Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Women Health Lec 6
Women Health Lec 6
Uploaded by
Shimaa Wahid0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views27 pagesMenopause is the permanent cessation of menstruation that occurs naturally around age 50. It marks the end of a woman's reproductive period. Common symptoms include hot flashes, night sweats, mood swings, sleep problems, and vaginal dryness. Menopause increases the risk of osteoporosis as estrogen levels decline, leading to less dense bones over time. Exercise, calcium and vitamin D supplements can help prevent bone loss and manage other menopause symptoms.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentMenopause is the permanent cessation of menstruation that occurs naturally around age 50. It marks the end of a woman's reproductive period. Common symptoms include hot flashes, night sweats, mood swings, sleep problems, and vaginal dryness. Menopause increases the risk of osteoporosis as estrogen levels decline, leading to less dense bones over time. Exercise, calcium and vitamin D supplements can help prevent bone loss and manage other menopause symptoms.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views27 pagesWomen Health Lec 6
Women Health Lec 6
Uploaded by
Shimaa WahidMenopause is the permanent cessation of menstruation that occurs naturally around age 50. It marks the end of a woman's reproductive period. Common symptoms include hot flashes, night sweats, mood swings, sleep problems, and vaginal dryness. Menopause increases the risk of osteoporosis as estrogen levels decline, leading to less dense bones over time. Exercise, calcium and vitamin D supplements can help prevent bone loss and manage other menopause symptoms.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 27
Menopause
Dr/ Eman Abd Elfatah
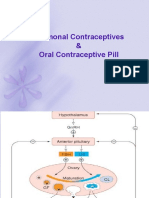
Menopause
• Climacteric: Period of time during which the
female pass from reproductive to non-
reproductive stage.
• Menopause: the physiological and permanent
cessation of menstruation( for 6 months or
one year) due to failure of ovarian function
Menopause age
Types of menopause
• 1- Natural : the body reacts to dropping levels
of estrogen and other hormones.
•
• 2- Artificial:- Surgical menopause may follow
an oophorectomy (removal of an ovary or
both ovaries), or radiation
Common menopausal symptoms
• 1- menstrual irregularities, amenorrhea
• 2- hot flash, night sweats,
• 3- mood swing,
• 4- insomnia,
• 5- vaginal dryness,
• 6- urinary problems,
• weight gain, memory & cognitive change and
fatigue
• Trunk obesity: The low estrogen levels in the
late stages of menopause may also impair the
function of leptin
• Estrogen affect the site of deposition of fat
• Atherosclerosis :
• estrogen maintain elasticity of vascular tissue
Hot flashes
• Transient recurrent period of heat sensation
and redness associated with sweet, increase in
temperature in face, neck head and breast
accompanied by anxiety palpitation affect
sleep pattern
• Decrease level of estrogen and increase level
of FSH
Changes during menpouse
• Breast: Atrophied and pendulous shape
• Genital system :Atrophy of ovary , uterus and
epithelium of the vagina make dryness and
dyspareunia
• PFM has receptor to estrogen level
• Less tone and liable to stress incontinence
Osteoporosis and Menopause
• decrease in the bone mineral density (BMD) in
which the bone matrix and minerals are lost
due to an excessive bone reabsorption
• Affect trabecular bone than cortical bone
• Increase osteoclast and decrease osteoblast
Bone remolding
• bone remolding: The osteoblasts are
responsible for the synthesis and the
osteoclasts for reabsorption of the bone
• 30 years of age, bone mass declines gradually
at rate of approximately 0.4% per year until
the menopause. With menopause, there is a 1
to 1.5%of total bone mass may occur.
Types of osteoporosis
• Primary osteoporosis is the deterioration of
bone mass that is unassociated with other
chronic illness
• related to aging and decreased gonadal
function, prolonged periods of inadequate
calcium intake, sedentary lifestyle and tobacco
and alcohol abuse also contribute to this
condition
• Secondary osteoporosis results from chronic
conditions. These chronic conditions include,
hyperparathyroidism, malignancies,
gastrointestinal diseases
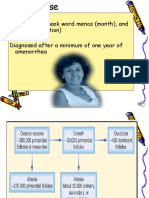
Diagnosis of osteoporosis
• (DEXA)scan is low levels of X-rays can measure
the bone mineral density of skeleton, as well
as specific points that are more likely to break
• A score above -1 is considered normal.
• -1 to -1.5 borderlines
• less than- 2.5 is osteoporosis
Dexa
Management of osteoporosis
• (A) Pharmacological treatment:
• calcium (generally 500 to 1000 mg/day),
• 800 IU of vitamin D daily
Aerobic exercises
• Exercise can also improve gait, balance,
coordination, proprioception, and muscle
strength, decrease truckle obesity and
decrease incidence of cardiovascular disease
• Aerobics decrease incidence of hot flashes
and depression in post menopausal women
Acupuncture point for hot flashes
• localized, (Sanyinjiao (sp6), Hegu (LI.4), Quchi
(LI.11), Fengchi (GB.20.), Guanyuan (CV 4.)
and Fuliu (KI7))
Biochemical effect of exercise on bone
• Regular weight-bearing exercise stimulates
bone formation and suppresses bone
resorption
• increase calcitonin hormone decreases the
serum parathyroid hormone
• Increase sex hormone bonding globulin and B
estradiol hormone
Piezoelectric effect of exercises
• Physical training increase mechanical load on
bone and increase bon mass
• Bone has piezoelectrical potential (capacity of
bone to transform mechanical signs into
electrical signs which stimulate bone cellular
activity and mineral deposition on the stress
points caused by ms contraction
Pulsed electromagnetic field
Pulsed electromagnetic field
• increasing alkaline phosphatase-specific
activity, calcitonin synthesis, and collagen
production.
• with 10 micro volt /cm and frequency
between 50-150 HZ for 1 hour /day can
slowing bone loss
• Ultrasound
• Scanner LLLT
Post natal complication
• Coccydenia
• Ligament injuries or displacement of the
coccyx
• Inflammation in ability to maintain sitting
position
• Treatment : US , PEMF, coccyx mobilization
• Gluteal ms contraction
After pain
• Pain due to uterine contraction to return to
normal site and size (involution)
• Increase in multiparous women
• May sustain 3-4 days after delivery
• Increase with lactation
• Treatment :: TENS
• Relaxation on face position
Breast engorgement
• Due to accumulation of milk in breast
• Pain with lactation
• Treatment
• Heat application before lactation
• Ice application after lactation
• Ultrasound from peripheral toward nipple
•
Blocked duct
• Non infected mastitis
• Pain tenderness , redness in one area in breast
• Continuous US , frequency 1 MHz2-3 minutes
• Intensity 1.5-2 W/cm
Cracked nipple
• IR for 10-15 minutes
• Scanty of milk
• scanner LLLt with wave length 6328
• Power 25 mw for 10 minutes daily for 10 days
`
You might also like
- Meno Pause&HRTsDocument27 pagesMeno Pause&HRTsMajed AlhuzaliNo ratings yet
- Menopause: Presented By: Ms. Ankita Lal Lecturer Department of Obstetrics & GynecologyDocument9 pagesMenopause: Presented By: Ms. Ankita Lal Lecturer Department of Obstetrics & GynecologyPrincess LizaNo ratings yet
- Assignment On MenopauseDocument13 pagesAssignment On MenopauseRashmi C S100% (2)
- The Climacteric Lecture 10Document9 pagesThe Climacteric Lecture 10Miss Mona100% (1)
- Physiology of MenopauseDocument35 pagesPhysiology of Menopauseamjad100% (1)
- Seminar MenopauseDocument51 pagesSeminar MenopauseKelvin SuNo ratings yet
- MenopauseDocument14 pagesMenopauseelinelisaNo ratings yet
- MenapauseDocument41 pagesMenapausehacker ammerNo ratings yet
- By. Pn. MurtiningsihDocument36 pagesBy. Pn. Murtiningsihrai100% (1)
- ORTHOPAEDICSDocument135 pagesORTHOPAEDICSJimmy MainaNo ratings yet
- Physiology of MenopauseDocument20 pagesPhysiology of Menopauseindriyani makmunNo ratings yet
- Menopause: Prepared By: Kriti Banstola B.Sc. NursingDocument42 pagesMenopause: Prepared By: Kriti Banstola B.Sc. NursingKriti BanstolaNo ratings yet
- Sports and Osteoporosis: Professor P.BalaDocument14 pagesSports and Osteoporosis: Professor P.BalaL JordyNo ratings yet
- MenopauseDocument15 pagesMenopauseKiprotich Titus NgetichNo ratings yet
- Menopause 2 - 221212 - 004259Document26 pagesMenopause 2 - 221212 - 004259ali ahmedNo ratings yet
- POstmenopausal BleedingDocument62 pagesPOstmenopausal BleedingIdham BaharudinNo ratings yet
- Medical Nutrition Therapy For Diseases of The MusculoskeletalDocument55 pagesMedical Nutrition Therapy For Diseases of The MusculoskeletalAnonymous keDlQbNo ratings yet
- Presentation Geriatric IncontinenceDocument28 pagesPresentation Geriatric IncontinenceJane SharpsNo ratings yet
- Topic Menopause and AdrenopauseDocument88 pagesTopic Menopause and AdrenopauseWikrom Keng WromKiNo ratings yet
- Menopause SeminarDocument8 pagesMenopause Seminarsuman guptaNo ratings yet
- MenopauseDocument32 pagesMenopauseAdefa Shiferaw100% (1)
- Physiology of MenopauseDocument21 pagesPhysiology of MenopauseHellenKyakuwaire100% (1)
- Menstrual Cycle PDFDocument2 pagesMenstrual Cycle PDFTandingco, Olivia Mari H.No ratings yet
- MENOPAUSEDocument4 pagesMENOPAUSEJoy KirumbaNo ratings yet
- Osteoporosis For Women Over 55Document27 pagesOsteoporosis For Women Over 55api-252297890No ratings yet
- MENOPAUSE SEMINAR OBG MSC Nursing 1st YearDocument11 pagesMENOPAUSE SEMINAR OBG MSC Nursing 1st YearVishwanath VisNo ratings yet
- Sports PT in WomenDocument28 pagesSports PT in WomenPraneeth KumarNo ratings yet
- 63 Puerprium and Its ComplicationsDocument39 pages63 Puerprium and Its ComplicationscollinsmagNo ratings yet
- Reproductive Physiology (Female)Document23 pagesReproductive Physiology (Female)هدى قحطان جليل100% (1)
- Menopause: by Muzamil OsmanDocument32 pagesMenopause: by Muzamil OsmanMuwanga faizoNo ratings yet
- MenopausepptDocument24 pagesMenopausepptluckyNo ratings yet
- Seminar 5 - Menopause, HRT, PMBDocument57 pagesSeminar 5 - Menopause, HRT, PMBAiman ArifinNo ratings yet
- Seminar ON MenopauseDocument43 pagesSeminar ON MenopauseGhaniRahmaniNo ratings yet
- G3 NCM 101 - Mobility and ExerciseDocument44 pagesG3 NCM 101 - Mobility and ExerciseItzayana SyNo ratings yet
- Nutrition and AgingDocument97 pagesNutrition and AgingfifidianNo ratings yet
- Nursing Process For Elderly With The Changes/ Disorder of Endocrine SystemDocument19 pagesNursing Process For Elderly With The Changes/ Disorder of Endocrine SystemNdawNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting Reproductive System FALL 2023Document104 pagesDrugs Affecting Reproductive System FALL 2023Bhruj PatelNo ratings yet
- Below The Knee AmputationDocument76 pagesBelow The Knee AmputationDarell M. Book50% (2)
- Low Back Pain Blue CrossDocument39 pagesLow Back Pain Blue CrossayazirezaNo ratings yet
- Menopouse 1 33Document33 pagesMenopouse 1 33Septi PanggabeanNo ratings yet
- Medical Nutrition Therapy For Diseases of The MusculoskeletalDocument55 pagesMedical Nutrition Therapy For Diseases of The MusculoskeletalSie ningsih100% (1)
- Slides in Powerpoint FormatDocument46 pagesSlides in Powerpoint FormatNailahRahmahNo ratings yet
- Week 1 DiseasesHealthylifestyleFeedbackmechanismDocument22 pagesWeek 1 DiseasesHealthylifestyleFeedbackmechanismAlice KrodeNo ratings yet
- Chronic IllnessDocument12 pagesChronic IllnessRegineCuasSulib100% (2)
- Exercise Prescription For Special PopulationDocument50 pagesExercise Prescription For Special PopulationMeera0% (1)
- Hormonal Contraception: Oral, Parenteral and Implanted ContraceptivesDocument14 pagesHormonal Contraception: Oral, Parenteral and Implanted ContraceptivesFrancia ToledanoNo ratings yet
- NCM14 2.common Aging Changes 2024Document28 pagesNCM14 2.common Aging Changes 2024Kathleen Kate MonsalveNo ratings yet
- 0 9. - Age and Gender and ExerciseDocument13 pages0 9. - Age and Gender and ExerciseSandiNo ratings yet
- Physiologic Changes of PregnancyDocument59 pagesPhysiologic Changes of PregnancymesseeeNo ratings yet
- Menopause: By: DR Jay M.DDocument12 pagesMenopause: By: DR Jay M.DHarinesh JayNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy CareDocument17 pagesPregnancy CareHONEYNo ratings yet
- Menopause and HRTDocument22 pagesMenopause and HRTdeepaNo ratings yet
- KIN - 308 - Developmental Anatomy - Fall2023Document77 pagesKIN - 308 - Developmental Anatomy - Fall2023brendanlmurphy123No ratings yet
- MenopauseDocument53 pagesMenopauseShandy Suwanto PutraNo ratings yet
- Hormonal ContraceptivesDocument25 pagesHormonal Contraceptivesmd easarur rahmanNo ratings yet
- Menopause: By: DR Buvanesh M.D (Msmu Moscow) Lourdes Medical Services SDN BHDDocument12 pagesMenopause: By: DR Buvanesh M.D (Msmu Moscow) Lourdes Medical Services SDN BHDHarinesh Jay100% (1)
- Musculoskeletal SeminarDocument96 pagesMusculoskeletal SeminardeebertoNo ratings yet
- Understanding Female CyclesDocument24 pagesUnderstanding Female CyclesAmbNo ratings yet
- Female Reproduction SystemDocument37 pagesFemale Reproduction SystemSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- Endometriosis, A Simple Guide to The Condition, Treatment And Related DisordersFrom EverandEndometriosis, A Simple Guide to The Condition, Treatment And Related DisordersNo ratings yet
- ISO 00426-1-1983 ScanDocument5 pagesISO 00426-1-1983 ScanthangNo ratings yet
- Appendix 11 Design FMEA ChecklistDocument16 pagesAppendix 11 Design FMEA ChecklistDearRed FrankNo ratings yet
- Edubba A Composite Text Ver3Document7 pagesEdubba A Composite Text Ver3RicardoNo ratings yet
- AASHTO - LRFD - Construction Specs-2nd Edition-2 PDFDocument664 pagesAASHTO - LRFD - Construction Specs-2nd Edition-2 PDFSharfaraz Hossain100% (1)
- Simple Stress and Strain Relationship: Stress and Strain in Two Dimensions, Principal Stresses, Stress Transformation, Mohr's CircleDocument67 pagesSimple Stress and Strain Relationship: Stress and Strain in Two Dimensions, Principal Stresses, Stress Transformation, Mohr's CircleMushini NagabhushanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3Document4 pagesLesson 3Justin Kean HakeemNo ratings yet
- Flood and Debris Loads On Bridges PHD Thesis Mark Jempson PDFDocument457 pagesFlood and Debris Loads On Bridges PHD Thesis Mark Jempson PDFThong NguyenNo ratings yet
- B-Housing and Living - 1Document2 pagesB-Housing and Living - 1Štěpánka OndrůškováNo ratings yet
- Dơnload A Simple Secret 2nd Edition M Brereton Full ChapterDocument24 pagesDơnload A Simple Secret 2nd Edition M Brereton Full Chapterjsfjarbin100% (4)
- XT0223S16128 Smart调试说明书 ENDocument81 pagesXT0223S16128 Smart调试说明书 ENBagwis100% (1)
- Anode InfoDocument5 pagesAnode InfoEberg NlnoNo ratings yet
- What Is Research Collaboration?Document19 pagesWhat Is Research Collaboration?adni_wgNo ratings yet
- FungiDocument100 pagesFungibhanklhonkNo ratings yet
- Marc AisenDocument33 pagesMarc AisenjeremyreedsNo ratings yet
- PP Vs Padillo - PSupt. Pinky Sayson - Acog - February 12, 2018Document3 pagesPP Vs Padillo - PSupt. Pinky Sayson - Acog - February 12, 2018Nelson LaurdenNo ratings yet
- GroutDocument2 pagesGroutMarina Gomáriz ElgerNo ratings yet
- 520SL SLB Guide en USDocument2 pages520SL SLB Guide en USBruce CanvasNo ratings yet
- 2023 TRB Annual Report CaltransDocument27 pages2023 TRB Annual Report CaltransasdfASFNo ratings yet
- 1.introduction To HydraulicsDocument32 pages1.introduction To HydraulicsJet Espejon JavierNo ratings yet
- Beyond The Brain - Text 1Document5 pagesBeyond The Brain - Text 1ivona0mati0No ratings yet
- Nervous Tissue.: Dr. Zahid Mehmood DPT, MS-NMPTDocument25 pagesNervous Tissue.: Dr. Zahid Mehmood DPT, MS-NMPTZahid Mehmood100% (1)
- Fan Basics and Selection CriteriaDocument6 pagesFan Basics and Selection CriteriaSangamesh WaranNo ratings yet
- Secondary and Tertiary Industries of PakistanDocument21 pagesSecondary and Tertiary Industries of PakistanMuhammad Talha Subhani0% (1)
- Irjet V3i4441 PDFDocument5 pagesIrjet V3i4441 PDFnisaNo ratings yet
- Evertz MVP Manual PDFDocument2 pagesEvertz MVP Manual PDFDavidNo ratings yet
- LTE UE Initial AccessDocument7 pagesLTE UE Initial Accesss0pnadisht0No ratings yet
- A PDFDocument4 pagesA PDFChandu ThorNo ratings yet
- FIN V1 Chap4 EconDocument15 pagesFIN V1 Chap4 EconV I S W A L S HNo ratings yet
- Expo Class Methods DetailedDocument7 pagesExpo Class Methods DetailedAlison2360No ratings yet
- Art Appreciation FinalDocument7 pagesArt Appreciation FinalJake Donely C. PaduaNo ratings yet