Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Vremena
Vremena
Uploaded by
Tratinčica Narcis0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views2 pagesThe document outlines the uses of various tenses in English, including the present simple, present continuous, past simple, past continuous, present perfect simple, present perfect continuous, past perfect, and past perfect continuous tenses. The present simple is used to describe facts, habits, states, headlines, instructions, summaries, and schedules. The present continuous emphasizes actions that are ongoing. The past simple refers to completed past actions and past habits. The past continuous describes ongoing past actions or changing states. The present perfect simple refers to recent or indefinite past events. The present perfect continuous emphasizes duration. The past perfect is used to refer to an event that occurred before another past event.
Original Description:
Original Title
vremena
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document outlines the uses of various tenses in English, including the present simple, present continuous, past simple, past continuous, present perfect simple, present perfect continuous, past perfect, and past perfect continuous tenses. The present simple is used to describe facts, habits, states, headlines, instructions, summaries, and schedules. The present continuous emphasizes actions that are ongoing. The past simple refers to completed past actions and past habits. The past continuous describes ongoing past actions or changing states. The present perfect simple refers to recent or indefinite past events. The present perfect continuous emphasizes duration. The past perfect is used to refer to an event that occurred before another past event.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views2 pagesVremena
Vremena
Uploaded by
Tratinčica NarcisThe document outlines the uses of various tenses in English, including the present simple, present continuous, past simple, past continuous, present perfect simple, present perfect continuous, past perfect, and past perfect continuous tenses. The present simple is used to describe facts, habits, states, headlines, instructions, summaries, and schedules. The present continuous emphasizes actions that are ongoing. The past simple refers to completed past actions and past habits. The past continuous describes ongoing past actions or changing states. The present perfect simple refers to recent or indefinite past events. The present perfect continuous emphasizes duration. The past perfect is used to refer to an event that occurred before another past event.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
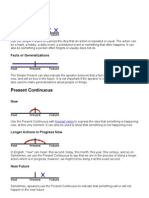
Present Simple
Generally refers to:
1. Facts that are always true
2. Habits
3. States
4. Headlines
5. Instructions and itineraries
6. Summaries of events
7. Historic present in narrative and funny stories
8. Future time reference for schedule, time table
Present (progressive) Continious
Generally refers to actions which are in progress at the moment
These can be temporary
They can be actually in progress
Or they can be generally in progress but not actually happening at the
moment
Past Simple
Generally refers to:
1. Completed actions in the past at a definite time
2. Past habits
3. Past states
Past (progressive) Continious
Generally refers to:
1. Actions in progres
2. Background description in narrative
3. Changing states
4. Repeated actions criticism
5. Unfulfilled past events
Present Perfect Simple
Generally refers to:
1. Recent events, without a definite time given
2. Indefinite events, which happened at an unknown time in the past. No
definite time is given.
3. Indefinite events which may have an obvious result in the present
4. With state verbs, a state which lasts up to the present
5. A habitual action in a period of time up to the present.
Present Perfect Continious
can refer to a range of meanings, depending on the time expression used and
the context
1. A state which lasts up to the present moment
2. An incomplete activity
3. The emphasis duration
4. A recently finished activity
5. A repeated activity
Past Perfect
A past event or situation which occured before another past event or situation
A time conjunction sometimes replaces the past perfect to show which of the
two past events occured first. In this case both events can be in the simple
past tense.
Past perfect continuous is used to emphasize the CONTINUITY and
DURATION of the past event before another past event or situation
You might also like
- PP UseDocument3 pagesPP Usejuan.arias2No ratings yet
- TensesDocument2 pagesTensesAnjali AgNo ratings yet
- Meeting 3 - TensesDocument8 pagesMeeting 3 - TensesRoni SiregarNo ratings yet
- CCS PPT!Document25 pagesCCS PPT!Dhien KinilitanNo ratings yet
- Future Tense and Its Aspect (English-I)Document13 pagesFuture Tense and Its Aspect (English-I)Subhankar AdhikaryNo ratings yet
- TENSE AND ASPECT Additional NotesDocument3 pagesTENSE AND ASPECT Additional NotesGuillermina EtcheverriaNo ratings yet
- SemanticsDocument7 pagesSemanticsrosydalriansyahNo ratings yet
- Topic 19Document10 pagesTopic 19Juan CesurNo ratings yet
- Understanding English Tenses A CompDocument2 pagesUnderstanding English Tenses A CompsoftifyrankNo ratings yet
- Present SimpleDocument3 pagesPresent SimpleLeiny MecheNo ratings yet
- Topic 4Document13 pagesTopic 4Ganesh MhaskeNo ratings yet
- English Grammar For A2 Level Students: OutlineDocument12 pagesEnglish Grammar For A2 Level Students: OutlineJuan Carlos Martinez ReynaNo ratings yet
- Verb Tense Consistency - RulesDocument5 pagesVerb Tense Consistency - RulesClydelle Garbino PorrasNo ratings yet
- Compilation in Oral Communication: Submitted By: Marilou Bragat Submitted To: Alfecca J. ObnimagaDocument4 pagesCompilation in Oral Communication: Submitted By: Marilou Bragat Submitted To: Alfecca J. Obnimagajonel ruleNo ratings yet
- Past Tenses in EnglishDocument19 pagesPast Tenses in EnglishXx Fred xXNo ratings yet
- Past/Present Tenses in EnglishDocument19 pagesPast/Present Tenses in EnglishXx Fred xXNo ratings yet
- Lessons 16 and 17 - The Tense-Aspect System PDFDocument44 pagesLessons 16 and 17 - The Tense-Aspect System PDFpedroa.oliv22No ratings yet
- Topic 19 - Real TimeDocument7 pagesTopic 19 - Real TimeHaydée PalomoNo ratings yet
- Perfect Tense ExplanationDocument5 pagesPerfect Tense ExplanationCheung ChristyNo ratings yet
- Verb Tenses: Present Simple Tense For Narratives orDocument3 pagesVerb Tenses: Present Simple Tense For Narratives orGeorge ProdanNo ratings yet
- Present Simple Tense For Narratives Or: Page 1 of 3Document3 pagesPresent Simple Tense For Narratives Or: Page 1 of 3CosorAndrei-AlexandruNo ratings yet
- English Tenses OverviewDocument5 pagesEnglish Tenses OverviewKarin PassmoreNo ratings yet
- Time, Tense, and AspectDocument6 pagesTime, Tense, and AspectEmily JamesNo ratings yet
- Se2 Ep08 NotesDocument4 pagesSe2 Ep08 NotesCosorAndrei-Alexandru100% (1)
- Bab 1 Tenses: (1) (Note 1)Document12 pagesBab 1 Tenses: (1) (Note 1)Ima Mulia MasnariaNo ratings yet
- Bab 1 Tenses: (1) (Note 1)Document12 pagesBab 1 Tenses: (1) (Note 1)اقصیٰ سجادNo ratings yet
- Tenses TimelinesDocument7 pagesTenses TimelinesaleNo ratings yet
- Simple TensesDocument2 pagesSimple TensesBunny BearNo ratings yet
- Sequence of TensesDocument7 pagesSequence of TensesZMG2010100% (1)
- Past Actions MeaningsDocument2 pagesPast Actions MeaningsANCA POPOVICINo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document1 pageUnit 2larisa jamiesonNo ratings yet
- Past Progressive Tense Is Used ToDocument1 pagePast Progressive Tense Is Used ToRika IrmadiyahNo ratings yet
- Lecture 03 Grammar L2Document5 pagesLecture 03 Grammar L2kofares7No ratings yet
- What Are The Roles of Tenses in English? Please Give Your Own ExamplesDocument2 pagesWhat Are The Roles of Tenses in English? Please Give Your Own ExamplesHung TranNo ratings yet
- SEMINAR Past Tenses in English LanguageDocument10 pagesSEMINAR Past Tenses in English LanguageSulejman BeširovićNo ratings yet
- Tenses of VerbsDocument32 pagesTenses of VerbsBafsk83% (6)
- UAS Bahasa Inggris - Lea Julita Y. Kiuk - 2006090010Document60 pagesUAS Bahasa Inggris - Lea Julita Y. Kiuk - 2006090010Lea Julita KiukNo ratings yet
- Future TenseDocument5 pagesFuture TensemonsieurboastalotNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Advanced GrammarDocument22 pagesChapter 2 - Advanced GrammarNguyễn Thanh TuyềnNo ratings yet
- Tense AspectDocument22 pagesTense AspectJessa Galletes Dela PeñaNo ratings yet
- Give Your Own Example To Every Case of Usage:: Since and ForDocument1 pageGive Your Own Example To Every Case of Usage:: Since and ForNorman PhuaNo ratings yet
- CBR GrammarDocument16 pagesCBR GrammarNita TambunanNo ratings yet
- Verb TensesDocument6 pagesVerb TensesnornNo ratings yet
- Simple Tenses: Using Shall/willDocument1 pageSimple Tenses: Using Shall/willarunabhatlaNo ratings yet
- TensesDocument7 pagesTensesredchillipaperNo ratings yet
- 2.Unit IV_Present Progressive (1)Document9 pages2.Unit IV_Present Progressive (1)GuadaaNo ratings yet
- All Past TensesDocument4 pagesAll Past TensesrobertoNo ratings yet
- Final DemoDocument10 pagesFinal DemoEmKey GCNo ratings yet
- Referring To Present TimeDocument18 pagesReferring To Present TimeDušan IsailovićNo ratings yet
- Exposición InglésDocument2 pagesExposición Ingléscciro90001No ratings yet
- First Certificate in English. Grammar Verb TensesDocument19 pagesFirst Certificate in English. Grammar Verb TensesGabriel ToselliNo ratings yet
- Bahasa Inggris (Softskill) "Tenses"Document14 pagesBahasa Inggris (Softskill) "Tenses"Syairoh MunawarohNo ratings yet
- Albertina Filipe Cuna Vicente Chissuane Soares Boaventura CumbeDocument11 pagesAlbertina Filipe Cuna Vicente Chissuane Soares Boaventura CumbeJervàcio ChambalNo ratings yet
- English Grammar - Module 42Document8 pagesEnglish Grammar - Module 42leticia camposNo ratings yet
- English Assignment: Tenses, Vocabulary Drills, ModifiersDocument10 pagesEnglish Assignment: Tenses, Vocabulary Drills, ModifiersAdiTya RaThoreNo ratings yet
- Conditional ClausesDocument6 pagesConditional ClausesYuhanidha SitiNo ratings yet
- Verb TensesDocument1 pageVerb TensesVanessa_anjosNo ratings yet
- Mastering English Tenses in 7 Days: A Comprehensive Guide to Verb Forms and UsageFrom EverandMastering English Tenses in 7 Days: A Comprehensive Guide to Verb Forms and UsageRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)