Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Science 10 Reviewer For 1ST Summative Test
Science 10 Reviewer For 1ST Summative Test
Uploaded by
Debbie Ann Laguindab0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
88 views2 pagesThis document provides a review for a Science 10 exam on plate tectonics and the Earth's interior. It defines key terms like hotspots, magma, seismic waves, and plate boundaries. It also lists the differences between surface waves and body waves. The review covers the evidence that supports plate tectonics like the ages of ocean floor rocks. It provides an overview of plate motion at different boundaries and features caused by convergence and divergence. The exam will focus on Modules 1 and 2 from the Science textbook and include multiple choice, identification, true/false, table completion, and essay questions.
Original Description:
Original Title
SCIENCE 10 REVIEWER FOR 1ST SUMMATIVE TEST
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides a review for a Science 10 exam on plate tectonics and the Earth's interior. It defines key terms like hotspots, magma, seismic waves, and plate boundaries. It also lists the differences between surface waves and body waves. The review covers the evidence that supports plate tectonics like the ages of ocean floor rocks. It provides an overview of plate motion at different boundaries and features caused by convergence and divergence. The exam will focus on Modules 1 and 2 from the Science textbook and include multiple choice, identification, true/false, table completion, and essay questions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
88 views2 pagesScience 10 Reviewer For 1ST Summative Test
Science 10 Reviewer For 1ST Summative Test
Uploaded by
Debbie Ann LaguindabThis document provides a review for a Science 10 exam on plate tectonics and the Earth's interior. It defines key terms like hotspots, magma, seismic waves, and plate boundaries. It also lists the differences between surface waves and body waves. The review covers the evidence that supports plate tectonics like the ages of ocean floor rocks. It provides an overview of plate motion at different boundaries and features caused by convergence and divergence. The exam will focus on Modules 1 and 2 from the Science textbook and include multiple choice, identification, true/false, table completion, and essay questions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
SCIENCE 10 REVIEWER FOR 1ST SUMMATIVE TEST Hotspot- concentration of the heat in the
mantle capable of creating magma
Magma- mass of molten rock formed at depth,
Two scientists who proposed the theory of including dissolved gases and crystals
Seafloor spreading: Harry Hess and Robert Dietz Mt. Everest- highest mountain in the world
Two main types of Seismic waves: Body wave Plate tectonics give rise to several geologic
and surface wave features and events
Suduction - process that describes how oceanic S wave is the second type of Earthquake wave
crust plunges into the Earth and destroyed at to be recorded in a seismic station
the mantle P waves can travel through liquids while S
Athenosphere- soft, weak and plastic layer that waves cannot
facilitates the movement of the lithospheric Love waves cause the most damage to
plate structures during an earthquake
Crust and upper mantle makes up the Earth's Coal beds were formed from the compaction
lithosphere and decomposition of swamp plants that lived
Oxygen- most abundant element on earth's million years ago
crust Mid ocean ridge serves as the origin of
2.6 g/cm3- average density of the crust lithospheric movement
India and Eurasia - plates that collided and Inner core is the deepest layer of the Earth
formed the Himalayas The age of rocks and the magnetic stripes in the
When Two tectonic plates collide, the oceanic ocean floor support the seafloor spreading
crust usually subducts beneath the continental Trenches are depression in the ocean floor
crust because it is denser that the continental caused by Subduction process
crust
Convergence of two continental plates produces
Convection current in the mantle is the driving no trench, no volcano and no island arc.
force that facilitates the movement of
The outer core is made up of molten material
lithospheric plates
and accounts for the Earth’s magnetic field
Magnetic reversal is also called magnetic flip.
The mantle is the middle layer of the Earth
Findings that support the Seafloor spreading
Seafloor spreading is believed to occur as hot
theory:
magma rises at the rift in the mid-ocean ridge
(1) Rocks are younger at the mid-ocean ridge.
The old seafloor is destroyed at the subduction
(2) Rocks far from the mid-ocean ridge are
zone and melts inside the mantle
older.
The Theory of Plate Tectonics helps explain the
(3) Sediments are thinner at the ridge.
formation and destruction of the Earth’s crust
(4) Rocks at the ocean floor are younger that
and its movement over time
those at the continents
Divergent boundary is formed when plates
Laurasia and Gondwanaland- two
move apart, creating a zone of tension
supercontinents that were formed from the
Convergent boundary is present when two
breakage of Pangea
plates collide
Rayleigh wave- type of surface wave where
Transform fault is characterized by plates that
most of the shaking from an earthquake is felt.
are sliding past each other
Alfred Wegener- German meteorologist who
proposed the Continental Drifting Theory
Difference between surface waves and body
Fossils- preserved remains or traces of
waves:
organisms from the remote past
Earthquake- vibration of Earth due to rapid
Surface waves can only travel through the
release of energy
surface of the Earth while body waves can travel
Tsunami- Japanese term for "harbor wave" and through the Earth’s inner layer
is a series of ocean waves with very long
wavelengths caused by large scale disturbances
of the ocean
Crust- the thinnest and the outermost layer of
the Earth that extends from the surface to
about 32 kilometers below.
Pangea- supercontinent that consisted of all the
present continents
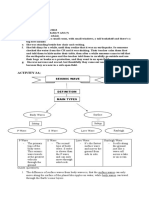
Type of Boundary Relative motion of the plates Geologic events/features
Convergent plates move towards each other volcano, volcanic island arc,
trench, tsunamis, earthquakes,
mountains
Divergent plates move away each other rift valleys, oceanic ridges,
earthquakes
Transform fault plates move alongside each other earthquakes
Coverage for Science 10 1st quarter exam:
Module 1: Plate Tectonics
pages 3-37 (Science Book)
Module 2: The Earth’s Interior
pages 39-79 (Science Book)
Type of Exam:
Multiple choice, Identification, True or False, Complete the Table and Essay
Study hard and Best of LUCK!
Ma’am Debbie
You might also like
- Help Your Kids With GeographyDocument259 pagesHelp Your Kids With GeographyopenfileNo ratings yet
- 1st Periodical Science 10 2019Document4 pages1st Periodical Science 10 2019Mark Kelvin DinongNo ratings yet
- (10th Grade Science) Brief Introduction of Gamma RaysDocument14 pages(10th Grade Science) Brief Introduction of Gamma RaysVinceRaymundRamaGonatoNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 10 Quarter 1 ReviewerDocument4 pagesSCIENCE 10 Quarter 1 ReviewerLeslie IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Handouts in Science 10Document2 pagesHandouts in Science 10CRISTIAN PORTUGALNo ratings yet
- Geology Summarize NotesDocument12 pagesGeology Summarize NotesShaila IvoryNo ratings yet
- Science 10 ReviewerDocument4 pagesScience 10 ReviewerAmber RamosNo ratings yet
- Earth Science ReviewerDocument6 pagesEarth Science ReviewerSALAMANCA, AZELEI B.No ratings yet
- Reviewer 1ST GradingDocument23 pagesReviewer 1ST Gradingpretty raul100% (2)
- Science Exam ReviewerDocument12 pagesScience Exam ReviewerRhyssa BacaniNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Summary of q1Document2 pagesScience 10 Summary of q1Aldrin Lumantas100% (1)
- Science q1 ReviewerDocument9 pagesScience q1 ReviewerG13 Intal, AnikaNo ratings yet
- Science G10 Reviewer Q1Document7 pagesScience G10 Reviewer Q1Hanna Samantha LisingNo ratings yet
- 1st Term Science Exam ReviewerDocument6 pages1st Term Science Exam ReviewerAndie MorenoNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer 1st QuarterDocument6 pagesScience Reviewer 1st Quartershane cadizNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument3 pagesScienceAna Beatrice Dubal100% (1)
- Science ReviewerDocument1 pageScience ReviewerJames Darren TadeoNo ratings yet
- Reviewer MapehDocument11 pagesReviewer MapehVan BatirNo ratings yet
- Science 10 First Quarter ReviewerDocument6 pagesScience 10 First Quarter ReviewerPlayer 456No ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Science 10: 1 Quarter ReviewerDocument6 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Science 10: 1 Quarter ReviewerKathrina ValienteNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Science: LithosphereDocument3 pagesReviewer in Science: LithosphereNatasha Loujille Collado100% (1)
- 2nd Quarter Reviewer in ScienceDocument3 pages2nd Quarter Reviewer in Sciencecali annaNo ratings yet
- Banban National High School Science 10Document4 pagesBanban National High School Science 10robert valdezNo ratings yet
- Science 10 2nd GRADING ExamDocument3 pagesScience 10 2nd GRADING ExamBeaulah Yliel BaliongNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic WavesDocument2 pagesElectromagnetic WavesAchilles Toring100% (1)
- Science NotesDocument55 pagesScience NotesSheila Marie U. RamirezNo ratings yet
- Seismic WaveDocument23 pagesSeismic WaveJoshua Melegrito Peralta100% (1)
- Music of The 20TH Century 1ST Quarter LessonDocument44 pagesMusic of The 20TH Century 1ST Quarter LessonMaurice OlivaresNo ratings yet
- Candon City, Ilocos Sur Grade 9 Reviewer School Year 2021 - 2022Document7 pagesCandon City, Ilocos Sur Grade 9 Reviewer School Year 2021 - 2022Aleah TungbabanNo ratings yet
- 1st Grading Earth and Life Science 2016-2017Document5 pages1st Grading Earth and Life Science 2016-2017Mariel VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Reviewer ScienceDocument7 pagesGrade 10 Reviewer ScienceAntonette TabilNo ratings yet
- G10 Physics CompendiumDocument41 pagesG10 Physics CompendiumJhin CortezNo ratings yet
- Science Try This!: Subtyp Es Subtyp EsDocument3 pagesScience Try This!: Subtyp Es Subtyp Esrr100% (1)
- Sci10 q2 Second Summative TestDocument2 pagesSci10 q2 Second Summative TestAilyn Carlos-Dizon100% (1)
- Earths Interior (2nd Summative Test)Document11 pagesEarths Interior (2nd Summative Test)ndramonedaNo ratings yet
- Mapeh G10 Reviewer Q1Document17 pagesMapeh G10 Reviewer Q1Hanna Samantha LisingNo ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter Reviewer in EnglishDocument7 pages2nd Quarter Reviewer in Englishcali annaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Science: Structure IsomersDocument2 pagesReviewer in Science: Structure IsomersSharlaine TandinganNo ratings yet
- Name: - Section: - ScoreDocument2 pagesName: - Section: - ScoreJoenald Kent Ordoña100% (1)
- Grade 10 Science SUMMATIVE TEST 3Document2 pagesGrade 10 Science SUMMATIVE TEST 3Vannie MonderoNo ratings yet
- 1Q Exam in Mapeh 10Document4 pages1Q Exam in Mapeh 10Dianne Mae DagaNo ratings yet
- The Earth's Interior: By: Junard A. AsentistaDocument75 pagesThe Earth's Interior: By: Junard A. AsentistaJunard AsentistaNo ratings yet
- BELA Reviewer ScienceDocument9 pagesBELA Reviewer ScienceIrene GantalaoNo ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter Final 10 MercuryDocument2 pages2nd Quarter Final 10 MercuryJoram Ray Obiedo100% (1)
- Q1-Week 1 - Find The CenterDocument21 pagesQ1-Week 1 - Find The CenterFrenzy Mei JobleNo ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter in Science Summary Grade 10Document2 pages2nd Quarter in Science Summary Grade 10zaraNo ratings yet
- Science 10 - Week 16Document6 pagesScience 10 - Week 16Mira VeranoNo ratings yet
- Science Second Quarter ReviewerDocument10 pagesScience Second Quarter ReviewercorinneNo ratings yet
- SUMMATIVE TEST IN SCIENCE 10 Week 3 & 4Document2 pagesSUMMATIVE TEST IN SCIENCE 10 Week 3 & 4Esther Mae Ann TrugilloNo ratings yet
- First Periodical Examination ReviewerDocument40 pagesFirst Periodical Examination ReviewerDeodat Boi LawsonNo ratings yet
- 1ST Quarter Exam Science 10Document8 pages1ST Quarter Exam Science 10Bryan de VeraNo ratings yet
- G10 Science Quarter I Summative TestDocument4 pagesG10 Science Quarter I Summative TestAriel Olar CuevasNo ratings yet
- 1st Grading Exam Science Grade 10Document2 pages1st Grading Exam Science Grade 10Ann Necdote100% (2)
- Science 10 - First Quarter (Summative Test) With Answer KeyDocument6 pagesScience 10 - First Quarter (Summative Test) With Answer KeyRussell AyadNo ratings yet
- Science 9 ReviewerDocument2 pagesScience 9 ReviewerSamuel Arthur G. DomingoNo ratings yet
- G10 Music - M2 - W2Document5 pagesG10 Music - M2 - W2Pat P. MonteNo ratings yet
- Second Periodic Test Grade10Document5 pagesSecond Periodic Test Grade10Marl Rina EsperanzaNo ratings yet
- Earth Science 8 ReviewerDocument11 pagesEarth Science 8 ReviewerBraynell Owen ClaroNo ratings yet
- Central Nervous System (CNS B. Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument10 pagesCentral Nervous System (CNS B. Autonomic Nervous SystemCid TristeNo ratings yet
- Long Test Science 10 2nd QuarterDocument29 pagesLong Test Science 10 2nd QuarterAple RigorNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument2 pagesScienceIciss Yumi AdvinculaNo ratings yet
- 4TH Q Exam V1Document2 pages4TH Q Exam V1Debbie Ann LaguindabNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology QuizDocument2 pagesBiotechnology QuizDebbie Ann LaguindabNo ratings yet
- 2ND Q Reviewer 23-24Document4 pages2ND Q Reviewer 23-24Debbie Ann LaguindabNo ratings yet
- Pre Test SimDocument2 pagesPre Test SimDebbie Ann LaguindabNo ratings yet
- LONG QUIZ 1st QDocument3 pagesLONG QUIZ 1st QDebbie Ann LaguindabNo ratings yet
- HOT SPOT ActivityDocument1 pageHOT SPOT ActivityDebbie Ann LaguindabNo ratings yet
- GASESDocument21 pagesGASESDebbie Ann LaguindabNo ratings yet
- Reproductive and Endocrine SystemsDocument38 pagesReproductive and Endocrine SystemsDebbie Ann LaguindabNo ratings yet
- Act 1 Quarter 2Document3 pagesAct 1 Quarter 2Debbie Ann LaguindabNo ratings yet
- 2ND Summative 23-24Document2 pages2ND Summative 23-24Debbie Ann LaguindabNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity & EvolutionDocument29 pagesBiodiversity & EvolutionDebbie Ann LaguindabNo ratings yet
- Em WavesDocument23 pagesEm WavesDebbie Ann LaguindabNo ratings yet
- Try EverythingDocument1 pageTry EverythingDebbie Ann LaguindabNo ratings yet
- Grading Rubric For DNA ModelDocument2 pagesGrading Rubric For DNA ModelDebbie Ann LaguindabNo ratings yet
- The 12 Rights of Filipino ChildrenDocument1 pageThe 12 Rights of Filipino ChildrenDebbie Ann Laguindab100% (1)
- Long Quiz - Dna RnaDocument2 pagesLong Quiz - Dna RnaDebbie Ann LaguindabNo ratings yet
- Triassic Period: Mesozoic EraDocument29 pagesTriassic Period: Mesozoic EraDebbie Ann LaguindabNo ratings yet
- Midgea Post Mock 2021 P1QDocument7 pagesMidgea Post Mock 2021 P1QSimon PeterNo ratings yet
- What Is GeographyDocument7 pagesWhat Is GeographyAshleigh Wray100% (1)
- 8 - Rock Mass Characterization (Pg. 7)Document7 pages8 - Rock Mass Characterization (Pg. 7)sudhakarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet - EcologyDocument4 pagesWorksheet - EcologyLilia BalaneNo ratings yet
- GT 2Document19 pagesGT 2RRRNo ratings yet
- Discovering Physical Geography 3rd Edition Arbogast Test BankDocument19 pagesDiscovering Physical Geography 3rd Edition Arbogast Test Banklisacarrysnomkeacx100% (14)
- Exogenic and Endogenic Process 1Document34 pagesExogenic and Endogenic Process 1hacker johnNo ratings yet
- Analisis Kualitas Sub DAS Citarum Hulu: Astri Mutia Ekasari, Hani Burhanudin, Irland FardaniDocument1 pageAnalisis Kualitas Sub DAS Citarum Hulu: Astri Mutia Ekasari, Hani Burhanudin, Irland FardaniabahaangNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Preliminary and Chapter 1 - PPTDocument28 pagesLecture 1 - Preliminary and Chapter 1 - PPTcrainvictor 45No ratings yet
- AP® Biology Instructor Solution Manual Part 2Document137 pagesAP® Biology Instructor Solution Manual Part 2hajin.wangvsNo ratings yet
- 2679 6192 1 PBDocument12 pages2679 6192 1 PBDirga JashinNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Basic Concepts and Principles in Ecology and Environmental ScienceDocument33 pagesWeek 2 Basic Concepts and Principles in Ecology and Environmental SciencejamaellajaneNo ratings yet
- Starburst Lab Rock CycleDocument3 pagesStarburst Lab Rock CycleMariam GuirguisNo ratings yet
- StratigraphyDocument21 pagesStratigraphyiskandar tuasamuNo ratings yet
- Problematic Soils PDFDocument84 pagesProblematic Soils PDFRY4NNo ratings yet
- Week 01 - Introduction & Importance of Geology in Civil EngineeringDocument26 pagesWeek 01 - Introduction & Importance of Geology in Civil EngineeringTariqMahmoodNo ratings yet
- Geology Index (KUET)Document2 pagesGeology Index (KUET)NJ Naeem Nowroz JahanNo ratings yet
- Natural Environment - WikipediaDocument1 pageNatural Environment - Wikipediamerissacustarddy346No ratings yet
- Geography Grade 9 t3Document9 pagesGeography Grade 9 t3Tarisha ChaytooNo ratings yet
- Soil Errosion'Document24 pagesSoil Errosion'prathaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 57Document50 pagesLesson 57CLARISSA TAGUBANo ratings yet
- Template JGeosREV IndonesiaDocument7 pagesTemplate JGeosREV IndonesiainfitharNo ratings yet
- Rock Cycle 2 ModifiedDocument19 pagesRock Cycle 2 ModifiedKernisha AdamsNo ratings yet
- ES10 Module 4Document36 pagesES10 Module 4Paulo M. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Layers of Earth Video QuestionsDocument3 pagesLayers of Earth Video QuestionsKaijalyn ForbesNo ratings yet
- S1 2015 301271 BibliographyDocument3 pagesS1 2015 301271 Bibliography2019410007No ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Layer of The Earth Noel EstebanDocument6 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Layer of The Earth Noel EstebanKier Dela CalzadaNo ratings yet
- Tectonic 6.5Document25 pagesTectonic 6.5book wormNo ratings yet
- Soil Science and Management 6th Edition Edward Plaster Test BankDocument7 pagesSoil Science and Management 6th Edition Edward Plaster Test BankDarla Lambe100% (41)