Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Turbocharger Vs Supercharger Download
Turbocharger Vs Supercharger Download
Uploaded by
Ritesh inamdarOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Turbocharger Vs Supercharger Download
Turbocharger Vs Supercharger Download
Uploaded by
Ritesh inamdarCopyright:
Available Formats
Turbocharger
vs supercharger pdf download
Supercharger vs turbocharger fuel efficiency. Turbocharger notes pdf. What is the difference between supercharger and turbocharger pdf.
As an auto enthusiast, there is a high chance you once toyed with the idea of improving your vehicle’s power output. There are many moves to pull to increase a car’s horsepower, including the use of a supercharger or turbocharger. Supercharger vs. turbocharger, which is which and how do they work? Many people confuse the two engine additions
and may wrongly use the two words interchangeably. Some pundits classify the turbocharger as a special type of supercharger. If you have questions about the supercharger vs. turbo debate, you are in the right place.
Stick on as we look at each of the two power boosters focusing on their functionality and differences. Supercharger The supercharger is a common feature in most speed-oriented vehicles, like sports cars, as it helps boost their power. It is an air compressor whose primary role is to boost the density and pressure of air entering the engine. The more
air that gets into the engine, the more fuel it takes for ignition, translating to more power. The supercharger is engine-driven, meaning it runs mechanically with the aid of a belt, chain, or shaft linked to the engine’s crankshaft. Before having an in-depth focus on the supercharger’s functionality, let us have a look at its history. Image Credit:
GarageDreams A Brief History of the Supercharger According to records, the first supercharger prototype was the work of G. Jones of Birmingham. It was around 1849, later taking the name the Roots design. The naming came after The Roots Brothers patented it in 1860. The Roots Brothers owned Roots Blower Company, which used the design in
their air movers.
A successful test of the supercharger on internal combustion engines came in 1878 under Dugald Clerk. In 1885, Gottlieb Daimler took a German patent for the supercharger on the internal combustion engine. Following closely was the patent that Louis Renault took for the centrifugal supercharger in 1902. Test on this power booster proved to be
impressive after its installation on a racecar in 1908. The racecar peaked at 100mph. Mercedes was the first car company to produce a vehicle series that featured the supercharger in the 1920s. The models used the Roots design. How the Supercharger Works To understand how the supercharger works, you have to understand the basics of the
combustion engine. The combustion engine has a combustion chamber where air and fuel mix. The resultant reaction causes the pistons to move, affecting movement. For more power, you need more fuel and air to burn. Here is where the supercharger comes through by providing more compressed air. There are three types of superchargers, as
highlighted below, and how they work. The Roots Type The Roots type is the earliest form of the supercharger. It has a pair of rotors that provide fast-moving air to the intake port. At the intake port, the high level of air gets compressed, triggering the supply of fuel to match the air intake. When the fuel burns, you get more power from the engine.
Twin-Screw Supercharger The twin-screw supercharger will compress air in the supercharger housing rather than the intake port, like the Root’s type. It has two rotors that look like screws that help draw in air and send the compressed air to the engine. Centrifugal Supercharger The centrifugal supercharger has a unique design that does away
with rotors. Instead, it uses a fan to bring in the air. Air comes in through its intake at high speed, then gets compressed and slowed down in its housing before it goes to the engine. There are also electric superchargers, such as those developed by Mercedes, to do away with engine dependence. Also Read: WHP vs. HP: What’re The Differences? The
Turbocharger On the other side of the turbocharger versus supercharger debate, we have the former. The turbocharger is a common car part when it comes to auto-tuning to boost performance. This car add-on takes advantage of the exhaust gases, which come out fast, dependent on ignition. Instead of letting the exhaust gases go to waste, the
turbocharger harnesses its power. This power booster is like a turbine that helps draw more air into the combustion chamber, driven by the leaving exhaust gases. History of the Turbocharger The history of the turbo goes back to the late 1800s when Gottlieb Daimler was experimenting with forced induction. His works formed the foundation of the
turbocharger. Alfred Buchi, a Swiss engineer, made a patent in 1905, which many consider being the dawn of this car power booster.
The first prototype came roughly ten years later, targeting aircraft, but failed to reach the intended targets. It did not make it to production. Several patents and prototypes followed in the coming years, the main focus being in aircraft manufacturing. Some of them include one in 1916 by Auguste Rateau for French fighter planes running on Renault
engines. Several tests showed that the turbo could aid the engine in avoiding power loss at higher altitudes. Commercial application of the turbocharger came through in 1925 in diesel ships. The engine add-ons showed a tremendous power boost of around 40%. The turbo was prominent on airplanes during World War 2, while its use in vehicles came
in the 1950s. Its adoption by motor vehicles had some hurdles, such as dealing with lag. Technological advancements sorted the lag issue to a great degree. Turbocharged cars were more prominent at the time as they help in reducing emissions and improve fuel economy.
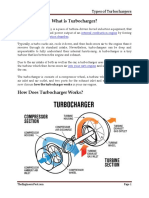
How Turbochargers Work The turbocharger consists of two impellers or fans situated on the same shaft. One fan is in the path of exhaust gases from the combustion chambers. As the exhaust gases get expelled, they turn the impeller, which in turn causes the other fan on the shaft to revolve. The other fun is in the car’s air intake, and its propulsion
draws in the air into the engine.
The drawn air is quite compressed, which makes it warmer, hence, less dense. There is a heat exchanger, which will cool the air before it goes into the cylinders. The turbocharger’s functionality is cyclical. The exhaust fumes turn the turbines, drawing in more air. More air draws in more fuel, and when it burns, it produces more exhaust gases, and
the process repeats. Supercharger vs.
Turbocharger Difference Supercharger vs. turbocharger difference is a critical area to focus on to know which add-on to go for. A thing that you should know is that the latter initially went by a turbosupercharger. It is because, at the time of its invention, any device that boosted a vehicle’s power via air pressure or density increase was a
supercharger. The two have many similarities; for example, both seek to improve the vehicle’s power output. However, the two differ in many areas, the most evident being their operation. The supercharger relies on engine power to run. It runs courtesy of a belt, chain, or shaft connected to the engine’s shaft. On the other hand, the turbocharger
runs on turbines powered by exhaust gases. It does not rely on the engine, instead of on the gases coming from the combustion chamber. You will find that powerful American car brands go for supercharging, the same as some European models. Turbo charging is the to-go boost for most Japanese models. ProCharger vs.
turbo, which one to go for? ProCharger is a centrifugal supercharger that uses less engine power than most superchargers. In this vein, the ProCharger is more efficient than most boosters. Compared to the turbo, you have the guarantee of a higher power threshold.
Supercharger vs. Turbocharger Fuel Efficiency A critical area to look at to know which is better, a turbocharger or supercharger, is fuel efficiency. Here, the focus is on how the boosters impact fuel consumption. When fixed to a smaller engine, they help improve their output and towing strength. So, which of the two is more efficient, consumption-
wise? You have to look at how they operate, and you will realize that the turbocharger takes the top spot. Turbo draws its power from exhaust gases leaving the engine to power it to bring more air for combustion. The supercharger relies on the engine to get the power to compress air and send it to the combustion spot. It may result in a power drop
of up to 20% despite having an efficiency of up to 40%. Supercharger vs. Turbocharger Price We will also focus on supercharger vs. turbocharger price discussion to better grasp these two car horsepower boosters. When getting one, you have to check on the price to see which one is friendly to your budget. Installing a supercharger will cost you
around $1000 to $7500, inclusive of labor. The price will depend on the size, manufacturer, and type of car. For a turbocharger, you may part with roughly $500 to $2500, together with labor. You may save some cash on labor if you have experience in such installations and fixtures, where the standard mechanics toolbox is all you need. However, if
you do not know how to go about it, you better consult a professional to handle it. Supercharger vs. Turbocharger Sound Sounds from the engine indicate many things; one of them may be the nature of its modification. It brings us to the supercharger vs. turbocharger sound. Superchargers produce much sound due to the suction effect as they draw
air into their assemblies. Twin-screw superchargers emit the most sound, and you may install them if you want to make a statement when driving on the streets. The centrifugal type will also produce a whistling sound as the compressed air leaves via its outlet. The higher the sound pitch translates to higher power output, something most car
enthusiasts target to show off their vehicles.
Turbochargers emit a lower pitch, more like a smooth whine. If you find noise to be a nuisance when driving, you can install a turbo on your vehicle’s engine. Beware of the sounds, taking note of any deviation, which may mean that you have engine problems. Supercharger vs. Turbocharger HP As severally hinted through this piece, both the
supercharger and turbocharger enhance the engine’s power output. They achieve this feat by compressing air to make it denser and supplying it to the engine for combustion. Supercharger vs. turbocharger HP output, which one comes on top? The supercharger will boost the power by up to 40-50%. The problem is that it derives its power from the
engine, and it takes roughly 20% of the engine’s power. Despite the power deduction, it still ensures that the vehicle runs on more power than similar models without the add-on. The turbocharger improves car power by roughly 30-40%. It is an excellent increment, though it suffers from lagging. In terms of power, the supercharger will provide more
than the turbocharger. Supercharger vs. Turbo Reliability When talking about reliability, you focus on your goals. The two power boosters are reliable, each having areas that stand out. For instance, the supercharger produces more power and does not lag when in operation. Power delivery is immediate; as such, you feel the effects instantly. It is
also efficient in low RPMs. The turbocharger brings its best in many areas like fuel economy, and it lowers emission levels. Additionally, it does not produce too much noise when running. When talking of reliability, it is a matter of the attributes you seek. You may consider it a biased tie. Supercharger vs. Turbocharger Power Delivery Superchargers
and turbochargers’ main difference comes in power delivery, mainly how they derive the power. The former runs mechanically, supported by the engine through a belt or chain. The latter is a turbine running on exhaust fumes. In power delivery, they bring their best to shoot up the horsepower. The supercharger will increase it by up to 50%, while
the turbo can register a 40% increment.
The supercharger’s downside in power delivery is that it consumes engine power to produce more horsepower. It lowers its efficiency. For the turbo, there is the lag, where it takes time to convert the exhaust gas speed to power. The good thing is that there are several tech developments to help beat turbo lag. Supercharger vs. Turbocharger Pros
and Cons Supercharger Pros The supercharger will provide more power to the engine, going to 50%. This is impressive horsepower uplift, ideal for sports cars. Additionally, the supercharger is easy to install if you have experience in handling auto works.
It delivers a decent power threshold at lower RPMs, and it has no lag, meaning you enjoy the effects straight away. It is very reliable, a thing you notice from its braking power increase of averagely 35%. Cons Sound production is one of the noticeable downsides of the supercharger.
If you do not love sounds when driving, the supercharger can be quite a nuisance, drawing attention to your car. It has compromised efficiency, considering it gets its force from the engine to generate more. Turbocharger Pros The turbocharger does not disappoint when it comes to the supply of compressed air to the intake. It amplifies the
horsepower up to 40%. It is also economical on fuel consumption as it relies on exhaust gases. The reusing of exhaust fumes reduces pollution. It also runs quietly, ideal if you love a peaceful driving moment. The turbocharger is a perfect add-on for high-altitude driving. Cons A significant downside to the turbocharger is the lag. It will take some time
before it produces ample power, compared to the supercharger, which has a more immediate action. Another disadvantage is its complex installation process. It is hard to install a turbocharger of your own, and you may need an experienced hand to assist you. Also Read: Radiator vs Intercooler: What is the Difference? Turbochargers vs
Superchargers YouTube Video Frequently Asked Questions( FAQs) Q: Is It Cheaper To Supercharge Or Turbocharge? When choosing between a supercharger and a turbocharger, you have to consider their respective costs. The turbocharger is, in most cases, cheaper than the supercharger, though it may have a higher installation price tag. The
turbocharger is also economical on fuel consumption; as such, it is the more pocket-friendly option. Q: Is Supercharger Safer Than Turbo? A look at the safety aspect, you see that the turbo and supercharger are very safe. The turbocharger’s edge of safety is where it uses exhaust fumes, reducing the vehicle’s emissions. The supercharger is easy to
install, presenting minimal hitches when fixing it to the engine. Q: Is Supercharging And Turbocharging The Same Thing? Supercharging and turbocharging work on the same principle of forced induction, which is the provision of compressed air to the internal combustion engine’s intake. While they have similar targets of improving the vehicle’s
force, their functionalities contrast. For supercharging, the booster relies on engine power through a belt, chains, or a shaft connected to the engine’s crankshaft. Turbocharging banks on exhaust gases to turn its fans to draw in air through the intake.
Q: Does A Turbo Or Supercharger Make More Power? The supercharger vs. turbo power output discussion looks at which of the two boosters is more powerful. Turbocharging has a threshold of 30-40%, while supercharging is at 40-50%. It is clear that supercharging will produce more power. It further holds the top spot as it does not lag.
Q: Do Superchargers Shorten Engine Life? The supercharger improves engine performance, but it can reduce its life if not used properly.
For instance, if the boost is powerful, it can cause the car part to wear fast. Q: Does Turbo Shorten Engine Life? A common myth about turbocharging is that it will reduce engine life. It is not valid, but if not correctly installed or faulty parts like the ignition time, it may contribute to engine degeneration. Final Word There are many ways to amplify
your car’s horsepower, including supercharging and turbocharging. As you may see from this piece, the two are different ways of getting a power lift, though they have the same target. They supply compressed air to the intake to mix with fuel for more force. Pick the more preferable of the two for your vehicle, depending on your goals.
Also, seek the services of a pro for installation if you are not experienced. Read More: Today we will study the difference between turbocharger and Supercharger in detail. Almost 19 points I have listed here to understand you. If you know already what is Turbo and Supercharger then directly you can move to the differences otherwise let’s know in
brief turbocharger and supercharger. It is a turbine-driven forced induction device that increases an internal combustion engine’s efficiency and also power output by forcing extra compressed air into the combustion chamber. The turbocharger is used in trains, cars, buses, and more engines. You can read the turbocharger in detail.
The supercharger is also called an air compressor. The function of an air compressor is to compress the fuel that means increasing the pressure of the fuel of an ic engine. Increasing the pressure of fuel means the burning of fuel will be more and fast, which will provide more work. Thus even supercharger works are the same. The main differences
between Turbocharger and Supercharger are Turbocharger is not connected directly to the engine and whereas a Supercharger is a direct connection with the engine through the belt. There are 19 points I have listed here. So let’s start at each point. Sl No.TurbochargerSupercharger1.The turbocharger is not connected directly to the engine.The
supercharger is a direct connection with the engine through a belt.2.It has smog-altering equipment that lowers the carbon emission.The supercharger does not have a wastegate. So the smog emits from a supercharger.
3.It uses exhaust gas for its energy.It is a connected crankshaft of the engine for its energy. 4.The spinning rate is 15000 RPMThe spinning rate is 50000 RPM.5.This is a device consisting of both the turbine and compressor mounted on the same shaft.This is basically a compressor.6.It does not need any extra power.Here in the supercharger extra
power is to be supplied.7.It drew power from exhaust gases.It drew power from the engine.8.Higher speed achieved.Greater acceleration is achieved.9.It takes time to spin up to the speed hence there is lag.Here no lag. Power delivers immediately.10.Difficult maintenance.Easy maintenance.11.This is costly.The cost is less.12.More efficient because
it drew power from exhaust gases.A supercharger is less efficient.13.Suitable for an engine with higher displacement.Suitable for an engine with lower displacement.14.Turbos won’t start operating until a sufficient amount of exhaust gases is produced.Superchargers start working as soon as the engine starts.15.Here a compressor is rotated by the
turbine.The compressor is rotated by the engine crankshaft through a belt.16.This is more complex.but this one is less complex.17.The intercooler requires here to for lowering the temperature of compressed air.The chances of the requirement of the intercooler are negligible. But some time is needed.18.The compressed air has a high temperature in
the turbocharger. The compressed air has a low temperature in the supercharger. 19.This is less reliable.This is more reliable.Turbocharger vs Supercharger Let me know what you think of this information. Is this information helps you? With the use of the comment box please comment on it. And let me know what other topics you want me to deliver.
Here I have attached a PDF. You can easily download it. Thank you for your valuable time in reading. Do check out our other great post.
You might also like
- Parts Manual D6R XLDocument795 pagesParts Manual D6R XLMuliadi Irawan100% (2)
- Man Industrial Gas Engines e 2866 e 302 Repair ManualDocument10 pagesMan Industrial Gas Engines e 2866 e 302 Repair ManualDavid100% (52)
- Worthington Manual PDFDocument71 pagesWorthington Manual PDFsubrataNo ratings yet
- Stirling Engine - A Beginners GuideDocument108 pagesStirling Engine - A Beginners Guideamsci99100% (5)
- 2 2 2 A Enginesimulator by Javier PrietoDocument3 pages2 2 2 A Enginesimulator by Javier Prietoapi-268997163No ratings yet
- 372electric Injection System PDFDocument42 pages372electric Injection System PDFAperc Taini Glbrt Rmx100% (1)
- Differences Between Superchargers & TurbochargersDocument3 pagesDifferences Between Superchargers & TurbochargersIzzadAfif1990No ratings yet
- Types of SuperchargersDocument5 pagesTypes of Superchargersravidra markapudiNo ratings yet
- For Those Contemplating Fitting A Supercharger As A Means of Performance EnhancementDocument2 pagesFor Those Contemplating Fitting A Supercharger As A Means of Performance EnhancementNguyễn NgọcNo ratings yet
- Diesel Vs PetrolDocument3 pagesDiesel Vs PetrolAFEWORKNo ratings yet
- The Words - TurbDocument4 pagesThe Words - TurbMoti LemiNo ratings yet
- Definition EssayDocument5 pagesDefinition Essayhondarider909No ratings yet
- Polytechnic University of ZacatecasDocument5 pagesPolytechnic University of ZacatecasANTONIO SANDATE CHAVEZNo ratings yet
- Turbocharger MatchingDocument24 pagesTurbocharger MatchingheideNo ratings yet
- Under Construction!!!! 1/25/08: SuperchargingDocument9 pagesUnder Construction!!!! 1/25/08: SuperchargingTalha Bin MujahidNo ratings yet
- J Perez Tech ReportDocument14 pagesJ Perez Tech ReportJuan J. PerezNo ratings yet
- Difference Between: Turbocharger Vs SuperchargerDocument14 pagesDifference Between: Turbocharger Vs SuperchargerMohammad Al QadomeNo ratings yet
- Race Cars: Induction System. They Compress The Air Flowing Into The Engine (SeeDocument7 pagesRace Cars: Induction System. They Compress The Air Flowing Into The Engine (SeeharryNo ratings yet
- Supercharger Turbo 3.31Document6 pagesSupercharger Turbo 3.31larasmoyoNo ratings yet
- Search: What Is A Turbocharger?Document3 pagesSearch: What Is A Turbocharger?aravindan476No ratings yet
- Turbo Basics ExplainedDocument5 pagesTurbo Basics ExplainedPawan Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Supercharging of Diesel EnginesDocument6 pagesSupercharging of Diesel EnginesPolavarapu Srinivasa RaoNo ratings yet
- Engine Modifications: Air in (Induction)Document5 pagesEngine Modifications: Air in (Induction)Muhammad TalhaNo ratings yet
- Engine Modifications: Air in (Induction)Document5 pagesEngine Modifications: Air in (Induction)Muhammad TalhaNo ratings yet
- Intro. To TurboDocument8 pagesIntro. To TurboKevin GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Engine Mapper S Subaru Tuning Guide V1.1Document17 pagesEngine Mapper S Subaru Tuning Guide V1.1Devine Light100% (1)
- Research Papers On Superchargers and TurbochargersDocument6 pagesResearch Papers On Superchargers and Turbochargerstys0v0kan1f3No ratings yet
- Welcome To Car Tuning TipsDocument60 pagesWelcome To Car Tuning TipsVeer Honda100% (1)
- Difference Between Turbocharger and Supercharger With PDFDocument3 pagesDifference Between Turbocharger and Supercharger With PDFLeo Abdul Aziz Billones100% (1)
- Turbo ChargersDocument11 pagesTurbo ChargersShakeeb AhmedNo ratings yet
- 03-Supercharging and TurbochargersDocument7 pages03-Supercharging and TurbochargersAHMADNo ratings yet
- Supercharging and TurbochargingDocument3 pagesSupercharging and Turbocharging13311A0341 S SHIVA SAI KIRANNo ratings yet
- Electric Fans: - We Americans Love Our CarsDocument11 pagesElectric Fans: - We Americans Love Our CarssammahajanNo ratings yet
- Turbo Engine: Mechfest 06 A Technical Paper Presentation On " " Submitted byDocument19 pagesTurbo Engine: Mechfest 06 A Technical Paper Presentation On " " Submitted byDeepak Satpathy0% (1)
- Why Turbo Super Charger Is Used in Diesel LocomotiveDocument5 pagesWhy Turbo Super Charger Is Used in Diesel LocomotiveDrSumedha SarmaNo ratings yet
- Additional PowersDocument26 pagesAdditional Powerslollie9832No ratings yet
- Fabrication of Turbocharger For Two Wheeler: Ahir Nischal A, Sofia Ali A, Darshan S Shah, Sneh R PrajapatiDocument8 pagesFabrication of Turbocharger For Two Wheeler: Ahir Nischal A, Sofia Ali A, Darshan S Shah, Sneh R PrajapatiDeepak sutarNo ratings yet
- Fto TuningDocument6 pagesFto TuningghettoglamourdjNo ratings yet
- Fuel Economy DesignDocument4 pagesFuel Economy Designwabule lydiaNo ratings yet
- Supercharging: Superchargers & TurbochargersDocument11 pagesSupercharging: Superchargers & TurbochargersAkhil Here100% (1)
- Turbocharger and SuperchargerDocument16 pagesTurbocharger and SuperchargerPrajwal ZinjadeNo ratings yet
- Supercharger VS TurbochargerDocument25 pagesSupercharger VS TurbochargerAllen CastorNo ratings yet
- Pre Drive Authorization With Turbo On Demand (Air From Suspensor and Tank)Document6 pagesPre Drive Authorization With Turbo On Demand (Air From Suspensor and Tank)Leo BoyNo ratings yet
- Gas Vs DieselDocument6 pagesGas Vs DieselArlyn FernandoNo ratings yet
- Turbocharger Vs Supercharger 1Document25 pagesTurbocharger Vs Supercharger 1Vibhor Jain100% (1)
- Engine Science Its More Than Just Engine PartsDocument6 pagesEngine Science Its More Than Just Engine Partshsingh1990No ratings yet
- Supercharging and TurbochargingDocument23 pagesSupercharging and TurbochargingTrain Placement CellNo ratings yet
- BoosterPlug Fuel Injection BookDocument42 pagesBoosterPlug Fuel Injection BookRichard Leo MoroniNo ratings yet
- Ic Engine: Assignment#02Document9 pagesIc Engine: Assignment#02Jawad ZafarNo ratings yet
- TurbochargerDocument64 pagesTurbochargerAmanpreet Singh100% (23)
- Turbocharger 4Document18 pagesTurbocharger 4safwansd750% (2)
- Optimizing Generator RPM For Standby Power Generation White PaperDocument4 pagesOptimizing Generator RPM For Standby Power Generation White PaperTaimoor AhmedNo ratings yet
- Supercharger ReportDocument24 pagesSupercharger ReportRohit RajNo ratings yet
- Feasibility StudyDocument17 pagesFeasibility StudyAnonymous 8jq5jBZjNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 2markDocument4 pagesUnit 3 2markNIKASH maniNo ratings yet
- Petrol Engine vs. Diesel EngineDocument12 pagesPetrol Engine vs. Diesel EngineGirish SahareNo ratings yet
- Hybrid Car: Test Drive: Regenerative Braking. The Electric Motor Applies Resistance To The Drivetrain CausingDocument2 pagesHybrid Car: Test Drive: Regenerative Braking. The Electric Motor Applies Resistance To The Drivetrain CausingKiru BaNo ratings yet
- What Is TurbochargerDocument7 pagesWhat Is TurbochargerKomarac DzemilNo ratings yet
- Torque and PowerDocument3 pagesTorque and Powertaha_eslamniaNo ratings yet
- How To Select A Turbocharger 0Document10 pagesHow To Select A Turbocharger 0heideNo ratings yet
- Truck Spec Training BookletDocument39 pagesTruck Spec Training BookletMark Mach AllenNo ratings yet
- Researchpaper 2016Document7 pagesResearchpaper 2016Aditya YadavNo ratings yet
- Turbo Charger LectureDocument6 pagesTurbo Charger LectureAbdelrhman Essam AttiaNo ratings yet
- 1977 Batavus ManualDocument32 pages1977 Batavus ManualRyan FulmerNo ratings yet
- Lombardini Superfocs Fuel SystemDocument3 pagesLombardini Superfocs Fuel SystemD.CORNEILLENo ratings yet
- Agricultural Power and Machinery - DCSuministrado - QUESTIONS 2011Document4 pagesAgricultural Power and Machinery - DCSuministrado - QUESTIONS 2011Gladys Ruth Paypa100% (3)
- Brief Petronas K200 Go Karts InfoDocument6 pagesBrief Petronas K200 Go Karts InfoAiddie GhazlanNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics of Internal Combustion EnginesDocument6 pagesFluid Mechanics of Internal Combustion EnginesJuan CarlosNo ratings yet
- Compresor Tu-Flo 501 Info Servicio PDFDocument36 pagesCompresor Tu-Flo 501 Info Servicio PDFroyert80No ratings yet
- Empty, Fill AdBlue TankDocument3 pagesEmpty, Fill AdBlue TankManuel Gutierrez UrzuaNo ratings yet
- Shop Manual Supplement Komatsu PC400 6, PC400LC 6, PC450 6, PC450LCDocument38 pagesShop Manual Supplement Komatsu PC400 6, PC400LC 6, PC450 6, PC450LCMilad Rahimi100% (2)
- Fault Detection and DiagnosisDocument20 pagesFault Detection and DiagnosisjudarangocaNo ratings yet
- WILLIUM H Automotive BookDocument435 pagesWILLIUM H Automotive Bookrahul jainNo ratings yet
- 3d PDF Demo PDFDocument1 page3d PDF Demo PDFsatishasdNo ratings yet
- R44 Service LettersDocument2 pagesR44 Service LettersNickNo ratings yet
- CATMX1301Document860 pagesCATMX1301renatoNo ratings yet
- Catalogo MahleDocument44 pagesCatalogo MahlejavierNo ratings yet
- AE86 Levin-TruenoDocument1 pageAE86 Levin-TruenoToshiba PortegeNo ratings yet
- Fuel Saving Vehicle ModificationsDocument131 pagesFuel Saving Vehicle Modificationssheila_diane100% (2)
- Title Dimensional Drawing For Engine 12M26 Drawing NODocument8 pagesTitle Dimensional Drawing For Engine 12M26 Drawing NOBắc Nhật100% (1)
- CS 140 - Instrukcja Obsługi - ENDocument48 pagesCS 140 - Instrukcja Obsługi - ENagapitplNo ratings yet
- Ashok Leyland 6DTI Engine Service ManualDocument20 pagesAshok Leyland 6DTI Engine Service ManualFLORES SANTIAGO CESAR MIGUELNo ratings yet
- ICE RevisionDocument4 pagesICE RevisionjehadyamNo ratings yet
- Kebijakan Dan Harga MigasDocument21 pagesKebijakan Dan Harga MigasLuki LukmanNo ratings yet
- Siemens Injector Test Data New6 PDFDocument20 pagesSiemens Injector Test Data New6 PDFJose HasinNo ratings yet
- D2876 Tga e NeuDocument208 pagesD2876 Tga e NeuDragos hirniaNo ratings yet
- Welcome How To Use This Catalogue: Ultimate Jaguar Parts SpecialistDocument114 pagesWelcome How To Use This Catalogue: Ultimate Jaguar Parts SpecialistVILARNo ratings yet
- NGH 38Document6 pagesNGH 38Jose Angel Guitart GonzalezNo ratings yet