Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ncert Solutions Class 8 Science Chapter 16
Ncert Solutions Class 8 Science Chapter 16
Uploaded by
JollyCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Chris Aceto - Championship BodybuildingDocument290 pagesChris Aceto - Championship Bodybuildingshanmumepco100% (49)
- CH 16Document7 pagesCH 16sneha2701choudharyNo ratings yet
- Excercises: AnswerDocument8 pagesExcercises: AnswervinayakNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 8 Science Chapter 16Document6 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 8 Science Chapter 16Danish XainNo ratings yet
- Class 8-Light-TB EX-SreejaDocument5 pagesClass 8-Light-TB EX-SreejaRAYAN ISWKNo ratings yet
- CLASS VIII SCIENCE CHAPTER-13 LightDocument6 pagesCLASS VIII SCIENCE CHAPTER-13 Lightarnav.chaudhary39923No ratings yet
- Light Class 8 Book-WPS OfficeDocument9 pagesLight Class 8 Book-WPS OfficeS.B.M.PADMESH SATHURAGIRINo ratings yet
- 8 Science 16 Light TextBook QnADocument20 pages8 Science 16 Light TextBook QnAkumaran RNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 LightDocument5 pagesChapter 16 Lightkalash iyerNo ratings yet
- LightDocument22 pagesLightAditya YaduvanshiNo ratings yet
- Light: S.No Regular Reflection Diffused Reflection 1. 2Document6 pagesLight: S.No Regular Reflection Diffused Reflection 1. 2bharat patelNo ratings yet
- CH Light QuestionsAnswerDocument7 pagesCH Light QuestionsAnswerjeewan761980No ratings yet
- Light Class.8 SolutionDocument7 pagesLight Class.8 Solutionpraty171510No ratings yet
- QA LightDocument7 pagesQA LightDomino CreationsNo ratings yet
- Question Bank - Light - Grade VIIIDocument5 pagesQuestion Bank - Light - Grade VIIIpk197679No ratings yet
- Ncert Solutions For Class 8 March 31 Science Chapter 16 LightDocument7 pagesNcert Solutions For Class 8 March 31 Science Chapter 16 LightVandana SainiNo ratings yet
- Light CW - Mod 1Document4 pagesLight CW - Mod 1Jayaprasanna VenkatesanNo ratings yet
- NCERT Exemplar Class 8 Science Solutions Chapter 16 LightDocument14 pagesNCERT Exemplar Class 8 Science Solutions Chapter 16 Lightanvu4848100% (1)
- CH 16 Light 2023Document4 pagesCH 16 Light 2023Anshul DessaiNo ratings yet
- Light NotesDocument5 pagesLight Notesmohannimmi9No ratings yet
- Chapter 16 Light-3Document4 pagesChapter 16 Light-3sabreenaapNo ratings yet
- Light Physics NotesDocument5 pagesLight Physics NotesWani Minham123No ratings yet
- Light Shadows and ReflectionDocument6 pagesLight Shadows and ReflectionPinki NegiNo ratings yet
- Class VIII LightDocument2 pagesClass VIII Lightbose baraniNo ratings yet
- Unit I PDFDocument15 pagesUnit I PDFsrinivas0sai-10% (1)
- Unit 16 (Light) : Multiple Choice Questions (MCQS)Document8 pagesUnit 16 (Light) : Multiple Choice Questions (MCQS)Narsi KumarNo ratings yet
- LightDocument7 pagesLightbaibhavdhamalaNo ratings yet
- NCERT Exemplar Solution Class 8 Science Chapter 16Document12 pagesNCERT Exemplar Solution Class 8 Science Chapter 16anvu4848No ratings yet
- CH-11 Light PPT-2Document33 pagesCH-11 Light PPT-2SUHANEERIYANo ratings yet
- Important Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 11Document14 pagesImportant Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 11moviezonyNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 11 Human Eye and Colourful World Important Questions 2022-23Document14 pagesCBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 11 Human Eye and Colourful World Important Questions 2022-23Rohan SenapathiNo ratings yet
- Lakhmir Singh Solutions Class 10 Physics Chapter 4 Reflection of LightDocument31 pagesLakhmir Singh Solutions Class 10 Physics Chapter 4 Reflection of Lightanilsisodia78No ratings yet
- Lakhmir Singh Solutions Feb23 Class 10 Physics Chapter 4 Reflection of LightDocument31 pagesLakhmir Singh Solutions Feb23 Class 10 Physics Chapter 4 Reflection of LightA.P. ABISEK100% (1)
- Light and Shadow 5 FEB 24Document7 pagesLight and Shadow 5 FEB 24ramasenNo ratings yet
- Reflection Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesReflection Lesson PlanSean O'Reilly100% (3)
- Chap - 3: Reflection of Light by Different Surfaces.: Think & DiscussDocument4 pagesChap - 3: Reflection of Light by Different Surfaces.: Think & Discusssreekanth-gannamaraju-6907No ratings yet
- Chapter 16 Light Class 8Document15 pagesChapter 16 Light Class 8Amaira KalsiNo ratings yet
- Physics 2Document11 pagesPhysics 2bort kortNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE10 Q2 M4 LightsMirrorsandLenses v3-EDITEDDocument22 pagesSCIENCE10 Q2 M4 LightsMirrorsandLenses v3-EDITEDRusty Gabriel Suyom100% (1)
- Lessonsections-17 1Document10 pagesLessonsections-17 1Ghazi DallyNo ratings yet
- Chung Cheng High School (Main) Sec 1 Physics Chapter E3Document16 pagesChung Cheng High School (Main) Sec 1 Physics Chapter E3Ken TanNo ratings yet
- 08 Science Light 01Document5 pages08 Science Light 01Ranjan RoyNo ratings yet
- Chapter-10 - Light: Reflection and RefractionDocument15 pagesChapter-10 - Light: Reflection and RefractionVineet SierraNo ratings yet
- Workbook Solution LightDocument6 pagesWorkbook Solution Lightsmi_santhoshNo ratings yet
- CbseDocument15 pagesCbseYaaroNo ratings yet
- This Explains Why Using Sunglasses Helps Avoid This Effect Your Rods Are Less Susceptible To The Sun's "Bleaching"Document6 pagesThis Explains Why Using Sunglasses Helps Avoid This Effect Your Rods Are Less Susceptible To The Sun's "Bleaching"Go TNo ratings yet
- Chapter Light Class 7 Chapter Q and ADocument9 pagesChapter Light Class 7 Chapter Q and ADaiwik GuptaNo ratings yet
- Bellringer: Chapter 17: Reflection and MirrorsDocument10 pagesBellringer: Chapter 17: Reflection and MirrorsGhazi DallyNo ratings yet
- Pinhole CameraDocument4 pagesPinhole CamerajainNo ratings yet
- Light NB WorkDocument4 pagesLight NB Workdakshsri24No ratings yet
- SLM QTR 2 Week 5 7Document21 pagesSLM QTR 2 Week 5 7pagayonmicaNo ratings yet
- GR 7 - LIGHT - ANSWER KEYDocument3 pagesGR 7 - LIGHT - ANSWER KEYJoseph JayakanthanNo ratings yet
- Title Card: Lesson 12: Mirror Images Are Laterally InvertedDocument16 pagesTitle Card: Lesson 12: Mirror Images Are Laterally InvertedNathan Francis Enzo NicolasNo ratings yet
- Notebook Work CH - 16 (Light)Document9 pagesNotebook Work CH - 16 (Light)Adhya MisraNo ratings yet
- Exercise Soln Reflection of LightDocument48 pagesExercise Soln Reflection of LightiTutor Classes BapiNo ratings yet
- Physics-6 LightDocument132 pagesPhysics-6 LightsamNo ratings yet
- Science: Modified Strategic Intervention MaterialsDocument26 pagesScience: Modified Strategic Intervention MaterialsFhien Garcia100% (2)
- X April Physics LightDocument2 pagesX April Physics Lightprasidh2021No ratings yet
- Human Eye and Colourful World QuestionsDocument12 pagesHuman Eye and Colourful World QuestionsSahishna SurapaneniNo ratings yet
- Through a Microscope: Something of the Science, Together with many Curious Observations Indoor and Out and Directions for a Home-made MicroscopeFrom EverandThrough a Microscope: Something of the Science, Together with many Curious Observations Indoor and Out and Directions for a Home-made MicroscopeNo ratings yet
- Ncert Solutions Class 8 Science Chapter 10Document10 pagesNcert Solutions Class 8 Science Chapter 10JollyNo ratings yet
- Ncert Solutions Class 8 Science Chapter 7Document9 pagesNcert Solutions Class 8 Science Chapter 7JollyNo ratings yet
- Ncert Solutions Class 8 Maths Chapter 1 Rational NumbersDocument10 pagesNcert Solutions Class 8 Maths Chapter 1 Rational NumbersJollyNo ratings yet
- Ncert Solutions Class 8 Maths Chapter 5 Data HandlingDocument13 pagesNcert Solutions Class 8 Maths Chapter 5 Data HandlingJollyNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - Topic 5 - 1-5 Basic Biopharmaceutical Unit OperationsDocument6 pagesWeek 1 - Topic 5 - 1-5 Basic Biopharmaceutical Unit OperationsCelineNo ratings yet
- English Unlimited Intermediate b1 Progress Test 3Document2 pagesEnglish Unlimited Intermediate b1 Progress Test 3Mohammad sadegh Heydari50% (2)
- 2018 Root Cause CategoriesDocument3 pages2018 Root Cause CategoriesRidwan AriefNo ratings yet
- Strategic Planning For Supply Chain Leaders: Capture An Actionable Strategic Plan On One PageDocument7 pagesStrategic Planning For Supply Chain Leaders: Capture An Actionable Strategic Plan On One PageVinith JoshuaNo ratings yet
- En 50288 7 Re 2x ST y PVC CableDocument3 pagesEn 50288 7 Re 2x ST y PVC CableH. NurzeinNo ratings yet
- 3Document22 pages3amanNo ratings yet
- AQ F215 Feeder Protection Device Instruction Manual v2.10 EnglishDocument546 pagesAQ F215 Feeder Protection Device Instruction Manual v2.10 EnglishRicardo LyraNo ratings yet
- Complete Civil 3D 2020 TOC SampleDocument67 pagesComplete Civil 3D 2020 TOC SampleLasno LasnoNo ratings yet
- 0594-0598 (1058) Analytical Instrument QualificationDocument5 pages0594-0598 (1058) Analytical Instrument QualificationRaf RafNo ratings yet
- Lab Report#03: Artifical Intelligence Submitted To: SUBMITTED BY: Muhammad Reg No.: DateDocument8 pagesLab Report#03: Artifical Intelligence Submitted To: SUBMITTED BY: Muhammad Reg No.: DateMuhammad SobanNo ratings yet
- Java Programs Java 1658665821Document37 pagesJava Programs Java 1658665821Spoorthi BNo ratings yet
- Biology Investigatory Experiments and Project ReportsDocument5 pagesBiology Investigatory Experiments and Project ReportsJasim AbdullaNo ratings yet
- Behavior and Strengths of Single Cast-In Anchors in Ultra-High-PerformanceDocument10 pagesBehavior and Strengths of Single Cast-In Anchors in Ultra-High-PerformancePrayush RajbhandariNo ratings yet
- Artikel 5 - 1Document8 pagesArtikel 5 - 1Sintalia DewiNo ratings yet
- Spesifikasi Produk SL-500Document2 pagesSpesifikasi Produk SL-500tekmed koesnadiNo ratings yet
- Mach3 USB Motion Card (JDSW43B) Installation ManualDocument35 pagesMach3 USB Motion Card (JDSW43B) Installation ManualCesxr Buttowski HNNo ratings yet
- Theory of Evolution by Natural SelectionDocument15 pagesTheory of Evolution by Natural Selectionpaula nicolle mostoles100% (1)
- ASME PipingDocument19 pagesASME PipingsingourNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Self StudyDocument80 pagesLecture 1 Self StudyYash ShahNo ratings yet
- University of Nigeria: Course Registration Form SESSION: 2019-2020Document1 pageUniversity of Nigeria: Course Registration Form SESSION: 2019-2020Barinua deekorNo ratings yet
- Aen Ibu07Document64 pagesAen Ibu07Thaovy VomaiNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Secondary 1 Checkpoint: Cambridge Assessment International EducationDocument20 pagesCambridge Secondary 1 Checkpoint: Cambridge Assessment International EducationSallyNo ratings yet
- Flight Planning For ATTDocument106 pagesFlight Planning For ATTTienek Lee100% (1)
- Notefull Reading Step1Document54 pagesNotefull Reading Step1Luis CorderoNo ratings yet
- Santi's Math 2nd Quarter ReviewerDocument9 pagesSanti's Math 2nd Quarter ReviewerAlyssa Renee Abaya CruzNo ratings yet
- HMT Lecture 8 - Heat ExchangersDocument16 pagesHMT Lecture 8 - Heat ExchangerstsegayNo ratings yet
- Eden - Atlantis ProjectDocument25 pagesEden - Atlantis ProjectLeomar MartínezNo ratings yet
- Solar Power PlantDocument13 pagesSolar Power PlantSsagar Kadam67% (3)
- MSDS Verimaster 824Document6 pagesMSDS Verimaster 824medo.k016No ratings yet
Ncert Solutions Class 8 Science Chapter 16
Ncert Solutions Class 8 Science Chapter 16
Uploaded by
JollyOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ncert Solutions Class 8 Science Chapter 16
Ncert Solutions Class 8 Science Chapter 16
Uploaded by
JollyCopyright:
Available Formats
NCERT Solutions for Class 8
Science
Chapter 16 – Light
1. Suppose you are in a dark room. Can you see objects in the room?
Can you see objects outside the room? Explain.
Ans: In a dark room one cannot see things in a room, but things outside the
room will be visible.
The reason for this is that the object is only visible when light from the object
reaches the eye. In a dark room, we cannot see objects because the rays of
light do not reach our eyes whereas in a lighted room, the rays of light
reflected from the objects reach our eyes making them visible for us.
2. Differentiate between regular and diffused reflection. Does diffused
reflection mean the failure of the laws of reflection?
Ans: Difference between regular and diffused reflection is as follows:
Regular Reflection Diffused Reflection
Regular Reflection takes place Diffused Reflection takes place
from a smooth and shiny on a rough or irregular surface.
surface.
All rays are parallel after The reflected rays are not
reflection. parallel to each other.
Diffused reflection is not due to the failure of the laws of reflection. It is
caused by the irregularities in the reflecting surface.
3. Mention against each of the following whether regular or diffused
reflection will take place when a beam of light strikes. Justify your
answer in each case.
a) Polished wooden table
Ans: A polished surface means the surface is very smooth, thus
regular reflection takes place.
b) Chalk powder
Ans: A diffused reflection takes place on a chalk powder because its
surface is uneven.
c) Cardboard surface
Class VIII Science www.vedantu.com 1
Ans: The surface of cardboard which reflects light is not smooth, thus
diffused reflection will take place from a cardboard surface.
d) Marble floor with water spread over it
Ans: The water spread over marble makes the surface very
Smooth which makes it act like a plane surface. Hence, regular reflection
takes place.
e) Mirror
Ans: The surface of the mirror is very smooth and shiny. Therefore, regular
reflection takes place.
f) Piece of paper
Ans: A piece of paper may look smooth, but it has many irregularities on
its surface. Thus, diffused reflection takes place.
4. State the laws of reflection.
Ans: Laws of reflection can be stated as follows:
i. The angle of reflection and angle of incidence are always equal to each
other.
ii. The incident ray, the normal at the point of incidence and the reflected
ray all lie in the same plane.
5. Describe an activity to show that the incident ray, the reflected ray
and the normal at the point of incidence lie in the same plane.
Ans:To perform this experiment take a plane mirror and place it on a plane
sheet of paper in a standing position with a block. Then draw an incidence
line AB on this paper. Mark the points on the paper by carefully looking on
the mirror. The line that goes after it appears on the screen. Draw a
perpendicular on the mirror line and then remove the mirror. Join the points to
make the reflected ray on the paper. You will observe that incident ray,
reflected ray and normal will be in the same plane, i.e. on the sheet of paper.
This verifies the law of reflection.
Class VIII Science www.vedantu.com 2
6. Fill in the blanks in the following.
a) A person 1 m in front of a plane mirror seems to be ____ m away
from his image.
Ans: A person 1 m in front of a plane mirror seems to be 2 m away from
his image.
b) If you touch your ________ ear with your right hand in front of a
plane mirror, it will be seen in the mirror that your right ear is
touched with your _________.
Ans: If you touch your left ear with your right hand in front of a plane
mirror, it will be seen in the mirror that your right ear is touched with your
left hand.
c) The size of the pupil becomes ________ when you see in dim light.
Ans: The size of the pupil becomes large when you see in dim light.
d) Night birds have _________ cones than rods in their eyes.
Ans: Night birds have lesser cones than rods in their eyes.
7. Angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
a) Always
b) Sometimes
c) Under special conditions
d) Never
Ans: (a) Always
Since, the first law of reflection states that the angle of incidence and
angle of reflection are always equal to each other.
8. Image formed by a plane mirror is
a) virtual, behind the mirror and enlarged.
b) virtual, behind the mirror and of the same size as the object.
c) real at the surface of the mirror and enlarged.
d) real, behind the mirror and of the same size as the object.
Ans: (b) Virtual, behind the mirror and of the same size as the object.
The image created by the plane mirror is built behind the mirror. This image
cannot be created on screen, so it produces a virtual image of the size as that
of the object.
9. Describe the construction of a kaleidoscope.
Ans: The Kaleidoscope is made up of three rectangular squares each about
Class VIII Science www.vedantu.com 3
15 cm long and 4 cm wide which are joined together to build a prism. They
are arranged in a circular cardboard tube. Note that the tube is slightly longer
than the screen straps. One end of the tube is closed with a cardboard disc
with a hole in the middle. To make the disk last longer, a piece of transparent
plastic paper is attached to the bottom of the cardboard disk. At the other end,
a round plate of the glass plane is fixed touching the mirrors.
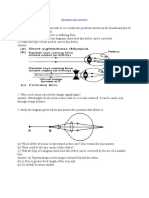
10. Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye.
Ans:
11. Gurmit wanted to perform Activity 16.8 using a laser torch. Her
teacher advised her not to do so. Can you explain the basis of the
teacher’s advice?
Ans: The intensity of the laser light is very high which is harmful for eye and
can cause a permanent defect in the eye. She can lose her eyesight also due to
severe damage to the retina. Therefore, it is advisable not to look at a laser
beam directly.
12. Explain how you can take care of your eyes.
Class VIII Science www.vedantu.com 4
Ans: To protect our eyes, the following precautions should be taken:
i. Do not read in too little or too much light.
ii. Wash your eyes frequently with cold water.
iii. Do not read by bringing your book too close to your eyes or keeping it
too far.
iv. Never rub your eyes.
v. If particles of dust go into our eyes, wash our eyes with clean water. If
there is no improvement go to a doctor.
13. What is the angle of incidence of a ray if the reflected ray is at an
angle of 90 to the incident ray?
Ans: We know that, angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
Therefore, twice of incidence angle is equal to 90 .
90
Thus, Angle of incidence i .
2
i 45
14. How many images of a candle will be formed if it is placed between
two parallel plane mirrors separated by 40 cm?
Ans: Since the mirrors are kept parallel to each other, Infinite no of images
will be formed due to multiple reflection between them.
15. Two mirrors meet at right angles. A ray of light is incident on one at
an angle of 30 as shown in Fig. 16.19 . Draw the reflected ray from
the second mirror.
Ans. From the first law of reflection, The angle of reflection and angle of
incidence are always equal to each other.
The diagram of the reflected ray from the second mirror is as follows:
Class VIII Science www.vedantu.com 5
16. Boojho stands at A just on the side of a plane mirror as shown in Fig.
16.20 . Can he see himself in the mirror? Also can he see the image of
objects situated at P,Q,R ?
Ans: A cannot see his image as the length of the mirror is too short on his
side. He can see the image of the objects at P and Q but cannot see the
object at R as can be inferred from the ray diagram.
17. Solve the below referring to the given diagram.
a) Find out the position of the image of an object situated at A in the
plane mirror.
Ans: The image of A is formed at behind the mirror at the same distance
as that of A from the mirror.
Class VIII Science www.vedantu.com 6
b) Can Paheli at B see this image?
Ans: Yes, Paheli at B can see the image.
c) Can Boojho at C see this image?
Ans: Yes, Boojho at C can see the image.
d) When Paheli moves from B to C , where does the image of A
move?
Ans: The image of A is unaffected by the movement of B and C .
Therefore, Paheli will be able to see the image of A while moving from B
to C .
Class VIII Science www.vedantu.com 7
You might also like
- Chris Aceto - Championship BodybuildingDocument290 pagesChris Aceto - Championship Bodybuildingshanmumepco100% (49)
- CH 16Document7 pagesCH 16sneha2701choudharyNo ratings yet
- Excercises: AnswerDocument8 pagesExcercises: AnswervinayakNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 8 Science Chapter 16Document6 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 8 Science Chapter 16Danish XainNo ratings yet
- Class 8-Light-TB EX-SreejaDocument5 pagesClass 8-Light-TB EX-SreejaRAYAN ISWKNo ratings yet
- CLASS VIII SCIENCE CHAPTER-13 LightDocument6 pagesCLASS VIII SCIENCE CHAPTER-13 Lightarnav.chaudhary39923No ratings yet
- Light Class 8 Book-WPS OfficeDocument9 pagesLight Class 8 Book-WPS OfficeS.B.M.PADMESH SATHURAGIRINo ratings yet
- 8 Science 16 Light TextBook QnADocument20 pages8 Science 16 Light TextBook QnAkumaran RNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 LightDocument5 pagesChapter 16 Lightkalash iyerNo ratings yet
- LightDocument22 pagesLightAditya YaduvanshiNo ratings yet
- Light: S.No Regular Reflection Diffused Reflection 1. 2Document6 pagesLight: S.No Regular Reflection Diffused Reflection 1. 2bharat patelNo ratings yet
- CH Light QuestionsAnswerDocument7 pagesCH Light QuestionsAnswerjeewan761980No ratings yet
- Light Class.8 SolutionDocument7 pagesLight Class.8 Solutionpraty171510No ratings yet
- QA LightDocument7 pagesQA LightDomino CreationsNo ratings yet
- Question Bank - Light - Grade VIIIDocument5 pagesQuestion Bank - Light - Grade VIIIpk197679No ratings yet
- Ncert Solutions For Class 8 March 31 Science Chapter 16 LightDocument7 pagesNcert Solutions For Class 8 March 31 Science Chapter 16 LightVandana SainiNo ratings yet
- Light CW - Mod 1Document4 pagesLight CW - Mod 1Jayaprasanna VenkatesanNo ratings yet
- NCERT Exemplar Class 8 Science Solutions Chapter 16 LightDocument14 pagesNCERT Exemplar Class 8 Science Solutions Chapter 16 Lightanvu4848100% (1)
- CH 16 Light 2023Document4 pagesCH 16 Light 2023Anshul DessaiNo ratings yet
- Light NotesDocument5 pagesLight Notesmohannimmi9No ratings yet
- Chapter 16 Light-3Document4 pagesChapter 16 Light-3sabreenaapNo ratings yet
- Light Physics NotesDocument5 pagesLight Physics NotesWani Minham123No ratings yet
- Light Shadows and ReflectionDocument6 pagesLight Shadows and ReflectionPinki NegiNo ratings yet
- Class VIII LightDocument2 pagesClass VIII Lightbose baraniNo ratings yet
- Unit I PDFDocument15 pagesUnit I PDFsrinivas0sai-10% (1)
- Unit 16 (Light) : Multiple Choice Questions (MCQS)Document8 pagesUnit 16 (Light) : Multiple Choice Questions (MCQS)Narsi KumarNo ratings yet
- LightDocument7 pagesLightbaibhavdhamalaNo ratings yet
- NCERT Exemplar Solution Class 8 Science Chapter 16Document12 pagesNCERT Exemplar Solution Class 8 Science Chapter 16anvu4848No ratings yet
- CH-11 Light PPT-2Document33 pagesCH-11 Light PPT-2SUHANEERIYANo ratings yet
- Important Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 11Document14 pagesImportant Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 11moviezonyNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 11 Human Eye and Colourful World Important Questions 2022-23Document14 pagesCBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 11 Human Eye and Colourful World Important Questions 2022-23Rohan SenapathiNo ratings yet
- Lakhmir Singh Solutions Class 10 Physics Chapter 4 Reflection of LightDocument31 pagesLakhmir Singh Solutions Class 10 Physics Chapter 4 Reflection of Lightanilsisodia78No ratings yet
- Lakhmir Singh Solutions Feb23 Class 10 Physics Chapter 4 Reflection of LightDocument31 pagesLakhmir Singh Solutions Feb23 Class 10 Physics Chapter 4 Reflection of LightA.P. ABISEK100% (1)
- Light and Shadow 5 FEB 24Document7 pagesLight and Shadow 5 FEB 24ramasenNo ratings yet
- Reflection Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesReflection Lesson PlanSean O'Reilly100% (3)
- Chap - 3: Reflection of Light by Different Surfaces.: Think & DiscussDocument4 pagesChap - 3: Reflection of Light by Different Surfaces.: Think & Discusssreekanth-gannamaraju-6907No ratings yet
- Chapter 16 Light Class 8Document15 pagesChapter 16 Light Class 8Amaira KalsiNo ratings yet
- Physics 2Document11 pagesPhysics 2bort kortNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE10 Q2 M4 LightsMirrorsandLenses v3-EDITEDDocument22 pagesSCIENCE10 Q2 M4 LightsMirrorsandLenses v3-EDITEDRusty Gabriel Suyom100% (1)
- Lessonsections-17 1Document10 pagesLessonsections-17 1Ghazi DallyNo ratings yet
- Chung Cheng High School (Main) Sec 1 Physics Chapter E3Document16 pagesChung Cheng High School (Main) Sec 1 Physics Chapter E3Ken TanNo ratings yet
- 08 Science Light 01Document5 pages08 Science Light 01Ranjan RoyNo ratings yet
- Chapter-10 - Light: Reflection and RefractionDocument15 pagesChapter-10 - Light: Reflection and RefractionVineet SierraNo ratings yet
- Workbook Solution LightDocument6 pagesWorkbook Solution Lightsmi_santhoshNo ratings yet
- CbseDocument15 pagesCbseYaaroNo ratings yet
- This Explains Why Using Sunglasses Helps Avoid This Effect Your Rods Are Less Susceptible To The Sun's "Bleaching"Document6 pagesThis Explains Why Using Sunglasses Helps Avoid This Effect Your Rods Are Less Susceptible To The Sun's "Bleaching"Go TNo ratings yet
- Chapter Light Class 7 Chapter Q and ADocument9 pagesChapter Light Class 7 Chapter Q and ADaiwik GuptaNo ratings yet
- Bellringer: Chapter 17: Reflection and MirrorsDocument10 pagesBellringer: Chapter 17: Reflection and MirrorsGhazi DallyNo ratings yet
- Pinhole CameraDocument4 pagesPinhole CamerajainNo ratings yet
- Light NB WorkDocument4 pagesLight NB Workdakshsri24No ratings yet
- SLM QTR 2 Week 5 7Document21 pagesSLM QTR 2 Week 5 7pagayonmicaNo ratings yet
- GR 7 - LIGHT - ANSWER KEYDocument3 pagesGR 7 - LIGHT - ANSWER KEYJoseph JayakanthanNo ratings yet
- Title Card: Lesson 12: Mirror Images Are Laterally InvertedDocument16 pagesTitle Card: Lesson 12: Mirror Images Are Laterally InvertedNathan Francis Enzo NicolasNo ratings yet
- Notebook Work CH - 16 (Light)Document9 pagesNotebook Work CH - 16 (Light)Adhya MisraNo ratings yet
- Exercise Soln Reflection of LightDocument48 pagesExercise Soln Reflection of LightiTutor Classes BapiNo ratings yet
- Physics-6 LightDocument132 pagesPhysics-6 LightsamNo ratings yet
- Science: Modified Strategic Intervention MaterialsDocument26 pagesScience: Modified Strategic Intervention MaterialsFhien Garcia100% (2)
- X April Physics LightDocument2 pagesX April Physics Lightprasidh2021No ratings yet
- Human Eye and Colourful World QuestionsDocument12 pagesHuman Eye and Colourful World QuestionsSahishna SurapaneniNo ratings yet
- Through a Microscope: Something of the Science, Together with many Curious Observations Indoor and Out and Directions for a Home-made MicroscopeFrom EverandThrough a Microscope: Something of the Science, Together with many Curious Observations Indoor and Out and Directions for a Home-made MicroscopeNo ratings yet
- Ncert Solutions Class 8 Science Chapter 10Document10 pagesNcert Solutions Class 8 Science Chapter 10JollyNo ratings yet
- Ncert Solutions Class 8 Science Chapter 7Document9 pagesNcert Solutions Class 8 Science Chapter 7JollyNo ratings yet
- Ncert Solutions Class 8 Maths Chapter 1 Rational NumbersDocument10 pagesNcert Solutions Class 8 Maths Chapter 1 Rational NumbersJollyNo ratings yet
- Ncert Solutions Class 8 Maths Chapter 5 Data HandlingDocument13 pagesNcert Solutions Class 8 Maths Chapter 5 Data HandlingJollyNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - Topic 5 - 1-5 Basic Biopharmaceutical Unit OperationsDocument6 pagesWeek 1 - Topic 5 - 1-5 Basic Biopharmaceutical Unit OperationsCelineNo ratings yet
- English Unlimited Intermediate b1 Progress Test 3Document2 pagesEnglish Unlimited Intermediate b1 Progress Test 3Mohammad sadegh Heydari50% (2)
- 2018 Root Cause CategoriesDocument3 pages2018 Root Cause CategoriesRidwan AriefNo ratings yet
- Strategic Planning For Supply Chain Leaders: Capture An Actionable Strategic Plan On One PageDocument7 pagesStrategic Planning For Supply Chain Leaders: Capture An Actionable Strategic Plan On One PageVinith JoshuaNo ratings yet
- En 50288 7 Re 2x ST y PVC CableDocument3 pagesEn 50288 7 Re 2x ST y PVC CableH. NurzeinNo ratings yet
- 3Document22 pages3amanNo ratings yet
- AQ F215 Feeder Protection Device Instruction Manual v2.10 EnglishDocument546 pagesAQ F215 Feeder Protection Device Instruction Manual v2.10 EnglishRicardo LyraNo ratings yet
- Complete Civil 3D 2020 TOC SampleDocument67 pagesComplete Civil 3D 2020 TOC SampleLasno LasnoNo ratings yet
- 0594-0598 (1058) Analytical Instrument QualificationDocument5 pages0594-0598 (1058) Analytical Instrument QualificationRaf RafNo ratings yet
- Lab Report#03: Artifical Intelligence Submitted To: SUBMITTED BY: Muhammad Reg No.: DateDocument8 pagesLab Report#03: Artifical Intelligence Submitted To: SUBMITTED BY: Muhammad Reg No.: DateMuhammad SobanNo ratings yet
- Java Programs Java 1658665821Document37 pagesJava Programs Java 1658665821Spoorthi BNo ratings yet
- Biology Investigatory Experiments and Project ReportsDocument5 pagesBiology Investigatory Experiments and Project ReportsJasim AbdullaNo ratings yet
- Behavior and Strengths of Single Cast-In Anchors in Ultra-High-PerformanceDocument10 pagesBehavior and Strengths of Single Cast-In Anchors in Ultra-High-PerformancePrayush RajbhandariNo ratings yet
- Artikel 5 - 1Document8 pagesArtikel 5 - 1Sintalia DewiNo ratings yet
- Spesifikasi Produk SL-500Document2 pagesSpesifikasi Produk SL-500tekmed koesnadiNo ratings yet
- Mach3 USB Motion Card (JDSW43B) Installation ManualDocument35 pagesMach3 USB Motion Card (JDSW43B) Installation ManualCesxr Buttowski HNNo ratings yet
- Theory of Evolution by Natural SelectionDocument15 pagesTheory of Evolution by Natural Selectionpaula nicolle mostoles100% (1)
- ASME PipingDocument19 pagesASME PipingsingourNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Self StudyDocument80 pagesLecture 1 Self StudyYash ShahNo ratings yet
- University of Nigeria: Course Registration Form SESSION: 2019-2020Document1 pageUniversity of Nigeria: Course Registration Form SESSION: 2019-2020Barinua deekorNo ratings yet
- Aen Ibu07Document64 pagesAen Ibu07Thaovy VomaiNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Secondary 1 Checkpoint: Cambridge Assessment International EducationDocument20 pagesCambridge Secondary 1 Checkpoint: Cambridge Assessment International EducationSallyNo ratings yet
- Flight Planning For ATTDocument106 pagesFlight Planning For ATTTienek Lee100% (1)
- Notefull Reading Step1Document54 pagesNotefull Reading Step1Luis CorderoNo ratings yet
- Santi's Math 2nd Quarter ReviewerDocument9 pagesSanti's Math 2nd Quarter ReviewerAlyssa Renee Abaya CruzNo ratings yet
- HMT Lecture 8 - Heat ExchangersDocument16 pagesHMT Lecture 8 - Heat ExchangerstsegayNo ratings yet
- Eden - Atlantis ProjectDocument25 pagesEden - Atlantis ProjectLeomar MartínezNo ratings yet
- Solar Power PlantDocument13 pagesSolar Power PlantSsagar Kadam67% (3)
- MSDS Verimaster 824Document6 pagesMSDS Verimaster 824medo.k016No ratings yet