Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Endiafe, Zandra A. Bsba-Hrdm Iv Prodman Assignment No. 2
Endiafe, Zandra A. Bsba-Hrdm Iv Prodman Assignment No. 2
Uploaded by
edithmonteroOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Endiafe, Zandra A. Bsba-Hrdm Iv Prodman Assignment No. 2
Endiafe, Zandra A. Bsba-Hrdm Iv Prodman Assignment No. 2
Uploaded by
edithmonteroCopyright:
Available Formats
Endiafe, Zandra A. BSBA-HRDM IV PRODMAN ASSIGNMENT NO.
PRODUCTIVITY Productivity is a measure of output from a production process, per unit of input. For example, labor productivity is typically measured as a ratio of output per labor-hour, an input. Productivity may be conceived of as a metric of the technical or engineering efficiency of production. As such, the emphasis is on quantitative metrics of input, and sometimes output. Productivity is distinct from metrics of locative efficiency, which take into account both the monetary value (price) of what is produced and the cost of inputs used, and also distinct from metrics of profitability, which address the difference between the revenues obtained from output and the expense associated with consumption of inputs.
EFFECTIVENESS AND EFFICIENCY Efficiency and effectiveness are both commonly used management terms. Yet, while they sound similar and start with the same letters, they both mean different things. Efficiency refers to doing things in a right manner. Scientifically, it is defined as the output to input ratio and focuses on getting the maximum output with minimum resources. Effectiveness, on the other hand, refers to doing the right things. It constantly measures if the actual output meets the desired output. Since efficiency is all about focusing on the process, importance is given to the means of doing things whereas effectiveness focuses on achieving the end goal. Effectiveness, on the other hand, believes in meeting the end goal and therefore takes into consideration any variables that may change in the future. In order to be efficient time and again, discipline and rigor is required. This can build inflexibility into the system. Effectiveness, on the other hand, keeps the long term strategy in mind and is thus more adaptable to the changing environment.
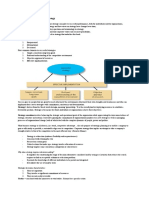
FACTORS THAT AFFECT PRODUCTIVITY Methods Method is a means or manner of procedure, especially a regular and systematic way of accomplishing something. Capital Capital is an accumulated stock of such wealth or its value Quality Quality is to gain the speed of automatic features such as spell checking and error correction. Technology Technology is the making, usage and knowledge of tools, techniques, craft, system or methods of organization in order to solve a problem or serve some purpose.
Management Management means that the other productivity might be achieved through improving organization and preparation for the other typing.
COMPETITIVENESS Companies must be competitive to sell their goods and services in the market place. Competitiveness is an important factor in determining whether a company prospers, barely gets by, or fails. Business organizations compete with one another in a variety of ways. Keys among them are price, quality, product or service differentiation, flexibility and time to perform certain activities. Competitiveness is how an organization meets the needs of customers relative to others that offer similar goods or services.
STRATEGY An organizations strategy has a long-term impact on the nature and characteristics of the organization. In large measure, strategies affect the ability of an organization to compete or, in the case of a nonprofit organization, the ability to serve its intended purpose. Strategy is a plan for achieving organizational goals. Strategy, a word of military origin, refers to a plan of action designed to achieve a particular goal. In military strategy is distinct from tactics, which are concerned with the conduct of an engagement, while strategy is concerned with how different engagements are linked. How a battle is fought is a matter of tactics: the terms and conditions that it is fought on and whether it should be fought at all is a matter of strategy, which is part of the four levels of warfare: political goals or grand strategy, strategy, operation, and tactic. Building on the work of many thinkers on the subject, one can define strategy as "a comprehensive way to try to pursue political ends, including the threat or actual use of force, in a dialectic of wills there have to be at least two sides to a conflict. These sides interact, and thus a Strategy will rarely be successful if it shows no adaptability.
TYPES OF STRATEGY Organization Strategy It means that the organization have an over-all strategy for the whole organization. Functional Strategy It means that it relates to each of the functional areas of the organization. Operations Strategy It is the narrower in scope dealing primarily with the operations aspect of the organization. It is also the approach that is consistent with the organization strategy which is used to guide the operations function. New Strategies 1. Quality Based Strategy Strategy that focuses on satisfying the customer by integrating quality into all phases of the organization. 2. Time Based Strategy Stategy that focuses on reducing the time required to accomplish various activities.
TIME-BASED INNOVATION Time-based innovation is an aspect of Lean Production. Time-based innovation is a standard procedure to get access to a machine, especially a working position with a computer and the functions of this computer within a certain span of time. Such granted access may be automatically terminated. It is a general approach that recognizes the importance of time and seeks to reduce the level of unproductive time in an organization. Benefits include: Quicker response times (reduced lead times) to meet changing market and customer needs Faster new product development Reduction in waste, therefore greater efficiency
You might also like
- Operation StrategyDocument22 pagesOperation StrategyKamaldeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management - Review and Discussion - CH 3-4Document4 pagesStrategic Management - Review and Discussion - CH 3-4bina15650% (1)
- Introduction To Educational ManagementDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Educational Managementanekira5871100% (4)
- Operations Strategy It Operations StrategyDocument9 pagesOperations Strategy It Operations StrategyApril Joy TamayoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Strategy ImplementationDocument46 pagesChapter 6 Strategy ImplementationBekam BekeeNo ratings yet
- Answers MA0052Document10 pagesAnswers MA0052piyushwinnNo ratings yet
- QltySystmsMngmnt AntoDocument11 pagesQltySystmsMngmnt AntoPrasobh NairNo ratings yet
- OM CHAPTER TWO FinalDocument13 pagesOM CHAPTER TWO FinaltesfalidetdawitNo ratings yet
- Operational Management Assignment PDFDocument7 pagesOperational Management Assignment PDFYonas D. Ebren100% (1)
- Chapter 2 - Competitiveness, Strategy & Productivity - 2Document46 pagesChapter 2 - Competitiveness, Strategy & Productivity - 2JeSsica Joy P. SantiagoNo ratings yet
- MB0052 - Strategic Management and Business Policy Assignment-Set 1Document8 pagesMB0052 - Strategic Management and Business Policy Assignment-Set 1Mustafa SayyedNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Strategic ManagementDocument8 pagesAssignment 1 Strategic ManagementManjeet YadavNo ratings yet
- Essay Question MidDocument11 pagesEssay Question Midrbaalsdy530No ratings yet
- OM CH 2Document23 pagesOM CH 2Nicole Anne Villanueva PacificoNo ratings yet
- Chapter ThreeDocument8 pagesChapter ThreeNura BasmerNo ratings yet
- Module 3 5Document11 pagesModule 3 5Esier Davies Paul MalabadNo ratings yet
- BPSM Assignment 1Document12 pagesBPSM Assignment 1Miral patelNo ratings yet
- POM Module1 Unit4Document10 pagesPOM Module1 Unit4KATHLYN ROSE OCAYNo ratings yet
- Strategy Tactics Mission: Competitiveness, Strategy, and ProductivityDocument6 pagesStrategy Tactics Mission: Competitiveness, Strategy, and ProductivityCharice Anne VillamarinNo ratings yet
- Strategic-Management-Notes-PDF 2Document71 pagesStrategic-Management-Notes-PDF 2AbigaelNo ratings yet
- Operations Strategy - Sbaa7027: Unit - IDocument117 pagesOperations Strategy - Sbaa7027: Unit - Ijugraj randhawaNo ratings yet
- Ambabai, Jhansi (U.P.) : College of Science & EngineeringDocument16 pagesAmbabai, Jhansi (U.P.) : College of Science & EngineeringAkancha GuptaNo ratings yet
- b2b Chap 4 ReviewerDocument10 pagesb2b Chap 4 ReviewerLee TeukNo ratings yet
- Op EqualDocument3 pagesOp Equalpamss28ssNo ratings yet
- Operations Management Lecture - 2Document6 pagesOperations Management Lecture - 2tusharNo ratings yet
- Competitiveness Strategy and ProductivityDocument24 pagesCompetitiveness Strategy and ProductivitynbdvNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2 AnswersDocument4 pagesQuiz 2 AnswersHana Demi DeeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document2 pagesChapter 2Annalyn Delizo BanayatNo ratings yet
- OM TQM - Lesson 5Document11 pagesOM TQM - Lesson 5necifag872No ratings yet
- Unit1 Strategic ManagementDocument15 pagesUnit1 Strategic Managementpuskarcing16No ratings yet
- Strategic It ManagementDocument28 pagesStrategic It ManagementwepariaddachristopherNo ratings yet
- REVIEWERStrategic ManagementDocument10 pagesREVIEWERStrategic ManagementDiane SarigumbaNo ratings yet
- MB0052-Strategic Management and Business Policy (Assignment-1)Document9 pagesMB0052-Strategic Management and Business Policy (Assignment-1)Anil KumarNo ratings yet
- Balanced ScorecardDocument9 pagesBalanced ScorecardFERNANDEZ, Ili Abba D.No ratings yet
- BUMA 20023: Strategic Management: Andal, Andrei Feyan P. Bsba HRM 1-1DDocument31 pagesBUMA 20023: Strategic Management: Andal, Andrei Feyan P. Bsba HRM 1-1DCurt Abenoja100% (1)
- Chapter 1: The Concept of StrategyDocument36 pagesChapter 1: The Concept of StrategyPalakNo ratings yet
- STM Concepts AnsersDocument8 pagesSTM Concepts AnsersKarthick Nathan ShanmuganathanNo ratings yet
- Strategic Cost Management Definition and ConceptDocument2 pagesStrategic Cost Management Definition and ConceptMia Joyce Roselada PanesaNo ratings yet
- Strategy: Strategy Is An Action That Managers Take To Attain One or More of The Organization's GoalsDocument4 pagesStrategy: Strategy Is An Action That Managers Take To Attain One or More of The Organization's Goalsma. isabella marcosNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 Strategic Management What Is Strategy?Document10 pagesUnit 8 Strategic Management What Is Strategy?Nisha SherpaNo ratings yet
- Operations Management - Chapter 3Document8 pagesOperations Management - Chapter 3David Van De Fliert50% (2)
- Operations Management For Hospitality ManagemenDocument41 pagesOperations Management For Hospitality ManagemenAngelo Chistian OreñadaNo ratings yet
- By: Rakhi AgarwalDocument22 pagesBy: Rakhi Agarwalsheng cruzNo ratings yet
- Organizing Operations For CompetitionDocument4 pagesOrganizing Operations For CompetitionMarica ShaneNo ratings yet
- Ignou MS-11 2011Document22 pagesIgnou MS-11 2011Ravichandra GowdaNo ratings yet
- Module 2 (OM)Document19 pagesModule 2 (OM)christy bijuNo ratings yet
- Resources Organization Mission Balanced Scorecard BusinessDocument4 pagesResources Organization Mission Balanced Scorecard BusinessA KNo ratings yet
- What Is Strategic Management (6.1)Document4 pagesWhat Is Strategic Management (6.1)rudomposiNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 Introduction To Strategic ManagementDocument105 pagesUnit-1 Introduction To Strategic ManagementKumar SnehalNo ratings yet
- Functional Level StrategyDocument3 pagesFunctional Level Strategyakumar84070375No ratings yet
- Strategic Cost ManagementDocument9 pagesStrategic Cost ManagementPreethi PadmanabhanNo ratings yet
- Operations ManagementDocument48 pagesOperations ManagementHarpoon BKNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1 Business Policy, Corporate Strategy, Basic Concept of Strategic ManagementDocument52 pagesUnit - 1 Business Policy, Corporate Strategy, Basic Concept of Strategic ManagementRaveena SharmaNo ratings yet
- What Is StrategyDocument24 pagesWhat Is StrategySmruti RanjanNo ratings yet
- Dr. Teresita P. Fampo: Report byDocument15 pagesDr. Teresita P. Fampo: Report byTeresita FampoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Organizing and StructureDocument21 pagesChapter 10 Organizing and StructurePaupau100% (1)
- Lecture 2 MayDocument33 pagesLecture 2 Mayaymoon.abdulrahimNo ratings yet
- Strategic Operations ManagementDocument3 pagesStrategic Operations ManagementAl Joshua Ü PidlaoanNo ratings yet
- SM 13 MarksDocument9 pagesSM 13 Marksabinaya kumaranNo ratings yet
- 20ODMBT721 - SM DoneDocument13 pages20ODMBT721 - SM DonekushNo ratings yet
- I. Operations StrategyDocument4 pagesI. Operations StrategyLovely Anne LeyesaNo ratings yet
- Strategic Analysis of Internal Environment of a Business OrganisationFrom EverandStrategic Analysis of Internal Environment of a Business OrganisationNo ratings yet
- Supplier Evaluation - The First Steps For Effective SourcingDocument10 pagesSupplier Evaluation - The First Steps For Effective Sourcingimroz_ali90No ratings yet
- Corporate Social Responsibility in India: A Case Study of Public and Private SectorDocument9 pagesCorporate Social Responsibility in India: A Case Study of Public and Private SectorMaithili SUBRAMANIANNo ratings yet
- HBR Research-Report Brightline PDFDocument16 pagesHBR Research-Report Brightline PDFNICOLAS ATIENCIANo ratings yet
- NTPC Mckinsey 7s FrameworkDocument27 pagesNTPC Mckinsey 7s Frameworkkanchan20667% (3)
- CCCJ Social Work Practicum Guide 2017Document24 pagesCCCJ Social Work Practicum Guide 2017Brittany OliphantNo ratings yet
- Permission LetterDocument6 pagesPermission LetterMELITO JR. CATAYLONo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - MANAGEMENT AND ORGANIZATIONDocument52 pagesChapter 2 - MANAGEMENT AND ORGANIZATIONHatem Dheer100% (1)
- Collaborative Public Management - O'Leary and Vij (ASPA Conf 2012)Document34 pagesCollaborative Public Management - O'Leary and Vij (ASPA Conf 2012)John Kamensky100% (2)
- Organisational CultureDocument3 pagesOrganisational Culturepammy313No ratings yet
- Understanding The Organization's Environment: Chapter SummaryDocument13 pagesUnderstanding The Organization's Environment: Chapter SummarySrinivas RaoNo ratings yet
- Volunteer and VolunteerismDocument40 pagesVolunteer and VolunteerismMary ellen AltavanoNo ratings yet
- Transformational Leadership and Organizational CultureDocument10 pagesTransformational Leadership and Organizational CultureGabriela Korodi0% (1)
- Challenges Faced by Sales ManagerDocument29 pagesChallenges Faced by Sales ManagerniharikkaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To HR:: Human Resource Management (HRM), A Relatively New TermDocument23 pagesIntroduction To HR:: Human Resource Management (HRM), A Relatively New TermMurali Krishnan0% (1)
- Research Paper On Human Behavior in OrganizationDocument5 pagesResearch Paper On Human Behavior in OrganizationafnkgosebapoaiNo ratings yet
- AMBO-101 - Business Management Functions and Practices - AssignmentDocument14 pagesAMBO-101 - Business Management Functions and Practices - AssignmentTanuj GhimireNo ratings yet
- Unit 01 Notes Full ChapterDocument12 pagesUnit 01 Notes Full ChapterSunil Kumar AgarwalaNo ratings yet
- Software Requirement Specification: Micro Finance SolutionsDocument14 pagesSoftware Requirement Specification: Micro Finance Solutionsshruti_04No ratings yet
- Name: Neil Pita Declaro Course: Med - 1 Subject: Phed 206 (Administration of Physical Education)Document1 pageName: Neil Pita Declaro Course: Med - 1 Subject: Phed 206 (Administration of Physical Education)Neil DeclaroNo ratings yet
- The Church: Leading by Example: Source: Michael Cassidy Christian Leadership in A Country of DiversityDocument44 pagesThe Church: Leading by Example: Source: Michael Cassidy Christian Leadership in A Country of DiversityAlen John PinheiroNo ratings yet
- Strategic ManagementDocument1 pageStrategic ManagementJordan CabaguingNo ratings yet
- Corporate Communication and The Corporate BrandDocument18 pagesCorporate Communication and The Corporate BrandVanshika KathuriaNo ratings yet
- The Structural Frame 2009Document17 pagesThe Structural Frame 2009Serien SeaNo ratings yet
- Institutional Supports: Engr. Jose Angelo S. Karagdag, MpaDocument22 pagesInstitutional Supports: Engr. Jose Angelo S. Karagdag, MpaJOSE ANGELO KARAGDAGNo ratings yet
- Definition of Job EvaluationDocument4 pagesDefinition of Job EvaluationDurga Prasad DashNo ratings yet
- Organization Need People and People Need OrganizationDocument2 pagesOrganization Need People and People Need Organizationmanit mahajan100% (7)
- 2.2 Organizational Structure DelayeringDocument8 pages2.2 Organizational Structure DelayeringDania QistinaNo ratings yet
- Bca 109 - Ica 108 CT 2Document2 pagesBca 109 - Ica 108 CT 2Navneet VishnoiNo ratings yet