Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DPSK QPSK Notes
DPSK QPSK Notes
Uploaded by
Fahad Ansari 20-2960 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
43 views6 pagesDPSK (Differential Phase Shift Keying) is a modulation technique where the phase of the modulated signal is shifted relative to the previous signal element based on the previous bit. A DPSK demodulator uses a balanced modulator with a 1-bit delay input and low pass filter to recover the original data bits based on whether the received and delayed signals have the same or different polarity. QPSK (Quadrature Phase Shift Keying) encodes two bits at a time by using four possible carrier phase shifts (0, 90, 180, 270 degrees), allowing it to carry information at double the rate of DPSK. A QPSK demodulator uses two PSK demodulators and low pass filters to simultaneously de
Original Description:
Original Title
Dpsk Qpsk Notes
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentDPSK (Differential Phase Shift Keying) is a modulation technique where the phase of the modulated signal is shifted relative to the previous signal element based on the previous bit. A DPSK demodulator uses a balanced modulator with a 1-bit delay input and low pass filter to recover the original data bits based on whether the received and delayed signals have the same or different polarity. QPSK (Quadrature Phase Shift Keying) encodes two bits at a time by using four possible carrier phase shifts (0, 90, 180, 270 degrees), allowing it to carry information at double the rate of DPSK. A QPSK demodulator uses two PSK demodulators and low pass filters to simultaneously de
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
43 views6 pagesDPSK QPSK Notes
DPSK QPSK Notes
Uploaded by
Fahad Ansari 20-296DPSK (Differential Phase Shift Keying) is a modulation technique where the phase of the modulated signal is shifted relative to the previous signal element based on the previous bit. A DPSK demodulator uses a balanced modulator with a 1-bit delay input and low pass filter to recover the original data bits based on whether the received and delayed signals have the same or different polarity. QPSK (Quadrature Phase Shift Keying) encodes two bits at a time by using four possible carrier phase shifts (0, 90, 180, 270 degrees), allowing it to carry information at double the rate of DPSK. A QPSK demodulator uses two PSK demodulators and low pass filters to simultaneously de
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 6
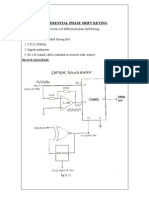
DPSK
In DPSK the phase of the modulated signal is shifted relative
to the previous signal element. The signal phase follows the
high or low state of the previous element.
bk dk=bk-dk-1 Product Output
Modulator DPSK
dk-1 XOR
C(t)
1 bit Delay
bk dk-1 XOR o/p
0 0 0
0 1 1
1 0 1
1 1 0
If next data bit is 1 there will be change in polarity in output
of XOR.
If next data bit is 0 there will be no change in polarity in
output of XOR.
The following figure represents the model waveform of DPSK.
The advantage with DPSK system is that it does not require a
synchronous carrier in the demodulator. So no local oscillator is
required at receiver side.
DPSK Demodulator
From the above figure, it is evident that the balance
modulator is given the DPSK signal along with 1-bit delay
input. Then the output is applied to a LPF. Then it is passed to
a shaper circuit, which is a comparator circuit, to recover the
original binary data as the output.
Case I : Let, both received DPSK and delayed signals have
same polarity and they are bk Ac sin ωct and bk Ac sin ωct. Then
the output of the balanced modulator =
bk Ac sin ωct × bk Ac sin ωct or (-bk Ac sin ωct)×(-bk Ac sin ωct)
= 𝒃𝟐𝒌 𝑨𝟐𝒄 sin2ωct
𝟏−𝐜𝐨𝐬𝟐𝛚𝒄 𝐭
= 𝒃𝟐𝒌 𝑨𝟐𝒄 [ ]
𝟐
𝒃𝟐𝒌 𝑨𝟐𝒄 𝒃𝒌 𝑨𝟐𝒄
= - cos2ωct
𝟐 𝟐
𝒃𝟐𝒌 𝑨𝟐𝒄
The output of LPF is and final output of the comparator
𝟐
is 1.
Case II : Let, both received and delayed signals are not of
same polarity and they are bk Ac sin ωct and -bk Ac sin ωct.
Then the output of the balanced modulator =
-bk Ac sin ωct × bk Ac sin ωct
= −𝒃𝟐𝒌 𝑨𝟐𝒄 sin2ωc1t
𝟏−𝐜𝐨𝐬𝟐𝛚𝒄 𝐭
= −𝒃𝟐𝒌 𝑨𝟐𝒄 [ ]
𝟐
𝒃𝟐𝒌 𝑨𝟐𝒄 𝒃𝒌 𝑨𝟐𝒄
=− + cos2ωct
𝟐 𝟐
𝒃𝟐𝒌 𝑨𝟐𝒄
The output of LPF is - and final output of the comparator
𝟐
is 0.
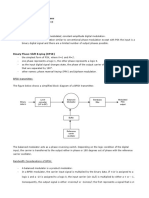
QPSK
QPSK sends two bits of digital information at a time. Instead
of the conversion of digital bits into a series of digital stream,
it converts them into bit pairs.
QPSK Modulator
The QPSK Modulator uses a bit-splitter, two multipliers with
local oscillator, a 2-bit serial to parallel converter, and a
summer circuit. Following is the block diagram for the same.
At the modulator’s input, the message signal’s even bits (i.e.,
2nd bit, 4th bit, 6th bit, etc.) and odd bits (i.e., 1st bit, 3rd bit,
5th bit, etc.) are separated by the bits splitter and they are
multiplied with the same carrier to generate odd PSK (called
as PSKI) and even PSK (called as PSKQ). But the PSKQ carrier
signal is phase shifted before being modulated.
The QPSK waveform for two-bits input is as follows, which
shows the modulated result for different instances of binary
inputs.
QPSK can carry information at a rate which is double of that
of DPSK. It is applied in cable modem, satellite communication
etc. It selects one of the four possible carrier phase shifts:
For bit pairs 00, 01,10,11 phase shifts of 0°, 90°,180°, 270° etc
can be obtained.
QPSK Demodulator
The QPSK Demodulator uses two PSK demodulator circuits
with local oscillator, two low pass filters, two square wave
generators to obtain the digital data and a 2-bit parallel to
serial converter. Following is the diagram for the same.
The two PSK detectors at the input of demodulator
simultaneously perform the demodulation and the pair of
bits are recovered here from the original data. These signals
after processing, are passed to the parallel to serial converter
and from the output the digital signal can be retrieved.
************************
You might also like
- Switching Power Supply Design: A Concise Practical HandbookFrom EverandSwitching Power Supply Design: A Concise Practical HandbookNo ratings yet
- Group1 Exp7 Surname FNDocument12 pagesGroup1 Exp7 Surname FNChristian Carl Gonzales CuarioNo ratings yet
- Wireless Communication-Digital Signaling For Fading ChannelsDocument25 pagesWireless Communication-Digital Signaling For Fading ChannelsPREMALATHA GOVINDNo ratings yet
- Phase Shift Keying & Quadrature Phase Shift KeyingDocument23 pagesPhase Shift Keying & Quadrature Phase Shift Keyingamit raoNo ratings yet
- Binary Phase Shift KeyingDocument10 pagesBinary Phase Shift KeyingMs.DEVI P100% (5)
- Mod 2Document7 pagesMod 2ANANDHU PILLAINo ratings yet
- LAb 4 PSKDocument9 pagesLAb 4 PSKJoseph MagonduNo ratings yet
- Digital ModulationDocument18 pagesDigital ModulationRohit DuttaNo ratings yet
- 15EC306J Cycle 2 ExptsDocument28 pages15EC306J Cycle 2 ExptsSanjeev KumarNo ratings yet
- Laboratory 3 - Phase Shift KeyingDocument12 pagesLaboratory 3 - Phase Shift KeyingJemimah Aniel ClimacoNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.3 Phase Shift Keying Aim: To Generate and Demodulate Phase Shift Keyed (PSK) Signal Using OCTAVE OnlineDocument6 pagesExperiment No.3 Phase Shift Keying Aim: To Generate and Demodulate Phase Shift Keyed (PSK) Signal Using OCTAVE OnlinevanithaNo ratings yet
- Gaussian Minimum Shift KeyingDocument52 pagesGaussian Minimum Shift KeyingMohamed EltahanNo ratings yet
- Digital Communication UNIT 3Document5 pagesDigital Communication UNIT 3Nihal GuptaNo ratings yet
- QPSK ProjectDocument6 pagesQPSK ProjectwenhuiooiNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.1 Phase Shift Keying (PSK/BPSK) Aim: To Generate and Demodulate Phase Shift Keyed (PSK) Signal Using MATLABDocument24 pagesExperiment No.1 Phase Shift Keying (PSK/BPSK) Aim: To Generate and Demodulate Phase Shift Keyed (PSK) Signal Using MATLABAmnaSajjadNo ratings yet
- PSK FSK Modulation and DemodulationDocument9 pagesPSK FSK Modulation and DemodulationNishantKumarNo ratings yet
- Differential Phase Shift KeyingDocument7 pagesDifferential Phase Shift Keyingtaherakhans100% (1)
- Subject Code Credit: Digital Communication UEC 607 4Document34 pagesSubject Code Credit: Digital Communication UEC 607 4Vedansh BeniwalNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 - 304, DcsDocument9 pagesAssignment 3 - 304, Dcsramjee26No ratings yet
- Digital Modulation Technique (U-2)Document82 pagesDigital Modulation Technique (U-2)lakshmikanth gNo ratings yet
- Lecture-12+13 (ASK FSK) Deepak Sharma CompleteDocument65 pagesLecture-12+13 (ASK FSK) Deepak Sharma CompleteSandeep SachanNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Slides PSK - QAMDocument87 pagesUnit 3 Slides PSK - QAMSam JonesNo ratings yet
- Lab 10Document6 pagesLab 10Mei QiiNo ratings yet
- PSK Transmitter:: PM C CDocument4 pagesPSK Transmitter:: PM C CPartha BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Digital Modulation Techniques in Mobile Communications: Fahredd'n Sadikoglu 1Document52 pagesDigital Modulation Techniques in Mobile Communications: Fahredd'n Sadikoglu 1Kapil VatsalNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Sep 15, 2022Document5 pagesAdobe Scan Sep 15, 2022Mylavarapu SriprithamNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.5, Simulation of DPSK Aim: To Plot The Bit Error Rate (BER) of Differential Phase Shift Keying (DPSK) Signal Using OCTAVEDocument5 pagesExperiment No.5, Simulation of DPSK Aim: To Plot The Bit Error Rate (BER) of Differential Phase Shift Keying (DPSK) Signal Using OCTAVEvanitha100% (2)
- Binary Phase Shift KeyingDocument48 pagesBinary Phase Shift KeyingAnonymous hhL6gc91% (11)
- Digital CommunicationDocument94 pagesDigital CommunicationNimesh SalunkheNo ratings yet
- Introduction (Modulation)Document46 pagesIntroduction (Modulation)jovan avery dalluayNo ratings yet
- Phase Shift Keying: Exp - No:01Document74 pagesPhase Shift Keying: Exp - No:01Sumit PatilNo ratings yet
- Programs Comm LabDocument78 pagesPrograms Comm Labnandy nandyNo ratings yet
- ASK - Amplitude Shift KeyingDocument15 pagesASK - Amplitude Shift KeyingAbhijith C SNo ratings yet
- 637625071886699517ece 18ecl67 E12 Notes DPSK&QPSKDocument11 pages637625071886699517ece 18ecl67 E12 Notes DPSK&QPSKchandanhc72048No ratings yet
- Quadrature (Or) Quaternary Phase Shift KeyingDocument8 pagesQuadrature (Or) Quaternary Phase Shift KeyingMs.DEVI P100% (5)
- CCE410:Digital Communication: Digital To Analog Conversion (PSK)Document22 pagesCCE410:Digital Communication: Digital To Analog Conversion (PSK)Ahmed TarekNo ratings yet
- Cac Loai Dieu CheDocument52 pagesCac Loai Dieu CheLênh Đênh Trên BiểnNo ratings yet
- Digital Modulation PDFDocument41 pagesDigital Modulation PDFPabitraMandal100% (1)
- ON Differential Phase Shift Keying (DPSK)Document12 pagesON Differential Phase Shift Keying (DPSK)Nithin PrakashNo ratings yet
- Ask FSKDocument65 pagesAsk FSKHarshitPalNo ratings yet
- 40G DQPSK Optical Transmission Technology 2Document18 pages40G DQPSK Optical Transmission Technology 2Giannis LazarouNo ratings yet
- PSKDocument4 pagesPSKTushar PatilNo ratings yet
- Task 1Document7 pagesTask 1Rana ElshamyNo ratings yet
- Notes in Phase Shift Keying BPSK QPSKDocument4 pagesNotes in Phase Shift Keying BPSK QPSKshanrei50% (2)
- Unit IV 2020Document78 pagesUnit IV 2020vaishnavi khilariNo ratings yet
- Differential Phase Shift Keying Modulation and DemodulationDocument9 pagesDifferential Phase Shift Keying Modulation and DemodulationananthaprathimaNo ratings yet
- Digital Carrier Systems: EE 442 - Spring SemesterDocument51 pagesDigital Carrier Systems: EE 442 - Spring SemesterGagleen KourNo ratings yet
- DPSKDocument4 pagesDPSKMohammad Faisal SiddiqiNo ratings yet
- Differnetial Phase Shift Keying (DPSK) : B Rahul, CH Manikanta, Choudhari Ojas, Cheema Shashank, G S Shashank April 12, 2013Document11 pagesDiffernetial Phase Shift Keying (DPSK) : B Rahul, CH Manikanta, Choudhari Ojas, Cheema Shashank, G S Shashank April 12, 2013Ojas Choudhari0% (1)
- Lecture 4 Phase-Shift Keying PDFDocument5 pagesLecture 4 Phase-Shift Keying PDFRokuichi Web ProgrammerNo ratings yet
- RohitDocument6 pagesRohitRohit YadavNo ratings yet
- Design and Synthesis of QPSK A Subsystem Module ofDocument6 pagesDesign and Synthesis of QPSK A Subsystem Module of39.Poulami MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Experiment 7: TheoryDocument2 pagesExperiment 7: Theorypankaj singhNo ratings yet
- DTT Principles: N. Jethi, Dir (E) DDK, BhubaneswarDocument34 pagesDTT Principles: N. Jethi, Dir (E) DDK, BhubaneswarShishir GuptaNo ratings yet
- Amplitude Shift KeyingDocument15 pagesAmplitude Shift Keyingraman yarramilliNo ratings yet
- Instituto Superior Técnico: 2 Semester 2012/2013Document5 pagesInstituto Superior Técnico: 2 Semester 2012/2013Milupa7No ratings yet
- Digital Carrier Systems PDFDocument40 pagesDigital Carrier Systems PDFNXTEN sportsNo ratings yet
- Binary Phase Shift KeyingDocument30 pagesBinary Phase Shift KeyingAnonymous lvhUQDya6No ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Exercises in Electronics: Operational Amplifier CircuitsFrom EverandExercises in Electronics: Operational Amplifier CircuitsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Signals and System Ankit Goyal NotesDocument36 pagesSignals and System Ankit Goyal NotesFahad Ansari 20-296No ratings yet
- Assignmnet 2Document7 pagesAssignmnet 2Fahad Ansari 20-296No ratings yet
- Eds PresentationDocument10 pagesEds PresentationFahad Ansari 20-296No ratings yet
- Internship PresentationDocument19 pagesInternship PresentationFahad Ansari 20-296No ratings yet
- Brushless DC Motor DrivesDocument4 pagesBrushless DC Motor DrivesFahad Ansari 20-296No ratings yet
- Rohini 41211408710Document2 pagesRohini 41211408710Fahad Ansari 20-2960% (1)
- Smart Grid PDFDocument3 pagesSmart Grid PDFFahad Ansari 20-296No ratings yet
- AM CircuitsDocument13 pagesAM CircuitsFahad Ansari 20-296No ratings yet
- CMOS Interview QuestionsDocument9 pagesCMOS Interview QuestionsarunNo ratings yet
- 3852Document27 pages3852Wana BilaNo ratings yet
- Using The Concept of Supermesh, Find The Current Through 8 Resistor in The Following CircuitDocument16 pagesUsing The Concept of Supermesh, Find The Current Through 8 Resistor in The Following CircuitMohiuddin JewelNo ratings yet
- (Charge RL Avec L 0.1) : Vs FFDocument1 page(Charge RL Avec L 0.1) : Vs FFDiaa Eddine BoudiafNo ratings yet
- 10 Ways To Fix SETUP and HOLD Violation: Static Timing Analysis (STA) Basic (Part-8) - VLSI ConceptsDocument6 pages10 Ways To Fix SETUP and HOLD Violation: Static Timing Analysis (STA) Basic (Part-8) - VLSI ConceptsAbhi AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Crown Prx512-A SCHDocument23 pagesCrown Prx512-A SCHDag SundbyNo ratings yet
- Unit-3 Data Flow Level & Switch Level Modeling: Digital Design Through VerilogDocument14 pagesUnit-3 Data Flow Level & Switch Level Modeling: Digital Design Through VerilogSrinivas NaiduNo ratings yet
- Mohammed SadiqDocument2 pagesMohammed Sadiqmohammed229No ratings yet
- Nodal Analysis Collection 2Document21 pagesNodal Analysis Collection 2Manoj ManmathanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 31: Jfets As Variable Resistors: Automatic Gain ControlDocument7 pagesLecture 31: Jfets As Variable Resistors: Automatic Gain ControlUdBlNo ratings yet
- Xiner-Xns15n120t C379748Document1 pageXiner-Xns15n120t C379748roby72No ratings yet
- Single/Dual/Quad, Ultra-High-Speed, +3V/+5V, Beyond-the-Rails ComparatorsDocument12 pagesSingle/Dual/Quad, Ultra-High-Speed, +3V/+5V, Beyond-the-Rails ComparatorsRicardo UrioNo ratings yet
- Wani sageer4317-PTCDocument16 pagesWani sageer4317-PTCWani SageerNo ratings yet
- Nota Unit 7Document36 pagesNota Unit 7F1036No ratings yet
- Chapter4-Flipflops and CountersDocument9 pagesChapter4-Flipflops and CountersNitin KumarNo ratings yet
- An Effective GDI (Gate Diffusion Input) Based 16 - Bit Shift Register Design For Power and Area OptimizationDocument9 pagesAn Effective GDI (Gate Diffusion Input) Based 16 - Bit Shift Register Design For Power and Area OptimizationIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- A 65-Nm CMOS Constant Current Source With ReducedDocument11 pagesA 65-Nm CMOS Constant Current Source With ReducedindorgNo ratings yet
- Docslide - Us Network AnanlysisDocument81 pagesDocslide - Us Network AnanlysiskannanchammyNo ratings yet
- Design and Simulation of Digital Phase Locked Loop Using MOSFET SPICE Models of 300nmDocument4 pagesDesign and Simulation of Digital Phase Locked Loop Using MOSFET SPICE Models of 300nmIJRT OnlineNo ratings yet
- Ec6401 Electronic Circuits II QBW (r2013)Document18 pagesEc6401 Electronic Circuits II QBW (r2013)Bharath PonNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet: HEF4538B MSIDocument8 pagesData Sheet: HEF4538B MSIkauanNo ratings yet
- Lec06 DS 2018-PrintDocument65 pagesLec06 DS 2018-PrintHưng PhạmNo ratings yet
- Burglar AlarmDocument2 pagesBurglar AlarmErole Technologies Pvt ltd Homemade Engineer100% (1)
- Digital Electronics Sample Chapter PDFDocument106 pagesDigital Electronics Sample Chapter PDFRokiniKumarasamyNo ratings yet
- Clipper and ClamperDocument35 pagesClipper and ClamperRahul YadavNo ratings yet
- TDA8920-PSU Manual PDFDocument5 pagesTDA8920-PSU Manual PDFStephen MeyerNo ratings yet
- 555Document80 pages555elpasanteNo ratings yet
- Relaxation Oscillators Triangular Waveform Generators: Two Mark Questions One Mark QuestionsDocument3 pagesRelaxation Oscillators Triangular Waveform Generators: Two Mark Questions One Mark QuestionsAbhinavNo ratings yet
- Digital Electronics (MCQ) PART-1Document7 pagesDigital Electronics (MCQ) PART-101ABHIGYAN MAJINo ratings yet