Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ratio Analysis
Ratio Analysis
Uploaded by
Abdul Muhaymin MahdiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ratio Analysis
Ratio Analysis
Uploaded by
Abdul Muhaymin MahdiCopyright:
Available Formats
RATIO ANALYSIS
Definition: Ratio Analysis is a quantitative method of gaining insight into a company’s liquidity,
operational efficiency, and profitability by studying its financial statements.
Ratio Analysis tell us: Investors and analysts employ ratio analysis to evaluate the financial
health of companies by scrutinizing past and current financial statements. Comparative data can
demonstrate how a company is performing over time and can be used to a telegraph likely future
performance. This data can also compare a company’s financial standing with industry averages
while measuring how a company stacks up against others within the same sector.
IMPORTANCE OF RATIO ANALYSIS:
To judge financial position.
To judge financial performance.
Financial decision.
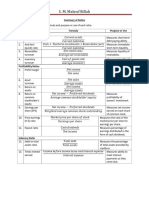
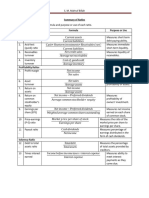
CLASSIFICATION OF RATIOS ON VARIOUS BASIS:
On The Basis Of On The Basis Of Profit And On The Basis Of Balance Sheet
Balance Sheet Loss Account and Profit And Loss Account
1) Current Ratio 1) Gross Profit Ratio 1) Stock Turnover Ratio
2) Liquid Ratio 2) Operating Ratio 2) Debtors Turnover Ratio
3) Absolute Liquid Ratio 3) Operating Profit Ratio 3) Payable Turnover Ratio
4) Debt Equity Ratio 4) Net Profit Ratio 4) Fixed Asset Turnover Ratio
5) Proprietary Ratio 5) Expense Ratio 5) Return on Equity
6) Capital Gearing Ratio 6) Interest Coverage Ratio 6) Return on Shareholder's
7) Assets-Proprietorship Fund
Ratio 7) Return on Capital
8) Capital Inventory to Employed
Working Capital Ratio 8) Capital Turnover Ratio
9) Ratio of Current Assets 9) Working Capital Turnover
to Fixed Assets Ratio
10) Return on Total Resources
11) Total Assets Turnover
You might also like
- Teste Ingles TecnologiaDocument5 pagesTeste Ingles TecnologiaMeninaDuMarNo ratings yet
- Bilco WellboreDocument27 pagesBilco WellboreJhonathan Miranda100% (4)
- English II Merchant of Venice Notes Compiled by Nilay Kumar Das PDFDocument2 pagesEnglish II Merchant of Venice Notes Compiled by Nilay Kumar Das PDFSubhadip RoyNo ratings yet
- Ratio AnalysisDocument9 pagesRatio AnalysisAbdullah shah khavreenNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting Ratio Anaylsis FormulasDocument2 pagesFinancial Accounting Ratio Anaylsis Formulasbasit111100% (1)
- Ratio AnalysisDocument25 pagesRatio Analysismba departmentNo ratings yet
- Report Writing GuidelinesDocument7 pagesReport Writing GuidelinesTaz UddinNo ratings yet
- MAhmed 3269 17132 1 Lecture Financial Ratio AnalysisDocument19 pagesMAhmed 3269 17132 1 Lecture Financial Ratio AnalysisTalha FarooquiNo ratings yet
- Ratios 1Document5 pagesRatios 1Ayush BankarNo ratings yet
- Fundflow and CashflowDocument10 pagesFundflow and CashflowmaraiaNo ratings yet
- Financial Statements and Cash Flow Analysis: Professor XXXXX Course Name / NumberDocument18 pagesFinancial Statements and Cash Flow Analysis: Professor XXXXX Course Name / Numbermuhammad usamaNo ratings yet
- Accounting - Financial Statements and Cash Flow Analysis - 0324322321 - 68871Document18 pagesAccounting - Financial Statements and Cash Flow Analysis - 0324322321 - 68871MFOZOUNINo ratings yet
- User PDFDocument37 pagesUser PDFrobelNo ratings yet
- Chap 2 - Ratio AnalysisDocument24 pagesChap 2 - Ratio AnalysisZubairBalochJatoi100% (1)
- Financial Ratio Analysis-RatiosDocument3 pagesFinancial Ratio Analysis-RatiosMikaela LacabaNo ratings yet
- Financial PlanningDocument24 pagesFinancial PlanningDayaan ANo ratings yet
- Ratio Analysis:: Liquidity Measurement RatiosDocument8 pagesRatio Analysis:: Liquidity Measurement RatiossammitNo ratings yet
- FMECO M.Test EM Question 23.03.2023Document6 pagesFMECO M.Test EM Question 23.03.2023tandelmohik10No ratings yet
- Ratio Analysis: 06/02/2020 1 Imlak Shaikh, PH.D, MDI GurgoanDocument43 pagesRatio Analysis: 06/02/2020 1 Imlak Shaikh, PH.D, MDI Gurgoanraghavendra_20835414No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 (Group 1)Document50 pagesChapter 4 (Group 1)Amal Fitra IriansahNo ratings yet
- Ratio AnalysisDocument28 pagesRatio Analysispatel_bhoomi_1989No ratings yet
- Ratio Analysis Theory and ProblemsDocument13 pagesRatio Analysis Theory and ProblemsPunit Kuleria100% (1)
- Summary of RatiosDocument1 pageSummary of RatiosShamima AkterNo ratings yet
- S. No. Ratios: Liqudity MeasurementDocument5 pagesS. No. Ratios: Liqudity MeasurementRameshkundar KumarNo ratings yet
- Cma Part 2 - Study Unit 6 Ratio Analysis Core ConceptsDocument4 pagesCma Part 2 - Study Unit 6 Ratio Analysis Core Conceptsmuneer13009505No ratings yet
- Finman Pre Mid NotesDocument25 pagesFinman Pre Mid NotesFor ProjectsNo ratings yet
- ACC 1100 Day 08&09 Ratio and Comparative AnalysisDocument32 pagesACC 1100 Day 08&09 Ratio and Comparative AnalysisMai Anh ĐàoNo ratings yet
- Ratio AnalysisDocument21 pagesRatio Analysissoumyasundar720No ratings yet
- Lesson10 enDocument32 pagesLesson10 enarshad mNo ratings yet
- Summary of RatiosDocument1 pageSummary of RatiosShamima AkterNo ratings yet
- Chapter - Iv Fund Flow AnalysisDocument22 pagesChapter - Iv Fund Flow AnalysisThanga DuraiNo ratings yet
- Financial Ratios FormulasDocument1 pageFinancial Ratios FormulasJawad AadiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 1Document37 pagesChapter 6 1Jin JinNo ratings yet
- Commonly Used RatiosDocument12 pagesCommonly Used RatioscyrilljoypNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement: Iasb FrameworkDocument3 pagesFinancial Statement: Iasb FrameworkFaizSheikhNo ratings yet
- Ratio Analysis: Submitted To Shruti MamDocument48 pagesRatio Analysis: Submitted To Shruti MamMD Gulshan100% (1)
- ACC 1100 Day 08&09 Ratio and Comparative AnalysisDocument32 pagesACC 1100 Day 08&09 Ratio and Comparative AnalysisMai Anh ĐàoNo ratings yet
- About Financial RatiosDocument6 pagesAbout Financial RatiosAmit JindalNo ratings yet
- Financial FormationDocument60 pagesFinancial FormationSandeep Soni100% (1)
- Assessment of Financial Condition: A Case Study of Saudi Construction CompaniesDocument9 pagesAssessment of Financial Condition: A Case Study of Saudi Construction Companiesفرفشه اضحك بجدNo ratings yet
- Lecture 06Document21 pagesLecture 06Syed NayemNo ratings yet
- Institutional Determinants of Capital Structure, A Competitive Study of Islamic & Commercial Banks in PakistanDocument2 pagesInstitutional Determinants of Capital Structure, A Competitive Study of Islamic & Commercial Banks in PakistanUMAR MUSHTAQNo ratings yet
- RatiosDocument8 pagesRatiosNashwa KhalidNo ratings yet
- Classification of RatiosDocument5 pagesClassification of Ratiostharani1771_32442248No ratings yet
- Manajemen KeuanganDocument43 pagesManajemen KeuanganShidrinia LatifahNo ratings yet
- FABM2 Module 06 (Q1-W7)Document8 pagesFABM2 Module 06 (Q1-W7)Christian Zebua75% (4)
- Analiza Pe Baza Bilantului Suciu Gheorghe 1Document6 pagesAnaliza Pe Baza Bilantului Suciu Gheorghe 1Airam AiramNo ratings yet
- Financial Management: Summary of Ratios Objective of Analysis Ratios To Be Computed Basic ComponentsDocument4 pagesFinancial Management: Summary of Ratios Objective of Analysis Ratios To Be Computed Basic ComponentsM AmmuNo ratings yet
- Fund Flow Statemen1tDocument12 pagesFund Flow Statemen1tYogesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Formulas FTDocument6 pagesFormulas FTAnkita JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Ratio Analysis: A Tool For Analysis and Interpretation of Financial StatementsDocument54 pagesRatio Analysis: A Tool For Analysis and Interpretation of Financial StatementsAjijur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Portfolio ManagementDocument15 pagesPortfolio ManagementtanviNo ratings yet
- I. Liquidity Ratios No Ratio Method of Computation SignificanceDocument14 pagesI. Liquidity Ratios No Ratio Method of Computation SignificanceVictor M Akbar TukanNo ratings yet
- Chapter (8) : Financial Ratios Analysis: February 2019Document31 pagesChapter (8) : Financial Ratios Analysis: February 2019ALAQMARRAJNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement AnalysisDocument10 pagesFinancial Statement AnalysischandanNo ratings yet
- AFS - FormulasDocument2 pagesAFS - FormulasWaqar AhmadNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Financial Statements - Ratio AnalysisDocument14 pagesAnalysis of Financial Statements - Ratio Analysissunil0507100% (1)
- Analyzing Investing ActivitiesDocument38 pagesAnalyzing Investing Activities6042001147No ratings yet
- Ratio AnalysisDocument33 pagesRatio AnalysisSamNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement and Cash Flow AnalysisDocument6 pagesFinancial Statement and Cash Flow AnalysisSandra MoussaNo ratings yet
- University of Technology, Jamaica Fundamentals of Finance (FOF) Unit 3: Financial Statements AnalysisDocument6 pagesUniversity of Technology, Jamaica Fundamentals of Finance (FOF) Unit 3: Financial Statements AnalysisBarby AngelNo ratings yet
- Internal Control of Fixed Assets: A Controller and Auditor's GuideFrom EverandInternal Control of Fixed Assets: A Controller and Auditor's GuideRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- PROFITABILITY RATIO MMDocument1 pagePROFITABILITY RATIO MMAbdul Muhaymin MahdiNo ratings yet
- Profitability RatioDocument1 pageProfitability RatioAbdul Muhaymin MahdiNo ratings yet
- Quick RatioDocument1 pageQuick RatioAbdul Muhaymin MahdiNo ratings yet
- Null 1Document4 pagesNull 1Abdul Muhaymin MahdiNo ratings yet
- Gail PPT QualitativeDocument10 pagesGail PPT QualitativeAbdul Muhaymin MahdiNo ratings yet
- Metropolitan University, SylhetDocument2 pagesMetropolitan University, SylhetAbdul Muhaymin MahdiNo ratings yet
- Abductive Reasoning and Publishing In: Academy of Management DiscoveriesDocument15 pagesAbductive Reasoning and Publishing In: Academy of Management DiscoveriesAbdul Muhaymin MahdiNo ratings yet
- Matal Haowa by Humayun AhmedDocument231 pagesMatal Haowa by Humayun AhmedAbdul Muhaymin MahdiNo ratings yet
- ChristopherDocument11 pagesChristopherAbdul Muhaymin MahdiNo ratings yet
- Case Study of British Petroleum and The Deepwater Horizon Disaster of 2010Document6 pagesCase Study of British Petroleum and The Deepwater Horizon Disaster of 2010Abdul Muhaymin MahdiNo ratings yet
- Alternative Banking ChannelDocument18 pagesAlternative Banking ChannelAbdul Muhaymin MahdiNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Marketing Management: Presented By: Brainy BuddiesDocument7 pagesPresentation On Marketing Management: Presented By: Brainy BuddiesAbdul Muhaymin MahdiNo ratings yet
- MakeAnimated PowerPoint Slide by PowerPoint SchoolDocument7 pagesMakeAnimated PowerPoint Slide by PowerPoint SchoolAbdul Muhaymin MahdiNo ratings yet
- IBA Question Solution BankDocument20 pagesIBA Question Solution BankAbdul Muhaymin Mahdi100% (1)
- Smith Smith Ashcroft BP Oil Spill ALR WP 2011Document26 pagesSmith Smith Ashcroft BP Oil Spill ALR WP 2011Abdul Muhaymin MahdiNo ratings yet
- Valiant Heroes of War of BangladeshDocument1 pageValiant Heroes of War of BangladeshAbdul Muhaymin MahdiNo ratings yet
- The 7 March SpeechDocument1 pageThe 7 March SpeechAbdul Muhaymin MahdiNo ratings yet
- Tin Goyenda Volume 6Document205 pagesTin Goyenda Volume 6Abdul Muhaymin MahdiNo ratings yet
- The United Front & Provincial General Election 1954Document1 pageThe United Front & Provincial General Election 1954Abdul Muhaymin MahdiNo ratings yet
- S.S. Hebberd - Philosophy of HistoryDocument320 pagesS.S. Hebberd - Philosophy of HistorySzoha TomaNo ratings yet
- Comm5010 InforgraphDocument5 pagesComm5010 InforgraphEdu MtushNo ratings yet
- Voting Preferences in The National Election A Case Among First-Time VotersDocument10 pagesVoting Preferences in The National Election A Case Among First-Time VotersInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Handling Unit Management in SAP Packing During Outbound ProcessDocument48 pagesHandling Unit Management in SAP Packing During Outbound ProcessmohannaiduramNo ratings yet
- Specifications: Shenzhen Sunlord Electronics Co., LTDDocument38 pagesSpecifications: Shenzhen Sunlord Electronics Co., LTDdabajiNo ratings yet
- ISB - Co2014 Consulting Case Book - FrameworksDocument24 pagesISB - Co2014 Consulting Case Book - Frameworksanshul suryanNo ratings yet
- Article LOUATIphenicienpuniqueDocument20 pagesArticle LOUATIphenicienpuniqueDabdoubidabdoubi DabdoubiNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument250 pagesPDFMarvellousNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes and KetonesDocument25 pagesAldehydes and KetonesShaira Mae Cuevillas0% (1)
- WTW TurbidityDocument6 pagesWTW TurbidityIndra AditamaNo ratings yet
- Granta Selector Installation GuideDocument7 pagesGranta Selector Installation Guidem.junaid143103No ratings yet
- Helix Board 24 FireWire MKIIDocument31 pagesHelix Board 24 FireWire MKIIJeremy MooreNo ratings yet
- WWW TSZ Com NP 2021 09 The-Bull-Exercise-Questions-And-Answers HTMLDocument11 pagesWWW TSZ Com NP 2021 09 The-Bull-Exercise-Questions-And-Answers HTMLAbhay PantNo ratings yet
- Greaves Cotton Ar 2018 1 PDFDocument168 pagesGreaves Cotton Ar 2018 1 PDFanand_parchureNo ratings yet
- Urban Development - 2Document3 pagesUrban Development - 2APSDPS17 OFFICENo ratings yet
- Front End LoadingDocument2 pagesFront End LoadingRyan SykesNo ratings yet
- VAL 225 Procedure For Performing Steam in Place SIP Validation SampleDocument14 pagesVAL 225 Procedure For Performing Steam in Place SIP Validation SampleSameh MostafaNo ratings yet
- Real Time Detection of Human Stress Using Sensors and Machine Learning TechniquesDocument12 pagesReal Time Detection of Human Stress Using Sensors and Machine Learning TechniquesA M WamiqueNo ratings yet
- Auvinet State of The Art 0Document7 pagesAuvinet State of The Art 0khernandez6491No ratings yet
- Budesonide (Drug Study)Document3 pagesBudesonide (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse6888No ratings yet
- MA3003 Standard EU ML Actuador - Electronico de GiroDocument70 pagesMA3003 Standard EU ML Actuador - Electronico de GirojaseriNo ratings yet
- Form 1 Admission Application (SE2)Document4 pagesForm 1 Admission Application (SE2)trueNo ratings yet
- An Overview On The Validation Approach For Steam Sterilization - Part II, Madalina Brindusa Boca Et. Al.Document9 pagesAn Overview On The Validation Approach For Steam Sterilization - Part II, Madalina Brindusa Boca Et. Al.bocam100% (1)
- Asres Abitie Kebede Dissertation ThesisDocument249 pagesAsres Abitie Kebede Dissertation ThesisJemal TeshaleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6-Highway Drainage DesignDocument27 pagesChapter 6-Highway Drainage DesignAbel MulugetaNo ratings yet
- 101 Electronics Projects 1977Document100 pages101 Electronics Projects 1977نهمياسباريراNo ratings yet
- Drone pg1Document1 pageDrone pg1kokiuaNo ratings yet