Professional Documents
Culture Documents
3rdq Science 10 Exam
3rdq Science 10 Exam
Uploaded by
Paulo M. Dela Cruz0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views3 pages1. The document is a science exam for 10th grade students at San Andres Vocational School in Catanduanes, Philippines. It contains 40 multiple choice questions testing knowledge of the endocrine and reproductive systems.
2. The questions cover topics like pituitary hormones, hormone production and regulation, menstrual cycle phases, gamete formation and function, and human reproduction.
3. The exam instructs students to choose the letter of the correct answer for each question and record it on their answer sheet. It wishes students good luck if they did not review, suggesting reviewing is important for doing well.
Original Description:
Original Title
3rdq science 10 exam
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. The document is a science exam for 10th grade students at San Andres Vocational School in Catanduanes, Philippines. It contains 40 multiple choice questions testing knowledge of the endocrine and reproductive systems.
2. The questions cover topics like pituitary hormones, hormone production and regulation, menstrual cycle phases, gamete formation and function, and human reproduction.
3. The exam instructs students to choose the letter of the correct answer for each question and record it on their answer sheet. It wishes students good luck if they did not review, suggesting reviewing is important for doing well.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views3 pages3rdq Science 10 Exam
3rdq Science 10 Exam
Uploaded by
Paulo M. Dela Cruz1. The document is a science exam for 10th grade students at San Andres Vocational School in Catanduanes, Philippines. It contains 40 multiple choice questions testing knowledge of the endocrine and reproductive systems.
2. The questions cover topics like pituitary hormones, hormone production and regulation, menstrual cycle phases, gamete formation and function, and human reproduction.
3. The exam instructs students to choose the letter of the correct answer for each question and record it on their answer sheet. It wishes students good luck if they did not review, suggesting reviewing is important for doing well.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
SAN ANDRES VOCATIONAL SCHOOL
San Andres, Catanduanes
THIRD QUARTER EXAM IN SCIENCE 10
NAME: _____________________________________ DATE: ____________
GRADE AND SECTION: _____________________ SCORE: __________
“Kung nag-review ka, handa ang may alam!
Kung hindi, good luck na lang!”
Multiple Choice
Direction: Read each statement carefully and write the LETTER of the correct answer on
your answer sheets.
1. Which of the following statements regarding pituitary hormones is false?
A) The hypothalamus makes oxytocin and antidiuretic hormone, which are transported the
posterior pituitary for storage.
B) Antidiuretic hormone, released by the posterior pituitary, causes urine volume to increase
and blood volume to decrease.
C) Luteinizing hormone, an anterior pituitary hormone, triggers ovulation of an egg from the
ovary and causes the ruptured follicle to produce progesterone and some estrogens.
D) Hyposecretion of follicle-stimulating hormone or luteinizing hormone leads to sterility in
both males and females.
2. Androgens are produced by the _______.
A) Ovaries B) testes C) hypothalamus D) islets of Langerhans
3. One of the two hormones made by the pituitary that help regulate reproductive cells is luteinizing
hormone. The other hormone is _______.
A) Androgens C) Epinephrine
B) Follicle stimulating hormone D) Norepinephrine
4. Calcium level in the blood is regulated by the:
A) Parathyroid and thyroid C) Testes
B) Adrenal medulla and pancreas D) Parathyroid and thymus
5. Which one of the following is NOT typical of the changes that follow the binding of a hormone to
its target cells:
A) plasma membrane permeability changes
B) cellular mutations occur
C) enzymes are activated or inactivated
D) mitosis is stimulated
6. Being lipid soluble, steroids can do all the following EXCEPT:
A) catalyze cyclic AMP
B) diffuse through the plasma membranes of target cells
C) enter the nucleus
D) activate genes to transcribe mRNA for protein synthesis
7. Estrogens and progesterone are produced by:
A) the testes. C) the adrenal glands.
B) the ovaries. D) the hypothalamus.
8. Most endocrine organs are motivated into action by other hormones; this type of stimulus is
called:
A) hormonal stimulus C) neural stimulus
B) humoral stimulus D) receptor-mediated stimulus
9. The body’s major metabolic hormone is released from the:
A) Pituitary B) Thyroid C) Thymus D) Hypothalamus
10. How is hormone secretion regulated?
A) by the nervous system C) by changes in blood composition
B) by other hormones D) all of the above
11. Target cells for hypothalamic releasing hormones are in the
A) thyroid B) hypothalamus C) anterior pituitary D) posterior pituitary
12. Most of the endocrine system is regulated by:
A) negative feedback mechanisms. C) hormone-receptor complexes.
B) positive feedback mechanisms. D) hormone-gene complexes.
13. The posterior pituitary gland stores and secretes
A) oxytocin and antidiuretic hormone
B) human growth hormone and thyroid stimulating hormone
C) prolactin and follicle stimulating hormone
D) glucocorticoids and androgens
14. The alpha cells of the pancreas secrete _______ which targets the _______.
A) glucagon; liver C) glucagon; kidney
B) melatonin; liver D) calcitonin; thyroid
15. The growth hormone produced by the pituitary gland is known as _______.
A) somatotropin B) prolactin C) luteinizing hormone D) follicle-stimulating hormone
16. The rate of metabolism of all body cells is regulated by _______.
A) parathyroid hormone B) aldosterone C) calcitonin D) thyroid hormone
17. The relatively constant internal environment of the body is maintained by _______.
A) negative feedback B) positive feedback C) homeostasis D) metabolism
18. The secretions from which of these glands differs between males and females?
A) Adrenal B) Parathyroid C) Gonadal D) Pancreas.
19. The two regulatory systems of the body are the endocrine system and the _______.
A) nervous system B) immune system C) circulatory system D) respiratory system
20. Why can a single endocrine hormone produce a wider spread of responses in more of the body
than a single nerve cell?
A) A single hormone can target many different responses, whereas a nerve only targets a
single response.
B) Blood can carry all the same hormones throughout the body simultaneously, producing
responses all over the body; nerve cells can only target a small number of cells.
C) Nerve cells and blood work together. The endocrine has nothing to do with the nervous
system.
D) Endocrine hormones only target a very small number of precise responses.
21. The term central nervous system refers to the:
A) autonomic and peripheral nervous systems C) brain and cranial nerves
B) brain, spinal cord, and cranial nerves D) brain and spinal cord
22. The peripheral nervous system consists of:
A) spinal nerves only C) cranial nerves only
B) the brain only D) the spinal and cranial nerves
23. The Schwann cells form a myelin sheath around the:
A) dendrites B) cell body C) nucleus D) axon
24. The neuron processes that normally receives incoming stimuli are called:
A) axons B) dendrites C) neurolemmas D) Schwann cells
25. Lobe that contains the primary motor area that enables voluntary control of skeletal muscle
movements:
A) parietal lobe B) temporal lobe C) occipital lobe D) frontal lobe
26. Afferent nerves are called ______, and motor nerves are called ______.
A) motor nerves; sensory nerves C) mixed nerves; motor nerves
B) peripheral nerves; cranial nerves D) sensory nerves; efferent nerves
27. The area of the brain stem that plays a role in consciousness and the awake/sleep cycle is the:
A) thalamus B) pineal gland C) limbic system D) cerebellum
28. Control of temperature, endocrine activity, metabolism, and thirst are functions associated with
the:
A) thalamus B) cerebellum C) hypothalamus D) cerebrum
29. The vital centers for the control of visceral activities such as heart rate, breathing, blood
pressure, swallowing, and vomiting are located in the:
A) pons B) midbrain C) cerebrum D) hypothalamus
30. Preparing the body for “fight-or-flight” response during threatening situations is the role of the:
A) sympathetic nervous system C) parasympathetic nervous system
B) cerebrum D) somatic nervous system
31. Which of the following statements is true about menstruation?
A) In a normal 28-day menstrual cycle, you would expect menstruation to last for
approximately 3 – 5 days.
B) During menstruation, the entire endometrium is shed.
C) During menstruation, only the functional layer of the endometrium is shed, while the
basal layer remains intact.
D) Absence of menstruation always indicates an active pregnancy.
32. At which point in the menstrual cycle a woman is most fertile?
A) Days 1 – 5 B) Days 9 – 16 C) Days 17 – 21 D) Days 22 – 28
33. Which of the following symptoms indicates that a woman is about to ovulate?
A) Decrease in basal body temperature C) Thickening of cervical mucus
B) Increase in basal body temperature D) Thinning of cervical mucus
34. In which of the following organs sperm cells are found?
A) Pancreas B) ovaries C) testes D) liver
35. Which of the following organs produce egg cells?
A) testes B) ovaries C) liver D) pancreas
36. What is the size of an egg cell compared to a sperm cell?
A) much larger B) much lighter C) much smaller D) faster swimmers
37. What organ carries the sperm cells from the testes to the urethra?
A) Vas deferens B) seminal vesicle C) scrotum D) testes
38. In what part of the reproductive system fertilized egg is developed?
A) ovary B) vagina C) uterus D) oviduct
39. Which of the following processes is under Follicular phase?
A) As estrogen levels rise, like a switch, it turns off the production of follicle-stimulating
hormone.
B) The rise in estrogen from the dominant follicle triggers a surge in the amount of luteinizing
hormone (LH) that your brain produces.
C) This causes the dominant follicle to release its egg from the ovary.
D) As the egg is released (a process called ovulation) it’s captured by finger-like projections on
the end of the fallopian tubes (fimbriae). The fimbriae sweep the egg into the fallopian tube.
40. Reproduction among human beings is necessary because
A) to perpetuate life C) to spread human race
B) to increase population rate D) to evade the world
41. The actual site of protein synthesis is the
A. nucleus B. mitochondrion C. chloroplast D. ribosome.
42. If the DNA template reads “ATA”, then which of the following would be the corresponding
sequence on the mRNA?
A. UAU B. ATA C. TUT D. UCU
43. The genetic code is based upon the reading of how many bases at a time?
A. one B. two C. three D. four
44. Amino acids are held together by __?__ bonds.
A. hydrogen B. peptide C. ionic D. high energy
45. How many codons are needed to specify three amino acids?
A. 3 B. 6 C. 9 D. 12
46. One similarity between DNA and messenger RNA molecules is that they both contain
a. the same sugar
b. genetic codes based on sequences of bases
c. a nitrogenous base known as uracil
d. double-stranded polymers
47. Which of the following is not part of protein synthesis?
A. replication B. translation C. transcription D. transpiration
48. A type of mutation wherein there are switches on a section of base pairs.
A. deletion B. substitution C. duplication D. insertion
49. In the RNA molecule, which nitrogen base is found in place of thymine?
A. guanine B. cytosine C. thymine D. uracil
50. Which defines a codon?
a. a protein that being transcription by breaking apart H bonds
b. a free-floating base that attaches to an open DNA strand
c. the genetic code word of three bases on mRNA that specify one amino acid
d. the strong bond between two complementary nitrogen bases
Prepared by:
sgnd PAULO M. DELA CRUZ
Teacher III
Noted:
sgnd EFREN T. GURROBAT
Head Teacher III, Science
You might also like
- Dr. Azam Anatomy NLC Notes For Dec 2021 ExamDocument134 pagesDr. Azam Anatomy NLC Notes For Dec 2021 ExamCastleKG100% (4)
- Chapter 45 Hormones and The Endocrine SystemDocument8 pagesChapter 45 Hormones and The Endocrine System123456789123456789hi100% (2)
- Endocrine System Practice TestDocument10 pagesEndocrine System Practice TestFarrah Turner Matthews0% (1)
- Study Questions Endocrine System: Answers Are Provided Below Each QuestionDocument26 pagesStudy Questions Endocrine System: Answers Are Provided Below Each QuestionEfanPutra100% (1)
- Chapter 45 NotesDocument4 pagesChapter 45 Notessadaf_5No ratings yet
- March 2017 PhysiologyDocument7 pagesMarch 2017 Physiologyjoanbless79No ratings yet
- نموذج احياء2Document4 pagesنموذج احياء2xibsjddhsNo ratings yet
- MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose The One Alternative That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionDocument46 pagesMULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose The One Alternative That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionGeico88No ratings yet
- Bsc2086 Ass. 1 SummerDocument51 pagesBsc2086 Ass. 1 SummerGeico88No ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument51 pagesEndocrine SystemMahenor Emad100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology EXAMDocument4 pagesAnatomy and Physiology EXAMEric SturdivantNo ratings yet
- Chapter 45 Hormones and The Endocrine SystemDocument12 pagesChapter 45 Hormones and The Endocrine System蔡旻珊No ratings yet
- Nội TiếtDocument17 pagesNội TiếtĐinh SángNo ratings yet
- STUDY QUESTIONS Endocrine System 1 - DR P Kumar Biochem-GeneticsDocument24 pagesSTUDY QUESTIONS Endocrine System 1 - DR P Kumar Biochem-Geneticsteklay100% (1)
- Chemical Coordination and Integration 90 QuestionsDocument92 pagesChemical Coordination and Integration 90 QuestionsananthiumiNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Science Sum. TestfinalDocument6 pagesGrade 10 Science Sum. TestfinalHAIDEENo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Quiz 1Document6 pagesEndocrine System Quiz 1hamid50% (2)
- Test PaperDocument4 pagesTest PaperKimberley TadeoNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System MCQsDocument6 pagesEndocrine System MCQsRashini FernandoNo ratings yet
- Zodiac Academy Endocrine MCQDocument5 pagesZodiac Academy Endocrine MCQMourian AmanNo ratings yet
- 170Q of Endocrine SystemDocument28 pages170Q of Endocrine SystemAbdallah MohamedNo ratings yet
- 3rd Quarter Exam Science 10Document5 pages3rd Quarter Exam Science 10ROMELYN GRACE BORBENo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Long TestDocument2 pagesEndocrine System Long Testshasagail50% (2)
- Summative Test Module 1 g10 3rdqtrDocument4 pagesSummative Test Module 1 g10 3rdqtrMarian Anion-GauranoNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Quiz 1 PDFDocument6 pagesEndocrine System Quiz 1 PDFshasagailNo ratings yet
- Chapter 45 Review QuestionsDocument10 pagesChapter 45 Review Questionsbiologystudent123No ratings yet
- Te-Control and Coordination Final Revisor (2023-24)Document69 pagesTe-Control and Coordination Final Revisor (2023-24)Gautam SharrmaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument12 pagesEndocrine SystemDanica NaldoNo ratings yet
- Final Exam AnatomyDocument8 pagesFinal Exam Anatomybillrn21No ratings yet
- Problem Set 2 EndocrinologyDocument12 pagesProblem Set 2 EndocrinologyJessica EtieneNo ratings yet
- TextDocument14 pagesTextOdigo OfujeNo ratings yet
- Untitled2 PDFDocument15 pagesUntitled2 PDFVANESSA AMELIONo ratings yet
- Answerd FINAL EXAM STUDENT-1Document4 pagesAnswerd FINAL EXAM STUDENT-1Omar H100% (1)
- MCQ Hap-II, Bp201tDocument39 pagesMCQ Hap-II, Bp201tANUJ DEVNo ratings yet
- Quiz #1 Q3 Science 10Document2 pagesQuiz #1 Q3 Science 10Jr Capanang0% (1)
- 3418 1701236940Document4 pages3418 1701236940SatnampreetNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Mcqs With Keys YT Insta Medico SlidesDocument8 pagesEndocrine System Mcqs With Keys YT Insta Medico SlidesYounas PandaNo ratings yet
- XI CH - 22 Chemical Control and CoordinationDocument16 pagesXI CH - 22 Chemical Control and Coordinationali imranNo ratings yet
- Exam Question Endocrine SystemDocument2 pagesExam Question Endocrine SystemTumabang DivineNo ratings yet
- Quizlet Chapter 18Document19 pagesQuizlet Chapter 18Dawlat SlamaNo ratings yet
- Final Exam AnatomyDocument7 pagesFinal Exam AnatomyBillAllenCacanindinNo ratings yet
- PTSCIDocument4 pagesPTSCIDaiseree SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Summative Test in ScienceDocument6 pagesSummative Test in ScienceRalph Rexor Macarayan BantuganNo ratings yet
- Biology Reviewer 2Document14 pagesBiology Reviewer 2Rick Xyvender PurisimaNo ratings yet
- Third Quarter Exam in Science 10Document3 pagesThird Quarter Exam in Science 10Marife GuadalupeNo ratings yet
- Ha&P - Semi ReviewerDocument71 pagesHa&P - Semi ReviewerLittle StuartNo ratings yet
- PH3. 2024. Endocrine Physiology Questions-1Document14 pagesPH3. 2024. Endocrine Physiology Questions-1School TeamNo ratings yet
- 4th PTDocument6 pages4th PTKath Belleza DebloisNo ratings yet
- Summative ExaminationDocument15 pagesSummative ExaminationFurcy SarsozaNo ratings yet
- Summative Exam On Nervous System and Endocrine SystemDocument3 pagesSummative Exam On Nervous System and Endocrine SystemKhiyah RhueNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology 1st Semester BSN MCQS, Educational Platform-1Document29 pagesAnatomy and Physiology 1st Semester BSN MCQS, Educational Platform-1Prince Masroor Ali Abro100% (1)
- Endocrine System McqsDocument7 pagesEndocrine System McqsRakhi Lal100% (2)
- Shum 104811Document12 pagesShum 104811Daniel GtsadkanNo ratings yet
- اسئلة فسلجة ثاني كورس ثانيDocument5 pagesاسئلة فسلجة ثاني كورس ثانيRad RYNo ratings yet
- APIIPractice QuestionsDocument18 pagesAPIIPractice QuestionsamandaNo ratings yet
- Coordination System Encircle The Best Answer of The Following QuestionsDocument13 pagesCoordination System Encircle The Best Answer of The Following Questionsnon elfNo ratings yet
- Human Body QuizDocument6 pagesHuman Body QuizJonathan Tolentino MercadoNo ratings yet
- OB QuizDocument45 pagesOB QuizJonas Marvin AnaqueNo ratings yet
- Intro To Human Anatomy & Physiology: Quick Review Notes Chapter 1From EverandIntro To Human Anatomy & Physiology: Quick Review Notes Chapter 1No ratings yet
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers HomeostasisFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers HomeostasisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Suggested Intervention For Development Needs IPCRF 2023Document6 pagesSuggested Intervention For Development Needs IPCRF 2023Paulo M. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- ES10 Module 5Document42 pagesES10 Module 5Paulo M. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Continental Drift Theory COT1Document4 pagesContinental Drift Theory COT1Paulo M. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- 4thq 2nd Modular Set BDocument1 page4thq 2nd Modular Set BPaulo M. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Program of WorksDocument4 pagesProgram of WorksPaulo M. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- ES10 Module 4Document36 pagesES10 Module 4Paulo M. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- 4thq 3rd Modular SummDocument1 page4thq 3rd Modular SummPaulo M. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- ES10 Module 5Document33 pagesES10 Module 5Paulo M. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- 1stq 6th ModularDocument2 pages1stq 6th ModularPaulo M. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- 1stq 1st ModularDocument1 page1stq 1st ModularPaulo M. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- 1stq 4th ModularDocument1 page1stq 4th ModularPaulo M. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- 1stq 7th ModularDocument1 page1stq 7th ModularPaulo M. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- 1stq 5th ModularDocument1 page1stq 5th ModularPaulo M. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Coop Tax Exemp LetterDocument2 pagesCoop Tax Exemp LetterPaulo M. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- 7sgdfgf PDFDocument438 pages7sgdfgf PDFPratik JadhavNo ratings yet
- AP Biology-Near Final DraftDocument1,931 pagesAP Biology-Near Final DraftHayden BuechlerNo ratings yet
- Bio p4Document18 pagesBio p4joumanaaa beckNo ratings yet
- Mutation and Types of MutationDocument5 pagesMutation and Types of MutationShahriar ShamimNo ratings yet
- Unit - 10 - General Characters and Classification of Fungi by Dr. Kirtika PadaliaDocument38 pagesUnit - 10 - General Characters and Classification of Fungi by Dr. Kirtika PadalianucleophilicmishraNo ratings yet
- Full Lab Report 3.0 PrintDocument14 pagesFull Lab Report 3.0 PrintSITI BAZILAH BINTI BILAK KPM-GuruNo ratings yet
- (Teach Yourself) David Le Vay, Jenny Stafford-Brown - Anatomy & Physiology - A Complete Introduction-John Murray Learning (2015)Document385 pages(Teach Yourself) David Le Vay, Jenny Stafford-Brown - Anatomy & Physiology - A Complete Introduction-John Murray Learning (2015)Teresa ChaoNo ratings yet
- Estrategias Inmunosupresivas de Tumores RabinovichDocument33 pagesEstrategias Inmunosupresivas de Tumores RabinovichLyanna StarkNo ratings yet
- Eibl2018 Article PlantCellCultureTechnologyInThDocument15 pagesEibl2018 Article PlantCellCultureTechnologyInThQuoc KhanhNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences Practical Task 1 Grade 12 2021Document9 pagesLife Sciences Practical Task 1 Grade 12 2021Mudalo MudauNo ratings yet
- Hematology: Monoclonal Gammapathies-Multiple Myeloma Lymphoma Hodgkin and Non HodgjknDocument29 pagesHematology: Monoclonal Gammapathies-Multiple Myeloma Lymphoma Hodgkin and Non HodgjknBelu DanielaNo ratings yet
- Theories of EvolutionDocument58 pagesTheories of EvolutionDhanush BmNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System TortoraDocument24 pagesIntegumentary System TortorasyafiqahNo ratings yet
- Case No. 6: Glucose 6 Phosphate Deficiency: Mham - First YearDocument52 pagesCase No. 6: Glucose 6 Phosphate Deficiency: Mham - First YearReham QueNo ratings yet
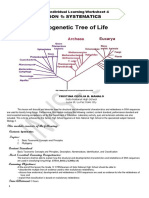
- Lesson 1: Systematics: Gen Bio 2 Individual Learning Worksheet 4Document11 pagesLesson 1: Systematics: Gen Bio 2 Individual Learning Worksheet 4Diana, Kate Deslen S.75% (4)
- Lembar Kerja Siswa Animalia 2Document4 pagesLembar Kerja Siswa Animalia 2donald kartika0% (1)
- Science 7Document5 pagesScience 7cattleya abelloNo ratings yet
- Mutant Variations and The Danger of LockdownsDocument6 pagesMutant Variations and The Danger of LockdownsjrvvfNo ratings yet
- Seed Formation and DevelopmentDocument12 pagesSeed Formation and DevelopmentSabir Ahamed90% (20)
- Classify Life According To Cellular StructureDocument17 pagesClassify Life According To Cellular StructureTshanna Roberts100% (1)
- DorperDocument17 pagesDorperFilipe CardosoNo ratings yet
- Al-Ameen Mission Study Circle: Neet (Ug)Document3 pagesAl-Ameen Mission Study Circle: Neet (Ug)MortojaNo ratings yet
- 06 - Solved - BSSC 10+2-29-1-2017 (Study)Document8 pages06 - Solved - BSSC 10+2-29-1-2017 (Study)HARISH KUMAR SHARMANo ratings yet
- Presentation WBC McqsDocument32 pagesPresentation WBC McqsKanchan LalwaniNo ratings yet
- Lazcano y Pereto. 2021. BioSystemsDocument6 pagesLazcano y Pereto. 2021. BioSystemsRenato AmosNo ratings yet
- Virtual Labs SurveyDocument4 pagesVirtual Labs SurveyJordanGoldmanNo ratings yet
- S4 Biology Summary Assessment 2022Document2 pagesS4 Biology Summary Assessment 2022Mutaganda Ami fideleNo ratings yet
- Career Prospects in Pharma IndustryDocument12 pagesCareer Prospects in Pharma Industrykumkum prakashNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid - WikipediaDocument1 pageNucleic Acid - WikipediaElton ViannaNo ratings yet