Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MATH (Reviewer) Midterm Calculus
MATH (Reviewer) Midterm Calculus
Uploaded by
Angge SarcenoOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MATH (Reviewer) Midterm Calculus
MATH (Reviewer) Midterm Calculus
Uploaded by
Angge SarcenoCopyright:
Available Formats
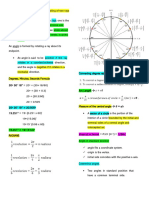
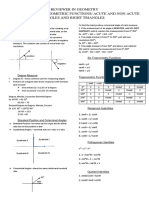
Trigonometry-branch of mathematics which deals witth triangle, x=(r2-y2)2
particularly triangles in a plane where are angle of the triangle is 90
degree. GRAPHS OF SINE AND CUSIVE FNCTION
Hipparchus of Bithynia (190-120 B.C) *periodic-repeat in cycle
*born iin nicaea in bithynia *periodic function- that repeat itself after a given value.
*founder of trigonometry *basic sine and cosine function have period of 2pie or 360
*chords of circles *sine and cosene (comtinous) no have breaks.
APPLICATION OF TRIGONOMETRY *Domain (infinity positive or negative)
*astronomy, navigation, music theory, electronics, mechanical *range(-1,1)
engineering, civil engineer, computer graphics and pharmacy. *sin (add)
APPLICATION OF TRIGONOMETRYR IN ASTRONOMY *cosine (even)
*used to measure the distance to nearby stars. SINUSOIDAL FUNCTION
APPLICATION OF TRIGONOMETRY IN ARCHITECTURE -same general shape as a sine or function.
*LEANARDO DA VINCI -sine and cosine function that have aregular period and angle.
*curved surfaces A= amplitude (difference between the highest and lowest point of a
APPLICATION OF TRIGONOMETRY IN GEOPHYSICAL SCIENCE curve)
*ocean, subduction zones, mapping, slope stability and parallax B=period (length it takes for wave to repeat itself)
ANGLES-figure formed or generated by the rotation of a line C= horizontal (shift, displacement, phase shft)
segment around fixed point. D= vertical (shift/translation)
INITIAL SIDE (1ST POSITION) FORMULA
TERMINAL SIDE (FINNAL SIDE) *PERIOD= 360/b
VERTEX (FIXED POINT) *INCREMENT= Period/4
DEGREE- SEXAGESINAL SYSTEM AND ANGLE FORMED BY ROTATION, To find c c=c/b
VERTEX EQUAL 1/ 360 OF COMPLETE REVOLUTION. THE WHOLE
ANGLE DIVIDED INTO 360 DEGREE OR A NO. THAT MULTIPLE BY 60.
REVOLUTIONAL- by terminal side in relation to the initial ssside
which equivalent to whole angle.
RADIAN- central angle/ radius/ circumference
CIRCULAR FUNCTION- having domain of real numbers.
-if “theta” is an angle standard position P(x’y) is any point other than
the origin on terminal side of “theta” and r= (x 2 + y2) 2
*THETA- commonly used as a variable to indicate angle
FORMULA
Sin (y) -sine Csc (1/y)-cosine
Cos (x) -cosine Sec(1/x)-secant
Tan(y/x) -tangent Cot(x/y)-
cotangent
given if it is not quadrant.
r=(x2=y2)2 y=(r2-x2)2
x2=r2-y2
You might also like
- IGCSE Mensuration FormulaDocument7 pagesIGCSE Mensuration FormulaBeshkaNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry ReviewerDocument10 pagesTrigonometry ReviewerNiko Ramarama100% (1)
- Creating Cognitively Demanding TasksDocument4 pagesCreating Cognitively Demanding Tasksapi-350301641No ratings yet
- Properties of Surfaces (Centre of Gravity & Moment of Inertia)Document48 pagesProperties of Surfaces (Centre of Gravity & Moment of Inertia)Tauseef100% (1)
- SAT II Math Level 2 Subject Test Notes: Trigonometric FunctionsDocument4 pagesSAT II Math Level 2 Subject Test Notes: Trigonometric Functionstomcantyyy100% (1)
- Plane Trigonometry 2017rgsDocument8 pagesPlane Trigonometry 2017rgsPaulynne Jhee BedicoNo ratings yet
- Pre Cal ReviewerDocument5 pagesPre Cal ReviewerMary RentozaNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry: Angle MeasuresDocument36 pagesTrigonometry: Angle MeasuresKiran Kumar100% (1)
- Maths & Mech FormulasDocument19 pagesMaths & Mech FormulasgunasekaranNo ratings yet
- Pre Cal 2 NotesDocument20 pagesPre Cal 2 NotesalessandrapamatianNo ratings yet
- Reviewer - Solid MensurationDocument6 pagesReviewer - Solid MensurationLorenz ArdienteNo ratings yet
- Plane and Solid GeometryDocument11 pagesPlane and Solid GeometryKawaii SamaNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Maths IIT Worksheet 2 Area and PerimeterDocument8 pagesGrade 9 Maths IIT Worksheet 2 Area and PerimetergeethaNo ratings yet
- TRIGODocument2 pagesTRIGOcarrot cakeNo ratings yet
- Notes - MathematicsDocument10 pagesNotes - MathematicsskyNo ratings yet
- PRECAL 2ndQDocument4 pagesPRECAL 2ndQCiouSNo ratings yet
- Geometric Shapes CalculsDocument41 pagesGeometric Shapes CalculsAhmed SakrNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 Graphs in Trigonometric FunctionsDocument16 pagesTopic 4 Graphs in Trigonometric FunctionslizetteNo ratings yet
- PDF Radius of Curvature CompressDocument7 pagesPDF Radius of Curvature CompressSollutions for techNo ratings yet
- Assgn 2Document34 pagesAssgn 2Daniel CryerNo ratings yet
- All Math FormulasDocument27 pagesAll Math FormulasMubassher Ahmed Shoaib100% (1)
- REVIEWERDocument3 pagesREVIEWERAaron Rapha RosalesNo ratings yet
- Pre Cal Exam Quarter 2Document6 pagesPre Cal Exam Quarter 2Hannah Balais100% (1)
- Plane Geometry: Appendix EDocument4 pagesPlane Geometry: Appendix Ejainendra_ismNo ratings yet
- Math OL Cambridge Formula SheetDocument9 pagesMath OL Cambridge Formula Sheetscarlettwitch2004No ratings yet
- Maths ProjectDocument18 pagesMaths ProjectSanjay JindalNo ratings yet
- All The Trig That You Need To KnowDocument16 pagesAll The Trig That You Need To Knowapi-3755447No ratings yet
- Formulas For Pre-Olympiad Competition Math: Eashan Gandotra 4 August 2017Document11 pagesFormulas For Pre-Olympiad Competition Math: Eashan Gandotra 4 August 2017jehovisti100% (1)
- Chapter 3 - Area - Volume (CIVIL ENGINEERING-ENGINEERING SURVEY)Document14 pagesChapter 3 - Area - Volume (CIVIL ENGINEERING-ENGINEERING SURVEY)second mnwwrhNo ratings yet
- Formulas Pre OlympiadDocument11 pagesFormulas Pre Olympiadbus9No ratings yet
- 1-Basic Mathematics-01-TheoryDocument37 pages1-Basic Mathematics-01-TheoryRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Pre-CalculusDocument13 pagesChapter 3 Pre-CalculusaiNo ratings yet
- Moment of Inertia1 PDFDocument26 pagesMoment of Inertia1 PDFAashish BhandariNo ratings yet
- CONICAL EQUAL-AREA PROJN. With II SP Partha Das - ABNSCDocument7 pagesCONICAL EQUAL-AREA PROJN. With II SP Partha Das - ABNSCpartha dasNo ratings yet
- Moment of Inertia1 PDFDocument26 pagesMoment of Inertia1 PDFAashish BhandariNo ratings yet
- Moment of Inertia1 PDFDocument26 pagesMoment of Inertia1 PDFAashish BhandariNo ratings yet
- Spherical Trigonometry Lecture SummaryDocument3 pagesSpherical Trigonometry Lecture SummaryRenderizzah FloraldeNo ratings yet
- Anna's AssignmentDocument16 pagesAnna's Assignmenttumaini murrayNo ratings yet
- 2 MathDocument5 pages2 MathAlexandra EscalonaNo ratings yet
- Assignment IN Vibration Engineering: Submitted By: Kim Dominic S. DejañoDocument34 pagesAssignment IN Vibration Engineering: Submitted By: Kim Dominic S. DejañoKim DejañoNo ratings yet
- MATHS ProjectDocument40 pagesMATHS ProjectShrija Padhi100% (1)
- Trigonometry Reviewer 1st QuarterDocument3 pagesTrigonometry Reviewer 1st QuarterLJ PapaNo ratings yet
- Plane Trigonometry: Trigonometry Angle Unit ConversionDocument5 pagesPlane Trigonometry: Trigonometry Angle Unit ConversionZairah Ann BorjaNo ratings yet
- Sky's AssignmentDocument7 pagesSky's AssignmentSamrawit MinilikNo ratings yet
- TrigonometryDocument101 pagesTrigonometryMarilyn LiconoNo ratings yet
- TrigonometryDocument12 pagesTrigonometryGwyneth Lei T. ManaoisNo ratings yet
- NGEC 9 Module 1 (Week 2-3) - Student Copy To UploadDocument93 pagesNGEC 9 Module 1 (Week 2-3) - Student Copy To Uploadvjan LeonorNo ratings yet
- Maths ProjectDocument18 pagesMaths ProjectSanjay JindalNo ratings yet
- Math12 - L4 (Trigo Functions of Angles)Document12 pagesMath12 - L4 (Trigo Functions of Angles)Lisa GarciaNo ratings yet
- Horizontal CurveDocument7 pagesHorizontal Curveصهيب هدير اكرم سعدالدينNo ratings yet
- Bogota2018 4 SpaceGroups ITA StudentsDocument97 pagesBogota2018 4 SpaceGroups ITA StudentsJesus MoralNo ratings yet
- Maths FormulaDocument11 pagesMaths FormulaSajjad HameedNo ratings yet
- Inverse Trigonometric FunctionsDocument288 pagesInverse Trigonometric FunctionsJennifer BanteNo ratings yet
- Regents Trigonometry: Study GuideDocument12 pagesRegents Trigonometry: Study GuideAdair ContemareroNo ratings yet
- Great Math Formula With ExamplesDocument37 pagesGreat Math Formula With Examplessandesh negi100% (1)
- Look Angles of SatelliteDocument13 pagesLook Angles of Satelliteshruti soni100% (1)
- Project On TrigonometryDocument30 pagesProject On TrigonometryRishu RajNo ratings yet
- Geometry 12 ReviewerDocument8 pagesGeometry 12 ReviewerBlanche Iris Estrel SiapnoNo ratings yet
- Blaw1final ReviewerDocument6 pagesBlaw1final ReviewerAngge SarcenoNo ratings yet
- Reflection W2 SHSDocument4 pagesReflection W2 SHSAngge SarcenoNo ratings yet
- Gable TaxationDocument2 pagesGable TaxationAngge SarcenoNo ratings yet
- Mesh Current Kirchhoff'sDocument4 pagesMesh Current Kirchhoff'sAngge SarcenoNo ratings yet
- Meeting MinutesDocument2 pagesMeeting MinutesAngge SarcenoNo ratings yet
- (Template) CU 6 Intermolecular ForcesDocument7 pages(Template) CU 6 Intermolecular ForcesAngge SarcenoNo ratings yet
- Gec Reviewer MTDocument1 pageGec Reviewer MTAngge SarcenoNo ratings yet
- Pre-Algebra - Final Exam - Solutions.practice 1Document8 pagesPre-Algebra - Final Exam - Solutions.practice 1Dream RichNo ratings yet
- Matlab File Uma011Document14 pagesMatlab File Uma011GUNJAN KHULLARNo ratings yet
- DEM4110 - Interpolation and Extrapolation - 2021Document74 pagesDEM4110 - Interpolation and Extrapolation - 2021henriettamunakombwe8No ratings yet
- Fall Prep Session Materials 2014-15 DraftDocument216 pagesFall Prep Session Materials 2014-15 Draftapi-283319039No ratings yet
- FinalExam Maths PDFDocument1 pageFinalExam Maths PDFNaveed IjazNo ratings yet
- Short Time Fourier TransformDocument37 pagesShort Time Fourier TransformHamada AlmasalmaNo ratings yet
- 2.5 Constructing and Solve EquationsDocument16 pages2.5 Constructing and Solve EquationsPrithikah PrakashNo ratings yet
- Sets, Relations and FunctionsDocument73 pagesSets, Relations and FunctionsAvnish Bhasin100% (1)
- Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC)Document3 pagesCyclic Redundancy Check (CRC)AhmadFatihinNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Using The Number Line To Model The Addition of IntegersDocument6 pagesLesson 2 Using The Number Line To Model The Addition of Integersapi-261894355No ratings yet
- 017 Final Exam TopicsDocument89 pages017 Final Exam TopicsAshley WeekesNo ratings yet
- Proof of Normal DistributionDocument5 pagesProof of Normal Distributionvc94No ratings yet
- Development of An Extended Quadratic Tetrahedron For Finite Element Analysis of Navier-Stokes ProblemsDocument37 pagesDevelopment of An Extended Quadratic Tetrahedron For Finite Element Analysis of Navier-Stokes ProblemsChandrakiran AlapatiNo ratings yet
- Q1 LAS2 Roots and Coefficients of Quadratic EquationsDocument6 pagesQ1 LAS2 Roots and Coefficients of Quadratic Equationskris krossNo ratings yet
- Differential Calculus: Mrs. Yolanda C. de Leon, LPT, Maed Instructor First Semester 2021-2022Document34 pagesDifferential Calculus: Mrs. Yolanda C. de Leon, LPT, Maed Instructor First Semester 2021-202229. Galapon, Mark Joshua M.No ratings yet
- Armstrong Solution PDFDocument53 pagesArmstrong Solution PDFHarold ContrerasNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Functions of Acute Angles: Assessment TasksDocument3 pagesTrigonometric Functions of Acute Angles: Assessment Tasksbyunbacooon456No ratings yet
- LOGS Mark SchemeDocument9 pagesLOGS Mark SchemeZakariya FarazNo ratings yet
- 03-Time-Domain Analysis of LTI SystemsDocument32 pages03-Time-Domain Analysis of LTI Systemsmesfin snowNo ratings yet
- Numopt 0Document163 pagesNumopt 0ayeniNo ratings yet
- 8 - The Singular Value Decomposition: Cmda 3606 Mark EmbreeDocument24 pages8 - The Singular Value Decomposition: Cmda 3606 Mark EmbreeMeenazNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Pictorial DrawingsDocument44 pagesChapter 5 Pictorial DrawingsVisan NaiduNo ratings yet
- Solve The Volterra Integral Equation by Using The Series Solution MethodDocument3 pagesSolve The Volterra Integral Equation by Using The Series Solution MethodMuhammad TauheedNo ratings yet
- JAN 24 Batch: Pre Mock - 02Document3 pagesJAN 24 Batch: Pre Mock - 02Quazi Sahil HossainNo ratings yet
- B.sc. (H) Mathematics Analysis IIDocument47 pagesB.sc. (H) Mathematics Analysis IIRenu ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- LAB 04 - Gauss Jordan and Inverse of Matrices in MATLABDocument5 pagesLAB 04 - Gauss Jordan and Inverse of Matrices in MATLABCan Raps100% (1)
- Math9 (Pivot)Document40 pagesMath9 (Pivot)Perez Raphael100% (2)
- Fourier Series - Brilliant Math & Science WikiDocument6 pagesFourier Series - Brilliant Math & Science WikiswadhinNo ratings yet
- Noc19 De04 Assignment Week 5Document4 pagesNoc19 De04 Assignment Week 5Sweta DashNo ratings yet