Professional Documents
Culture Documents
LABMAN Midterm Organzing
LABMAN Midterm Organzing
Uploaded by
Rachelle May DyOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
LABMAN Midterm Organzing
LABMAN Midterm Organzing
Uploaded by
Rachelle May DyCopyright:
Available Formats
SYSTEMS
ORGANIZING
& STAFFING THE LABORATORY Primary task
defined duties that are necessary because of the
nature of system’s products or services.
ORGANIZING
● It is the process of identifying and grouping
of the work to be performed, defining and
delegating responsibility and authority and Hierarchy of system
establishing relationship for the purpose of
enabling the people to work most the process of whereby self-contained
effectively together in accomplishing subsystems developed within a parent
objectives. It is the backbone of organization such as laboratory within a hospital.
management.
OVERVIEW OF ORGANIZATIONAL SYSTEM Open system
these are systems that interact with their
ORGANIZATION SYSTEM environment by both receiving and delivering
product services.
Means the collection Self-contained
of people working collection of
together under a interacting and
defined structure for interdependent Equilibrium
the purpose of components working
achieving pre- together toward a this is a state of stability within and between the
determined outcome common purpose. system and its environment..
Example is there are
head of the laboratory
and other staff having Self- Regulation
their own duties and
responsibilities is the feedback process by which the system
monitors performance and provides information
to its members
.
CHARACTERISTICS OF ORGANIZATIONAL ORGANIZATIONAL SYSTEM’S 3 DISTINCT
DUMAPAY, RACHELLE MAY
H.
1
● The workforce or staff who perform their
FUNCTIONS duties and responsibilities.
INPUT TRANSFORM OUTPUT WORK
MECHANISM ATION It is the MECHANISM ● Division of tasks so that everyone is
It is the internal It is the indispensable.
process process process of
through which whereby delivering the
needed resources goods and ORGANIZATIONAL DESIGN
resources are received services
1. Functional component
acquired and through the produced to
● It is the hierarchal organizational levels.
replaced. input channels the external
There is a clear understanding of
are converted environment.
responsibilities and authority. It functions
into the
best when the departments are engaged in
products and
repetitive, efficient and routine tasks.
services
produced by ● Traditional organizational chart:
the a. Tall structure- many management layers
organization b. Flat structure- few management layers
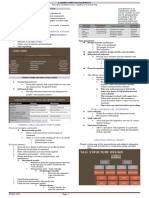
LABORATORY ORGANIZATION STRUCTURE
HOSPITAL ADMINISTRATOR
LABORATORY ORGANIZATION
PATHOLOGIST
INPUT TRANSFORM OUTPUT
CHIEF MEDTECH
Specimen ATION Test Results
Test request PROCESS INDIVIDUAL DISCIPLINES
Supplies Staff 2. Self-contained component
Instrument ● is arranged along a common platform.
Process There is subdivision of work areas
according to specialization.
● Specialty testing- is focused on examining
4 IMPORTANT ASPECTS OF CONGRUENCY special specimens.
● Clinical services- are concerned with
MODEL routine or special laboratory examinations.
FORMAL ORGANIZATION Anatomical services- cover biopsy,
● The officially sanctioned lines of authority histopathology, autopsy etc.
assigned by the owners of organization, ● Transfusion services- is an extension of
with the responsibility to carry out the the blood banking station.
organization’s designed duties. INFORMAL ORGANIZATION -> CLINICAL
INFORMAL ORGANIZATION SERVICES-> TRANSFUSION SERVICES ->
● Alliances that form outside the boundaries
of the formal organization from the ANATOMIC SERVICES
interaction and allegiance of people with AUTHOR’S INITIALS
common interest. LABORATORY AS A SELF-CONTAINED
PEOPLE ORGANIZATION
DUMAPAY, RACHELLE MAY
H.
2
3. Matric component LEVEL OF AUTHORITY
● Each staff member can have an ● Authority is the legal right to command
independent functions irrespective of actions by others and to enforce
whether they are assigned to any of the compliance. It empowers one to do a job
sections in the laboratory or performing that is essential for the leader to
routine or special tests. accomplish the task. It goes with a
4. Matric component responsibility. Every staff is accountable in
the task assigned to him/her
● it reflects an information technology
model. It also consists of units or
realignment of work to reduce duplication LEVEL OF AUTHORITY
and expand revenue generating services. ● These are the types of communication and
Example is some laboratories have satellite the barriers of communication.
laboratory which part of networking
services. LEVEL OF AUTHORITY
● It is the designated function of a
department head to divide and delegate
FACTORS THAT INFLUENCE THE DESIGN AND tasks or workload to avoid confusion and
STRUCTURE OF THE ORGANIZATION complications.
1. Organizational goals and strategic
PRINCIPLES OF ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE
direction
- it is imperative to set goals and objectives in order
AND AUTHORITY
to give direction for the organization’s journey Departmentalization- related activities are
towards the achievement of its mission and vision. grouped together to expedite the production
2. Technological capabilities- process, that is specialization.
- it refers to the kind of services they can offer.
Decentralization- the decision-making process is
3. Size brought as close to those who are actually
- it is the basis for determining the classification of performing the work as possible.
the laboratory.
4. Environment Unity of command- each individual must have
- it refers to the specific location of the laboratory. only one boss.
The profitability of the laboratory is dependent on
its location.
Scalar principle- supervision should be a linear
5.Leadership style, member behavior and system providing a direct
organizational structure vertical link form the board of directors to the
- the success of the laboratory is the responsibility lowest level worker.
of the management.
ELEMENTS OF LABORATORY ORGANIZATION Span control- there is a definable limit to the
number of people one person can effectively
supervise, within the limits of specific work
Level of Level of Division of condition
AUTHORITY COMMUNICAT WORK AUTHOR’S INITIALS
ION Exception principle- the manager and stall are
able to do their jobs without having to check with
DUMAPAY, RACHELLE MAY
H.
3
the supervisor about every detail. appraisals
● these are written declarations of given job
positions.
STAFFING AND SCHEDULING THE LABORATORY
● Job Description
● The laboratory require considerably
● this supplements the organization by
different education and training personnel.
providing definition to all position . It
Each is unique discipline embodying large
defines the employees interactions with
volume of technical data and employing
people and how the position is integrated
different analytical techniques and
into entire organization
instrumentation. With regard to laboratory
staffing, the sheer growth and diversity of
laboratory services clearly demonstrate
SECTIONS OF A JOB DESCRIPTION SHOULD
the need for specialization of personnel. INCLUDE THE FOLLOWING
Efficient and effective selection, grouping ● a) Title of the organization- includes the
and utilization of personnel constitute a name of the facility, location, department
major responsibility. and sections.
● b) Job title
JOB DESIGN ● c) Job specifications- position summary.
● d) Summary of duties for the position
1. JOB ● e) Reporting of duties for the position
● Is a collection of tasks, duties and ● f) Preparer
responsibilities assig to an individual. ● g) Date of preparation
2. JOB DESIGN ● h) Approval signatures
● is the process of organizing work into jobs
3. JOB ANALYSIS- 3. Scheduling
● is the process of collecting and analyzing ● builds on staffing information and focuses
information about tasks, work flow and on matching people on a day to day basis
jobs being done in an organization so that with the fluctuating workload of the
job descriptions, work standards and laboratory
performance appraisal systems can be
developed RULES IN SCHEDULING
1. No more than 5 consecutive working days for
APPLICATION OF JOB DESIGN INFORMATION each individual.
1. STAFFING 2. Provide 2 consecutive day offs except in the rare
● the process of matching the number and case where the individual prefers split of day offs.
types of people with jobs that meet the 3. Within the possibilities. Give the individual the shift
goals and structure of the organization. It he wants.
is done by: 4. Rotate weekend and holiday off with as much
a. Identification of workforce requirement. fairness as possible.
b. Inventory of people available 5. Post schedule at least 3 weeks in advance, even
c. Recruitment selection ore if possible.
d. Promotion of staff 6. Stick to the schedule as closely as possible, and
e. Appraisal make changes only when essential and only after
f. Planning career of employees discussion with others concerned.
7. Provide the opportunity to ask for AUTHOR’S INITIALS
specific day off
g. Training and development
occasion
2. Job description and performance
DUMAPAY, RACHELLE MAY
H.
4
OTHER ISSUES IN ORGANIZATION
1. Re-Organization
● is the process which an existing
organization undergoes that brings about
changes in size and shape of the
organization structure. The reason for
organization are growth and adaptation.
2. Re-Engineering
● iis the re-organizing work processes in an
organization. Flow diagram the specific
work processes to determine if more
effective process could be implemented.
Example: use of robotics to automate
computerization, pneumatic tube system
to transport specimens.
3. Benchmarking
● is the process whereby the best process in
one organization is modified to fit similar
processes in another organization.
Examples: cost per test, number of test
performed per full time employee.
AUTHOR’S INITIALS
DUMAPAY, RACHELLE MAY
H.
5
You might also like
- Iso - Iec 27013Document64 pagesIso - Iec 27013Fabiop_b100% (1)
- Managing Performance:: Executive SummaryDocument5 pagesManaging Performance:: Executive SummaryMajala MwakotaNo ratings yet
- Silicon Valley North_ A High-Tech Cluster of Innovation and Entrepreneurship (Technology, Innovation, Entrepreneurship and Competitive Strategy) (Technology, ... Entrepreneurship and Competitive Strategy) ( PDFDrive.com ).pdfDocument360 pagesSilicon Valley North_ A High-Tech Cluster of Innovation and Entrepreneurship (Technology, Innovation, Entrepreneurship and Competitive Strategy) (Technology, ... Entrepreneurship and Competitive Strategy) ( PDFDrive.com ).pdfuttam pundirNo ratings yet
- NEC 4 Alliance ContractDocument2 pagesNEC 4 Alliance ContractDavid WoodhouseNo ratings yet
- Mis of DellDocument17 pagesMis of DellMohammad Al Amin71% (7)
- MAPR Notes PDFDocument8 pagesMAPR Notes PDFgigihdNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Organizing and StaffingDocument3 pagesLesson 2 Organizing and Staffing12 Newton - Cayetano, Arafe Nicole A.No ratings yet
- Lab MNGT 3Document6 pagesLab MNGT 3Cejay Erl MagnoNo ratings yet
- ORGANIZINGDocument40 pagesORGANIZINGAd AstraNo ratings yet
- OrgDocument13 pagesOrgAllen KateNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 6Document32 pagesCHAPTER 6Eni Syafina RoslanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11Document19 pagesChapter 11Madhav AroraNo ratings yet
- ORGANIZING Part For AssignmentDocument21 pagesORGANIZING Part For AssignmentChathushka RanatungaNo ratings yet
- SPM CH 3Document20 pagesSPM CH 3Alvika KurniaNo ratings yet
- LAB-MGT Quiz ReviewDocument3 pagesLAB-MGT Quiz ReviewArielle MarvicNo ratings yet
- All LesonsDocument58 pagesAll LesonsCelestine MarivelezNo ratings yet
- Five Main Steps of The Organizing ProcessDocument3 pagesFive Main Steps of The Organizing ProcessAlly GuiaoNo ratings yet
- Laboratory OrganizationDocument6 pagesLaboratory OrganizationaraacadseraNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Q) Would You Rather Work in A Mechanistic Organization or An Organic Organization? WhyDocument3 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Q) Would You Rather Work in A Mechanistic Organization or An Organic Organization? Whyjay kumarNo ratings yet
- ORGMANDocument10 pagesORGMANMAYON NAGANo ratings yet
- DCC40132 Topic 2 Organisational Structures Project Life Cycle in Project ManagementDocument43 pagesDCC40132 Topic 2 Organisational Structures Project Life Cycle in Project ManagementDharveen Raj SaravananNo ratings yet
- Emgt Finals ReviewerDocument23 pagesEmgt Finals ReviewerNoelle Reese AlfaroNo ratings yet
- Principles of Organization, Staffing and Scheduling - Laboratory ManagementDocument3 pagesPrinciples of Organization, Staffing and Scheduling - Laboratory Managementcjyulo99710No ratings yet
- Bsr307 Building Maintenance Ii: Organisation StructureDocument19 pagesBsr307 Building Maintenance Ii: Organisation Structurenur sheNo ratings yet
- Process ManagementDocument111 pagesProcess ManagementScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- BT CH 5 StartDocument81 pagesBT CH 5 StartSwan HtNo ratings yet
- CH 4Document8 pagesCH 4483-ROHIT SURAPALLINo ratings yet
- 4 Unit - 4-Organizing and Staffing The LaboratoryDocument14 pages4 Unit - 4-Organizing and Staffing The LaboratoryRomar DurianNo ratings yet
- Engineering Process Education Presentation in Orange White Simple StyleDocument30 pagesEngineering Process Education Presentation in Orange White Simple Styleromulodumagit25No ratings yet
- The Definition of ManagementDocument5 pagesThe Definition of ManagementQuan NguyenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Organizing and StaffingDocument65 pagesChapter 3 - Organizing and StaffingManvendra Pratap Singh Bisht80% (5)
- PHAR1203 Module 3 Organizing ReviewerDocument4 pagesPHAR1203 Module 3 Organizing ReviewerRowella Villar TacadaoNo ratings yet
- 3 - OrganizingDocument7 pages3 - OrganizingJOHANNA RACHEL VILLASISNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3-Organizational StructuresDocument34 pagesChapter 3-Organizational StructuresOrly Eluna AdanzaNo ratings yet
- NRG 402 PrefinalDocument18 pagesNRG 402 Prefinaljustinalzate01No ratings yet
- ORGANIZINGDocument3 pagesORGANIZINGLenie DegraciaNo ratings yet
- Wipro 2Document5 pagesWipro 2KESHAV AGARWALNo ratings yet
- Ch.1) Operations and ProductivityDocument22 pagesCh.1) Operations and ProductivityBibek KhanalNo ratings yet
- Organisational Effectiveness Assessment SlidesDocument91 pagesOrganisational Effectiveness Assessment SlidesayuekamNo ratings yet
- 07 Organising AddendumDocument3 pages07 Organising AddendumAbubakarNo ratings yet
- Organizing Function PDF Leadership And, Management Cpa KasnebDocument5 pagesOrganizing Function PDF Leadership And, Management Cpa KasnebEmanuelLeipaNo ratings yet
- CEPB323 Slide - Topic 2 Organization Structure (Sem 2 20172018)Document16 pagesCEPB323 Slide - Topic 2 Organization Structure (Sem 2 20172018)razNo ratings yet
- Five Basic Parts of The Organization: Oj OrroDocument18 pagesFive Basic Parts of The Organization: Oj OrroYun Seo BinNo ratings yet
- Historical Background of ManagementDocument36 pagesHistorical Background of Managementeric labordoNo ratings yet
- Organizational Development and Change Assignment Summary - Chapter No. 5Document11 pagesOrganizational Development and Change Assignment Summary - Chapter No. 5FarwaSajjadNo ratings yet
- Organizing and Staffing-Week 3-Session 2Document21 pagesOrganizing and Staffing-Week 3-Session 2Kat JornadalNo ratings yet
- Audit Comparative TableDocument5 pagesAudit Comparative TableScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Laboratory ManagementDocument22 pagesLaboratory Managementchocoholic potchiNo ratings yet
- Designing Adaptive Organization and Managing Change and InnovationDocument27 pagesDesigning Adaptive Organization and Managing Change and InnovationRobert John PerezNo ratings yet
- Organisational Effectiveness 1ADocument178 pagesOrganisational Effectiveness 1ABandile ShobaNo ratings yet
- Lec03 - Lab Management - TransesDocument3 pagesLec03 - Lab Management - TransesHANNAH N. RULIDANo ratings yet
- Manu ReviewerDocument5 pagesManu ReviewerIrish VargasNo ratings yet
- 10 Basic Organizational DesignDocument10 pages10 Basic Organizational DesignraflynmNo ratings yet
- Organizing (Done Highlight)Document37 pagesOrganizing (Done Highlight)Lyka TorresNo ratings yet
- 3 Organisation-Level Diagnosis (2) RevisedDocument10 pages3 Organisation-Level Diagnosis (2) RevisedRosyta Nur AzizahNo ratings yet
- GG and CSR ReportDocument52 pagesGG and CSR ReportDianne Pearl DelfinNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Operations Management: You Should Be Able ToDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Operations Management: You Should Be Able TotentenjhayNo ratings yet
- Organizational Structure: Jeff Madura Ch.8Document12 pagesOrganizational Structure: Jeff Madura Ch.821.125 Daniar Casta CabaseNo ratings yet
- Online NotebookDocument32 pagesOnline NotebookRanveer GurjarNo ratings yet
- 11 The Quality WorkplaceDocument36 pages11 The Quality Workplace19100641No ratings yet
- OMLG4Lesson1 2Document23 pagesOMLG4Lesson1 2Khassie B. GrandeNo ratings yet
- Capter Two OrganizationDocument53 pagesCapter Two Organizationمختبرات ابوسارةNo ratings yet
- Module4 OrganizationStructureDocument26 pagesModule4 OrganizationStructureTieu ChauNo ratings yet
- Software Quality Assurance: Dr. R. MallDocument128 pagesSoftware Quality Assurance: Dr. R. Mallgitu583No ratings yet
- Zyme Channelview Pos DatasheetDocument2 pagesZyme Channelview Pos Datasheetanirban_surNo ratings yet
- Contract ManagementDocument12 pagesContract ManagementSebastian GarciaNo ratings yet
- ISO Certification in Textile SectorDocument16 pagesISO Certification in Textile Sectorahmed-tanveer100% (1)
- BIBF Courses Calendar 2022Document13 pagesBIBF Courses Calendar 2022TNo ratings yet
- Workshop 6 AnsDocument5 pagesWorkshop 6 AnsSAMUEL THOMASNo ratings yet
- Add1 - Reoi - PMC CSRRP WB 09122019Document3 pagesAdd1 - Reoi - PMC CSRRP WB 09122019TawakkalNo ratings yet
- E-Procurem - Andra PredeshDocument38 pagesE-Procurem - Andra PredeshRanjith EkanayakeNo ratings yet
- BUS 516 - Chapter 6 - Foundations of Business IntelligenceDocument63 pagesBUS 516 - Chapter 6 - Foundations of Business IntelligenceArju LubnaNo ratings yet
- Organisation Behaviour PDFDocument280 pagesOrganisation Behaviour PDFAdnan AdNo ratings yet
- Weele.5th Ed - Chapter 01.2010Document19 pagesWeele.5th Ed - Chapter 01.2010ravin100% (1)
- 1831 73 4303 1 10 20220907Document12 pages1831 73 4303 1 10 20220907Jordan KopongNo ratings yet
- Astral LTD Finance ProjectDocument55 pagesAstral LTD Finance Projectshubhamkumar.bhagat.23mbNo ratings yet
- Term 1 2019 Mid-Term and Final Exam TimetableDocument1 pageTerm 1 2019 Mid-Term and Final Exam TimetableSope DalleyNo ratings yet
- TOP 10 BPO Industries in The PhilippinesDocument11 pagesTOP 10 BPO Industries in The Philippinestoodeim100% (1)
- Effect of Youth Unemployment in NigeriaDocument4 pagesEffect of Youth Unemployment in NigeriaEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Logistics ExamDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Logistics ExamBhanu AUGMENTNo ratings yet
- Kalahi CIDSS Project ManualDocument190 pagesKalahi CIDSS Project ManualRegina Zagala100% (6)
- Model - Student Version: MODULE 13 CORAL BAY HOSPITAL: Traditional Project AnalysisDocument23 pagesModel - Student Version: MODULE 13 CORAL BAY HOSPITAL: Traditional Project AnalysisHassanNo ratings yet
- 6 Halal Policy PDFDocument1 page6 Halal Policy PDFSaid SaidiNo ratings yet
- Trading Business Plan ExampleDocument50 pagesTrading Business Plan ExampleJoseph QuillNo ratings yet
- Annexure C Department of LabourDocument3 pagesAnnexure C Department of LabourMariusNo ratings yet
- SAP Subcontracting Process PDFDocument10 pagesSAP Subcontracting Process PDFajayshamli80% (5)
- ABO - Week 5 Budgeting and Market ResponsesDocument30 pagesABO - Week 5 Budgeting and Market Responsesjinman bongNo ratings yet
- Is0200c SMDocument290 pagesIs0200c SMGlen MorenoNo ratings yet
- Topic 05 All Possible QuestionsDocument9 pagesTopic 05 All Possible QuestionsMaxamed Cabdi KariimNo ratings yet