Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SCIENCE 7 REVIEWER Prefinal
SCIENCE 7 REVIEWER Prefinal
Uploaded by
Aine YahOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
SCIENCE 7 REVIEWER Prefinal
SCIENCE 7 REVIEWER Prefinal
Uploaded by
Aine YahCopyright:
Available Formats
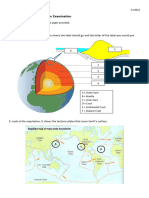
SCIENCE 7 REVIEWER MESOSPHERE – middle and coldest layer where meteors
burn up
GLOBE - a three-dimensional representation/model of THERMOSPHERE – hottest layer and where Aurora
the earth Borealis occur
EXOSPHERE – outermost layer where satellites are
*IMAGINARY LINES ON THE GLOBE* stationed
LATITUDE – imaginary horizontal line that runs from east
to west GREENHOUSE EFFECT – process of trapping the heat by
LONGITUDE – imaginary vertical line that runs from north the greenhouse gases keeping the temperature of the
to south earth warm
PRIME MERIDIAN – an imaginary line that divides the GREENHOUSE GASES – they have the ability to absorb
earth into eastern (right) and western (left) hemispheres and trap the heat (carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous
at 00 longitude oxide, water vapor and ozone)
GLOBAL WARMING - the gradual increase in temperature
*SPECIAL LATITUDES* of the earth
EQUATOR – an imaginary line that divides the earth into
northern (above) and southern (below) hemispheres at 00 BREEZE - A localized wind experienced by those people
latitude living near a coastal area
TROPIC OF CANCER – lies at 23.50N latitude LAND BREEZE - formed when air moves from the land to
TROPIC OF CAPRICORN - lies at 23.50S latitude the sea
ARCTIC CIRCLE – lies at 66.50N latitude SEA BREEZE - formed when air moves from the sea to the
ANTARCTIC CIRCLE - lies at 66.50S latitude land
*Warm air rises, cool air sinks
TROPICAL ZONE – located between the Tropic of Cancer *Wind moves from an area with high pressure to an area
and Capricorn. with low pressure
TEMPERATE ZONE – between the Tropic of Cancer and MONSOON - seasonal wind of the Indian Ocean and
Arctic Circle and between Tropic of Capricorn and Southern Asia, blowing from the southwest in summer
Antarctic Circle which experiences the 4 types of seasons and from the northeast in winter
– winter, spring, summer and fall AMIHAN – (Northeast Monsoon) - draws "cold, dry air"
POLAR ZONE – between the Arctic Circle and North Pole from Siberia, China, and Japan, from October to March
and between Antarctic Circle and South Pole, HABAGAT – (Southwest Monsoon) – brings hot humid
characterized by very cold climate weather experienced from July to September
TROPICAL CLIMATE – characterized by abundant rainfall,
high humidity and high temperature
ITCZ – INTERTROPICAL CONVERGENCE ZONE - lies in the
equatorial trough where the southwest and northeast
trade winds converge or meet.
RENEWABLE RESOURCES – resources that can grow again
or can be replaced after it is consumed. *FACTORS AFFECTING THE SEASONS*
Examples: water, solar radiation, plants, animals and wind tilt of the Earth’s axis (23.5 degrees)
NON-RENEWABLE RESOURCES - resources that cannot be revolution of the earth around the sun
replaced or may take a very long time to replace once length of daytime
consumed. JUNE– Northern hemisphere faces the sun-Summer:
Examples: soil, rocks and minerals, coal, petroleum, oil Southern hemisphere tilted away from the Sun-Winter
SUSTAINABILITY - the practice of using resources wisely DECEMBER – Southern hemisphere faces the sun-
so that future generations can benefit from them. Summer: Northern hemisphere tilted away from the Sun-
POLLUTION - the presence in the environment of a Winter
substance that has harmful or poisonous effects MARCH – equinox - equal day and night both
OVERFISHING - the removal of marine living resources to hemispheres: Northern hemisphere-Spring equinox;
levels that are too low for sustaining viable populations Southern hemisphere-Autumnal equinox
SEPTEMBER – equinox - equal day and night both
ATMOSPHERE – great mass of air that envelops the earth, hemispheres: Northern hemisphere-Autumnal equinox;
composed of 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, 1% argon and Southern hemisphere-Spring equinox
0.038% carbon dioxide and other gases. APHELION – the point of the Earth’s orbit from the Sun
TROPOSPHERE – lowest layer where weather occurs ECLIPSE - phenomenon occurs when there is partial or
STRATOSPHERE – where aircrafts fly and ozone layer is total blocking of light of one celestial object by another
Found SOLAR ECLIPSE – moon is between the Sun and Earth
*Ozone layer – made up of ozone which filters out most blocking the light from the Sun casting a shadow on the
of the sun’s UV radiation Earth
You might also like
- Final Exam 2014-QuestionDocument2 pagesFinal Exam 2014-QuestionPannhaa100% (2)
- Introduction To Geography of KarnatakaDocument48 pagesIntroduction To Geography of KarnatakaAnonymous zyWGXsxhd450% (2)
- Hydro Tsaka GeoDocument7 pagesHydro Tsaka GeoJohn Carlwin TagleNo ratings yet
- Long Test Reviewer in Science 7Document3 pagesLong Test Reviewer in Science 7iamzyryuNo ratings yet
- Climate and Global Systems Earth SciDocument6 pagesClimate and Global Systems Earth SciClarence DeitaNo ratings yet
- Bsed Major in Social StudiesDocument3 pagesBsed Major in Social Studiesgiadocallas24No ratings yet
- ELS ReviewerDocument10 pagesELS ReviewerJoaquin PayaoNo ratings yet
- Hydro AtmosphereDocument3 pagesHydro AtmosphereJohn Bryan De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Q4 Sci Exam ReviewersDocument3 pagesQ4 Sci Exam ReviewersDestine AvellanoNo ratings yet
- Climate ChangeDocument9 pagesClimate ChangeLeilaNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science - Atmosphere1Document61 pagesEnvironmental Science - Atmosphere1whether913No ratings yet
- Earth AstroDocument55 pagesEarth AstroBel Esguerra CabillonNo ratings yet
- Group 4 - Earth's Air PortionDocument35 pagesGroup 4 - Earth's Air PortionamorjulianadanielleNo ratings yet
- O Level Geography Notes Physical NotesDocument157 pagesO Level Geography Notes Physical NotesBrendon T100% (3)
- The Earth'S Atmosp Here: Joshua C DascoDocument20 pagesThe Earth'S Atmosp Here: Joshua C DascoWarren Leonardo BelgaNo ratings yet
- Big Bang TheoryDocument2 pagesBig Bang TheoryNene FortalejoNo ratings yet
- MathematicsDocument49 pagesMathematicsherryntonyNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Earths Characteristics and Its SubsystemDocument5 pagesModule 1 Earths Characteristics and Its SubsystemNicole LeriaNo ratings yet
- Atmosphere Solar Energy and ClimateDocument14 pagesAtmosphere Solar Energy and ClimateRoy MapingereNo ratings yet
- Week 21 Learning PacketDocument12 pagesWeek 21 Learning PacketAizel Nova AranezNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 HandoutsDocument3 pagesLesson 2 HandoutsHazel AlohaNo ratings yet
- Earth SciDocument9 pagesEarth SciChelsea AndreaNo ratings yet
- Interactions in The AtmosphereDocument5 pagesInteractions in The Atmospherekxilxx_whoNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - Earths SubsystemDocument25 pagesWeek 1 - Earths SubsystemDarwin ValdezNo ratings yet
- Geo 2 ReviewerDocument2 pagesGeo 2 ReviewerClifford ImsonNo ratings yet
- AtmosphereDocument12 pagesAtmospherelovemhiz431No ratings yet
- Earth and Life ScienceDocument9 pagesEarth and Life ScienceCris BabieraNo ratings yet
- University of PNG - Earth Sciences: The AtmosphereDocument36 pagesUniversity of PNG - Earth Sciences: The AtmosphereTenielleNo ratings yet
- Biophysical Environments: The AtmosphereDocument5 pagesBiophysical Environments: The AtmosphereAnanya UppalNo ratings yet
- Teacher Background: Earth'S Atmosphere: Layers of The AtmosphereDocument7 pagesTeacher Background: Earth'S Atmosphere: Layers of The AtmosphereIndhumathiNo ratings yet
- Chem Lab (Module 3)Document12 pagesChem Lab (Module 3)Erianne ReyesNo ratings yet
- 2 - Solar and Earth RadiationDocument7 pages2 - Solar and Earth RadiationErwin LudeveseNo ratings yet
- Pointers: Layers of The Earth's AtmosphereDocument4 pagesPointers: Layers of The Earth's AtmosphereMorTech JulietStore BatahoyNo ratings yet
- Hydro Chapter 3Document7 pagesHydro Chapter 3Roel SebastianNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer 4th QuarterDocument3 pagesScience Reviewer 4th Quarterrosalahmer24No ratings yet
- Reviewer in ScienceDocument2 pagesReviewer in ScienceMary JoyNo ratings yet
- Solar RadiationDocument4 pagesSolar RadiationVikram DasNo ratings yet
- Science 9 3RD Quarter ReviewerDocument11 pagesScience 9 3RD Quarter ReviewerJulienne Eila AlcartadoNo ratings yet
- AtmosphereDocument11 pagesAtmosphereQasim BokhariNo ratings yet
- Earth Sci ReviewerDocument7 pagesEarth Sci ReviewerSoysoy GalaxyNo ratings yet
- Atmosphere HandoutDocument82 pagesAtmosphere HandoutalyssaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01 The Earth's AtmosphereDocument34 pagesChapter 01 The Earth's Atmosphereannah piehNo ratings yet
- Geography Prelims: Biophysical InteractionsDocument2 pagesGeography Prelims: Biophysical InteractionsAnanya UppalNo ratings yet
- PHYSICAL SCIENCE FINALS Test 1Document3 pagesPHYSICAL SCIENCE FINALS Test 1Sunshine FrigillanaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of Atmosphere: Composition of Atmosphere Layers of Atmosphere Cloud Formation Types of CloudsDocument24 pagesChemistry of Atmosphere: Composition of Atmosphere Layers of Atmosphere Cloud Formation Types of CloudsJoshua PerezNo ratings yet
- Science 3.2Document3 pagesScience 3.2idio valensiaNo ratings yet
- Earth's Air and Water EnvironmentDocument18 pagesEarth's Air and Water Environmentkim paulo prejillanoNo ratings yet
- Module 1 (CCS)Document47 pagesModule 1 (CCS)nithya.a.sNo ratings yet
- Science Dictionary: Imus Institute of Science and TechnologyDocument16 pagesScience Dictionary: Imus Institute of Science and Technologydenise blaireNo ratings yet
- Weather and ClimateDocument24 pagesWeather and Climatedefinite ChibvongodzeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 345Document5 pagesLecture 345Thyrone Jay D RamirezNo ratings yet
- Earth SystemsDocument31 pagesEarth SystemsJoshua DavidNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science CutieDocument9 pagesEarth and Life Science CutieHeeseung SimpNo ratings yet
- Weather and ClimateDocument9 pagesWeather and ClimateI'am PhilNo ratings yet
- REVIEW Q4 Grade 7Document17 pagesREVIEW Q4 Grade 7CrimsonuuNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer Layer of The AtmosphereDocument6 pagesScience Reviewer Layer of The AtmosphereJeomari Dela rosaNo ratings yet
- Geography ReviewerDocument4 pagesGeography ReviewerAbet Barile100% (2)
- The Composition of The Earth's AtmosphereDocument81 pagesThe Composition of The Earth's AtmosphereChristie Joy BuctonNo ratings yet
- The Solar System and The Earth: By: Chrizza May SabarreDocument36 pagesThe Solar System and The Earth: By: Chrizza May SabarreLulu BritanniaNo ratings yet
- Structure of The AtmosphereDocument2 pagesStructure of The AtmosphereIlham Husain BhatNo ratings yet
- Hydrology Class 01 31 2023Document3 pagesHydrology Class 01 31 2023Kamii Ryu DumpNo ratings yet
- Hydro GraphDocument2 pagesHydro GraphWilliam WongNo ratings yet
- Flood Vulnerability Assessment Using Geospatial Techniques: Chennai, IndiaDocument13 pagesFlood Vulnerability Assessment Using Geospatial Techniques: Chennai, IndiaprabhuNo ratings yet
- Slave Point FormationDocument2 pagesSlave Point FormationHeikkiNo ratings yet
- The Mediterranean A Biodiversity Hotspot Under ThreatDocument16 pagesThe Mediterranean A Biodiversity Hotspot Under ThreatMarko ĆaletaNo ratings yet
- Pengaruh Perambatan Hutan Terhadap Aspek Hidrologi.: AbstractDocument7 pagesPengaruh Perambatan Hutan Terhadap Aspek Hidrologi.: AbstractSalsa kimNo ratings yet
- Mr. Adryan J. ValiaoDocument60 pagesMr. Adryan J. ValiaoBenj Jamieson Duag100% (1)
- Netherlands Offshore F3 Block - CompleteDocument5 pagesNetherlands Offshore F3 Block - CompleteTumpal B NainggolanNo ratings yet
- 02 Green Skills II Revision NotesDocument4 pages02 Green Skills II Revision Notesadityasharma6261srNo ratings yet
- Basin Hydrogeology StudyDocument58 pagesBasin Hydrogeology Study2304480No ratings yet
- 018 PlanktonDocument38 pages018 PlanktonAijaz AliNo ratings yet
- Super Volcano Listening Quiz-230303Document2 pagesSuper Volcano Listening Quiz-230303Анастасія РубанNo ratings yet
- Deltas Reservoir System SLIDES MEDCO 2006Document43 pagesDeltas Reservoir System SLIDES MEDCO 2006Te Siem Bro LayukaNo ratings yet
- Our Sustainability Commitment For 2030 - L'Oréal For The FutureDocument9 pagesOur Sustainability Commitment For 2030 - L'Oréal For The FutureChau AnhNo ratings yet
- Santorini 1Document31 pagesSantorini 1Miki Mihaela100% (2)
- Unit IV Environmental PollutionDocument72 pagesUnit IV Environmental PollutionAvaneeshNo ratings yet
- Educ 520 - Interdisciplinary Unit PlanDocument9 pagesEduc 520 - Interdisciplinary Unit Planapi-281427494No ratings yet
- Year 9 Geography End of Year Examination H 2012Document4 pagesYear 9 Geography End of Year Examination H 2012kamrunnisaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Geography Form 3&4Document263 pagesUnderstanding Geography Form 3&4JOHN100% (2)
- Salty Matters: Silica Mobility and Replaced Evaporites: 2 - Replaced Caso4Document17 pagesSalty Matters: Silica Mobility and Replaced Evaporites: 2 - Replaced Caso4PauloNo ratings yet
- Fractured Basement ReservoirDocument1 pageFractured Basement ReservoirGrida ViantiskaNo ratings yet
- Aquifer TestDocument152 pagesAquifer TestHaychiNo ratings yet
- Snoqualmie Valley Flooding BookletDocument14 pagesSnoqualmie Valley Flooding BookletJeremy WestlakeNo ratings yet
- Dam Break Assessment PDFDocument41 pagesDam Break Assessment PDFrajesh005100% (1)
- Report TacheometryDocument11 pagesReport Tacheometryhibby_tomey33% (3)
- Esc-Formation of EarthDocument33 pagesEsc-Formation of Earthapi-219086016No ratings yet
- Massie1976 3Document183 pagesMassie1976 3Harun CingozNo ratings yet
- Geo 9 Ch5 Natural Vegetation and Wildlife NotesDocument7 pagesGeo 9 Ch5 Natural Vegetation and Wildlife NotesAahaan KhatriNo ratings yet
- Lesson 9 ClimateDocument30 pagesLesson 9 ClimateBelle JariolneNo ratings yet