Professional Documents
Culture Documents
INFERTILITY
INFERTILITY
Uploaded by
yxly imperialOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
INFERTILITY
INFERTILITY
Uploaded by
yxly imperialCopyright:
Available Formats
NCM 109 – MATERNAL LEC
2ND SEMESTER | MIDTERMS
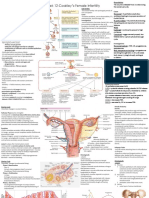
TOPIC 2: INFERTILITY/SUBFERTILITY
INFERTILITY /SUBFERTILITY - Condition that occurs when adhesions
or scaring bind adjacent organs together
Infertility – inability to conceive a child or sustain a
pregnancy to birth. CAUSES OF SUBFERTILITY
a couple is infertile if they do not become In Males:
pregnant after at least 1 year of unprotected Disturbance in spermatogenesis
sex or the woman keeps having Inadequate production of FSH and LH in the
miscarriages. pituitary
Obstruction in seminiferous tubules, ducts,
Subfertility – most often used today or vessels
delay in conceiving Development of autoimmunity
possibility of conceiving naturally exists, but Problems in ejaculation
it takes longer than average excessive exposure to X-rays or radioactive
can be related to age substances, stress
In Females
TYPES OF INFERTILITY Limited production of FHS or LH
1. Primary Infertility - there have been no Anovulation
previous conceptions Problems of ova transport
2. Secondary Infertility - there has been a Uterine tumors
previous viable pregnancy but there is
Cervical Vaginal Factors
inability to conceive at present
Poor nutrition
3. Sterility - inability to conceive because of
known condition (e.g., absence of uterus)
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS OF INFERTILITY AND
SUBFERTILITY
CAUSES OF INFERTILITY
1. Abnormal Menstruation
- Cause of infertility is multifactorial
2. No Menstruation
3. Irregular Menstruation
1. Severe Endometriosis
4. Painful Menstruation
- cells of endometrium grow outside the
5. Skin Changes
uterus.
6. Dark Hair Growth
2. Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
7. Loss or Thinning of Hair
- Inflammation of reproductive organs of a
8. Weight Gain
woman.
3. Ovulation Disorders
DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURES
- Most common cause of infertility.
1. Semen Analysis
- Inability of a woman to produce egg
- a.k.a sperm count or male fertility test -
cells during menstruation.
measures the amount and quality of a
4. Elevated Prolactin
man's semen and sperm
- a.k.a Prolactinoma
- lab test that evaluates sperm count,
- excess prolactin can cause production
motility, morphology and more
of breastmilk in men and women who
2. Ovulation Monitoring Assessment
are not pregnant.
- helps identify the most fertile days each
5. Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome
month
- Women with PCOS may not ovulate.
requires monitoring to distinguish
They have high levels of androgen, and
normal and abnormal ovarian cycles
have many small cysts on the ovaries.
3. Tubal Patency Assessment
6. Benign Uterine Fibroids
- it starts with a normal ultrasound (using
- Tumors arising from smooth muscle
a vaginal probe) to assess your uterus,
tissues within the uterus.
- ovaries and pelvis.
7. Pelvic Adhesions
- to determine if the fallopian tubes are
open and free of disease. It is commonly
2
NCM 109 – MATERNAL LEC
2ND SEMESTER | MIDTERMS
TOPIC 2: INFERTILITY/SUBFERTILITY
done in women with an infertility
diagnosis.
HEALTH TEACHINGS
MEDICAL MANAGEMENT 1. Maintenance of body weight
1. Clomiphene Citrate – stimulate the growth 2. Avoid fertility impairing medications
of an ovarian follicle containing an egg 3. Avoid smoking and alcohol
2. Letrozole – helpful aid to induce an egg to 4. Psychological support
develop and be released in women 5. Stay informed
3. Gonadotropins – stimulate the ovary directly 6. Stay physically active to maintain fitness
to produce multiple eggs
4. Bromocriptine – used when ovulation
problems are caused by excess production
of prolactin by the pituitary gland
SURGICAL MANAGEMENT
1. Hysteroscopy – can be used diagnostically -
find the cause of abdominal bleeding
2. Laparoscopy – minimally invasive surgery -
Uses a system containing a small camera
and operating instruments to see the
reproductive organs
3. Tubal Surgeries – removal of tubes or
blockage in the tubes close to the uterus -
Can improve the chances of pregnancy with
IVF
NURSING MANAGEMENT
1. Assess hormone levels and whether a
woman is ovulating
2. Provide the couple with accurate
information about human reproduction,
infertility treatments, and prognosis for
pregnancy
3. Identify and treat possible causes of
infertility
NURSING DIAGNOSIS
1. Anticipatory grieving related to failure to
conceive or sustain a pregnancy
2. Deficient knowledge related to measures to
promote fertility
3. Powerlessness related to repeated
unsuccessful attempts at achieving
conception
4. Fear related to possible outcome of infertility
studies
5. Anxiety related to what the process of
fertility testing will entail
6. Hopelessness related to perception of no
viable alternatives to usual perceptions
7. Situational low self-esteem related to the
apparent inability to conceive
2
You might also like
- Sujok Color Points PDFDocument55 pagesSujok Color Points PDFAnonymous BGQNXl890% (20)
- Preclinical Anatomy Review 2023: For USMLE Step 1 and COMLEX-USA Level 1From EverandPreclinical Anatomy Review 2023: For USMLE Step 1 and COMLEX-USA Level 1Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Case Study - Ectopic PregnancyDocument10 pagesCase Study - Ectopic Pregnancykristine keen buanNo ratings yet
- MCN2 Prelim-NotesDocument4 pagesMCN2 Prelim-NotesChris AnnNo ratings yet
- Module 6 - MCN TransesDocument3 pagesModule 6 - MCN TransesCarl UyNo ratings yet
- OB LecDocument18 pagesOB LecSofia ThefirstNo ratings yet
- SDL 3Document3 pagesSDL 3bekbekk cabahugNo ratings yet
- School of Health and Allied Health Sciences Nursing DepartmentDocument2 pagesSchool of Health and Allied Health Sciences Nursing DepartmentRosemarie R. ReyesNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The Reproductive SystemDocument10 pagesDisorders of The Reproductive SystemRose Kathreen Quintans AuxteroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21 Reproductive TechnologiesDocument5 pagesChapter 21 Reproductive TechnologiesAllaine AlvarezNo ratings yet
- NCM 109 Midterms - Infertility L2Document7 pagesNCM 109 Midterms - Infertility L2Leigh Angelika Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Hadawale N. M, Thorat R. M., Gaikwad D. D., Jadhav S. LDocument4 pagesHadawale N. M, Thorat R. M., Gaikwad D. D., Jadhav S. LAditya VirayudhaNo ratings yet
- Gestational Conditions HandoutDocument17 pagesGestational Conditions HandoutFilamae Jayahr Caday100% (4)
- Ncmhce108 Endterm NotesDocument3 pagesNcmhce108 Endterm NotesNicole GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Supplemental Notes in Maternal Bullets Family PlanningDocument3 pagesSupplemental Notes in Maternal Bullets Family Planningjohn paul richard mindanaoNo ratings yet
- Forensic PsychologyDocument4 pagesForensic PsychologyAlison BationNo ratings yet
- OBSTETRICS - Midterms - 1.1 - Diagnosis of Pregnancy - TRANSDocument5 pagesOBSTETRICS - Midterms - 1.1 - Diagnosis of Pregnancy - TRANSAi Gutierrez100% (1)
- MCN Lect Multiple Pregnancy Hydramnios PosttermDocument5 pagesMCN Lect Multiple Pregnancy Hydramnios PosttermAmethystNo ratings yet
- 2 Topics at RiskDocument5 pages2 Topics at RiskGeraldine PatayanNo ratings yet
- Multiple PregnancyDocument26 pagesMultiple PregnancyRaj PatelNo ratings yet
- Semi Finals CHAPTER IVDocument5 pagesSemi Finals CHAPTER IVjacobprince0016No ratings yet
- Care of Couples With Infertility ProblemsDocument3 pagesCare of Couples With Infertility ProblemsLORNA ARTUGUENo ratings yet
- SDL 3 MCN 1Document3 pagesSDL 3 MCN 1Milagros Florita100% (1)
- Quiz 1Document7 pagesQuiz 1TrishaNo ratings yet
- 5 6093573606699171929Document20 pages5 6093573606699171929Sara KhanNo ratings yet
- NCM107 1Document52 pagesNCM107 1Sarah Shane Cortes CortesNo ratings yet
- Maternal High Risk Factors (High Risk Pregnancies)Document20 pagesMaternal High Risk Factors (High Risk Pregnancies)Charmy UbiñaNo ratings yet
- Infertility: PGI Ira Mikkaella GenobisDocument49 pagesInfertility: PGI Ira Mikkaella GenobisIra Mikkaella GenobisNo ratings yet
- Reproductive DisordersDocument2 pagesReproductive Disorderskara.adolacion-19No ratings yet
- InfertilityDocument30 pagesInfertilityEka KurniatiNo ratings yet
- Obg AbortionDocument62 pagesObg Abortionkashyap priyankaNo ratings yet
- Erogenous ZonesDocument2 pagesErogenous ZonesMelizza Fajardo BañanoNo ratings yet
- NCM 109 - Infertilifty MGTDocument5 pagesNCM 109 - Infertilifty MGTYsabelle GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Sex and FertDocument17 pagesWeek 2 Sex and FertAbmil Ching TinggalongNo ratings yet
- MCN 2 Lec Topic 3 TRANNIESDocument8 pagesMCN 2 Lec Topic 3 TRANNIESKrizelle MesinaNo ratings yet
- KriptorkismusDocument14 pagesKriptorkismusMutiara Prima DianaNo ratings yet
- In Vitro FertilizationDocument30 pagesIn Vitro FertilizationDianna RoseNo ratings yet
- Psychological Changes of PregnancyDocument2 pagesPsychological Changes of PregnancyMicah NayraNo ratings yet
- Invitro FertilizationDocument2 pagesInvitro FertilizationAryanNo ratings yet
- Difficulty of Conceiving-McnDocument4 pagesDifficulty of Conceiving-McnMary Leshiel TamayoNo ratings yet
- High Risk Prenatal CareDocument4 pagesHigh Risk Prenatal CareKatherine Gayle GuiaNo ratings yet
- Hydatidiform Mole OutlineDocument3 pagesHydatidiform Mole Outlineyxly imperialNo ratings yet
- Module 6 Problems in Reproduction 2023Document45 pagesModule 6 Problems in Reproduction 2023DemokGraganzaJrNo ratings yet
- Definition of Premature Rapture of Membrane (Document3 pagesDefinition of Premature Rapture of Membrane (Merly Grael LigligenNo ratings yet
- Completed ABORTION SEMINARDocument31 pagesCompleted ABORTION SEMINARkalla sharon100% (1)
- Maternal Reviewer NervanzDocument20 pagesMaternal Reviewer NervanzRovic GasmenNo ratings yet
- Week 12-Female InfertilityDocument2 pagesWeek 12-Female InfertilityJaimie Charlotte Marie LangilleNo ratings yet
- NCM 109 Semi Final CHAPTER IVDocument6 pagesNCM 109 Semi Final CHAPTER IV37. Vanesa mae ReyesNo ratings yet
- Cmca at RiskDocument11 pagesCmca at RiskAyanami PascuaNo ratings yet
- Mullerian Duct AbnormalitiesDocument4 pagesMullerian Duct AbnormalitiesrohitNo ratings yet
- In-Vitro Fertilisation: Shruti Samal ROLL NUMBER - 1120096 B.Sc. Life Science Second SemesterDocument20 pagesIn-Vitro Fertilisation: Shruti Samal ROLL NUMBER - 1120096 B.Sc. Life Science Second SemesterSHRUTI SAMALNo ratings yet
- Wk. 5 SubfertilityDocument75 pagesWk. 5 Subfertilitycgalero.feudilimanNo ratings yet
- Cmca Mother NotesDocument5 pagesCmca Mother Notesyutanakamotoyuta29No ratings yet
- Ncm107 Summarization of MCNDocument40 pagesNcm107 Summarization of MCNArlyn Faith AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Ethics FinalDocument7 pagesEthics FinalMADIZA AMBOLNo ratings yet
- Breech PresentationffDocument8 pagesBreech Presentationffminte ziNo ratings yet
- MCN Topic 1 Basic ConceptsDocument7 pagesMCN Topic 1 Basic ConceptsDiana CalderonNo ratings yet
- High Risk Ob Notes 1Document20 pagesHigh Risk Ob Notes 1pinpindalgoNo ratings yet
- Instructional Learning Guide: Course Audit in Maternal and Child NursingDocument18 pagesInstructional Learning Guide: Course Audit in Maternal and Child NursingMaynard PascualNo ratings yet
- FIFTHDocument20 pagesFIFTHJuhainie Dipatuan MagundacanNo ratings yet
- Alternatives To ChildbirthDocument4 pagesAlternatives To ChildbirthMaria Donabella OngueNo ratings yet
- Hydatidiform Mole OutlineDocument3 pagesHydatidiform Mole Outlineyxly imperialNo ratings yet
- Cervical InsuffficiencyDocument2 pagesCervical Insuffficiencyyxly imperialNo ratings yet
- ANOVULATIONDocument2 pagesANOVULATIONyxly imperialNo ratings yet
- Im A Thousand Yet MyselfDocument19 pagesIm A Thousand Yet Myselfyxly imperialNo ratings yet
- 36 Bio Adsorbent Potential of Coconut Cocos Nucifera L. Husk in Treating Simulated Lead Contaminated Soil SUPER FINALDocument61 pages36 Bio Adsorbent Potential of Coconut Cocos Nucifera L. Husk in Treating Simulated Lead Contaminated Soil SUPER FINALyxly imperialNo ratings yet
- Endometriosis PathophysiologyDocument4 pagesEndometriosis PathophysiologyGeLa GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Primary and Secondary Anenorrhea 2016-2017Document24 pagesPrimary and Secondary Anenorrhea 2016-2017zianab ali100% (1)
- Infertility CausesDocument3 pagesInfertility Causesapi-3733640No ratings yet
- Menorrhagia (Heavy Menstrual Bleeding)Document55 pagesMenorrhagia (Heavy Menstrual Bleeding)Aizi DwimeilaNo ratings yet
- ContraceptionDocument39 pagesContraceptionapi-3705046100% (3)
- Short Answers Chapter 1 Page 3Document42 pagesShort Answers Chapter 1 Page 3Leen AlodatNo ratings yet
- McAllister - David MSN FP6021 Assessment 1 Attempt 2Document6 pagesMcAllister - David MSN FP6021 Assessment 1 Attempt 2David McAllisterNo ratings yet
- Nat Prog Book 1 PDFDocument430 pagesNat Prog Book 1 PDFIoana Brăteanu100% (1)
- OBGYN 1st Round 2021 AnsweredDocument14 pagesOBGYN 1st Round 2021 AnsweredMuhammed Mostafa100% (5)
- INTRODUCTION of Anger MGNTDocument63 pagesINTRODUCTION of Anger MGNTRoshani VichareNo ratings yet
- SonoSim Objectives BreastDocument8 pagesSonoSim Objectives Breastkingjameson1No ratings yet
- Gensoc ModuleDocument56 pagesGensoc ModuleLovely Victoria DeluteNo ratings yet
- Ovarian CystDocument26 pagesOvarian CystAlmyr RimandoNo ratings yet
- Intro On Ovulation and FertilityDocument2 pagesIntro On Ovulation and FertilitylookloNo ratings yet
- Hormone Guide 5x5 Grid 25x25 EnglishDocument2 pagesHormone Guide 5x5 Grid 25x25 EnglishlordNo ratings yet
- Menarche: First Occurrence of MenstruationDocument8 pagesMenarche: First Occurrence of MenstruationSheeba StalinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21: Gonadal Function: by Marissa GrotzkeDocument21 pagesChapter 21: Gonadal Function: by Marissa GrotzkeJanielle FajardoNo ratings yet
- Renewing Female Balance Pms Breast Uterine Ovarian Annas ArchiveDocument52 pagesRenewing Female Balance Pms Breast Uterine Ovarian Annas Archivenathanford1No ratings yet
- Menopause Semester 6 (IMTU)Document37 pagesMenopause Semester 6 (IMTU)nyangaraNo ratings yet
- Concept of Ovulation in AyurvedaDocument6 pagesConcept of Ovulation in Ayurvedasan MunNo ratings yet
- Prince or PrincessDocument63 pagesPrince or PrincessRoel PlmrsNo ratings yet
- How Do Organisms Reproduce - Class 10 Science SA2 NCERT Solutions Free PDF DownloadDocument11 pagesHow Do Organisms Reproduce - Class 10 Science SA2 NCERT Solutions Free PDF Downloadmedi plusNo ratings yet
- Gonadal Hormones & Inhibitors Contraceptives: DR Dhoro Clinical PharmacologyDocument34 pagesGonadal Hormones & Inhibitors Contraceptives: DR Dhoro Clinical PharmacologykelvinNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Introduction To Maternity Pediatric Nursing 6th Edition Leifer Solutions Manual PDFDocument36 pagesDwnload Full Introduction To Maternity Pediatric Nursing 6th Edition Leifer Solutions Manual PDFgreeningquinovic25yn2100% (14)
- Soal Untuk Peserta OSCEDocument8 pagesSoal Untuk Peserta OSCEchebonk13No ratings yet
- 3893 ID Faktor Risiko Yang Mempengaruhi Kejadian Dismenore PrimerDocument8 pages3893 ID Faktor Risiko Yang Mempengaruhi Kejadian Dismenore PrimerNur lailah sakinahNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions: ReproductionDocument12 pagesMultiple Choice Questions: ReproductionJohn Osborne100% (1)
- Obg - 9.4.20 (Forenoon) Unit 12 - Infertility and Its ManagementDocument81 pagesObg - 9.4.20 (Forenoon) Unit 12 - Infertility and Its ManagementElakkiyaanu64 Elakkiyaanu64No ratings yet
- MenstrualcyclelecturedrirabonDocument32 pagesMenstrualcyclelecturedrirabonHananya ManroeNo ratings yet