Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
35 viewsA7 Structural Organization in Animals Min
A7 Structural Organization in Animals Min
Uploaded by
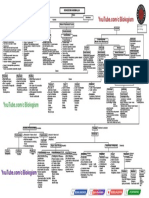
DME MPonline1) The document discusses the structural organization and reproductive systems of various animals including the common Indian earthworm and American cockroach.
2) It describes the male and female reproductive systems of earthworms, noting the location and structure of testes, ovaries, sperm ducts, and spermathecae.
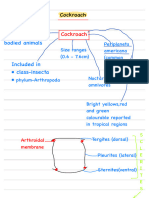
3) The reproductive system of cockroaches is also outlined, identifying the location of testes, accessory glands, spermathecae, ovaries, and oviducts.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Locomotion & Movement - Micronotes PDFDocument2 pagesLocomotion & Movement - Micronotes PDFANKITA MANDAVI67% (3)
- 人脑图谱 PDFDocument1 page人脑图谱 PDFzmNo ratings yet
- HAPS Pulmonary Ventilation ActivityDocument4 pagesHAPS Pulmonary Ventilation ActivityLucelle AdanteNo ratings yet
- Sleep Apnea Concept MapDocument1 pageSleep Apnea Concept Mapashleydean100% (2)
- Wall ChartDocument1 pageWall ChartLila Joy100% (3)
- Gas ExchangeDocument15 pagesGas ExchangeOsolemio Mer100% (1)
- Supernotes Complete Class 12thDocument46 pagesSupernotes Complete Class 12thmummyjha909No ratings yet
- Animals Study Guide - Yeshen a. (2-4)Document5 pagesAnimals Study Guide - Yeshen a. (2-4)krisamikaela1123No ratings yet
- Chief Taxonomic Subdivisions and Organ Systems of The Animal PhylaDocument2 pagesChief Taxonomic Subdivisions and Organ Systems of The Animal PhylaL P100% (1)
- Digestive System, Urinary System, Skeletal SystemDocument1 pageDigestive System, Urinary System, Skeletal Systemandrea.baceovaNo ratings yet
- 31 Reproductive System 1 Male - Read-OnlyDocument6 pages31 Reproductive System 1 Male - Read-Onlyzhuoranliu2019No ratings yet
- Urogenital System Embryology (ANA204) OFRDocument8 pagesUrogenital System Embryology (ANA204) OFROloruntomi AdesinaNo ratings yet
- Kingdom AnimiliaDocument1 pageKingdom AnimiliaNoman ZakiNo ratings yet
- Concept Map On Reproductive System (Final)Document1 pageConcept Map On Reproductive System (Final)Hazel Ann GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Taxonomy SheetDocument1 pageTaxonomy Sheetlettresaccelerer.0eNo ratings yet
- Animal Kingdom Digital NotesDocument20 pagesAnimal Kingdom Digital NotesKshreeNo ratings yet
- Paliy-: MunchinaDocument2 pagesPaliy-: MunchinasrishtiNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Lecture Reproductive SystemDocument8 pagesAnaphy Lecture Reproductive SystemNycole YlananNo ratings yet
- Human ReproductionDocument16 pagesHuman ReproductionNajeela khaleelNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Animalia SummaryDocument2 pagesKingdom Animalia Summaryaayzah2005No ratings yet
- Kingdom Animalia SummaryDocument2 pagesKingdom Animalia Summaryaqeel abdullah100% (1)
- Summary of Different Parasites: Man ManDocument1 pageSummary of Different Parasites: Man ManNurhayati HasanahNo ratings yet
- Summary of Different Parasites PDFDocument1 pageSummary of Different Parasites PDFRyan aginta 1100% (1)
- GGGGGGG: Bloodpotenc y Hitpoints Amaranth BloodDocument2 pagesGGGGGGG: Bloodpotenc y Hitpoints Amaranth BloodWannes IkkuhyuNo ratings yet
- Kidney AmatomyDocument1 pageKidney AmatomyCarlotta ranalliNo ratings yet
- Animalia File 2023-1Document12 pagesAnimalia File 2023-1Syed Zee Waqar GillaniNo ratings yet
- Human Reproduction Male Reproductive System: (Continued)Document11 pagesHuman Reproduction Male Reproductive System: (Continued)Meeta DeviNo ratings yet
- CockroachDocument13 pagesCockroachVaiditNo ratings yet
- CockroachDocument26 pagesCockroachVaiditNo ratings yet
- 12-1) Human Reproductive SystemDocument64 pages12-1) Human Reproductive SystemVK GNo ratings yet
- Dioecious Sexual Commensal Free-Living Locomotion: ParapodiaDocument4 pagesDioecious Sexual Commensal Free-Living Locomotion: ParapodiaRenz GarciaNo ratings yet
- EarthwormDocument24 pagesEarthwormAlakesh Coldplay KalitaNo ratings yet
- Key Points KINGDOM ANIMALIA EngeeconDocument2 pagesKey Points KINGDOM ANIMALIA EngeeconUsama Iqbal33% (3)
- Hsslive Xii Zoology Vijayabheri 2024Document4 pagesHsslive Xii Zoology Vijayabheri 2024ajithaprabhath123No ratings yet
- Kingdom Animilia - BiologismDocument1 pageKingdom Animilia - BiologismMuhammad SibtainNo ratings yet
- Male Anatomy ChartDocument2 pagesMale Anatomy ChartKikikikimmyNo ratings yet
- PHYSIOFemaleReproMARQUINO DUMLAODocument8 pagesPHYSIOFemaleReproMARQUINO DUMLAOGabby ElardoNo ratings yet
- Scan 08 Sep 2020Document3 pagesScan 08 Sep 2020Zenia XoNo ratings yet
- Kingdom AnimaliaDocument2 pagesKingdom AnimaliaZoology InterestsNo ratings yet
- Stink BugDocument2 pagesStink BugAnime sub españolNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Animalia: Phylum Digestive SystemDocument1 pageKingdom Animalia: Phylum Digestive Systemayesha shaikhNo ratings yet
- Xii - Human Reproduction NotesDocument10 pagesXii - Human Reproduction Notesallemonster1234No ratings yet
- Ento Main Paper AssignmentDocument1 pageEnto Main Paper AssignmentRohit VermaNo ratings yet
- Practice Test Planner Phase-01 For CF-OYM - AY - 2024-25 Version 1.0Document4 pagesPractice Test Planner Phase-01 For CF-OYM - AY - 2024-25 Version 1.0Kushal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Life History of AngiospermDocument45 pagesLife History of AngiospermgbgbkrishnaNo ratings yet
- Beige Modern Business Organization Chart GraphDocument1 pageBeige Modern Business Organization Chart GraphEDGAR SANCHEZNo ratings yet
- MCA (107) T - Module 1, 2, 3Document27 pagesMCA (107) T - Module 1, 2, 3Gulayan, Renz Bryelle T.No ratings yet
- Anatomy of Flowering PlantsDocument22 pagesAnatomy of Flowering Plantsaviralk49No ratings yet
- Clinpara Lec M2Document11 pagesClinpara Lec M2eumhir7No ratings yet
- IGCSE Biology NotesDocument21 pagesIGCSE Biology NotesalfaazmcsNo ratings yet
- Tortora GenitalDocument53 pagesTortora GenitalChaori NurfadillahNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 07-Mar-2023Document1 pageAdobe Scan 07-Mar-2023Vriddhi AhujaNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System TransesDocument5 pagesReproductive System Transesadrielvamos28No ratings yet
- Kingdom AnimaliaDocument2 pagesKingdom AnimaliaAli KamranNo ratings yet
- L1.2 The Male Reproductive SystemDocument24 pagesL1.2 The Male Reproductive SystemCreeper RulezNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument7 pagesReproductive SystemArvin ManaloNo ratings yet
- CEREBELLUMDocument1 pageCEREBELLUMOscar Orengo AlbertorioNo ratings yet
- Organisms 202453 175710Document1 pageOrganisms 202453 175710neetnanu26No ratings yet
- Neural Control - MicronotesDocument2 pagesNeural Control - MicronotesDhruv MalaviyaNo ratings yet
- Phylum PlatyhelminthesDocument4 pagesPhylum PlatyhelminthesRenz GarciaNo ratings yet
- Chest PhysiotherapyDocument7 pagesChest PhysiotherapyNikhil Mohan100% (1)
- Principles and Practice of Anesthesia For Thoracic Surgery by Peter Slinger (Z-Lib - Org) (1) - 284-307Document24 pagesPrinciples and Practice of Anesthesia For Thoracic Surgery by Peter Slinger (Z-Lib - Org) (1) - 284-307VERONICA PARI TOLANo ratings yet
- Arterial Blood Gas AnalysisDocument6 pagesArterial Blood Gas AnalysisMaribee Tagayun EspirituNo ratings yet
- Thoracic Pathology: Dr. Fatima Ejaz PT Ms Neuro Physical TherapyDocument24 pagesThoracic Pathology: Dr. Fatima Ejaz PT Ms Neuro Physical Therapykim suhoNo ratings yet
- Bustamante, Anjaneth C. Bsrtp-3ADocument13 pagesBustamante, Anjaneth C. Bsrtp-3AMite giteNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Medical Emergencies in The Dental Office 7th Edition Stanley F MalamedDocument3 pagesTest Bank For Medical Emergencies in The Dental Office 7th Edition Stanley F MalamedJohnCampbellyacer97% (34)
- What Are Hyperinflated LungsDocument2 pagesWhat Are Hyperinflated LungsAnthony LopezNo ratings yet
- GetCWExternalDocument SDS Carbon RemoverDocument15 pagesGetCWExternalDocument SDS Carbon RemoverAVINASH ANAND RAONo ratings yet
- Adjuncts To Mechanical Ventilation: Tantani SugimanDocument36 pagesAdjuncts To Mechanical Ventilation: Tantani SugimanAndi Upik FathurNo ratings yet
- Nursing Management of Children With Bronchial AsthmaDocument17 pagesNursing Management of Children With Bronchial AsthmaalmishalnetNo ratings yet
- What Is Acute BronchitisDocument11 pagesWhat Is Acute BronchitisKerri-DojhnHallNo ratings yet
- 186 Flux Pen MsdsDocument4 pages186 Flux Pen MsdsNicolae ChirilaNo ratings yet
- A Mathematical Model of The Human Respiratory System: W.F. Fincham and F.T. TehraniDocument9 pagesA Mathematical Model of The Human Respiratory System: W.F. Fincham and F.T. TehraniDayana VieiraNo ratings yet
- 1st Periodic Test - Science 9Document4 pages1st Periodic Test - Science 9Lani Bernardo Cuadra100% (1)
- Hbpe4303 Pengenalan Anatomi Dan FisiologiDocument20 pagesHbpe4303 Pengenalan Anatomi Dan FisiologiumangsenoraNo ratings yet
- Bronchiectasis PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesBronchiectasis PathophysiologyKim Gonzales86% (7)
- Acetonitrile: Safety Data SheetDocument9 pagesAcetonitrile: Safety Data SheetSri HariNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of The NewbornDocument72 pagesNursing Care of The NewbornCathreen Agatha FuleNo ratings yet
- Baby Gender Determination in Scuba DiversDocument9 pagesBaby Gender Determination in Scuba DiversDaniel CaskNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System PhysiologyDocument35 pagesRespiratory System PhysiologySherwan R Shal100% (2)
- Fish RespirationDocument17 pagesFish RespirationfangirltonNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System Anatomy, Assessment & Diagnostic TestsDocument24 pagesRespiratory System Anatomy, Assessment & Diagnostic TestsPrince Rener Velasco PeraNo ratings yet
- Group 1: Medico Legal Aspect of DeathDocument19 pagesGroup 1: Medico Legal Aspect of DeathTIPAY, EMELIE L.100% (1)
- Voice ProductionDocument16 pagesVoice ProductionAnj De Luna AlbaNo ratings yet
- The Cause and Prevention of CancerDocument11 pagesThe Cause and Prevention of CancerJoseph SabidoNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 1 - Respiratory SystemDocument1 pageLECTURE 1 - Respiratory SystemJeremiah AndalNo ratings yet
- Full Download PDF of Medical Assisting: Administrative and Clinical Procedures 6th Edition by Kathryn Booth (Ebook PDF) All ChapterDocument43 pagesFull Download PDF of Medical Assisting: Administrative and Clinical Procedures 6th Edition by Kathryn Booth (Ebook PDF) All Chaptervrymantorfs100% (7)
A7 Structural Organization in Animals Min
A7 Structural Organization in Animals Min
Uploaded by
DME MPonline0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
35 views1 page1) The document discusses the structural organization and reproductive systems of various animals including the common Indian earthworm and American cockroach.
2) It describes the male and female reproductive systems of earthworms, noting the location and structure of testes, ovaries, sperm ducts, and spermathecae.
3) The reproductive system of cockroaches is also outlined, identifying the location of testes, accessory glands, spermathecae, ovaries, and oviducts.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1) The document discusses the structural organization and reproductive systems of various animals including the common Indian earthworm and American cockroach.
2) It describes the male and female reproductive systems of earthworms, noting the location and structure of testes, ovaries, sperm ducts, and spermathecae.
3) The reproductive system of cockroaches is also outlined, identifying the location of testes, accessory glands, spermathecae, ovaries, and oviducts.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
35 views1 pageA7 Structural Organization in Animals Min
A7 Structural Organization in Animals Min
Uploaded by
DME MPonline1) The document discusses the structural organization and reproductive systems of various animals including the common Indian earthworm and American cockroach.
2) It describes the male and female reproductive systems of earthworms, noting the location and structure of testes, ovaries, sperm ducts, and spermathecae.
3) The reproductive system of cockroaches is also outlined, identifying the location of testes, accessory glands, spermathecae, ovaries, and oviducts.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
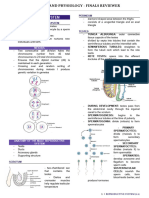
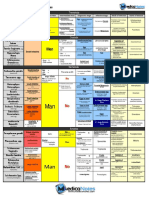
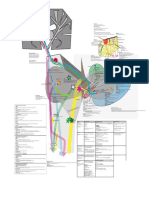
STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION IN ANIMALS
Rana tigrana Periplaneta Americana
Cold-blooded nocturnal omnivores
Male Reproductive system
-Pain of testes at 4th-6th abdominal
Common indian varieties segment.
Male Reproductive system
Peretima and Lumbricus -Genital pouch has -1) Anus
- Testes : Pair of yellowish 2) Male genital pore
ovoid structures, adheres to 3) Phallomere
upper part of kidneys by -Anal style present
mesorchium. Reproductive System
( Hermaphrodite )
Male- 2pairs of testes (10th and 11th). Female Reproductive system
-Vas differentia upto 18th segment. -Pain of ovories at 2th-6th abdominal
Female Reproductive system -One pair of accessory gland in segment.
17th and 19th segments. -Genital pouch has -1)Female gonopore
- A pair of ovories situated -4 pairs of spermathecae in 6th 2)Spermathecal pores
near kidneys. - 9th Segments. 3)Collateral glands
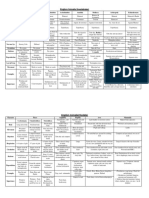
Tight- check the flow between cells.
- No functional connection Animal tissue Cell junction -Anal style absent.
Gap- helps in between cells’ communication.
with kidneys by mesorchium. Female- 1 Pair of ovories at 12th
Adhering- cements the cells together. intersegmental septa of and 13th. EXCRETORY SYSTEM
-Ovorian funnels beneath ovories. Respiratory System
1) Epithelial Tissue Excretory organ - Nephridia
-Oviduct opens on 14th segment -Trachea, divided into tracheoles
as female genital pore. -Integumentary - attached to the living -Tracheoles carry oxygen to all body
Fertilization of body wall from 3rd to end.
ii) Simple: made of single layer of cells. iii) Compound parts.
- External in water. i) Glandular: Columnar and -Septal - present on both sides of
- Development involves a cuboidal are specialized and intersegmental septa of 15th to end. -Trachea opens via spiracles.
squamous squamous
larval stage, tadpole. for secretion. -Pharyngeal as- 3 paired tufts in 4th – 6th
- function is exchange of material, filtration & - Protection against abrasion.
- Tadpole Adult.
Unicellular – goblet cells of alimentary canal little absorption.
segments.
- Epidermis of skin, hair & oral
-Nephridia regulate volume and composition of
Vascular system
Multicellular – salivary glands - lining cavity organs like heart, lungs etc. cavity. body fluids. -Open type
Endocrine – Pituitary, thymus -They start as a funnel to connects excess -Blood,called Haemolymph has
Circulatory System Exocrine – sweat & sebaceous glands Cuboidal fluid from coelomic chamber. colorless plasma and haemocytes.
Columnar
-Heart: 3-Chambered, - Absorption & -Deliver body waste to body to body wall -Alary muscles help in circulation.
2 Artia + 1 Ventricle. 2) CONNECTIVE TISSUE - Protection & secretion. surface through pore.
secretion. -Heart is dorsal and 13 chambered.
-Ventricle opens into conus - tubules and ducts - Epiglottis & mammary
arteriosus on ventral side LOOSE DENSE SPECIALIZED glands.
of glands & surface
of heart. - Areolar - Regular - lymph of ovary. Sensory system Alimentary canal
-Blood from heart is carried - Adipose - Blood Columnar Cuboidal - No eyes but sensitive to light &
to all body parts by arterial - Irregular -Divided into - Foregut, midgut and
- Bones - secretion & touch.
system. - help in mechanical & chemical hindgut.
- Cartilage absorption. - Chemoreceptors 7 for response to
stress. -Mouth opens into Pharynx
chemical stimuli.
- Gastrointestinal - sweat glands, and cand & - Sense organs located on anterior Oesophagus Crop (food storing
tract. female urethra. part of body region) Gizzard, where grinding
Blood Vascular system
3) NEURAL TISSUE of food occurs Hepatic Caeca
-Heart + Blood vessels + Midgut Malpighian tubules
Blood. Ciliated Psuedo – stratified Digestive System Hindgut.
-RBCS are nucleated and - Movement of I- 3 segment Terminal mouth opens in buccal
red in color - Protection & movevment Nervous system -Hindgut is divided into ileum, Colon
mucous & egg. cavity.
- Represent by Ganglia. and rectum.
- Respiration tract & - Salivary glands,trachea, Muscular Pharynx 5-7 segment.
and male urethra. - Ganglia arranged on ventral Oesophagus -Rectum opens out through anus.
fallopian tube. 8-9 segment.
paired nerve cord. helps in grinding soil and
Gizzard
Lymphatic system - The bifurcated nerve cord joins the decaying leaues.
-Lymph + Lymph channel
cerebral ganglia dorsally to from stomach 9-14 segment - calciferous General Features
LOREM IPSUM nerve ring. Body Head
+ Lymph nodes. gland neutralizes humic acid Prothorax
- cerebral ganglia commands muscu- in humus Thorax Mesothorax
-Lymph has no RBC's 4) MUSCULAR TISSUE lar responses. intestine 15- last segment - Open into Abdomen Metathorax
-skeletal/ striated -long & cylindrical Anus. (covered by hard chitinous exoskeleton made of
present in-limbs, tongue & pharynx typhlosole Characterised by presence of NAG )
-Smooth / Unstriated -walls of viscer- internal medial fold of dorsal -Head has compound eye, Ocellus and
Digestive system Respiratory system wall.
al organ antennae.
-Short alimentary canal -spindle shaped with pointed end - No specialized breathing organ system. -Has mosaic vision for nocturnal vision
+ digestive glands. -Carcliac -Long & cylindrical
- Exchange occurs via moist body surface into (Covering of mouth) MORPHOLOGY
-Mouth Buccal cavity -Uninucleate
Stomach Intestine -Presentin Heart blood stream.
rectum cloaca. (5-9 segments)
-Digested food is absorbed
within intestine and (14-16)
undigested solid waste is Nervous system CLOSED CIRCULATORY SYSTEM (14 segments)
removed via cloaca.
- has blood vessels, capillaries and heart. (18 segments)
Central Peripheral Autonomic
- contraction helps blood circulation in one
Respiratory system direction.
Land- Buccal cavity skin Brain Cranial Sympathetic - smaller blood vessels supply the gut, nerve
and Lungs as pulmonary nerves cord & body wall.
Spiral cord Parasympathetic
respiratory organs.
Spiral - Blood glands in 4th 5th & 6th segment
Water- Skin acts as nerves produce blood cells & hems globin.
cutaneous respiratory
organ. -Brain- present in cranium, has 3 parts:-
1) Fore brain 2) Mid brain 3) Hind brain
anand_mani16 DR. Anand Mani https://www.anandmani.com/ https://discord.io/anandmani t.me/anandmani001
You might also like
- Locomotion & Movement - Micronotes PDFDocument2 pagesLocomotion & Movement - Micronotes PDFANKITA MANDAVI67% (3)
- 人脑图谱 PDFDocument1 page人脑图谱 PDFzmNo ratings yet
- HAPS Pulmonary Ventilation ActivityDocument4 pagesHAPS Pulmonary Ventilation ActivityLucelle AdanteNo ratings yet
- Sleep Apnea Concept MapDocument1 pageSleep Apnea Concept Mapashleydean100% (2)
- Wall ChartDocument1 pageWall ChartLila Joy100% (3)
- Gas ExchangeDocument15 pagesGas ExchangeOsolemio Mer100% (1)
- Supernotes Complete Class 12thDocument46 pagesSupernotes Complete Class 12thmummyjha909No ratings yet
- Animals Study Guide - Yeshen a. (2-4)Document5 pagesAnimals Study Guide - Yeshen a. (2-4)krisamikaela1123No ratings yet
- Chief Taxonomic Subdivisions and Organ Systems of The Animal PhylaDocument2 pagesChief Taxonomic Subdivisions and Organ Systems of The Animal PhylaL P100% (1)
- Digestive System, Urinary System, Skeletal SystemDocument1 pageDigestive System, Urinary System, Skeletal Systemandrea.baceovaNo ratings yet
- 31 Reproductive System 1 Male - Read-OnlyDocument6 pages31 Reproductive System 1 Male - Read-Onlyzhuoranliu2019No ratings yet
- Urogenital System Embryology (ANA204) OFRDocument8 pagesUrogenital System Embryology (ANA204) OFROloruntomi AdesinaNo ratings yet
- Kingdom AnimiliaDocument1 pageKingdom AnimiliaNoman ZakiNo ratings yet
- Concept Map On Reproductive System (Final)Document1 pageConcept Map On Reproductive System (Final)Hazel Ann GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Taxonomy SheetDocument1 pageTaxonomy Sheetlettresaccelerer.0eNo ratings yet
- Animal Kingdom Digital NotesDocument20 pagesAnimal Kingdom Digital NotesKshreeNo ratings yet
- Paliy-: MunchinaDocument2 pagesPaliy-: MunchinasrishtiNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Lecture Reproductive SystemDocument8 pagesAnaphy Lecture Reproductive SystemNycole YlananNo ratings yet
- Human ReproductionDocument16 pagesHuman ReproductionNajeela khaleelNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Animalia SummaryDocument2 pagesKingdom Animalia Summaryaayzah2005No ratings yet
- Kingdom Animalia SummaryDocument2 pagesKingdom Animalia Summaryaqeel abdullah100% (1)
- Summary of Different Parasites: Man ManDocument1 pageSummary of Different Parasites: Man ManNurhayati HasanahNo ratings yet
- Summary of Different Parasites PDFDocument1 pageSummary of Different Parasites PDFRyan aginta 1100% (1)
- GGGGGGG: Bloodpotenc y Hitpoints Amaranth BloodDocument2 pagesGGGGGGG: Bloodpotenc y Hitpoints Amaranth BloodWannes IkkuhyuNo ratings yet
- Kidney AmatomyDocument1 pageKidney AmatomyCarlotta ranalliNo ratings yet
- Animalia File 2023-1Document12 pagesAnimalia File 2023-1Syed Zee Waqar GillaniNo ratings yet
- Human Reproduction Male Reproductive System: (Continued)Document11 pagesHuman Reproduction Male Reproductive System: (Continued)Meeta DeviNo ratings yet
- CockroachDocument13 pagesCockroachVaiditNo ratings yet
- CockroachDocument26 pagesCockroachVaiditNo ratings yet
- 12-1) Human Reproductive SystemDocument64 pages12-1) Human Reproductive SystemVK GNo ratings yet
- Dioecious Sexual Commensal Free-Living Locomotion: ParapodiaDocument4 pagesDioecious Sexual Commensal Free-Living Locomotion: ParapodiaRenz GarciaNo ratings yet
- EarthwormDocument24 pagesEarthwormAlakesh Coldplay KalitaNo ratings yet
- Key Points KINGDOM ANIMALIA EngeeconDocument2 pagesKey Points KINGDOM ANIMALIA EngeeconUsama Iqbal33% (3)
- Hsslive Xii Zoology Vijayabheri 2024Document4 pagesHsslive Xii Zoology Vijayabheri 2024ajithaprabhath123No ratings yet
- Kingdom Animilia - BiologismDocument1 pageKingdom Animilia - BiologismMuhammad SibtainNo ratings yet
- Male Anatomy ChartDocument2 pagesMale Anatomy ChartKikikikimmyNo ratings yet
- PHYSIOFemaleReproMARQUINO DUMLAODocument8 pagesPHYSIOFemaleReproMARQUINO DUMLAOGabby ElardoNo ratings yet
- Scan 08 Sep 2020Document3 pagesScan 08 Sep 2020Zenia XoNo ratings yet
- Kingdom AnimaliaDocument2 pagesKingdom AnimaliaZoology InterestsNo ratings yet
- Stink BugDocument2 pagesStink BugAnime sub españolNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Animalia: Phylum Digestive SystemDocument1 pageKingdom Animalia: Phylum Digestive Systemayesha shaikhNo ratings yet
- Xii - Human Reproduction NotesDocument10 pagesXii - Human Reproduction Notesallemonster1234No ratings yet
- Ento Main Paper AssignmentDocument1 pageEnto Main Paper AssignmentRohit VermaNo ratings yet
- Practice Test Planner Phase-01 For CF-OYM - AY - 2024-25 Version 1.0Document4 pagesPractice Test Planner Phase-01 For CF-OYM - AY - 2024-25 Version 1.0Kushal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Life History of AngiospermDocument45 pagesLife History of AngiospermgbgbkrishnaNo ratings yet
- Beige Modern Business Organization Chart GraphDocument1 pageBeige Modern Business Organization Chart GraphEDGAR SANCHEZNo ratings yet
- MCA (107) T - Module 1, 2, 3Document27 pagesMCA (107) T - Module 1, 2, 3Gulayan, Renz Bryelle T.No ratings yet
- Anatomy of Flowering PlantsDocument22 pagesAnatomy of Flowering Plantsaviralk49No ratings yet
- Clinpara Lec M2Document11 pagesClinpara Lec M2eumhir7No ratings yet
- IGCSE Biology NotesDocument21 pagesIGCSE Biology NotesalfaazmcsNo ratings yet
- Tortora GenitalDocument53 pagesTortora GenitalChaori NurfadillahNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 07-Mar-2023Document1 pageAdobe Scan 07-Mar-2023Vriddhi AhujaNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System TransesDocument5 pagesReproductive System Transesadrielvamos28No ratings yet
- Kingdom AnimaliaDocument2 pagesKingdom AnimaliaAli KamranNo ratings yet
- L1.2 The Male Reproductive SystemDocument24 pagesL1.2 The Male Reproductive SystemCreeper RulezNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument7 pagesReproductive SystemArvin ManaloNo ratings yet
- CEREBELLUMDocument1 pageCEREBELLUMOscar Orengo AlbertorioNo ratings yet
- Organisms 202453 175710Document1 pageOrganisms 202453 175710neetnanu26No ratings yet
- Neural Control - MicronotesDocument2 pagesNeural Control - MicronotesDhruv MalaviyaNo ratings yet
- Phylum PlatyhelminthesDocument4 pagesPhylum PlatyhelminthesRenz GarciaNo ratings yet
- Chest PhysiotherapyDocument7 pagesChest PhysiotherapyNikhil Mohan100% (1)
- Principles and Practice of Anesthesia For Thoracic Surgery by Peter Slinger (Z-Lib - Org) (1) - 284-307Document24 pagesPrinciples and Practice of Anesthesia For Thoracic Surgery by Peter Slinger (Z-Lib - Org) (1) - 284-307VERONICA PARI TOLANo ratings yet
- Arterial Blood Gas AnalysisDocument6 pagesArterial Blood Gas AnalysisMaribee Tagayun EspirituNo ratings yet
- Thoracic Pathology: Dr. Fatima Ejaz PT Ms Neuro Physical TherapyDocument24 pagesThoracic Pathology: Dr. Fatima Ejaz PT Ms Neuro Physical Therapykim suhoNo ratings yet
- Bustamante, Anjaneth C. Bsrtp-3ADocument13 pagesBustamante, Anjaneth C. Bsrtp-3AMite giteNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Medical Emergencies in The Dental Office 7th Edition Stanley F MalamedDocument3 pagesTest Bank For Medical Emergencies in The Dental Office 7th Edition Stanley F MalamedJohnCampbellyacer97% (34)
- What Are Hyperinflated LungsDocument2 pagesWhat Are Hyperinflated LungsAnthony LopezNo ratings yet
- GetCWExternalDocument SDS Carbon RemoverDocument15 pagesGetCWExternalDocument SDS Carbon RemoverAVINASH ANAND RAONo ratings yet
- Adjuncts To Mechanical Ventilation: Tantani SugimanDocument36 pagesAdjuncts To Mechanical Ventilation: Tantani SugimanAndi Upik FathurNo ratings yet
- Nursing Management of Children With Bronchial AsthmaDocument17 pagesNursing Management of Children With Bronchial AsthmaalmishalnetNo ratings yet
- What Is Acute BronchitisDocument11 pagesWhat Is Acute BronchitisKerri-DojhnHallNo ratings yet
- 186 Flux Pen MsdsDocument4 pages186 Flux Pen MsdsNicolae ChirilaNo ratings yet
- A Mathematical Model of The Human Respiratory System: W.F. Fincham and F.T. TehraniDocument9 pagesA Mathematical Model of The Human Respiratory System: W.F. Fincham and F.T. TehraniDayana VieiraNo ratings yet
- 1st Periodic Test - Science 9Document4 pages1st Periodic Test - Science 9Lani Bernardo Cuadra100% (1)
- Hbpe4303 Pengenalan Anatomi Dan FisiologiDocument20 pagesHbpe4303 Pengenalan Anatomi Dan FisiologiumangsenoraNo ratings yet
- Bronchiectasis PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesBronchiectasis PathophysiologyKim Gonzales86% (7)
- Acetonitrile: Safety Data SheetDocument9 pagesAcetonitrile: Safety Data SheetSri HariNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of The NewbornDocument72 pagesNursing Care of The NewbornCathreen Agatha FuleNo ratings yet
- Baby Gender Determination in Scuba DiversDocument9 pagesBaby Gender Determination in Scuba DiversDaniel CaskNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System PhysiologyDocument35 pagesRespiratory System PhysiologySherwan R Shal100% (2)
- Fish RespirationDocument17 pagesFish RespirationfangirltonNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System Anatomy, Assessment & Diagnostic TestsDocument24 pagesRespiratory System Anatomy, Assessment & Diagnostic TestsPrince Rener Velasco PeraNo ratings yet
- Group 1: Medico Legal Aspect of DeathDocument19 pagesGroup 1: Medico Legal Aspect of DeathTIPAY, EMELIE L.100% (1)
- Voice ProductionDocument16 pagesVoice ProductionAnj De Luna AlbaNo ratings yet
- The Cause and Prevention of CancerDocument11 pagesThe Cause and Prevention of CancerJoseph SabidoNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 1 - Respiratory SystemDocument1 pageLECTURE 1 - Respiratory SystemJeremiah AndalNo ratings yet
- Full Download PDF of Medical Assisting: Administrative and Clinical Procedures 6th Edition by Kathryn Booth (Ebook PDF) All ChapterDocument43 pagesFull Download PDF of Medical Assisting: Administrative and Clinical Procedures 6th Edition by Kathryn Booth (Ebook PDF) All Chaptervrymantorfs100% (7)