Professional Documents
Culture Documents
KidneysRole in Homeostasis
KidneysRole in Homeostasis
Uploaded by
Krizie Ann FernandoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
KidneysRole in Homeostasis
KidneysRole in Homeostasis
Uploaded by
Krizie Ann FernandoCopyright:
Available Formats
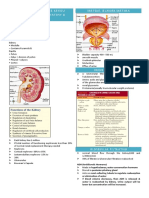
Calcitrol: activates
Vitamin D
Antidiuretic hormone
(ADH): vasopressin
Erythropoietin: maintain Adjust blood volume by Hydrogen Ion Excretion: the alteration of certain
normal red blood cell count conserving amino acids in the renal tubeles results in a
or eliminating water in urine diffusion of ammonia into the kidneys where it
Parathyroid picks up excess hydrogen ions and is excreted as
Production ammonium
Hormone (PTH)
of Regulation of
Hormones Blood Volume
Bicarbonate Formation: Phosphate
Aldosterone: Regulation of becomes acidic and extra hydrogen ions
renin-angiotensin- Acid-Base Balance are excreted in the urine
aldosterone
system
Bicarbonate Reabsorption: the kidney restore
Kidney's bicarbonate by releasing hydrogen ions and
Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP): Role in Homeostasis holding bicarbonate ions
inhibits reabsorption of Na+ and
water
Potassium: Maintain membrane
Regulation of potential of nerves and muscles
Hypertension:
Blood Pressure
1. Peripheral vasodilation
2. Diuresis (increase urine output) Regulation of Magnesium: Important for normal
3. Natriuresis (increase excretion Electrolyte neuromuscular activity
Na+ in urine) & Mineral
Balance
Hypotension: increase Calcium: Important for bone density,
renin blood clotting, neurotransmitter release
1. Peripheral Metabolic Waste
vasoconstricrion Excretion
2. Decrease urine Sodium & Chloride: Influence
formation movement of water and impacts blood
3. Increase cardiac volume and blood pressure
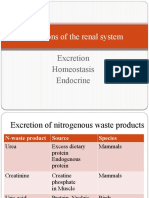
output Urea: when protein Creatinine: an indicator of kidney
4. Increase blood is broken function.
volume down, the end A rise in plasma creatinine is usually Phosphorus: Important buffer of
product is urea indicative of renal dysfunction hydrogen in body fluid and urine
Submitted by: Krizie Ann Atienza
You might also like
- Chronic Kidney Disease Pathophysiology Schematic DiagramDocument3 pagesChronic Kidney Disease Pathophysiology Schematic Diagramnursing concept maps100% (5)
- 3 HAGenBio - 1stterm - 20182019 - LAB3 - CENTRAL DOGMADocument4 pages3 HAGenBio - 1stterm - 20182019 - LAB3 - CENTRAL DOGMAJulius GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Vol 20 1 PossessionDocument10 pagesVol 20 1 PossessionMichel SilvaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysilogy of Primary HypertensionDocument1 pagePathophysilogy of Primary Hypertensionromeo rivera75% (4)
- Pathophysiology - ESRDDocument5 pagesPathophysiology - ESRDheiyu100% (3)
- Acute Kidney Injury Concept MapDocument1 pageAcute Kidney Injury Concept MapKEn PilapilNo ratings yet
- Diuretics - AMBOSS PDFDocument9 pagesDiuretics - AMBOSS PDFOpio Isaac100% (1)
- RBC Components O Carrying Adaptation To Low Arterial O Content O TissueDocument2 pagesRBC Components O Carrying Adaptation To Low Arterial O Content O TissueKristel AbeNo ratings yet
- PathophyDocument1 pagePathophyJhe Zelle CabacunganNo ratings yet
- Dietary Management - Renal DisordersDocument8 pagesDietary Management - Renal DisordersReanne Mae AbreraNo ratings yet
- Control of Peripheral CirculationBDocument3 pagesControl of Peripheral CirculationBlengliaoNo ratings yet
- Week12 13 RENAL PhysiologyDocument41 pagesWeek12 13 RENAL Physiologyirwan kastellaNo ratings yet
- Electrolyte - Water BalanceDocument5 pagesElectrolyte - Water BalancechrisibinuNo ratings yet
- 3 AntihypertensiveDocument33 pages3 AntihypertensiveJericho De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- AntihypertensionDocument17 pagesAntihypertension백지원 (소네트리)No ratings yet
- CC1 NPNDocument2 pagesCC1 NPNElijah Mae MundocNo ratings yet
- Urinary System: - Ridho IslamieDocument27 pagesUrinary System: - Ridho IslamieLaksmi DwiNo ratings yet
- Amylase, Lipase, LDH, Trop I (Tabulated)Document9 pagesAmylase, Lipase, LDH, Trop I (Tabulated)maja.amora.swuNo ratings yet
- Askep GGK Dan HDDocument44 pagesAskep GGK Dan HDRachMa Soeneng VyanpyolNo ratings yet
- Drugsaffecting GIsystemDocument12 pagesDrugsaffecting GIsystemJanine mae MacaraigNo ratings yet
- 2 - Concept Map 4Document4 pages2 - Concept Map 4keshav singhNo ratings yet
- ELECTROLYTES EditedDocument6 pagesELECTROLYTES EditedKrystel Bea DinqueNo ratings yet
- Heart 3Document25 pagesHeart 3migas1996No ratings yet
- Antihypertensive AgentsDocument97 pagesAntihypertensive AgentsL2 - MAKILALA, Zion joy B.No ratings yet
- Functions of The Renal SystemDocument30 pagesFunctions of The Renal SystemBlessing ChirwaNo ratings yet
- Perioperative Care Acid Base ElectrolytesDocument7 pagesPerioperative Care Acid Base ElectrolytesIlyas HarunNo ratings yet
- By: Yzobelle RedondoDocument4 pagesBy: Yzobelle RedondoArabelle GONo ratings yet
- Liver CirrhosisDocument1 pageLiver CirrhosisJAMES PATRICK MONTEMAYORNo ratings yet
- 2long Term Regulation of Blood PressureDocument21 pages2long Term Regulation of Blood PressureamrendraNo ratings yet
- Intranscellular Fluid Interstitial Fluid Transcellular FluidDocument19 pagesIntranscellular Fluid Interstitial Fluid Transcellular FluidCharish Dwayne Bautista PondalesNo ratings yet
- Renal Pharma 3Document14 pagesRenal Pharma 3Pranjali WeladiNo ratings yet
- CC - DAY 5 - PRE-TEST RationalizationDocument23 pagesCC - DAY 5 - PRE-TEST RationalizationVincent AmitNo ratings yet
- Perlis CRF Renal ReplacementDocument65 pagesPerlis CRF Renal ReplacementFikri SeptianNo ratings yet
- Water Follows Sodium (Via OsmoticDocument3 pagesWater Follows Sodium (Via OsmoticMark Vincent SahagunNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology OF Anti-Hypertensive: Siti SyarifahDocument38 pagesPharmacology OF Anti-Hypertensive: Siti SyarifahAnnurul Badry IINo ratings yet
- Uri - S4Document1 pageUri - S4Ghasaq F. KareemNo ratings yet
- Presentation I PC II RENALDocument58 pagesPresentation I PC II RENALSuhayb CumarNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology: Ms. Gelianne Alba-Loquez, RNDocument6 pagesPharmacology: Ms. Gelianne Alba-Loquez, RNjulinka beyla yansonNo ratings yet
- Electrolytes LecDocument4 pagesElectrolytes LecMichelle San Miguel FeguroNo ratings yet
- Principles of Dialysis: Diffusion, Convection, and Dialysis MachinesDocument3 pagesPrinciples of Dialysis: Diffusion, Convection, and Dialysis MachinesDenisa Carmen ColiofNo ratings yet
- Kidneys BiochemistryDocument53 pagesKidneys BiochemistryMi PatelNo ratings yet
- 3.3 KidneyDocument54 pages3.3 KidneySurvin KandhariNo ratings yet
- University of San CarlosDocument2 pagesUniversity of San CarlosAnton RossiniNo ratings yet
- Pcol MidtermsDocument25 pagesPcol MidtermsnoyaNo ratings yet
- Electrolyte 1Document8 pagesElectrolyte 1Ylooner QuitsNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Acute Renal FailureDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Acute Renal FailureAina HaravataNo ratings yet
- Urinary Sys@completeDocument48 pagesUrinary Sys@completeGhina MengalNo ratings yet
- Mekanisme Dari Blood Pressure Regulation 1. Hemodynamic Factors (CO, TPR, Etc)Document9 pagesMekanisme Dari Blood Pressure Regulation 1. Hemodynamic Factors (CO, TPR, Etc)Caroline AgathaNo ratings yet
- PhysiologyDocument15 pagesPhysiologyrefsq ahkNo ratings yet
- 2023 - 01 - 23 1 - 17 PM Office LensDocument6 pages2023 - 01 - 23 1 - 17 PM Office LensKUMAR SUMITNo ratings yet
- Feedback Mechanisms Stimulus Receptor Control Center Effector ResponseDocument1 pageFeedback Mechanisms Stimulus Receptor Control Center Effector ResponsekimNo ratings yet
- Urinary System: Quick Review Review of Urinary Anatomy & Physiology Ureters, Bladder, UrethraDocument6 pagesUrinary System: Quick Review Review of Urinary Anatomy & Physiology Ureters, Bladder, UrethraLongyapon Sheena StephanieNo ratings yet
- Kuliah Mineral 2015-2016Document20 pagesKuliah Mineral 2015-2016molenNo ratings yet
- Chronic Renal Failure 2Document66 pagesChronic Renal Failure 2Octaviani ElparesiNo ratings yet
- Esrd Diagram PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesEsrd Diagram PathophysiologySTEPHANIE JOSUE100% (1)
- Kelompok Bhs Inggrtios .Id - enDocument16 pagesKelompok Bhs Inggrtios .Id - enAgustinusNo ratings yet
- Dietary RequirementsDocument7 pagesDietary RequirementsdadaksaNo ratings yet
- 0764 Group 1 Magallanes, Maricris Manuel, Einna Milo, Juna Mogamog, Trisha Nacion, KaelaDocument5 pages0764 Group 1 Magallanes, Maricris Manuel, Einna Milo, Juna Mogamog, Trisha Nacion, KaelaCarrie Joy DecalanNo ratings yet
- Clinical Chemistry 1-Nonprotein Nitrogenous (NPN) CompoundsDocument12 pagesClinical Chemistry 1-Nonprotein Nitrogenous (NPN) CompoundsGeorge Carr PlazaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Body Fluids, Water-Salt and Acid-Base BalanceDocument69 pagesChapter 6 Body Fluids, Water-Salt and Acid-Base Balancefatin harrisNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis: Maintenance of The Constancy of The Internal Environment of The BodyDocument26 pagesHomeostasis: Maintenance of The Constancy of The Internal Environment of The BodyBrandy BishopNo ratings yet
- Arcadia Reptile 2018Document32 pagesArcadia Reptile 2018marianpcbNo ratings yet
- NITROSAMINESDocument10 pagesNITROSAMINESRicha Arora100% (1)
- 3E Birthright - FeatsDocument10 pages3E Birthright - Featstanelorn266100% (2)
- Marriage Astrology - Manglik Astrology - What Is Mangal DoshaDocument10 pagesMarriage Astrology - Manglik Astrology - What Is Mangal DoshaSri VaishaliniNo ratings yet
- Cucurbitaceae FamilyDocument1 pageCucurbitaceae FamilyMark Emriel ParlanNo ratings yet
- Quality Control of Sterile ProductsDocument21 pagesQuality Control of Sterile Productskunasahu1100% (3)
- Ginantara Ecoturism MangroveDocument12 pagesGinantara Ecoturism MangroveC2-89Henricus Rotarius Octavianus TariganNo ratings yet
- Apg 1Document13 pagesApg 1Manu MohamedNo ratings yet
- Faces of Biophilia in Contemporary TurkishDocument108 pagesFaces of Biophilia in Contemporary TurkishBuse AslanNo ratings yet
- The Biology and Role of CD44 in Cancer Progression: Therapeutic ImplicationsDocument23 pagesThe Biology and Role of CD44 in Cancer Progression: Therapeutic ImplicationsZihao WuNo ratings yet
- NEET FTS 2024 PlannerDocument1 pageNEET FTS 2024 Plannerrapidrai81No ratings yet
- Lab 2Document8 pagesLab 2alyssa cambaNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Medical Science I Final Report (Proteomic & BSL)Document12 pagesFundamental Medical Science I Final Report (Proteomic & BSL)Vivian VallenciaNo ratings yet
- Timber Press Spring 2016 CatalogDocument76 pagesTimber Press Spring 2016 CatalogTimber Press100% (2)
- Specimen Collection and ProcessingDocument7 pagesSpecimen Collection and ProcessingJangHanbyul100% (1)
- 1st Quarterly Exam in Personal Development Sy 2019 2020 Answer KeyDocument4 pages1st Quarterly Exam in Personal Development Sy 2019 2020 Answer KeyJerixan Portes100% (1)
- Cilia 2018Document1 pageCilia 2018Anna Beatriz Silva EspindolaNo ratings yet
- Integral City 2.0 Online Conference Proceedings: Executive SummaryDocument3 pagesIntegral City 2.0 Online Conference Proceedings: Executive SummaryMarilyn HamiltonNo ratings yet
- The API 2000 LC/MS/MS SystemDocument4 pagesThe API 2000 LC/MS/MS Systemdangerous0No ratings yet
- Vaginal CytologyDocument4 pagesVaginal Cytologyابراهيم عبدالله100% (1)
- Lembar Soal: Penilaian Tengah SemesterDocument6 pagesLembar Soal: Penilaian Tengah Semesterkholilur Rohman ZaenNo ratings yet
- Questions 19Document2 pagesQuestions 19rona hegarnaNo ratings yet
- Nature - Neuro2001 - Genetics With Cover Page v2Document7 pagesNature - Neuro2001 - Genetics With Cover Page v2raghadNo ratings yet
- The Magic Kingdom CompendiumDocument48 pagesThe Magic Kingdom Compendiumlorrnem100% (1)
- Philsci Questionnaire FinalDocument15 pagesPhilsci Questionnaire Finalandrea dyanne AzoresNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1 Introduction To Food Microbiology MicrobiologyDocument20 pagesUNIT 1 Introduction To Food Microbiology MicrobiologyHarsh DwivediNo ratings yet
- Webinar EU Medical Device Regulation Jun 28 2017 v2Document42 pagesWebinar EU Medical Device Regulation Jun 28 2017 v2Thulasi VasudevanNo ratings yet