Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Anova Final
Anova Final
Uploaded by
Hazelle CarpioOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Anova Final
Anova Final
Uploaded by
Hazelle CarpioCopyright:
Available Formats
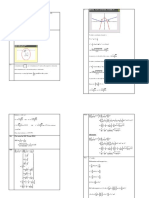
Light Sample Size Mean Sum of Squares Between Sum of Squares Within
Condition Question (ni) (xi_bar) Groups (SSB) Groups (SSW)
SSB_red_light = SSW_red_light =
Red Light Q1 3 2.5 1.791666667 0.1666666667
Red Light Q2 3 1.5
Red Light Q3 3 0.875
Red Light Q4 3 2
Red Light Q5 3 3
Red Light Q6 3 3
Red Light Q7 3 3
Red Light Q8 3 3
SSW_no_light =
No Light Q1 3 1.25 SSB_no_light = 1.069444444 0.2083333333
No Light Q2 3 2
No Light Q3 3 0
No Light Q4 3 1
No Light Q5 3 2
No Light Q6 3 1
No Light Q7 3 1
No Light Q8 3 1.666666667
SSB_orange_light = SSW_orange_light =
Orange Light Q1 3 0.25 0.7013888889 0.0694444444
Orange Light Q2 3 2
Orange Light Q3 3 1.25
Orange Light Q4 3 1.333333333
Orange Light Q5 3 1
Orange Light Q6 3 1
Orange Light Q7 3 1.333333333
Orange Light Q8 3 1
Null hypothesis (H0): The means of the different light conditions for each question are equal.
Alternative hypothesis (Ha): The means of the different light conditions for at least one question are not
equal.
To test the hypotheses, we perform an F-test using the calculated values of SSB and SSW. The F-statistic
is calculated as:
F = (SSB / (k - 1)) / (SSW / (N – k
First, we need to calculate the degrees of freedom for the numerator (dfn) and the denominator (dfd)
for the F-distribution.
The degrees of freedom for the numerator (dfn) is equal to the number of groups minus 1.
dfn = k - 1
The degrees of freedom for the denominator (dfd) is equal to the total number of observations minus
the number of groups.
dfd = N - k
In our case, we have three groups (Red Light, No Light, and Orange Light) and a total of 24 observations.
dfn = 3 - 1 = 2
dfd = 24 - 3 = 21
Next, we calculate the mean sum of squares between groups (MSB) and the mean sum of squares within
groups (MSW).
MSB = SSB / dfn
MSW = SSW / dfd
For Red Light:
MSB_red_light = 1.791666667 / 2
MSW_red_light = 0.1666666667 / 21
For No Light:
MSB_no_light = 1.069444444 / 2
MSW_no_light = 0.2083333333 / 21
For Orange Light:
MSB_orange_light = 0.7013888889 / 2
MSW_orange_light = 0.0694444444 / 21
Now, we calculate the F-statistic:
F_red_light = MSB_red_light / MSW_red_light
F_no_light = MSB_no_light / MSW_no_light
F_orange_light = MSB_orange_light / MSW_orange_light
Finally, we compare the calculated F-statistic with the critical F-value at α = 0.05 and determine if we
reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis.
The critical F-value for α = 0.05 with dfn = 2 and dfd = 21 is approximately 3.49 (from the F-distribution
table).
Comparing the F-statistics:
If F_red_light > 3.49, we reject the null hypothesis for the Red Light group.
If F_no_light > 3.49, we reject the null hypothesis for the No Light group.
If F_orange_light > 3.49, we reject the null hypothesis for the Orange Light group.
Dichotomy
Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 Q5 Q6 Q7 Q8 Q9 Total
Red Light 6 0 3 3 0 3 1 3 2 19
No Light 3 2 2 3 0 3 1 3 2 19
Orange Light 1 1 3 1 1 2 1 1 1 12
Total 10 3 8 7 1 8 3 7 5 50
Grand Mean (Xbar) 2 2 2.66 2.33 0.33 2.66 1.33 2.33 1.66 2
Sum of Squares (SS) Degrees of Freedom (df) Mean Square (MS)
Between 30.66 2 15.33
Within 58.33 27 2.16
Total 88 29 -
F-statistic Critical F-value (α=0.05)
7.10 3.36
Hypotheses:
H0 (Null Hypothesis): The means are equal for all light conditions and questions.
Ha (Alternative Hypothesis): At least one mean is different for the light conditions and questions.
Since the calculated F-statistic (7.10) is greater than the critical F-value (3.36) at a significance level of
α=0.05, we reject the null hypothesis. This means that there is evidence to suggest that at least one
mean is different among the light conditions and questions.
You might also like
- 2016 SAJC H2 Maths Promo Exam (Solution)Document7 pages2016 SAJC H2 Maths Promo Exam (Solution)Vincent See100% (2)
- Mat 223 - Ch3-DeterminantsDocument43 pagesMat 223 - Ch3-DeterminantsSasikumar SekarNo ratings yet
- PHYF214 Exp 08 Grating Lab ReportDocument5 pagesPHYF214 Exp 08 Grating Lab ReportPragun nandaNo ratings yet
- Chem 101 Recit. Week 3 Ch5,7Document4 pagesChem 101 Recit. Week 3 Ch5,7Brad CabrielNo ratings yet
- New York City Department of Education NYC Results On The New York State 2006-2012 ELA Test (Grades 3-8) Citywide Summary Results For All StudentsDocument6 pagesNew York City Department of Education NYC Results On The New York State 2006-2012 ELA Test (Grades 3-8) Citywide Summary Results For All StudentsPatrick Sykes-CraigNo ratings yet
- 11exam#1 - Solution KeyDocument6 pages11exam#1 - Solution KeyTaylor DavisNo ratings yet
- Atomic Emission Spectra Write UpDocument9 pagesAtomic Emission Spectra Write UpebrohusainiNo ratings yet
- EE407 Lec 15 16 1Document67 pagesEE407 Lec 15 16 1singhhv21No ratings yet
- Lecture33 PDFDocument5 pagesLecture33 PDFAnkan GayenNo ratings yet
- MT 2 Exam 2005 - Answer KeyDocument8 pagesMT 2 Exam 2005 - Answer KeySamuel WongNo ratings yet
- The Method of Proton SecondsDocument30 pagesThe Method of Proton SecondsIan BeardsleyNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 SolDocument6 pagesAssignment 3 SolChuah Chian YeongNo ratings yet
- JEE Advanced 2016 Paper I SolutionDocument31 pagesJEE Advanced 2016 Paper I SolutionBINIDASMSNo ratings yet
- Verendia, Nichole Angelica J. - q2 Worksheet 1 (Genchem)Document5 pagesVerendia, Nichole Angelica J. - q2 Worksheet 1 (Genchem)Patty KrabbyNo ratings yet
- Final EM2 2021 Perm 1 VNov22Document14 pagesFinal EM2 2021 Perm 1 VNov22Il MulinaioNo ratings yet
- Unit Iv Design of ExperimentsDocument34 pagesUnit Iv Design of ExperimentsMathioli Senthil0% (1)
- Lecture 2Document11 pagesLecture 2hidanwfNo ratings yet
- 5.111 Exam 1 Practice PDFDocument9 pages5.111 Exam 1 Practice PDF15klaNo ratings yet
- Review of Nuclear Physics-I Review of Nuclear Physics-II: Rutherford's Model Protons, Neutrons, ElectronsDocument4 pagesReview of Nuclear Physics-I Review of Nuclear Physics-II: Rutherford's Model Protons, Neutrons, ElectronsFabio MiguelNo ratings yet
- An Approach: Proton-SecondsDocument60 pagesAn Approach: Proton-SecondsIan BeardsleyNo ratings yet
- Exa Eco II Reevaluacion 2013 Javi ENGLISH DEFINITIVO SOLUZIONIDocument3 pagesExa Eco II Reevaluacion 2013 Javi ENGLISH DEFINITIVO SOLUZIONIdamian camargoNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen SpectrumDocument12 pagesHydrogen SpectrumNurhadyatiNo ratings yet
- Areas and Quantiles of The Normal Distribution: Mean Standard DeviationDocument12 pagesAreas and Quantiles of The Normal Distribution: Mean Standard DeviationHeidy CoelloNo ratings yet
- ACJC JC2 H2 Maths 2012 Year End Exam Solutions Paper 1Document10 pagesACJC JC2 H2 Maths 2012 Year End Exam Solutions Paper 1ofji4oNo ratings yet
- Exam1 02A PDFDocument6 pagesExam1 02A PDFCrizaldo MempinNo ratings yet
- Operation Research - MTH601 Fall 2007 Assignment 04 SolutionDocument6 pagesOperation Research - MTH601 Fall 2007 Assignment 04 SolutionMARIA NINUNo ratings yet
- Topic6 ReadingDocument13 pagesTopic6 ReadingJeannetteNo ratings yet
- Practice Test 3 Current PDFDocument9 pagesPractice Test 3 Current PDFBabeejay2No ratings yet
- Related Through A 4RDocument8 pagesRelated Through A 4Ramitav_chak9523No ratings yet
- A 2D Electromagnetic Scattering Solver For MatlabDocument23 pagesA 2D Electromagnetic Scattering Solver For MatlabjalopeztNo ratings yet
- CLS ENG 23 24 XI Phy Target 1 Level 1 Chapter 1Document25 pagesCLS ENG 23 24 XI Phy Target 1 Level 1 Chapter 1sarthakyedlawar04No ratings yet
- Balanced Incomplete BlockDocument4 pagesBalanced Incomplete BlockItalo GranatoNo ratings yet
- YJC H1Maths 2013 Prelim SolnDocument8 pagesYJC H1Maths 2013 Prelim SolnAnonymous OOLcOxAVPNo ratings yet
- Large N Arnab RudraDocument38 pagesLarge N Arnab RudraYau Stein100% (2)
- ANOVA of Unequal Sample SizesDocument7 pagesANOVA of Unequal Sample SizesSHARMAINE CORPUZ MIRANDANo ratings yet
- CamScanner 12-26-2023 15.13Document29 pagesCamScanner 12-26-2023 15.13jpww6yr972No ratings yet
- Lec-8 Digital Signal Processing by ProakisDocument17 pagesLec-8 Digital Signal Processing by ProakisMuhammad AqilNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Categorical Data: Learning ObjectivesDocument34 pagesAnalysis of Categorical Data: Learning Objectives2oooveeeNo ratings yet
- Ecmock5 QueDocument24 pagesEcmock5 QueAmitKumarNo ratings yet
- IJSO 2007 - THEORY - Solution and Marking Scheme - FinalDocument9 pagesIJSO 2007 - THEORY - Solution and Marking Scheme - Finalalphamale173100% (3)
- JEE - MAIN - 2016 Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics CODE E (Solution) Part-A: PhysicsDocument36 pagesJEE - MAIN - 2016 Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics CODE E (Solution) Part-A: PhysicsSourabhNo ratings yet
- 1.6.2 RCBD (Hale) - Supp ReadingDocument13 pages1.6.2 RCBD (Hale) - Supp ReadingTeflon SlimNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ElectrostaticsDocument38 pagesIntroduction To ElectrostaticsRamon Lopez Lapiña100% (1)
- Analysis & Design of Algorithms (3466)Document4 pagesAnalysis & Design of Algorithms (3466)Tooba Hassan 364-FSS/BSIAA/F19No ratings yet
- 116 hw4Document6 pages116 hw4thermopolis3012No ratings yet
- Econometrics C18-S4 Group 5 - EDocument20 pagesEconometrics C18-S4 Group 5 - EParas Mani DhakalNo ratings yet
- Financial Econometrics and Modelling: Turkey, UsaDocument18 pagesFinancial Econometrics and Modelling: Turkey, Usaburievaasal14No ratings yet
- 3) S1 Representation and Summary of Data - DispersionDocument31 pages3) S1 Representation and Summary of Data - DispersionPrince YugNo ratings yet
- 4 Lecture of Operation Research 2: Primal-Dual Computations: Example No. 1Document7 pages4 Lecture of Operation Research 2: Primal-Dual Computations: Example No. 1jhdmssNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Variance (Anova) Part 2 Two-Way Anova ReplicationDocument18 pagesAnalysis of Variance (Anova) Part 2 Two-Way Anova ReplicationFarrukh JamilNo ratings yet
- Chapter6 AnalysisDocument33 pagesChapter6 AnalysisAmyra OropesaNo ratings yet
- Chpter 3-Simplex AlgorithmDocument34 pagesChpter 3-Simplex AlgorithmabdullaNo ratings yet
- 2014 H2 Maths Prelim Papers - RJC P1 Solution PDFDocument12 pages2014 H2 Maths Prelim Papers - RJC P1 Solution PDFcherylhzyNo ratings yet
- FAL (2022-23) CSE3002 ETH Reference Material II 29-Nov-2022 Examples On Mamdani FIS SystemDocument5 pagesFAL (2022-23) CSE3002 ETH Reference Material II 29-Nov-2022 Examples On Mamdani FIS SystemMani XhorNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 4B, Spring 2007: Question Page Points ScoreDocument8 pagesChemistry 4B, Spring 2007: Question Page Points ScoreatlalokNo ratings yet
- Skewed Normal Distribution of Return Assets in Call European Option PricingDocument12 pagesSkewed Normal Distribution of Return Assets in Call European Option PricinghendrikraharjoNo ratings yet
- Question Has Only One Correct Answer. in Case You Wish To Change An Answer, Erase The Old AnswerDocument3 pagesQuestion Has Only One Correct Answer. in Case You Wish To Change An Answer, Erase The Old AnswerDhananjay SinghNo ratings yet
- Ap2011 Solutions 06Document14 pagesAp2011 Solutions 06Sesario PratamaNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Physics 2015 Tutorial SolutionsDocument24 pagesNuclear Physics 2015 Tutorial SolutionsSwee Boon OngNo ratings yet
- CIATIP CH 2 CarpioDocument2 pagesCIATIP CH 2 CarpioHazelle CarpioNo ratings yet
- Lit Review in IO PSYCHDocument4 pagesLit Review in IO PSYCHHazelle CarpioNo ratings yet
- E.E Research PaperDocument16 pagesE.E Research PaperHazelle CarpioNo ratings yet
- Group 6Document72 pagesGroup 6Hazelle CarpioNo ratings yet
- Decision Making and Hypothesis Testing 1 PDFDocument40 pagesDecision Making and Hypothesis Testing 1 PDFKush Singh ChibberNo ratings yet
- General Considerations For Research WritingDocument8 pagesGeneral Considerations For Research WritinghatssyNo ratings yet
- QUARTER-PLAN-FOR-ONLINE-THAT-HAVE-NO-SHIFTING Mary Cris Presbitero FINALDocument4 pagesQUARTER-PLAN-FOR-ONLINE-THAT-HAVE-NO-SHIFTING Mary Cris Presbitero FINALMary CrisNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3.2 WILCOXON RANK SUM TESTDocument16 pagesChapter 3.2 WILCOXON RANK SUM TESTNurul Najwa FatihahNo ratings yet
- Ho - ANOVA ExampleDocument4 pagesHo - ANOVA ExampleIbne HameedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Methodology Rubric: Dissertation Title Author ReviewerDocument2 pagesChapter 3: Methodology Rubric: Dissertation Title Author ReviewerReii Saraga Sajulan100% (1)
- Data Collection ToolsDocument19 pagesData Collection ToolsMahmudulHasanHirokNo ratings yet
- Stat and Proba Module Week 1Document2 pagesStat and Proba Module Week 1Bernadeth MorgadoNo ratings yet
- 09.measurement and Scaling - Noncomparative Scaling Techniques PDFDocument30 pages09.measurement and Scaling - Noncomparative Scaling Techniques PDFGaurav SharmaNo ratings yet
- Educational MeasurementDocument3 pagesEducational MeasurementNiel NisperosNo ratings yet
- Z TestDocument39 pagesZ Testanmolgarg12950% (2)
- GovquotaDocument736 pagesGovquotaroh iniNo ratings yet
- Parenting Questionnaire-AlabamaDocument10 pagesParenting Questionnaire-AlabamaSterea GenovevaNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Learning 1 Unit 3 Topic 4 Item AnalysisDocument20 pagesAssessment of Learning 1 Unit 3 Topic 4 Item AnalysisRoxanne MendezNo ratings yet
- Marketing Research IntroductionDocument40 pagesMarketing Research IntroductionBalaji N100% (5)
- Analisis Kuantitatif PDFDocument10 pagesAnalisis Kuantitatif PDFSiti QamariaNo ratings yet
- 1430 Mbbsbdsfinalmeritlist201819 PDFDocument205 pages1430 Mbbsbdsfinalmeritlist201819 PDFVINEETH VinnuNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 Two Variable Regression Analysis Interval Estimation and Hypothesis TestingDocument36 pagesTopic 6 Two Variable Regression Analysis Interval Estimation and Hypothesis TestingOliver Tate-DuncanNo ratings yet
- Research MethodologyDocument58 pagesResearch MethodologyRab Nawaz100% (2)
- Assessment of BIM Implementation Among M PDFDocument9 pagesAssessment of BIM Implementation Among M PDFShafira & GeaNo ratings yet
- Business Research MCQsDocument20 pagesBusiness Research MCQsJay PatelNo ratings yet
- Nurul Adhiyanti Putri-10511244012Document109 pagesNurul Adhiyanti Putri-10511244012sd negeri 2 jojoNo ratings yet
- PE 4 ChecklistDocument1 pagePE 4 ChecklistMonique Eloise GualizaNo ratings yet
- Department of Applied Mathematics Chapter 5. Non-Parametric TestsDocument12 pagesDepartment of Applied Mathematics Chapter 5. Non-Parametric TestsArunkumarNo ratings yet
- SAP Prelim KeyDocument1 pageSAP Prelim Keymobile legendsNo ratings yet
- Quarter 4 Module 1 Test-of-HypothesisDocument26 pagesQuarter 4 Module 1 Test-of-HypothesisXiao ChenNo ratings yet
- Sr. No. Application No. Name of The Student Seat NoDocument24 pagesSr. No. Application No. Name of The Student Seat NoBhakti Nath MishraNo ratings yet
- Module II Research PlanDocument9 pagesModule II Research PlanDr Linda Mary SimonNo ratings yet
- Amity School of Business:, Semester IV Research Methodology and Report Preparation Dr. Deepa KapoorDocument23 pagesAmity School of Business:, Semester IV Research Methodology and Report Preparation Dr. Deepa KapoorMayank TayalNo ratings yet