Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 viewsTransformer Types - Josue Montalvo
Transformer Types - Josue Montalvo
Uploaded by
Gael GutierrezThe document discusses different classifications of transformers based on their use, cooling method, insulating medium, and core construction. Transformers are classified according to their use into distribution transformers, power transformers, autotransformers, HVDC transformers, test transformers, special power transformers, and instrument transformers. They are also classified based on their cooling method and insulating medium. Regarding core construction, transformers can have vertical limbs or five legs, use a stack or wound core, and be made of silicon steel sheets or amorphous metal sheets.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Nothing But Motion by Dewey B. LarsonDocument308 pagesNothing But Motion by Dewey B. LarsonArnold Anderhalden100% (1)
- Lab Report RodrigoDocument5 pagesLab Report RodrigoRodrigo Andrade0% (1)
- Transformer PresentationDocument86 pagesTransformer Presentationmuaz_aminu1422100% (5)
- TransformersDocument3 pagesTransformersMaham NaseerNo ratings yet
- TRANSFORMERDocument2 pagesTRANSFORMERmohammadham242No ratings yet
- EM Transformer Report (Final)Document12 pagesEM Transformer Report (Final)ismail.beee21pnecNo ratings yet
- Introduction TransformerDocument24 pagesIntroduction TransformerNimesha KavindiNo ratings yet
- Working Principle of Transformer: Definition of Transformer. Since There Is No Rotating or Moving Part SoDocument33 pagesWorking Principle of Transformer: Definition of Transformer. Since There Is No Rotating or Moving Part SoBrahmpal BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Group Project - TransformersDocument5 pagesGroup Project - TransformerscadaxeshpatelNo ratings yet
- AsutoshDocument15 pagesAsutoshpiyushanandaghadaiNo ratings yet
- Ology: Pusa Institute of TechnDocument33 pagesOlogy: Pusa Institute of TechnDeepesh KNo ratings yet
- Adelect/Eleng12/ Electric Circuits 2Document12 pagesAdelect/Eleng12/ Electric Circuits 2Rom AndutanNo ratings yet
- Noman Tariq 2019ch02Document9 pagesNoman Tariq 2019ch02Noman TariqNo ratings yet
- Kel It ReportDocument23 pagesKel It ReportshaluNo ratings yet
- Electrical Transformer Is A Static Electrical Machine Which Transforms Electrical Power From One Circuit To Another CircuitDocument35 pagesElectrical Transformer Is A Static Electrical Machine Which Transforms Electrical Power From One Circuit To Another CircuitNh Chuminda YapaNo ratings yet
- Transformers: What Is An Electric Transformer?Document14 pagesTransformers: What Is An Electric Transformer?Mohamed IbrahemNo ratings yet
- Oriental College: TechnologyDocument17 pagesOriental College: TechnologyRashid M AnsariNo ratings yet
- Transformers: What Is An Electric Transformer?Document14 pagesTransformers: What Is An Electric Transformer?Mohamed IbrahemNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Transformers and Its ApplicationsDocument27 pagesPresentation On Transformers and Its ApplicationsPRANAVNo ratings yet
- Types of TransformersDocument11 pagesTypes of TransformersAbdulGhaffarNo ratings yet
- Classification and Design AspectsDocument45 pagesClassification and Design AspectsNandiniNo ratings yet
- TRANSFORMERS LectureDocument6 pagesTRANSFORMERS LecturebabesgremarNo ratings yet
- Xmer (Small)Document11 pagesXmer (Small)VivekNo ratings yet
- TransformersDocument18 pagesTransformerssuicidesquadee21No ratings yet
- Classification of The TransformerDocument7 pagesClassification of The TransformerSintiya TarannumNo ratings yet
- TRANSFORMERDocument7 pagesTRANSFORMERChristian ArceoNo ratings yet
- Module 2 TransformersDocument70 pagesModule 2 TransformersaliyumaidamisaNo ratings yet
- EET EM I Assignment 2 SolveDocument5 pagesEET EM I Assignment 2 SolveNobita NobiNo ratings yet
- EET EM I Assignment 2Document5 pagesEET EM I Assignment 2Nobita NobiNo ratings yet
- Transformer: Pritish Sharma EL-395-2K17Document22 pagesTransformer: Pritish Sharma EL-395-2K17Pritish SharmaNo ratings yet
- Physics Transformer Project Calss XLLDocument14 pagesPhysics Transformer Project Calss XLLPraveena S BNo ratings yet
- Power AssignmentDocument8 pagesPower AssignmentHaseeb AdilNo ratings yet
- Question 01Document9 pagesQuestion 01Ahmed zia tahirNo ratings yet
- The State of The Art in Engineering Methods For TRDocument10 pagesThe State of The Art in Engineering Methods For TRVictor Julián Fernández CarrazanaNo ratings yet
- Single Phase TransformersDocument50 pagesSingle Phase TransformersDevi Sri PrasadNo ratings yet
- Working Principle of Transformer: The Working Procedure On HowDocument6 pagesWorking Principle of Transformer: The Working Procedure On HowkNo ratings yet
- EE - TransformerDocument5 pagesEE - TransformerNiño PerezNo ratings yet
- Types of TransformersDocument7 pagesTypes of TransformersTyron FrancisNo ratings yet
- TransformerDocument27 pagesTransformerAmeen Khan NiaziNo ratings yet
- Types of TransformersDocument16 pagesTypes of TransformersTahamee SHAIKHNo ratings yet
- 01 - Introduction of TransformerDocument43 pages01 - Introduction of TransformerDanielle Aubrey TerencioNo ratings yet
- Transformer 1Document29 pagesTransformer 1utharun3No ratings yet
- U21 Assigment 1Document57 pagesU21 Assigment 1Mostafa ElngarNo ratings yet
- TRANSFORMERDocument5 pagesTRANSFORMERmohammadham242No ratings yet
- Synergy TransformerDocument2 pagesSynergy TransformerKrupal MehtaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Substation (GRID) : Generating Station SwitchyardsDocument21 pagesElectrical Substation (GRID) : Generating Station SwitchyardsTariqNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2013-14 CP1182 24-Oct-2013 RM01 Lecture-1Document13 pagesFALLSEM2013-14 CP1182 24-Oct-2013 RM01 Lecture-1VineethMenonNo ratings yet
- At 2Document13 pagesAt 2Altaher Bushra AdamNo ratings yet
- Transformers: What Is An Electric Transformer?Document8 pagesTransformers: What Is An Electric Transformer?Mohamed IbrahemNo ratings yet
- 1.list Out Trouble Shooting Techniques For Transformer TransformerDocument30 pages1.list Out Trouble Shooting Techniques For Transformer Transformerrohith mukkamalaNo ratings yet
- Transformer Anubhav Pandey 12 ProjectDocument16 pagesTransformer Anubhav Pandey 12 Projectxmr7777777donttakeshitNo ratings yet
- (Pick The Date) : YPE THE Company NameDocument18 pages(Pick The Date) : YPE THE Company NameAbhishek ThomasNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document186 pagesUnit 3Sahil SinghNo ratings yet
- Classes of InsulationDocument8 pagesClasses of InsulationarjunNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 TransformerDocument76 pagesChapter 2 TransformerShikoyeniNo ratings yet
- Modul 9 Mesin Listrik 1 PDFDocument22 pagesModul 9 Mesin Listrik 1 PDFaswardiNo ratings yet
- TransformerDocument15 pagesTransformerMohd ArizNo ratings yet
- Transformer 2Document3 pagesTransformer 2mohammadham242No ratings yet
- ReportDocument21 pagesReporthrishikesh anvekarNo ratings yet
- Phy PDFDocument15 pagesPhy PDFzoro118921No ratings yet
- What Is A Transformer?: - Voltage Levels - The Medium Used in The Core - Arrangements of Windings - Installation PlaceDocument2 pagesWhat Is A Transformer?: - Voltage Levels - The Medium Used in The Core - Arrangements of Windings - Installation PlaceKudamala Hari Prasad ReddyNo ratings yet
- Generation and Transmission of Electric Power: Lecture Notes of the Generation and Transmission of Electric Power CourseFrom EverandGeneration and Transmission of Electric Power: Lecture Notes of the Generation and Transmission of Electric Power CourseNo ratings yet
- Download: Free Download Ordinary Level Physics A F Abbott PDF - Rar ##BEST##Document2 pagesDownload: Free Download Ordinary Level Physics A F Abbott PDF - Rar ##BEST##Lameck JosephNo ratings yet
- The Szilard-Chalmers ReactionDocument4 pagesThe Szilard-Chalmers ReactionInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology100% (1)
- CBSE Class 10 Science HOTs Question BankDocument63 pagesCBSE Class 10 Science HOTs Question BankSobana Itharaji75% (4)
- Class LectureDocument68 pagesClass LectureMahelat RangoNo ratings yet
- Practice Test For General Chemistry 2 Auburn UniversityDocument15 pagesPractice Test For General Chemistry 2 Auburn UniversityibejtmNo ratings yet
- Student Exploration: Energy Conversions: Light, Heat, Wind, and HydrogenDocument5 pagesStudent Exploration: Energy Conversions: Light, Heat, Wind, and HydrogenKatie FriasNo ratings yet
- LimitedDocument7 pagesLimiteds.shahjalalshakilNo ratings yet
- Science: Whole Brain Learning SystemDocument16 pagesScience: Whole Brain Learning SystemKayrell AquinoNo ratings yet
- Corrosion: Standard Grade ChemistryDocument4 pagesCorrosion: Standard Grade ChemistryStashy LoteNo ratings yet
- Basic Chemistry For Biology Lab ActivityDocument9 pagesBasic Chemistry For Biology Lab ActivityHaris Khan100% (1)
- Phy331 L1Document20 pagesPhy331 L1Dharmesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Kusadasi ACEMPDocument5 pagesKusadasi ACEMPapacheNo ratings yet
- Disclosure To Promote The Right To InformationDocument31 pagesDisclosure To Promote The Right To Informationashishjawale7No ratings yet
- Chapter: Environmental Issues: BIOLOGY - AssignmentDocument10 pagesChapter: Environmental Issues: BIOLOGY - Assignmentyogesh ahireNo ratings yet
- WWW Quora Com What Is A Geostationary and Why Is It at 35 786 KMDocument2 pagesWWW Quora Com What Is A Geostationary and Why Is It at 35 786 KMJournal ArtNo ratings yet
- ProjectDocument16 pagesProjectpothugunta charanNo ratings yet
- That Shapes Look Familiar!Document32 pagesThat Shapes Look Familiar!Bernadeth DaracanNo ratings yet
- Calculating Weld Volume and Weight: Welding CostsDocument4 pagesCalculating Weld Volume and Weight: Welding CostsMehmet SoysalNo ratings yet
- Red Oxy BrochureDocument16 pagesRed Oxy BrochureSlick LegionNo ratings yet
- CHE61203 Pollution ControlDocument27 pagesCHE61203 Pollution ControlPorkkodi SugumaranNo ratings yet
- What Causes Magnetism?: - What Is The Origin of Magnetic Fields?Document28 pagesWhat Causes Magnetism?: - What Is The Origin of Magnetic Fields?Suhaela NajlaNo ratings yet
- ASTM D4289-03 Standard Test Method For Elastomer Compatibility of Lubricating Greases and FluidsDocument8 pagesASTM D4289-03 Standard Test Method For Elastomer Compatibility of Lubricating Greases and FluidsCan ERTANNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Investigatory ProjectDocument18 pagesChemistry Investigatory ProjectSubhikshaNo ratings yet
- Potassium Permanganate TitrationsDocument70 pagesPotassium Permanganate TitrationsDarius SutherlandNo ratings yet
- Digital Unit Plan Template Unit Title: 2 Law of Thermodynamics Name: Ernesto Del Villar Content Area: Physics Grade Level: High School PhysicsDocument3 pagesDigital Unit Plan Template Unit Title: 2 Law of Thermodynamics Name: Ernesto Del Villar Content Area: Physics Grade Level: High School Physicsapi-277536571No ratings yet
- Co-Ordination Compound Ex-4 Solution For Vedantu TatvaDocument9 pagesCo-Ordination Compound Ex-4 Solution For Vedantu TatvaAbhinav ThapliyalNo ratings yet
- CV KuDocument3 pagesCV KuPatricia AlfrinNo ratings yet
- Updated Slides of Compressible FlowsDocument39 pagesUpdated Slides of Compressible FlowsFurqan YousafzaiNo ratings yet
Transformer Types - Josue Montalvo
Transformer Types - Josue Montalvo
Uploaded by
Gael Gutierrez0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views4 pagesThe document discusses different classifications of transformers based on their use, cooling method, insulating medium, and core construction. Transformers are classified according to their use into distribution transformers, power transformers, autotransformers, HVDC transformers, test transformers, special power transformers, and instrument transformers. They are also classified based on their cooling method and insulating medium. Regarding core construction, transformers can have vertical limbs or five legs, use a stack or wound core, and be made of silicon steel sheets or amorphous metal sheets.
Original Description:
Original Title
Transformer types - Josue Montalvo
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses different classifications of transformers based on their use, cooling method, insulating medium, and core construction. Transformers are classified according to their use into distribution transformers, power transformers, autotransformers, HVDC transformers, test transformers, special power transformers, and instrument transformers. They are also classified based on their cooling method and insulating medium. Regarding core construction, transformers can have vertical limbs or five legs, use a stack or wound core, and be made of silicon steel sheets or amorphous metal sheets.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views4 pagesTransformer Types - Josue Montalvo
Transformer Types - Josue Montalvo
Uploaded by
Gael GutierrezThe document discusses different classifications of transformers based on their use, cooling method, insulating medium, and core construction. Transformers are classified according to their use into distribution transformers, power transformers, autotransformers, HVDC transformers, test transformers, special power transformers, and instrument transformers. They are also classified based on their cooling method and insulating medium. Regarding core construction, transformers can have vertical limbs or five legs, use a stack or wound core, and be made of silicon steel sheets or amorphous metal sheets.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 4
Montalvo Segura Josue Aramis
Read and do an essay about the transformer types and conections.
The transformes is used to raise or lower the voltage in the supply network of the
power system wich serve to transmit electric power over great distance and
distribute it among consumers.
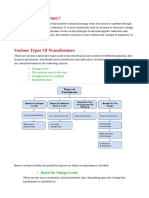
The transformers are classified into various categories, according to their Use,
Cooling method, Insulating medium and Core construction.
Classification according to Transformers use
Transformers are classified according to their use into the following:
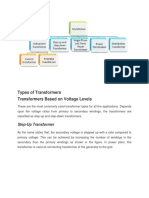
Distribution Transformers:
They are used in distribution networks in order to transmit energy from the medium
voltage network to the low voltage network of the consumers. Their rated power
usually ranges from 50 to 1600 kVA.
Power Transformers:
They are used in high-power generating stations for voltage step-up and in
transmission substations for voltage step-up or step-down. Usually they are of
power greater than 2 MVA.
Autotransformers:
They are used for voltage transformation within relatively small limits, for
connection of electric energy systems of various voltages, and for starting
alternating current motors
HVDC Transformers:
They are key components in HVDC transmission systems. The HVDC transformers
react as coupling elements between the connected ac grids and high-power
rectifiers, and are necessary for adapting the voltage. They insulate the rectifier
itself from the ac grid and generate a phase shift.
Test Transformers:
They are used for the execution of performance tests with high or ultrahigh voltage.
Special Power Transformers:
They are used for special applications, for example, traction systems, furnaces,
and welding.
Instrument Transformers:
They are used for the accurate measurement of voltage or current.
Telecommunication Transformers:
They are used in telecommunication applications aiming at the reliable
reproduction of a signal over a wide range of frequency and voltage.
Classification according to Transformers Cooling method
The identification of oil-immersed transformers according to the cooling method is
expressed by a four-letter code. The first letter expresses the internal cooling
medium in contact with the windings. The second letter identifies the circulation
mechanism for the internal cooling medium. The third letter identifies the external
cooling medium. The fourth letter identifies the circulation mechanism for external
cooling medium.
This type of transformers are classified according to their cooling method and they
are four classifications:
ONAF: oil natural air forced
OFAN: oil forced air natural
OFAF: oil forced air forced
OFWF: oil forced water forced
Classification according to Transformers Insulating medium
Transformers are classified according to their insulating medium into the following:
Oil-Immersed Transformers:
The insulating medium is mineral oil or synthetic (silicon) oil.
Dry Type Transformers:
The cooling is implemented with natural air circulation and the windings are usually
insulated with materials of H or F class.
Resin Type Transformers:
The resin type transformer is a dry type transformer insulated with epoxy resin cast
under vacuum.
Classification according to Transformers Core construction
Transformers are classified according to their core construction into the following
categories:
circuit of three-phase Transformers are the followings:
With Vertical Limbs:
The magnetic flux of one leg must flow through the other two legs and the flux also
flows through the windings of the other phases, that is, the transformer has no free
return of the flux.
With Five Legs (Vertical Limbs):
Free return of the flux through the external legs.
Two different technologies for stacking the electrical steel sheets of
the magnetic material of the core:
Stack Core:
The layers of the sheets of the magnetic material are placed one over the other
and vertical and horizontal layers are overlapped
Wound Core:
The magnetic circuit is of shell type and the sheets are wound.
Two different materials are used for core construction:
Silicon Steel Sheet:
The silicon steel sheet that is used for core construction is an alloy consisting of
97% iron and 3% silicon. This material is crystalline. The silicon steel sheets have
thickness from 0.18 to 0.5 mm.
Amorphous Metal Sheet:
The amorphous metal sheet that is used for core construction is an alloy consisting
of 92% iron, 5% silicon, and 3% boron. This material is not crystalline. It has 70%
lower no-load loss than silicon steel. The thickness of the amorphous metal sheet
is 0.025 mm, that is, it is about 10 times thinner than the typical thickness of silicon
steel sheet.
You might also like
- Nothing But Motion by Dewey B. LarsonDocument308 pagesNothing But Motion by Dewey B. LarsonArnold Anderhalden100% (1)
- Lab Report RodrigoDocument5 pagesLab Report RodrigoRodrigo Andrade0% (1)
- Transformer PresentationDocument86 pagesTransformer Presentationmuaz_aminu1422100% (5)
- TransformersDocument3 pagesTransformersMaham NaseerNo ratings yet
- TRANSFORMERDocument2 pagesTRANSFORMERmohammadham242No ratings yet
- EM Transformer Report (Final)Document12 pagesEM Transformer Report (Final)ismail.beee21pnecNo ratings yet
- Introduction TransformerDocument24 pagesIntroduction TransformerNimesha KavindiNo ratings yet
- Working Principle of Transformer: Definition of Transformer. Since There Is No Rotating or Moving Part SoDocument33 pagesWorking Principle of Transformer: Definition of Transformer. Since There Is No Rotating or Moving Part SoBrahmpal BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Group Project - TransformersDocument5 pagesGroup Project - TransformerscadaxeshpatelNo ratings yet
- AsutoshDocument15 pagesAsutoshpiyushanandaghadaiNo ratings yet
- Ology: Pusa Institute of TechnDocument33 pagesOlogy: Pusa Institute of TechnDeepesh KNo ratings yet
- Adelect/Eleng12/ Electric Circuits 2Document12 pagesAdelect/Eleng12/ Electric Circuits 2Rom AndutanNo ratings yet
- Noman Tariq 2019ch02Document9 pagesNoman Tariq 2019ch02Noman TariqNo ratings yet
- Kel It ReportDocument23 pagesKel It ReportshaluNo ratings yet
- Electrical Transformer Is A Static Electrical Machine Which Transforms Electrical Power From One Circuit To Another CircuitDocument35 pagesElectrical Transformer Is A Static Electrical Machine Which Transforms Electrical Power From One Circuit To Another CircuitNh Chuminda YapaNo ratings yet
- Transformers: What Is An Electric Transformer?Document14 pagesTransformers: What Is An Electric Transformer?Mohamed IbrahemNo ratings yet
- Oriental College: TechnologyDocument17 pagesOriental College: TechnologyRashid M AnsariNo ratings yet
- Transformers: What Is An Electric Transformer?Document14 pagesTransformers: What Is An Electric Transformer?Mohamed IbrahemNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Transformers and Its ApplicationsDocument27 pagesPresentation On Transformers and Its ApplicationsPRANAVNo ratings yet
- Types of TransformersDocument11 pagesTypes of TransformersAbdulGhaffarNo ratings yet
- Classification and Design AspectsDocument45 pagesClassification and Design AspectsNandiniNo ratings yet
- TRANSFORMERS LectureDocument6 pagesTRANSFORMERS LecturebabesgremarNo ratings yet
- Xmer (Small)Document11 pagesXmer (Small)VivekNo ratings yet
- TransformersDocument18 pagesTransformerssuicidesquadee21No ratings yet
- Classification of The TransformerDocument7 pagesClassification of The TransformerSintiya TarannumNo ratings yet
- TRANSFORMERDocument7 pagesTRANSFORMERChristian ArceoNo ratings yet
- Module 2 TransformersDocument70 pagesModule 2 TransformersaliyumaidamisaNo ratings yet
- EET EM I Assignment 2 SolveDocument5 pagesEET EM I Assignment 2 SolveNobita NobiNo ratings yet
- EET EM I Assignment 2Document5 pagesEET EM I Assignment 2Nobita NobiNo ratings yet
- Transformer: Pritish Sharma EL-395-2K17Document22 pagesTransformer: Pritish Sharma EL-395-2K17Pritish SharmaNo ratings yet
- Physics Transformer Project Calss XLLDocument14 pagesPhysics Transformer Project Calss XLLPraveena S BNo ratings yet
- Power AssignmentDocument8 pagesPower AssignmentHaseeb AdilNo ratings yet
- Question 01Document9 pagesQuestion 01Ahmed zia tahirNo ratings yet
- The State of The Art in Engineering Methods For TRDocument10 pagesThe State of The Art in Engineering Methods For TRVictor Julián Fernández CarrazanaNo ratings yet
- Single Phase TransformersDocument50 pagesSingle Phase TransformersDevi Sri PrasadNo ratings yet
- Working Principle of Transformer: The Working Procedure On HowDocument6 pagesWorking Principle of Transformer: The Working Procedure On HowkNo ratings yet
- EE - TransformerDocument5 pagesEE - TransformerNiño PerezNo ratings yet
- Types of TransformersDocument7 pagesTypes of TransformersTyron FrancisNo ratings yet
- TransformerDocument27 pagesTransformerAmeen Khan NiaziNo ratings yet
- Types of TransformersDocument16 pagesTypes of TransformersTahamee SHAIKHNo ratings yet
- 01 - Introduction of TransformerDocument43 pages01 - Introduction of TransformerDanielle Aubrey TerencioNo ratings yet
- Transformer 1Document29 pagesTransformer 1utharun3No ratings yet
- U21 Assigment 1Document57 pagesU21 Assigment 1Mostafa ElngarNo ratings yet
- TRANSFORMERDocument5 pagesTRANSFORMERmohammadham242No ratings yet
- Synergy TransformerDocument2 pagesSynergy TransformerKrupal MehtaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Substation (GRID) : Generating Station SwitchyardsDocument21 pagesElectrical Substation (GRID) : Generating Station SwitchyardsTariqNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2013-14 CP1182 24-Oct-2013 RM01 Lecture-1Document13 pagesFALLSEM2013-14 CP1182 24-Oct-2013 RM01 Lecture-1VineethMenonNo ratings yet
- At 2Document13 pagesAt 2Altaher Bushra AdamNo ratings yet
- Transformers: What Is An Electric Transformer?Document8 pagesTransformers: What Is An Electric Transformer?Mohamed IbrahemNo ratings yet
- 1.list Out Trouble Shooting Techniques For Transformer TransformerDocument30 pages1.list Out Trouble Shooting Techniques For Transformer Transformerrohith mukkamalaNo ratings yet
- Transformer Anubhav Pandey 12 ProjectDocument16 pagesTransformer Anubhav Pandey 12 Projectxmr7777777donttakeshitNo ratings yet
- (Pick The Date) : YPE THE Company NameDocument18 pages(Pick The Date) : YPE THE Company NameAbhishek ThomasNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document186 pagesUnit 3Sahil SinghNo ratings yet
- Classes of InsulationDocument8 pagesClasses of InsulationarjunNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 TransformerDocument76 pagesChapter 2 TransformerShikoyeniNo ratings yet
- Modul 9 Mesin Listrik 1 PDFDocument22 pagesModul 9 Mesin Listrik 1 PDFaswardiNo ratings yet
- TransformerDocument15 pagesTransformerMohd ArizNo ratings yet
- Transformer 2Document3 pagesTransformer 2mohammadham242No ratings yet
- ReportDocument21 pagesReporthrishikesh anvekarNo ratings yet
- Phy PDFDocument15 pagesPhy PDFzoro118921No ratings yet
- What Is A Transformer?: - Voltage Levels - The Medium Used in The Core - Arrangements of Windings - Installation PlaceDocument2 pagesWhat Is A Transformer?: - Voltage Levels - The Medium Used in The Core - Arrangements of Windings - Installation PlaceKudamala Hari Prasad ReddyNo ratings yet
- Generation and Transmission of Electric Power: Lecture Notes of the Generation and Transmission of Electric Power CourseFrom EverandGeneration and Transmission of Electric Power: Lecture Notes of the Generation and Transmission of Electric Power CourseNo ratings yet
- Download: Free Download Ordinary Level Physics A F Abbott PDF - Rar ##BEST##Document2 pagesDownload: Free Download Ordinary Level Physics A F Abbott PDF - Rar ##BEST##Lameck JosephNo ratings yet
- The Szilard-Chalmers ReactionDocument4 pagesThe Szilard-Chalmers ReactionInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology100% (1)
- CBSE Class 10 Science HOTs Question BankDocument63 pagesCBSE Class 10 Science HOTs Question BankSobana Itharaji75% (4)
- Class LectureDocument68 pagesClass LectureMahelat RangoNo ratings yet
- Practice Test For General Chemistry 2 Auburn UniversityDocument15 pagesPractice Test For General Chemistry 2 Auburn UniversityibejtmNo ratings yet
- Student Exploration: Energy Conversions: Light, Heat, Wind, and HydrogenDocument5 pagesStudent Exploration: Energy Conversions: Light, Heat, Wind, and HydrogenKatie FriasNo ratings yet
- LimitedDocument7 pagesLimiteds.shahjalalshakilNo ratings yet
- Science: Whole Brain Learning SystemDocument16 pagesScience: Whole Brain Learning SystemKayrell AquinoNo ratings yet
- Corrosion: Standard Grade ChemistryDocument4 pagesCorrosion: Standard Grade ChemistryStashy LoteNo ratings yet
- Basic Chemistry For Biology Lab ActivityDocument9 pagesBasic Chemistry For Biology Lab ActivityHaris Khan100% (1)
- Phy331 L1Document20 pagesPhy331 L1Dharmesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Kusadasi ACEMPDocument5 pagesKusadasi ACEMPapacheNo ratings yet
- Disclosure To Promote The Right To InformationDocument31 pagesDisclosure To Promote The Right To Informationashishjawale7No ratings yet
- Chapter: Environmental Issues: BIOLOGY - AssignmentDocument10 pagesChapter: Environmental Issues: BIOLOGY - Assignmentyogesh ahireNo ratings yet
- WWW Quora Com What Is A Geostationary and Why Is It at 35 786 KMDocument2 pagesWWW Quora Com What Is A Geostationary and Why Is It at 35 786 KMJournal ArtNo ratings yet
- ProjectDocument16 pagesProjectpothugunta charanNo ratings yet
- That Shapes Look Familiar!Document32 pagesThat Shapes Look Familiar!Bernadeth DaracanNo ratings yet
- Calculating Weld Volume and Weight: Welding CostsDocument4 pagesCalculating Weld Volume and Weight: Welding CostsMehmet SoysalNo ratings yet
- Red Oxy BrochureDocument16 pagesRed Oxy BrochureSlick LegionNo ratings yet
- CHE61203 Pollution ControlDocument27 pagesCHE61203 Pollution ControlPorkkodi SugumaranNo ratings yet
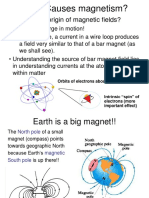
- What Causes Magnetism?: - What Is The Origin of Magnetic Fields?Document28 pagesWhat Causes Magnetism?: - What Is The Origin of Magnetic Fields?Suhaela NajlaNo ratings yet
- ASTM D4289-03 Standard Test Method For Elastomer Compatibility of Lubricating Greases and FluidsDocument8 pagesASTM D4289-03 Standard Test Method For Elastomer Compatibility of Lubricating Greases and FluidsCan ERTANNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Investigatory ProjectDocument18 pagesChemistry Investigatory ProjectSubhikshaNo ratings yet
- Potassium Permanganate TitrationsDocument70 pagesPotassium Permanganate TitrationsDarius SutherlandNo ratings yet
- Digital Unit Plan Template Unit Title: 2 Law of Thermodynamics Name: Ernesto Del Villar Content Area: Physics Grade Level: High School PhysicsDocument3 pagesDigital Unit Plan Template Unit Title: 2 Law of Thermodynamics Name: Ernesto Del Villar Content Area: Physics Grade Level: High School Physicsapi-277536571No ratings yet
- Co-Ordination Compound Ex-4 Solution For Vedantu TatvaDocument9 pagesCo-Ordination Compound Ex-4 Solution For Vedantu TatvaAbhinav ThapliyalNo ratings yet
- CV KuDocument3 pagesCV KuPatricia AlfrinNo ratings yet
- Updated Slides of Compressible FlowsDocument39 pagesUpdated Slides of Compressible FlowsFurqan YousafzaiNo ratings yet