Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Qpro 4ha Engls 121201
Qpro 4ha Engls 121201
Uploaded by
Mehar Tariq GoheerCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- XVS1100 V-Star 1100 (99-00) Service ManualDocument420 pagesXVS1100 V-Star 1100 (99-00) Service Manualbullwinkle105477675% (8)
- Making Copper Wire Earrings: More Than 150 Wire-Wrapped DesignsFrom EverandMaking Copper Wire Earrings: More Than 150 Wire-Wrapped DesignsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (6)
- Cylindrical Compression Helix Springs For Suspension SystemsFrom EverandCylindrical Compression Helix Springs For Suspension SystemsNo ratings yet
- Wire Jewelry Tutorial: Grapes Chandelier EarringsFrom EverandWire Jewelry Tutorial: Grapes Chandelier EarringsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Wired Chinese Knot, Wire Jewelry Tutorial: Layer Coiled Crystal Pearls EarringsFrom EverandWired Chinese Knot, Wire Jewelry Tutorial: Layer Coiled Crystal Pearls EarringsRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Beaded Bugs: Make 30 Moths, Butterflies, Beetles, and Other Cute CrittersFrom EverandBeaded Bugs: Make 30 Moths, Butterflies, Beetles, and Other Cute CrittersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (1)
- A Guide to Vintage Audio Equipment for the Hobbyist and AudiophileFrom EverandA Guide to Vintage Audio Equipment for the Hobbyist and AudiophileNo ratings yet
- Chainsaw Carving for Beginners: Patterns and 250 Step-by-Step PhotosFrom EverandChainsaw Carving for Beginners: Patterns and 250 Step-by-Step PhotosNo ratings yet
- Rope and Harness Work on the Farm - With Information on Rope Construction and Various Knots Used on the FarmFrom EverandRope and Harness Work on the Farm - With Information on Rope Construction and Various Knots Used on the FarmNo ratings yet
- Crocheted Hoods and Cowls: 20 Enchanting Designs for Women 7 Adorable Animal Hoods for KidsFrom EverandCrocheted Hoods and Cowls: 20 Enchanting Designs for Women 7 Adorable Animal Hoods for KidsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- PC Sensor: WarningDocument2 pagesPC Sensor: WarningMd. Hanif SanketNo ratings yet
- 1-1 Bal-Con / Balloon Breaker Height 1-2 Peg PositionDocument5 pages1-1 Bal-Con / Balloon Breaker Height 1-2 Peg PositionMd. Hanif SanketNo ratings yet
- Cradle 1 Adjustment Standard: 1-1 Compressed Air PressureDocument10 pagesCradle 1 Adjustment Standard: 1-1 Compressed Air PressureMd. Hanif SanketNo ratings yet
- Magazine: 1-1 Chute GuideDocument5 pagesMagazine: 1-1 Chute GuideMd. Hanif SanketNo ratings yet
- Upper Yarn Sensor 1 Adjustment Standard: 1-1 VOS SettingsDocument2 pagesUpper Yarn Sensor 1 Adjustment Standard: 1-1 VOS SettingsMd. Hanif SanketNo ratings yet
- Drum 1 Adjustment Standard: 1-1 Removing & Mounting The DrumDocument4 pagesDrum 1 Adjustment Standard: 1-1 Removing & Mounting The DrumMd. Hanif SanketNo ratings yet
- Re-Tie Pipe 1 Adjustment Standard: 1-1 Clamp Angle & PositionDocument4 pagesRe-Tie Pipe 1 Adjustment Standard: 1-1 Clamp Angle & PositionMd. Hanif SanketNo ratings yet
- Adjustment Standards & ManitenanceDocument24 pagesAdjustment Standards & ManitenanceMd. Hanif SanketNo ratings yet
- Magazine Conveyor 1 Adjustment StandardDocument4 pagesMagazine Conveyor 1 Adjustment StandardMd. Hanif SanketNo ratings yet
- Suction Mouth 1 Adjustment Standard: 1-1 ParallelismDocument4 pagesSuction Mouth 1 Adjustment Standard: 1-1 ParallelismMd. Hanif SanketNo ratings yet
- GE Fanuc Automation: NSK Spindle Unit SeriesDocument130 pagesGE Fanuc Automation: NSK Spindle Unit SeriesbrodawielkiNo ratings yet
- Bearings With Replaceable Split Bronze Bushings: Instruction ManualDocument4 pagesBearings With Replaceable Split Bronze Bushings: Instruction ManualCAT CYLINDERNo ratings yet
- MR - Moyeux Ar - Heuliez-Iveco Tous TypesDocument10 pagesMR - Moyeux Ar - Heuliez-Iveco Tous TypesSami KhalilNo ratings yet
- Dongnam British Security - Hose Crane - ManualDocument107 pagesDongnam British Security - Hose Crane - ManualVladyslav BibkoNo ratings yet
- Lubricant Storage, Stability, and Estimated Shelf Life: Marine Lubricants Information Bulletin No. 1Document2 pagesLubricant Storage, Stability, and Estimated Shelf Life: Marine Lubricants Information Bulletin No. 1Lucho DomNo ratings yet
- Torq-Matic Automated Floor Wrench: Preventive Maintenance Guide (Model TM120-110/125)Document1 pageTorq-Matic Automated Floor Wrench: Preventive Maintenance Guide (Model TM120-110/125)Alejandra Noguera GiraldoNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Management AssignmentDocument19 pagesMaintenance Management AssignmentSatadeep DattaNo ratings yet
- Operaciones de Mantenimiento de Circuito de CargaDocument10 pagesOperaciones de Mantenimiento de Circuito de CargaCris HallasiNo ratings yet
- YFM350 SuplementarioDocument69 pagesYFM350 SuplementarioنهمياسباريراNo ratings yet
- Broschure Gland Packing Teadit 2Document2 pagesBroschure Gland Packing Teadit 2Desmon GultomNo ratings yet
- Tecnologia em Rolamentos IIIDocument197 pagesTecnologia em Rolamentos IIIJako MishyNo ratings yet
- ParkerDocument167 pagesParkerSamuel Lopez BenitesNo ratings yet
- Shell Morlina: Versatile Protection Industrial ApplicationsDocument2 pagesShell Morlina: Versatile Protection Industrial ApplicationsAnonymous 8lxxbNcA0sNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument26 pagesUntitledSunni GallegosNo ratings yet
- Parts Stock YEIDocument5 pagesParts Stock YEIAmon KiayNo ratings yet
- Manual Del Operador 5000 9000Document309 pagesManual Del Operador 5000 9000Saul Montecino FloresNo ratings yet
- CASE STUDY-RevisedDocument34 pagesCASE STUDY-RevisedJastine Filosopo EspinasNo ratings yet
- Lewmar Vinç Servis KlavuzuDocument28 pagesLewmar Vinç Servis KlavuzuFuat TİMURNo ratings yet
- PnomatikkatalogDocument71 pagesPnomatikkatalogManova JNo ratings yet
- DTS 600 800manual.161120101Document12 pagesDTS 600 800manual.161120101Ivan RonNo ratings yet
- Eco700s 1400SDocument6 pagesEco700s 1400SDavidNo ratings yet
- Nautilus Brochure SFKDocument8 pagesNautilus Brochure SFKACES8891No ratings yet
- Manual de Servicio: MT09A MT09AGDocument570 pagesManual de Servicio: MT09A MT09AGLaura CaballeroNo ratings yet
- FP-1 To 5Document115 pagesFP-1 To 5jeebs0991No ratings yet
- Ottocoll® Hitack: The Hybrid Adhesive With High Initial AdhesionDocument4 pagesOttocoll® Hitack: The Hybrid Adhesive With High Initial AdhesionJoeNo ratings yet
- 100K-2GSR - M100K HAWKJAW SR MANUAL Rev D PDFDocument217 pages100K-2GSR - M100K HAWKJAW SR MANUAL Rev D PDFNestor MorenoNo ratings yet
- HPCL Business CaseDocument10 pagesHPCL Business Casesanandan0% (1)
- InDieTapping PDFDocument12 pagesInDieTapping PDFsansagithNo ratings yet
- Grease UsDocument24 pagesGrease UsSiap SiapNo ratings yet
Qpro 4ha Engls 121201
Qpro 4ha Engls 121201
Uploaded by
Mehar Tariq GoheerCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Qpro 4ha Engls 121201
Qpro 4ha Engls 121201
Uploaded by
Mehar Tariq GoheerCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter Mach Splicer
4Ha Air Splicer
Names of Each Part
Splicer cutter
Clamp plate
Untwisting pipe 1
Pre
Sec
Yarn holding lever
Front plate
Yarn guide lever
Untwisting pipe
Splicer nozzle
Splicer cutter
Clamp plate
1 Doc No. P240
Chapter 4Ha Version 120401
Sec 1 Adjustment Standard
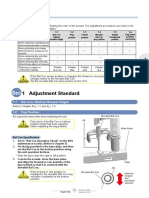
1-1 Compressed Air
Make the following air pressure adjustments for the untwisting (P1 pipe) and the splicing (P2 pipe).
P1 pipe 0.65 MPa (Fixed)
0.3 to 0.65 MPa (The P2 pipe air pressure varies depending on the yarn count
P2 pipe
and type)
● Adjustment guideline for the P2 pipe air pressure
- If the yarn breaks from the blasting operation due to high air pressure, lower the air pressure for splicing.
- If the splice strength is inadequate (loose), raise the air pressure.
- If the splice strength is inadequate (breaks or too thin), lower the air pressure.
* When lowering the air pressure, lower it to below the target value, then set the value so that it increases.
* Refer to Chapter 2 for details on the air pressure adjustment method.
1
Sec
After adjustment, ensure that the splicing strength and yarn appearance are appropriate.
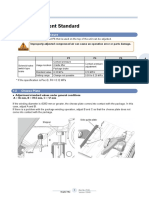
1-2 Untwisting Pipe
To obtain good splices, adjust the untwisting pipe to optimize the untwisting performance. If the untwisting
performance is inadequate, the splice strength or elongation retention rates will be reduced.
If the S-twist or Z-twist has changed, make the necessary adjustments as well.
Untwisted Pipe Setting & Press Marks
There are two press marks on the bushing side and one on the untwisting pipe side. Match the settings with
the untwisting direction of the yarn, and align the untwisting pipe mark with the bushing mark, as illustrated in
the diagram below.
* The position of the mark varies depending on the type of untwisting pipe: pipe for standard yarn or special
untwisting pipe (with a colored end).
For Z-twist yarns For S-twist yarns
Bush
Mark
Untwisting pipe for normal
yarns
M
Mark
Untwisting
pipe
Special untwisting pipe
(with colored end)
2 Doc No. P240
Chapter 4Ha Version 120402
Untwisting Performance Adjustment Untwisting pipe
Adjust by moving the untwisting pipe forward or
backward using the adjustment gauge. (Adjustments Bush
must be made in increments of 0.1 mm)
- If the section to be untwisted is long and the ends
are tangled and too fine, adjust and move it inward.
- If the section to be untwisted is short, adjust and
move it outward. Front Rear
The untwisting pipe is fixed in place by inserting the plug first and then screwing in the
screw as shown in the diagram below. Loosen the screw prior to making the untwisting pipe
adjustment.
Screw
Plug
1
Sec
Untwisting pipe
Since the untwisting pipe is ceramic, over-tightening the fixing screw may cause the pipe
to fracture or break. As a general guideline, the tightening torque for the fixing screws is
between 0.2 and 0.3 N•m.
When the “Untwisting Performance Adjustment” is Inadequate
For both the S-twist and Z-twist yarns, the more the yarn is twisted, the more the untwisting pipe should be
turned. The forward or rear position of the untwisting pipe must also be re-adjusted. The adjustments are made
in increments of 3°.
[Untwisting pipe setting and turning direction]
For Z-twist yarns For S-twist yarns
[Counterclockwise] [Clockwise]
Untwisting pipe for normal
yarns
Special untwisting pipe
3 Doc No. P240
Chapter 4Ha Version 120401
Condition of the Untwisted Yarn
● Normal
Short fibers (51 mm or less)
Brush tip form
15 to 20 mm
Splice has satisfactory
Long fibers (over 51 mm) appearance and strength
Loose fibers in parallel
(moderate bulkiness)
20 to 25 mm
● When the untwisting pipe is set forward from the normal position or is over-twisted
Short fibers Large dispersion of strength
- No bulkiness Fiber ball
- Blown fibers are tangled at end
- Fibers are overblown Thin 1
Sec
Long fibers
- No bulkiness
Large dispersion of strength
- Some of the fibers are tangled
● When the untwisting pipe is set backward from the normal position
Short fibers and long fibers Low strength due to pull-out
Untwisted part is short
Thick
4 Doc No. P240
Chapter 4Ha Version 120401
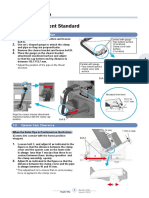
1-3 Yarn Holding Lever
Yarn holding lever
Yarn Holding Lever Setting
1. Stop the splicer at the stage illustrated in the
diagram on the right using the unit check
mode.
* Refer to Chapter 3 for details on the check mode.
2. Turn the yarn holding pin (eccentric pin) to
adjust the distance (“A” shown in diagram
on right) between the end of the yarn holding
lever on the bottom side and the front plate.
[Adjustment range]
Yarn holding lever
Adjustment dimension
[A] (mm) 1
Sec
J2 1.5 to 2.5 Bolt
J1, H 2.0 to 3.0
E, K 5.0 to 6.0 A
Yarn holding adjustment
pin (Eccentric pin)
Yarn Holding Lever Width Front plate separator
Adjust the width of the yarn holding lever so that it fits
in between the front plate separators. Leave about 0.5
mm of clearance so that there is no contact, as shown
by the “B” points in the diagram on the right.
The area indicated by the arrows in the diagram is bent
and adjusted. Do not bend at the front end. Yarn holding lever
5 Doc No. P240
Chapter 4Ha Version 120401
1-4 Tightening the Timing Belt
Turn and adjust the motor.
Motor fixing bolt
Ensure that the belt is not too slack
or too taut. (Recommended tension:
30.2 – 40.6 N)
Malfunctions could occur if the
tension is out of the recommended
range.
Motor
1
Sec
1-5 VOS Settings
The VOS settings are listed below. Change the setting conditions when necessary.
Yarn Joining Device Select “Air”
Splicer Nozzle Type Select the splicer nozzle being used
Yarn Type for Splicing Select the appropriate setting from : STD / SPANDEX / WOOLEN
Adjustment of overlapping splice length
[Adjustment guideline]
Select from Position 1 to 8
- If the splice is too long or too thick, set a position closer to “Position 8”
- If the splice is thin or the strength is inadequate, set a position closer to
“Position 1”
Short
POSITION 8
Splice Length
Yarn
Long POSITION 1
Splicer Cutter Type Select “Standard Cutter" or “Clamp Cutter”
Untwisting Time [A] Set the compressed air discharge time for untwisting
Splicing Time [C] Set the compressed air discharge time for splicing
6 Doc No. P240
Chapter 4Ha Version 120401
Sec 2 Maintenance
2-1 Inspection
Frequency Item Guideline
Daily Remove cotton fly from the splicer Clean with air gun
- Check splice for appearance and strength (Pull gauge)
- Check the cutter sharpness (visual check)
- Check for any air discharge errors or faults
Weekly Splice check
- Check whether or not the air is continuing to discharge
or is not discharging at all (visual and sound check, as
well as splicing performance check)
When the yarn
Splice check (P2 pressure, splice
process is Check splice for appearance and strength (Pull gauge)
length)
changed
After removing the cotton fly from the cutter, lubricate 2
Sec
the axis (blade lubrication not required)
* ISO VG10 (Bearing oil)
Splicer cutter
Every 3 months
(clamp cutter specs only)
Remove the splicer and clean (use Cartridge attaching/
removing wrench)
Every 6 months Splicer
* In particular, remove the cotton fly stuck to the cam
surface and the bearings.
Clean with cleaning brush
Remove dirt and stains from inside the
Yearly
untwisting pipe.
7 Doc No. P240
Chapter 4Ha Version 120401
2-2 Precaution When Mounting Splicer Nozzle
1. Fit the splicer nozzle on the pipe with the
O-ring, and insert it all the way to the back of O ring
the pipe.
* If it is difficult to insert, apply grease to the O-ring.
* Lithium-based grease
Splicer
nozzle
Bolt
2. Tighten the bolt.
1
2
Sec
Do not tighten the bolt if the splicer
nozzle does not insert all the way to
the back of the pipe (when there is
a 1 mm gap or greater between the
front plate and the splicer nozzle).
The ceramic may fracture or break.
2-3 Precaution When Mounting Splicer Cutter
There are two splicer cutters, an upper and a lower.
Splicer cutter Bolt
(Lower shown on the right)
- Apply locking adhesive to the bolt
before mounting the splicer cutter.
- Since the splicer cutter is ceramic,
over-tightening the fixing bolt may
cause the cutter to fracture or
break.
As a general guideline, the
tightening torque for the bolt is
between 0.2 and 0.3 N•m.
- Wipe off any excess locking
adhesive on the attachment side of
the shim.
If you do not do so, the shim may
not operate.
- As a general guideline, the
tightening torque for the stud is
between 0.45 and 0.55 N•m.
- Be sure not to touch the splicer
cutter as it can cause injury.
Shim Stud
8 Doc No. P240
Chapter 4Ha Version 121201
Sec 3 Consumables
If the parts below are worn causing a failure or problem, replace the worn part or parts with a new one.
Bush A (3 locations)
Bearing A
(2 locations)
Timing belt
Bearing B
3
Sec
Bush B (4 locations)
Washer (teflon)
Bush C (2 locations)
9 Doc No. P240
Chapter 4Ha Version 121101
Sec 4 Problems When Splicing
4-1 Problems & Countermeasures
Problem Cause Countermeasures
The settingi air pressure for Pipe P1 or pipe Check the air pressure
P2 is not properly (Refer to Chapter 4Ha, 1-1)
Solenoid Valve operation error Replace the valve
In the case of short fibers, the yarn holding
lever setting is inadequate or the fiber Re-adjust the yarn holding lever
Frequent splicing error holding lever width is too narrow, resulting in (Refer to Chapter 4Ha, 1-3)
a gap
Re-adjust the untwisting lever
Poor untwisting
(Refer to Chapter 4Ha, 1-2)
Set the splice length closer to “Position 1”
Splice length is too short.
(Refer to Chapter 4Ha, 1-5)
4
Sec
P2 pressure is too low. Raise the air pressure
Set the splice length closer to “Position 8”
Splice length is too long
Splice is easily pulled out (Refer to Chapter 4Ha, 1-5)
Re-adjust the untwisting lever
Poor untwisting
(Refer to Chapter 4Ha, 1-2)
P2 pressure is too high Lower the air pressure
Splice is either cut and too Set the splice length closer to “Position 1”
Splice length is too short
weak or thin and too weak. (Refer to Chapter 4Ha, 1-5)
Re-adjust the untwisting lever
Too much untwisting
(Refer to Chapter 4Ha, 1-2)
Long tail on splice
Set the splice length closer to “Position 8”
Splice length is too long
(Refer to Chapter 4Ha, 1-5)
Yarn is not accepted by
Yarn is caught by the suction mouth Check for scratches and yarn waste
splicer nozzle
- Remove cotton fly from the cutter
Splicer cutter is dull
- Replace the cutter
- Check the clamp operation
- Either repair the scratch or damage on the
Thick splice at one side Insufficient clamping of upper and lower
yarn guide lever, or replace it
only, or tailing yarns
- Wipe and clean any impurities stuck to the
yarn guide lever
Inadequate setting of untwisting pipe Re-adjust the untwisting lever
on one side (Refer to Chapter 4Ha, 1-2)
Double ending of lower - Remove any yarn waste
yarn - Check the lowering position
- Check for scratches or damage on the
Length of yarn drawn into re-tie pipe is too
spinning bobbins
short
- Check the blower static pressure
- Check the kink preventer
(Refer to Chapter 4Ma)
- Check the spinning bobbins
Re-tie pipe double picking
- Check the re-tie pipe operation
4-2 Notes Relating to Strength Measurement
● Measure both the “parent yarn” and the “spliced yarn” on the winding unit 10 times each,
alternating back and forth, and calculate the minimum strength and the average retention rate.
● The spliced yarn shares the same features with its “parent yarn.” So do not measure the “parent
yarn” and the “spliced yarn” on different spinning bobbins.
10 Doc No. P240
Chapter 4Ha Version 120401
4-3 Retention Rates
Knots made by a knotter tend to cause resistance because they can get caught when the yarn is drawn
through in subsequent winding processes. As a result, the knots need to be stronger.
For splicers, however, the strength of the splice can be slightly lower than the strength of the parent yarn,
because there are no knots in the splices and they can stretch. As a general guideline, refer to the rates below
for the minimum strength required for splices.
Yarn for yarn counts thinner than
50% or more of the average strength of the parent yarn
Ne20'S
Yarn for yarn counts thicker than
30% or more of the average strength of the parent yarn
Ne20'S
4/5
Sec
Sec 5 Three-tier Nozzle [Option]
5-1 Names of Each Part & Mounting Method
O ring
Screw
Bolt
Front plate Main nozzle
Subnozzle
The splicer nozzle assembly consists of a main nozzle and two supplementary twisting nozzles, forming three-
tier.
The main nozzle and the subnozzle have been assembled together with fine adjustment.
Do not disassemble them as doing so could lower performance or cause damage.
* Refer to Chapter 4Ha, 2-2 for details on precaution when mounting splicer nozzle.
5-2 VOS Settings
The VOS settings listed below are added to the lists in Chapter 4Ha, 1-5. Change the compressed air
discharge time when necessary.
Twisting Time [C] Set the compressed air discharge time for the main nozzle
Three-tier Nzzl Spl Tm [E] Set the compressed air discharge time for the subnozzle
11 Doc No. P240
Chapter 4Ha Version 120401
You might also like
- XVS1100 V-Star 1100 (99-00) Service ManualDocument420 pagesXVS1100 V-Star 1100 (99-00) Service Manualbullwinkle105477675% (8)
- Making Copper Wire Earrings: More Than 150 Wire-Wrapped DesignsFrom EverandMaking Copper Wire Earrings: More Than 150 Wire-Wrapped DesignsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (6)
- Cylindrical Compression Helix Springs For Suspension SystemsFrom EverandCylindrical Compression Helix Springs For Suspension SystemsNo ratings yet
- Wire Jewelry Tutorial: Grapes Chandelier EarringsFrom EverandWire Jewelry Tutorial: Grapes Chandelier EarringsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Wired Chinese Knot, Wire Jewelry Tutorial: Layer Coiled Crystal Pearls EarringsFrom EverandWired Chinese Knot, Wire Jewelry Tutorial: Layer Coiled Crystal Pearls EarringsRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Beaded Bugs: Make 30 Moths, Butterflies, Beetles, and Other Cute CrittersFrom EverandBeaded Bugs: Make 30 Moths, Butterflies, Beetles, and Other Cute CrittersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (1)
- A Guide to Vintage Audio Equipment for the Hobbyist and AudiophileFrom EverandA Guide to Vintage Audio Equipment for the Hobbyist and AudiophileNo ratings yet
- Chainsaw Carving for Beginners: Patterns and 250 Step-by-Step PhotosFrom EverandChainsaw Carving for Beginners: Patterns and 250 Step-by-Step PhotosNo ratings yet
- Rope and Harness Work on the Farm - With Information on Rope Construction and Various Knots Used on the FarmFrom EverandRope and Harness Work on the Farm - With Information on Rope Construction and Various Knots Used on the FarmNo ratings yet
- Crocheted Hoods and Cowls: 20 Enchanting Designs for Women 7 Adorable Animal Hoods for KidsFrom EverandCrocheted Hoods and Cowls: 20 Enchanting Designs for Women 7 Adorable Animal Hoods for KidsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- PC Sensor: WarningDocument2 pagesPC Sensor: WarningMd. Hanif SanketNo ratings yet
- 1-1 Bal-Con / Balloon Breaker Height 1-2 Peg PositionDocument5 pages1-1 Bal-Con / Balloon Breaker Height 1-2 Peg PositionMd. Hanif SanketNo ratings yet
- Cradle 1 Adjustment Standard: 1-1 Compressed Air PressureDocument10 pagesCradle 1 Adjustment Standard: 1-1 Compressed Air PressureMd. Hanif SanketNo ratings yet
- Magazine: 1-1 Chute GuideDocument5 pagesMagazine: 1-1 Chute GuideMd. Hanif SanketNo ratings yet
- Upper Yarn Sensor 1 Adjustment Standard: 1-1 VOS SettingsDocument2 pagesUpper Yarn Sensor 1 Adjustment Standard: 1-1 VOS SettingsMd. Hanif SanketNo ratings yet
- Drum 1 Adjustment Standard: 1-1 Removing & Mounting The DrumDocument4 pagesDrum 1 Adjustment Standard: 1-1 Removing & Mounting The DrumMd. Hanif SanketNo ratings yet
- Re-Tie Pipe 1 Adjustment Standard: 1-1 Clamp Angle & PositionDocument4 pagesRe-Tie Pipe 1 Adjustment Standard: 1-1 Clamp Angle & PositionMd. Hanif SanketNo ratings yet
- Adjustment Standards & ManitenanceDocument24 pagesAdjustment Standards & ManitenanceMd. Hanif SanketNo ratings yet
- Magazine Conveyor 1 Adjustment StandardDocument4 pagesMagazine Conveyor 1 Adjustment StandardMd. Hanif SanketNo ratings yet
- Suction Mouth 1 Adjustment Standard: 1-1 ParallelismDocument4 pagesSuction Mouth 1 Adjustment Standard: 1-1 ParallelismMd. Hanif SanketNo ratings yet
- GE Fanuc Automation: NSK Spindle Unit SeriesDocument130 pagesGE Fanuc Automation: NSK Spindle Unit SeriesbrodawielkiNo ratings yet
- Bearings With Replaceable Split Bronze Bushings: Instruction ManualDocument4 pagesBearings With Replaceable Split Bronze Bushings: Instruction ManualCAT CYLINDERNo ratings yet
- MR - Moyeux Ar - Heuliez-Iveco Tous TypesDocument10 pagesMR - Moyeux Ar - Heuliez-Iveco Tous TypesSami KhalilNo ratings yet
- Dongnam British Security - Hose Crane - ManualDocument107 pagesDongnam British Security - Hose Crane - ManualVladyslav BibkoNo ratings yet
- Lubricant Storage, Stability, and Estimated Shelf Life: Marine Lubricants Information Bulletin No. 1Document2 pagesLubricant Storage, Stability, and Estimated Shelf Life: Marine Lubricants Information Bulletin No. 1Lucho DomNo ratings yet
- Torq-Matic Automated Floor Wrench: Preventive Maintenance Guide (Model TM120-110/125)Document1 pageTorq-Matic Automated Floor Wrench: Preventive Maintenance Guide (Model TM120-110/125)Alejandra Noguera GiraldoNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Management AssignmentDocument19 pagesMaintenance Management AssignmentSatadeep DattaNo ratings yet
- Operaciones de Mantenimiento de Circuito de CargaDocument10 pagesOperaciones de Mantenimiento de Circuito de CargaCris HallasiNo ratings yet
- YFM350 SuplementarioDocument69 pagesYFM350 SuplementarioنهمياسباريراNo ratings yet
- Broschure Gland Packing Teadit 2Document2 pagesBroschure Gland Packing Teadit 2Desmon GultomNo ratings yet
- Tecnologia em Rolamentos IIIDocument197 pagesTecnologia em Rolamentos IIIJako MishyNo ratings yet
- ParkerDocument167 pagesParkerSamuel Lopez BenitesNo ratings yet
- Shell Morlina: Versatile Protection Industrial ApplicationsDocument2 pagesShell Morlina: Versatile Protection Industrial ApplicationsAnonymous 8lxxbNcA0sNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument26 pagesUntitledSunni GallegosNo ratings yet
- Parts Stock YEIDocument5 pagesParts Stock YEIAmon KiayNo ratings yet
- Manual Del Operador 5000 9000Document309 pagesManual Del Operador 5000 9000Saul Montecino FloresNo ratings yet
- CASE STUDY-RevisedDocument34 pagesCASE STUDY-RevisedJastine Filosopo EspinasNo ratings yet
- Lewmar Vinç Servis KlavuzuDocument28 pagesLewmar Vinç Servis KlavuzuFuat TİMURNo ratings yet
- PnomatikkatalogDocument71 pagesPnomatikkatalogManova JNo ratings yet
- DTS 600 800manual.161120101Document12 pagesDTS 600 800manual.161120101Ivan RonNo ratings yet
- Eco700s 1400SDocument6 pagesEco700s 1400SDavidNo ratings yet
- Nautilus Brochure SFKDocument8 pagesNautilus Brochure SFKACES8891No ratings yet
- Manual de Servicio: MT09A MT09AGDocument570 pagesManual de Servicio: MT09A MT09AGLaura CaballeroNo ratings yet
- FP-1 To 5Document115 pagesFP-1 To 5jeebs0991No ratings yet
- Ottocoll® Hitack: The Hybrid Adhesive With High Initial AdhesionDocument4 pagesOttocoll® Hitack: The Hybrid Adhesive With High Initial AdhesionJoeNo ratings yet
- 100K-2GSR - M100K HAWKJAW SR MANUAL Rev D PDFDocument217 pages100K-2GSR - M100K HAWKJAW SR MANUAL Rev D PDFNestor MorenoNo ratings yet
- HPCL Business CaseDocument10 pagesHPCL Business Casesanandan0% (1)
- InDieTapping PDFDocument12 pagesInDieTapping PDFsansagithNo ratings yet
- Grease UsDocument24 pagesGrease UsSiap SiapNo ratings yet