Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Formula Cheat Sheet
Formula Cheat Sheet
Uploaded by
Jia AliOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Formula Cheat Sheet
Formula Cheat Sheet
Uploaded by
Jia AliCopyright:
Available Formats
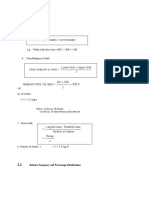
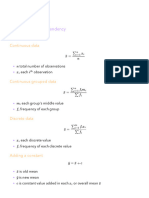
Median for Ungrouped Data Median for Grouped Data
A data set has n number of observations
median = L + n -cf h ( (
If n is odd , 2 f
( n+1
th
2 (
median = term Where
L = Lower limit of median class
If n is even , n = Total frequency
cf = Cumulative frequency of the class preceeding
term + n+2
th
( n2 ( ( (
th
term
2 the median class
median = f = Frequency of the median class
2
h= Class width
When the data is arranged either in ascending or descending order
Mode is the value which occurs most frequently in a set of observations
Mode for Ungrouped Data
i.e. number with highest frequency
Mode for Grouped Data Where f2 = frequency of class succeeding
L = Lower limit of modal class modal class
mode = L +
( fm- f1
2fm-f1-f2
xh
( fm= Frequency of modal class
f1 = frequency of class preceeding modal class
f = Frequency of the median class
h= Width of modal class
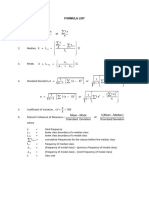
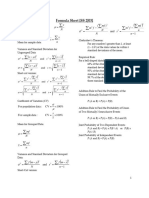
STATISTICS
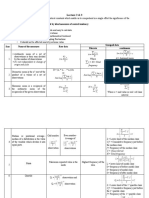
Measures of Dispersion Measures of Dispersion or variation provides an idea of how observations are
spread out or scattered throughout the data
Different Measures of Dispersion
(1) Range (2) Mean deviation (3) Quartile deviation (4) Standard deviation (5) Variance (6) Coefficient of Variance
Range The difference between the largest value and the smallest value is called Range.
Where,
Range = L - S Coefficient of Range = L - S L = Largest value
L+S
S = Smallest value
Mean Deviation For a given data with n observations x1, x2, x3..., xn , the deviation from mean x is given by,
n
Σ |xi- x|
i=1
Mean Deviation = n
Variance The mean of the square of deviations from mean is called variance, denoted by σ2.
n
Σ (xi- x)2
i=1
σ =
2
n
Standard deviation
The positive square root of variance is called as standard deviation, Σ (xi- x)2
i=1
denoted by σ σ = n
Standard deviation for Ungrouped Data Standard deviation for Grouped Data
(1) Direct method (2) Mean method
n Where
Σ fidi2
i=1 di= (xi- x)
σ=
[ ]
n n 2 n Where
Σ x2i Σ di2
n
Σ xi Σ fi
σ= i=1 - i=1 σ = i=1
di= (xi- x) i=1 fi= Frequency value of the
n n n corresponding data points xi
Coefficient of It is the ratio of standard deviation to the mean of data. It is expressed σ
C.V.= x 100%
variation in percentage and used to compare two or more data sets. x
You might also like
- Solutions Manual Production Operations Analysis 6th Edition Steven NahmiasDocument28 pagesSolutions Manual Production Operations Analysis 6th Edition Steven NahmiasAli Veli46% (13)
- Fundamentals of Hypothesis Testing One-Sample TestsnewDocument18 pagesFundamentals of Hypothesis Testing One-Sample TestsnewWinnie Ip100% (2)
- Math11statprob FinalsDocument28 pagesMath11statprob FinalsNeil Trezley Sunico BalajadiaNo ratings yet
- TEST 2, CMTH 380, Summer 2022Document14 pagesTEST 2, CMTH 380, Summer 2022Dineth GunasekeraNo ratings yet
- 11.univariate and Bivariate Analysis of DataDocument18 pages11.univariate and Bivariate Analysis of DataDaxita Rachchha100% (1)
- Stat FormulaDocument2 pagesStat FormulaAshishNo ratings yet
- Asset v1 Expertelearn+KCETCC2022+VAC2022+Type@Asset+Block@M14 KCET SYN HA Crash 22Document30 pagesAsset v1 Expertelearn+KCETCC2022+VAC2022+Type@Asset+Block@M14 KCET SYN HA Crash 22Dhanush KharviNo ratings yet
- PDF PDFDocument23 pagesPDF PDFKiaraNo ratings yet
- Lower Limit + Upper Limit Class Midpoint or Mark 2Document8 pagesLower Limit + Upper Limit Class Midpoint or Mark 2Shah AlyahyaNo ratings yet
- BBS I Formulae StatisticsDocument22 pagesBBS I Formulae StatisticsNikel ShahiNo ratings yet
- Maths - Class - 12 - Statistics and ProbabilityDocument9 pagesMaths - Class - 12 - Statistics and ProbabilitySathya kirubaNo ratings yet
- Research Methodology Module XIDocument2 pagesResearch Methodology Module XIraghav singhalNo ratings yet
- 66572468b4406f001882c55f_##_19_Statistics_TheoryDocument2 pages66572468b4406f001882c55f_##_19_Statistics_TheorytanuskapadhyNo ratings yet
- Statistics English 781679327228760Document15 pagesStatistics English 781679327228760devrajsinghyadav987No ratings yet
- G 10 Statistics 2022 23Document43 pagesG 10 Statistics 2022 23shalima shabeerNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Statistics and Probability PDFDocument27 pagesUnit 4 Statistics and Probability PDFcodieNo ratings yet
- Measures of DispersionDocument7 pagesMeasures of DispersionAdnan55No ratings yet
- Math Note - STATISTICS - FORMULASDocument4 pagesMath Note - STATISTICS - FORMULASNesrine LaradjiNo ratings yet
- GOY AL Brothers Prakashan: X X X X X NDocument22 pagesGOY AL Brothers Prakashan: X X X X X N2007naxayan2007No ratings yet
- Eng 2015 Prelims ReviewerDocument11 pagesEng 2015 Prelims ReviewerJERICHO ESTIALBONo ratings yet
- Formulas (Appendix)Document2 pagesFormulas (Appendix)nr syhdhNo ratings yet
- StatisticsDocument10 pagesStatisticsLyrics World РусскийNo ratings yet
- Descriptive Statistics PDFDocument23 pagesDescriptive Statistics PDFKARAN SINGH-MBANo ratings yet
- Mean For Ungrouped DataDocument2 pagesMean For Ungrouped DataKashif MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Applied Statistics RulesDocument4 pagesApplied Statistics RulesAhmed Mostafa ElmowafyNo ratings yet
- Notes StatDocument6 pagesNotes StatHana GNo ratings yet
- Measure of LocationsDocument6 pagesMeasure of LocationsSidra SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Δ f f Δ f f: Median=L+ n f f XiDocument3 pagesΔ f f Δ f f: Median=L+ n f f XiAshekin MahadiNo ratings yet
- Statistics Notes DLDocument7 pagesStatistics Notes DLShannon LimNo ratings yet
- Statistics: Measures of Central TendencyDocument1 pageStatistics: Measures of Central TendencyJaswant SubudhiNo ratings yet
- Measures of Dispersion or Measures of VariabilityDocument6 pagesMeasures of Dispersion or Measures of Variabilitytasnimsamiha785No ratings yet
- CH 15 Class 11th Statistics Formula SheetDocument4 pagesCH 15 Class 11th Statistics Formula SheetHarsh BislaNo ratings yet
- Statistical Indicators of Univariate Data - Descriptive AnalysisDocument4 pagesStatistical Indicators of Univariate Data - Descriptive AnalysismihaipaulxNo ratings yet
- CCCJ Statistics Formula Sheet & TablesDocument11 pagesCCCJ Statistics Formula Sheet & TablesMÿ Ñämē Ïĥz TäñëkîãNo ratings yet
- MAS202 - Assignment 2: Exercise 1Document16 pagesMAS202 - Assignment 2: Exercise 1Tran Thu Hang (K15 HL)No ratings yet
- Notes STA408 - Chapter 3Document17 pagesNotes STA408 - Chapter 3syahidahMNo ratings yet
- Bless® Bless®: Adjei-Gyan BlessedDocument2 pagesBless® Bless®: Adjei-Gyan BlessedLa MarNo ratings yet
- Intro StatisticsDocument9 pagesIntro StatisticsLuke CruzNo ratings yet
- Formulae - For Test 1Document4 pagesFormulae - For Test 1Hạnh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- SOCI1005 Descriptive Statistics-Part 2Document17 pagesSOCI1005 Descriptive Statistics-Part 2Gisahnie RankineNo ratings yet
- N FX or N X X F L X: Appendix 1 (1) Formula List Sample MeasurementsDocument3 pagesN FX or N X X F L X: Appendix 1 (1) Formula List Sample Measurements123456No ratings yet
- Test-1-Formula SheetDocument1 pageTest-1-Formula SheetliviannadebiasiNo ratings yet
- Statistics - Mind Maps - Arjuna JEE 2024Document1 pageStatistics - Mind Maps - Arjuna JEE 2024fanscartoon26No ratings yet
- 65bcc919ce24d0001802a358 ## Statistics Mind MapsDocument1 page65bcc919ce24d0001802a358 ## Statistics Mind Mapsvkfanclub524No ratings yet
- Stats 1 FormulaeDocument26 pagesStats 1 FormulaeLokesh Tejveer SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 14 StatisticsDocument33 pagesChapter - 14 StatisticsYash GoyalNo ratings yet
- StatisticsDocument4 pagesStatisticsHemant KumarNo ratings yet
- Chap 1Document26 pagesChap 1Ngan Tran Nguyen ThuyNo ratings yet
- SDS 302 Formula Sheet: N X X SSDocument2 pagesSDS 302 Formula Sheet: N X X SSHân BảoNo ratings yet
- 8 Measures of DispersionDocument6 pages8 Measures of Dispersion99210041290No ratings yet
- Formula Sheet Final ExamDocument5 pagesFormula Sheet Final Examanushad.freeNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability: Variance of The Sample Mean Population Standard Deviation of The Sampling DistributionDocument5 pagesStatistics and Probability: Variance of The Sample Mean Population Standard Deviation of The Sampling DistributionAndrea GamutanNo ratings yet
- Adv - Stat. Formula FINALDocument22 pagesAdv - Stat. Formula FINALPhilingon CuñadoNo ratings yet
- SSC JSO Formula BankDocument17 pagesSSC JSO Formula BankektadhullNo ratings yet
- S1-In A NutshellDocument12 pagesS1-In A NutshelldaliatarekboushraNo ratings yet
- StatsDocument9 pagesStatsqz9np6m2bbNo ratings yet
- Engineering Statistic FormulaeDocument5 pagesEngineering Statistic FormulaeYiXuanYeoNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central Tendency Lec 2Document5 pagesMeasures of Central Tendency Lec 2elakkiyaNo ratings yet
- Continuous Serles: Short-Cut Method - A NDocument3 pagesContinuous Serles: Short-Cut Method - A N21ubha116 21ubha116No ratings yet
- MATH 204 Handout 3Document7 pagesMATH 204 Handout 3Rover NoayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 Points To RememberDocument3 pagesChapter 15 Points To RememberMokshita JainNo ratings yet
- 2basic Statistics FormulaDocument24 pages2basic Statistics Formulatexmart vzmNo ratings yet
- Statistics Midterms NotesDocument8 pagesStatistics Midterms Noteskt. rznNo ratings yet
- Universiti Teknologi Mara Test 1Document2 pagesUniversiti Teknologi Mara Test 1syakiraNo ratings yet
- Green's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)From EverandGreen's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)No ratings yet
- DCCN Lecture 22 LLC SublayerDocument17 pagesDCCN Lecture 22 LLC SublayerJia AliNo ratings yet
- DAA - Week 11 - Lecture 1 - Longest Common SubsequenceDocument9 pagesDAA - Week 11 - Lecture 1 - Longest Common SubsequenceJia AliNo ratings yet
- ProbabilityDocument18 pagesProbabilityJia AliNo ratings yet
- 21108185-PR CNDCDocument4 pages21108185-PR CNDCJia AliNo ratings yet
- IndexingDocument66 pagesIndexingJia AliNo ratings yet
- Construction of Frequency Distribution & GraphsDocument5 pagesConstruction of Frequency Distribution & GraphsJia AliNo ratings yet
- Discrete RandomDocument18 pagesDiscrete RandomJia AliNo ratings yet
- Assignment#01 Graphs & PlotsDocument1 pageAssignment#01 Graphs & PlotsJia AliNo ratings yet
- Dsa Project ReportDocument8 pagesDsa Project ReportJia AliNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis TestingDocument17 pagesHypothesis TestingAdïtyã RäjpūtNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 PDFDocument3 pagesChapter 6 PDFNoorKamaL AankNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Practice Exam: Multiple ChoiceDocument6 pagesChapter 11 Practice Exam: Multiple Choicegulzira3amirovnaNo ratings yet
- DR Mervet Elmhalawy Time SeriesDocument54 pagesDR Mervet Elmhalawy Time SeriesMohamed AsimNo ratings yet
- 1 Statistical-TestsDocument42 pages1 Statistical-TestsHenry Arthur ZinkynutsNo ratings yet
- Methods and Principles of Statistical Analysis: 2.1 Recommended Textbooks On StatisticsDocument18 pagesMethods and Principles of Statistical Analysis: 2.1 Recommended Textbooks On Statisticsbunzz1No ratings yet
- StatsDocument4 pagesStatsSteph GonzagaNo ratings yet
- Point EstimationDocument13 pagesPoint EstimationTarun Goyal100% (1)
- Bentler and Bonett, 1980Document19 pagesBentler and Bonett, 1980Faten bakloutiNo ratings yet
- Binder (1998) - RQFA - 11 111-137Document27 pagesBinder (1998) - RQFA - 11 111-137nira_110No ratings yet
- The JASP Data Library 1st EditionDocument427 pagesThe JASP Data Library 1st Editionijopme uhamkaNo ratings yet
- Sesi 5 TWO SAMPLE TEST Levine - Smume7 - ch10Document44 pagesSesi 5 TWO SAMPLE TEST Levine - Smume7 - ch10Kevin Aditya100% (1)
- Chapter 01-The Roles of Statistics in EngineeringDocument13 pagesChapter 01-The Roles of Statistics in EngineeringLoc QuanNo ratings yet
- Essay Question On ARIMA ModelsDocument15 pagesEssay Question On ARIMA Modelsynhinguyen610No ratings yet
- Test Bank For Managing For Quality and Performance Excellence 10th EditionDocument30 pagesTest Bank For Managing For Quality and Performance Excellence 10th Editionannettelunaeotpwnsfij100% (28)
- Time Series EconometricsDocument223 pagesTime Series Econometricsfenomanana100% (1)
- Best Practice Recommendations For Using Structural Equation Modelling in Psychological ResearchDocument16 pagesBest Practice Recommendations For Using Structural Equation Modelling in Psychological ResearchPriyashree RoyNo ratings yet
- Sample Mean Sample Standard Deviation N Standard Error 40.35 5.35 25 1.07 40.35 5.35 25 1.07Document3 pagesSample Mean Sample Standard Deviation N Standard Error 40.35 5.35 25 1.07 40.35 5.35 25 1.07Kajek FirstNo ratings yet
- Correlation and RegressionDocument35 pagesCorrelation and RegressionBuvanesh Buvi VnrNo ratings yet
- Statistics Question PaperDocument4 pagesStatistics Question PaperSufi KhanNo ratings yet
- Multiple Regression Analysis and Model BuildingDocument57 pagesMultiple Regression Analysis and Model BuildingReader88% (8)
- Spss 1Document15 pagesSpss 1Shearer AlansNo ratings yet
- BBA 213 Test Jun20Document3 pagesBBA 213 Test Jun20Divine DanielNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 With LessonsDocument11 pagesUnit 5 With LessonsAndrea SerranoNo ratings yet
- Skripsi Tablet FeDocument7 pagesSkripsi Tablet FeYessiana Luthfia BahriNo ratings yet