDocument17 pagesChild, Adolescent, AND Adult LearningDarlene Rautt MapaNo ratings yet
- Week 6 HumanisticDocument24 pagesWeek 6 HumanisticTESL10620 Aida Nur Athilah Binti Mat SohNo ratings yet
- Handouts From Week 10 To Week 12 Summation of ReportDocument5 pagesHandouts From Week 10 To Week 12 Summation of ReportAkoni si ARARNo ratings yet
- Module - Gonzales - Facilitating LearningDocument6 pagesModule - Gonzales - Facilitating Learningariannerose gonzalesNo ratings yet
- TEFL - Lesson 4Document6 pagesTEFL - Lesson 4jammurlammerNo ratings yet
- Activity-Based LearningDocument18 pagesActivity-Based Learningfreyshelraquel.ricablancaNo ratings yet
- Do The Progressivist Teachers Strive To Simulate in The Classroom Life in TheDocument4 pagesDo The Progressivist Teachers Strive To Simulate in The Classroom Life in ThestudentNo ratings yet
- Principles of LearningDocument4 pagesPrinciples of LearningJoy Mae MoralesNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Adult Learning: - Kedar RayamajhiDocument32 pagesIntroduction To Adult Learning: - Kedar RayamajhiBaaniya NischalNo ratings yet
- Teaching Aptitude 1Document6 pagesTeaching Aptitude 1hampamNo ratings yet
- Module 2 FLCTDocument7 pagesModule 2 FLCTJerico VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- EDUC 102 Principles of TeachingDocument7 pagesEDUC 102 Principles of TeachingMiralyn TevesNo ratings yet
- 9 Theories of Teaching Science...Document6 pages9 Theories of Teaching Science...Julius GallegoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document10 pagesChapter 7Luarez, Jessa S.No ratings yet
- Ed 111 - Group 3Document9 pagesEd 111 - Group 3Jay Ann DiazNo ratings yet
- The Teaching Profession - Chapter 5Document7 pagesThe Teaching Profession - Chapter 5George Kevin TomasNo ratings yet
- Teaching MethodologiesDocument7 pagesTeaching MethodologiesJovelyn PamaosNo ratings yet
- Educ 2 - Module 1.2Document5 pagesEduc 2 - Module 1.2Maybz TingsonNo ratings yet
- Adult LearningDocument12 pagesAdult LearningDhimasAjiZuandaNo ratings yet
- Principal of Adult LearningDocument14 pagesPrincipal of Adult Learningfbi5123No ratings yet
- Episode-2-The-Learners-Characteristics-and-Needs (Uploaded)Document6 pagesEpisode-2-The-Learners-Characteristics-and-Needs (Uploaded)Maria TamayoNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document5 pagesModule 1Dhaze OjanoNo ratings yet
- LAC Nov. 18,2022 Strategies and Technique in Teaching ScienceDocument31 pagesLAC Nov. 18,2022 Strategies and Technique in Teaching ScienceCharm Vergara100% (1)
- Acilitating: University of Mindanao Tagum CampusDocument25 pagesAcilitating: University of Mindanao Tagum CampusClara ArejaNo ratings yet
- English for Students of Educational Sciences: Educational SciencesFrom EverandEnglish for Students of Educational Sciences: Educational SciencesNo ratings yet
- Do and DontsDocument1 pageDo and DontsmarcNo ratings yet
- MethodologyDocument1 pageMethodologymarcNo ratings yet
- CropProtection1Module JBPaulite 2020PRELIMDocument54 pagesCropProtection1Module JBPaulite 2020PRELIMmarcNo ratings yet
- Independent Study 1st SemDocument36 pagesIndependent Study 1st SemmarcNo ratings yet
- AngelouDocument1 pageAngeloumarcNo ratings yet
- Learning Worksheet No.12 in Organization and Management: Reward System, Employee Relation and MovementsDocument4 pagesLearning Worksheet No.12 in Organization and Management: Reward System, Employee Relation and MovementsjingNo ratings yet
- Using Recognize How Students Build and Rebuild UnderstandingDocument7 pagesUsing Recognize How Students Build and Rebuild UnderstandingsantimosNo ratings yet
- DanDocument3 pagesDanMeme SalamanteNo ratings yet
- Audio-Visual Medias and ComputersDocument3 pagesAudio-Visual Medias and ComputersPriyankaNo ratings yet
- Background of The StudyDocument2 pagesBackground of The StudyImee BorinagaNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Detailed Lesson Plan in MAPEH 6Document11 pagesDepartment of Education: Detailed Lesson Plan in MAPEH 6jamz juneNo ratings yet
- 0 - SITXHRM001 Learner Workbook V1.1 ACOT - dn341Document31 pages0 - SITXHRM001 Learner Workbook V1.1 ACOT - dn341bhshdjnNo ratings yet
- Individual Work 2 - Student Self-Assessment of SkillsDocument3 pagesIndividual Work 2 - Student Self-Assessment of SkillsVivien De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Fractions - 3rd Grade Learning Support - Madalyn EquiDocument5 pagesFractions - 3rd Grade Learning Support - Madalyn Equiapi-549445196No ratings yet
- EDU 623 Final ProjectDocument15 pagesEDU 623 Final ProjectCara CaseNo ratings yet
- PR2 ActivityDocument1 pagePR2 ActivityCherieJavilinarFandialanNo ratings yet
- Women in Literature Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesWomen in Literature Lesson Planapi-413937683No ratings yet
- Bhupathiraju Ravi SanjayvarmaDocument2 pagesBhupathiraju Ravi SanjayvarmaramyaNo ratings yet
- Reading Unit Two: Getting OrganizedDocument4 pagesReading Unit Two: Getting Organizedmahmoud albiakNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Game-Based Learning On Students'Document13 pagesThe Effect of Game-Based Learning On Students'Ismi IrniNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument8 pagesLesson PlanaliyairyaniNo ratings yet
- Teacher Wellbeing Focus PaperDocument3 pagesTeacher Wellbeing Focus PaperThiri Min SinNo ratings yet
- Case Study Libanan 1Document12 pagesCase Study Libanan 1Jeric Duran Oledan100% (1)
- Yes, We Can! Secondary 1Document146 pagesYes, We Can! Secondary 1Luis Ramon Cota PinedaNo ratings yet
- RPMS COVER KRAs MT1-MT4 by TeacherDocument13 pagesRPMS COVER KRAs MT1-MT4 by TeacherJefferson MorenoNo ratings yet
- DLL (July 17 - 21) Math 10Document3 pagesDLL (July 17 - 21) Math 10Jer LoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1. Measurement Assessment and EvDocument6 pagesChapter 1. Measurement Assessment and EvAkari ChanNo ratings yet
- Why I Want To Be A Teacher Essay-2Document2 pagesWhy I Want To Be A Teacher Essay-2api-540726087No ratings yet
- Creative Thinking SkillsDocument35 pagesCreative Thinking SkillshotmaleprabhuNo ratings yet
- Polytechnic University of The PhilippinesDocument3 pagesPolytechnic University of The PhilippinesEmmanuel SidaNo ratings yet
- Personality Factors and SLADocument17 pagesPersonality Factors and SLAKaren Banderas ManzanoNo ratings yet
- DLL TLE Cookery Grade10 Quarter1 Week3Document5 pagesDLL TLE Cookery Grade10 Quarter1 Week3Judith AlmendralNo ratings yet