Professional Documents
Culture Documents
F Four Types of Data Revised 5.10.17
F Four Types of Data Revised 5.10.17
Uploaded by
Abdulhafiz AbakemalOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
F Four Types of Data Revised 5.10.17
F Four Types of Data Revised 5.10.17
Uploaded by
Abdulhafiz AbakemalCopyright:
Available Formats
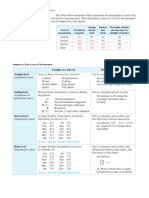
Four Types of Data
Nominal Ordinal Interval Ratio
What can we do
with these data?
Can we: Nominal Ordinal Interval Ratio
Add No No Yes Yes
Subtract No No Yes Yes
Multiply No No No Yes
Divide No No No Yes
Nominal Ordinal (Status) Interval Ratio (Growth)
Examples: Examples: Examples: Examples:
1 = Proficient 1. Percentile Rank (PR), 1. Year (A.D.) 1. Iowa Assessment National
2 = Non Proficient National Percentile Rank 2. Fahrenheit Standard Score (NSS)
(NPR), Iowa Percentile 3. Celsius 2. MAP - RIT Scores
1 = Females Rank (IPR), AEA CBM 4. Standard Scores 3. CBM/DIBELS/FAST - Raw
2 = Males Percentile Ranks (WJ, Stanford, Scores
2. Class Rank WIAT, IQ, etc) 4. Percent (percent correct,
3. Grade and Age percent on task, etc…)
Equivalents 5. Frequency, duration, etc…
4. BRI/DRA Scores raw scores
5. Rubric Scores 6. Lexile
6. Likert Scale Scores 7. Normal Curve Equivalents
(NCE)
Can Calculate: Can Calculate: Can Calculate: Can Calculate:
Mode Median and Mode Median and Mode Mean, Median and Mode
But we can:
Calculate number and percents within categories,
establish baselines and track data across years
Definitions:
Nominal – A scale of measurement in which numbers stand for names.
Ordinal – A way of measuring that ranks (puts them in an order) on some variable. The difference
between the ranks needs not be equal (unequal intervals between units of measure).
Interval – A scale or measurement that describes variables in such a way that the distance between
any two adjacent units of measure (or intervals) is the same, but in which there is no meaningful
zero point - can add and subtract.
Ratio – A measurement or scale in which any two adjoining values are the same distance apart and
in which there is a true zero point - can add, subtract, multiply and divide.
Resource provided by AEA 267 © 2014 Permission granted to educational organizations to copy and use http://www.aea267.k12.ia.us
You might also like
- Norms and UsesDocument4 pagesNorms and UsesDevshree DantaleNo ratings yet
- 4 Chapter 1 - Introduction To StatisticsDocument20 pages4 Chapter 1 - Introduction To StatisticsCharlie RNo ratings yet
- Scale of MeasurementDocument35 pagesScale of MeasurementRashmiNo ratings yet
- 01 - Introduction To StatisticsDocument38 pages01 - Introduction To StatisticsMUHAMMAD UMAR GURCHANINo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Review of Basic ConceptsDocument23 pagesChapter 1 Review of Basic ConceptsKookie ChimchimNo ratings yet
- 03 Basic Data Types LmsDocument17 pages03 Basic Data Types LmsRami HaidarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1. IntroductionDocument39 pagesChapter 1. IntroductionNasrima D. Macaraya100% (1)
- EES401-Quantitative Data Analysis in Earth and Environmental SciencesDocument12 pagesEES401-Quantitative Data Analysis in Earth and Environmental SciencesAkhil Ratan MishraNo ratings yet
- 5 Statistical AnalysisDocument8 pages5 Statistical AnalysisGetnet MollaNo ratings yet
- Gm103C Data-Analytics: 1. Basic ProbabilityDocument13 pagesGm103C Data-Analytics: 1. Basic ProbabilityRoshan JamesNo ratings yet
- Makalah Presentasi High Performance ConsultingDocument18 pagesMakalah Presentasi High Performance ConsultingDiana AgustikaNo ratings yet
- Basic Statistical ConceptsDocument28 pagesBasic Statistical ConceptsrolandNo ratings yet
- Ils 2Document2 pagesIls 2arrikate4No ratings yet
- KS3 Year 9 Maths 2022 1Document1 pageKS3 Year 9 Maths 2022 1vinodNo ratings yet
- Statistical Foundations - Intro 64zlfDocument86 pagesStatistical Foundations - Intro 64zlfmanda sridhar100% (1)
- Unit Plan Grade 8 UnitDocument26 pagesUnit Plan Grade 8 Unitapi-381868432No ratings yet
- 3 Sacles of MeasurementsDocument2 pages3 Sacles of Measurementsपशुपति नाथNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Review of Basic ConceptsDocument23 pagesChapter 1 Review of Basic ConceptsKookie ChimchimNo ratings yet
- 02 Ordinal DataDocument21 pages02 Ordinal DatamalekNo ratings yet
- Operational Foundation of StatisticsDocument59 pagesOperational Foundation of StatisticsA Y I E SNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Variables and Data TypesDocument26 pagesMeasurement of Variables and Data TypessureshNo ratings yet
- VPT2 Analysis Technique Presentation 10-26-16Document22 pagesVPT2 Analysis Technique Presentation 10-26-16bmack2150% (2)
- Chapter 2 Assembling of Statistical DataDocument14 pagesChapter 2 Assembling of Statistical Dataryzen rtxNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Maam KiranDocument51 pagesChapter 7 Maam KiranNeehan FatimaNo ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between OrdinalDocument3 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between Ordinalomar alimuddinNo ratings yet
- Session 6: Measurement Scale & Questionnaire DesignDocument76 pagesSession 6: Measurement Scale & Questionnaire DesignLi PerfectNo ratings yet
- Stat RevisionDocument23 pagesStat Revisiongamingleague777No ratings yet
- Lesson 2: Types of Measurements & Measurement of ScalesDocument4 pagesLesson 2: Types of Measurements & Measurement of ScalesMa'am Ferl GshsNo ratings yet
- Roadmap For A Statistical InvestigationDocument2 pagesRoadmap For A Statistical InvestigationAbhishekKumarNo ratings yet
- Nursing Research ModuleDocument3 pagesNursing Research ModuleRomeo RiveraNo ratings yet
- Topic-1 - STA 104 - 124Document61 pagesTopic-1 - STA 104 - 124Sheikh Mohammad ForhadNo ratings yet
- Use of Statistics in Our Daily Life: Example 1 Data Types (P 54)Document8 pagesUse of Statistics in Our Daily Life: Example 1 Data Types (P 54)KellyNo ratings yet
- Statistics: DerivationDocument17 pagesStatistics: DerivationRoMiecar ColipanoNo ratings yet
- WEEK 1 Data and SamplingDocument33 pagesWEEK 1 Data and SamplingkvelezNo ratings yet
- APznzaZnjmllHn4LwnCpKqtDHfEDYRRDJLBcTgtaHmz4xK78VQk6ztsT7ICAWo7n3B1cdF-AS_1kK2TFf2s6hWxyKaF9Le7ddjddmlJ1gq...vmRTMqjStk0N8V8Uw1rNS8npR8VhcqpJER_vjyaALG1_-QbpHe4l7JiOj-jNPzWy4ilbePCpFPtFlDu2oGUBBPWTq8DwZDvn4HDGPdc4492JYYEBkbBe9P2M0=Document49 pagesAPznzaZnjmllHn4LwnCpKqtDHfEDYRRDJLBcTgtaHmz4xK78VQk6ztsT7ICAWo7n3B1cdF-AS_1kK2TFf2s6hWxyKaF9Le7ddjddmlJ1gq...vmRTMqjStk0N8V8Uw1rNS8npR8VhcqpJER_vjyaALG1_-QbpHe4l7JiOj-jNPzWy4ilbePCpFPtFlDu2oGUBBPWTq8DwZDvn4HDGPdc4492JYYEBkbBe9P2M0=rakshita bansalNo ratings yet
- Level of MeasurementDocument11 pagesLevel of MeasurementAngel Marie CahanapNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Basic StatisticsDocument75 pagesChapter 2 - Basic StatisticsJake RunionsNo ratings yet
- Session 1 ISM May 2024Document59 pagesSession 1 ISM May 2024oishika.troisNo ratings yet
- Part 4 MeasurementDocument33 pagesPart 4 Measurementchaudharylalit025No ratings yet
- Ghulammurtaza - 2044 - 3780 - 1 - Chapter 6 The Measurement ScalesDocument34 pagesGhulammurtaza - 2044 - 3780 - 1 - Chapter 6 The Measurement ScalesUzair SoomroNo ratings yet
- Stat 1602 Chapter 1 NotesDocument3 pagesStat 1602 Chapter 1 Notes陈昊No ratings yet
- Chapter Ten & ElevenDocument19 pagesChapter Ten & ElevenaliNo ratings yet
- VariablesDocument2 pagesVariablesRuffy AbdulazisNo ratings yet
- PsychAssess 13 TableStatisticsDocument7 pagesPsychAssess 13 TableStatisticsMaricrise FernandezNo ratings yet
- Reeditedresearch Method ch05 Measurement and - Validity - Eng - mgl2Document48 pagesReeditedresearch Method ch05 Measurement and - Validity - Eng - mgl2Ганзориг МиксаресNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan 1 PDFDocument26 pagesPertemuan 1 PDFdhafi keceNo ratings yet
- 2 Some Important ConceptsDocument5 pages2 Some Important ConceptsGR FaisalNo ratings yet
- Scales of Measurement: Youtube Facebook: Researchcoachfb Linkedin Medium: Research-CoachDocument9 pagesScales of Measurement: Youtube Facebook: Researchcoachfb Linkedin Medium: Research-CoachFawad Latif100% (1)
- Apprentice Teaching: Lesson Plan Summary TemplateDocument6 pagesApprentice Teaching: Lesson Plan Summary Templateapi-538475699No ratings yet
- Module 7Document21 pagesModule 7Kashika AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Session-5 BRM PDFDocument13 pagesSession-5 BRM PDFKrishna AgarwalNo ratings yet
- SER (I) - 2015 - 2 - Measurement and ScalesDocument6 pagesSER (I) - 2015 - 2 - Measurement and ScalesAna Maria BorcanNo ratings yet
- Epi - Epidemiologic MeasuresDocument80 pagesEpi - Epidemiologic MeasuresTofik Mohammad MuseNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1-Statistics Introduction-Defining, Displaying and Summarizing DataDocument53 pagesLecture 1-Statistics Introduction-Defining, Displaying and Summarizing DataDstormNo ratings yet
- Levels of MeasurementDocument11 pagesLevels of MeasurementACCESS PHNo ratings yet
- OLIVO - Lesson-1-Statistics-Quiz (1)Document2 pagesOLIVO - Lesson-1-Statistics-Quiz (1)Christine Joy DañosNo ratings yet
- Module 1 StatisticsDocument6 pagesModule 1 StatisticsPhielle MarilenNo ratings yet
- NOIRDocument1 pageNOIRhombosa2h8No ratings yet
- Internship ReportDocument18 pagesInternship ReportAbdulhafiz AbakemalNo ratings yet
- Ch. 1 1Document19 pagesCh. 1 1Abdulhafiz AbakemalNo ratings yet
- Exploring The Challenges and Coping Strategies of Street ChildrenDocument23 pagesExploring The Challenges and Coping Strategies of Street ChildrenAbdulhafiz AbakemalNo ratings yet
- Haramaya UniversityDocument22 pagesHaramaya UniversityAbdulhafiz Abakemal90% (10)
- Welansa WegayehuDocument57 pagesWelansa WegayehuAbdulhafiz AbakemalNo ratings yet
- 5045 Nongmaithem Robindro Singh Biniam Kassa 350930Document20 pages5045 Nongmaithem Robindro Singh Biniam Kassa 350930Abdulhafiz AbakemalNo ratings yet
- Multi PageDocument136 pagesMulti PageAbdulhafiz AbakemalNo ratings yet
- Full Research Milk.Document26 pagesFull Research Milk.Abdulhafiz AbakemalNo ratings yet
- Ka So Teh A Proposal A WassaDocument30 pagesKa So Teh A Proposal A WassaAbdulhafiz AbakemalNo ratings yet
- GovernanceDocument19 pagesGovernanceAbdulhafiz AbakemalNo ratings yet
- Attachment of Trainees To Public Institutions For Practical TrainingDocument3 pagesAttachment of Trainees To Public Institutions For Practical TrainingAbdulhafiz AbakemalNo ratings yet
- Revised ESMSGDocument178 pagesRevised ESMSGAbdulhafiz AbakemalNo ratings yet
- Attachments: Appendix Viii Environment Assessment and Watershed ManagementDocument53 pagesAttachments: Appendix Viii Environment Assessment and Watershed ManagementAbdulhafiz AbakemalNo ratings yet
- Fundamental of Statistics Lecture-IDocument18 pagesFundamental of Statistics Lecture-IRahul SinghNo ratings yet
- Lesson4.2 Deciles and PercentileDocument9 pagesLesson4.2 Deciles and PercentileSmiley UyNo ratings yet
- Leadership Orientation Self AssessmentDocument3 pagesLeadership Orientation Self Assessmentapi-407234770No ratings yet
- Transportation Engineering - Lab ReportDocument14 pagesTransportation Engineering - Lab ReportlearnafrenNo ratings yet
- RED - Risk (Version 3.2)Document36 pagesRED - Risk (Version 3.2)gman444No ratings yet
- Q4 Mathematics 10 - Module 3Document21 pagesQ4 Mathematics 10 - Module 3txm4kb4h46100% (1)
- 1.1 Permutation and CombinationDocument54 pages1.1 Permutation and CombinationRovelyn delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 PDFDocument27 pagesChapter 3 PDFShiv NeelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - : Measures of VariabilityDocument6 pagesChapter 2 - : Measures of VariabilityWalid RahmanNo ratings yet
- DIAGNOSTIC TEST 2nd Sem g10Document6 pagesDIAGNOSTIC TEST 2nd Sem g10ericmilamattim67% (3)
- Percentile Quartile RankDocument22 pagesPercentile Quartile RankGaurav NikhilNo ratings yet
- Learning Area Grade Level Quarter Date I. Lesson Title Ii. Most Essential Learning Competencies (Melcs) Iii. Content/Core ContentDocument3 pagesLearning Area Grade Level Quarter Date I. Lesson Title Ii. Most Essential Learning Competencies (Melcs) Iii. Content/Core ContentCln byln0% (1)
- Class Test 1 Revision NotesDocument10 pagesClass Test 1 Revision NotesHarry KwongNo ratings yet
- Volume 2 - BBDocument355 pagesVolume 2 - BBavinashkives21No ratings yet
- Mathematics - Advance Algebra and Statistics Pre-Test: DirectionsDocument2 pagesMathematics - Advance Algebra and Statistics Pre-Test: DirectionsCessNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 WORKSHEET 2 Data HandlingDocument4 pagesGrade 12 WORKSHEET 2 Data Handlingmichael jonesNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 & 2 Slides - Biostatistics 2016Document46 pagesLecture 1 & 2 Slides - Biostatistics 2016merinbosco100% (1)
- Week 7 8Document22 pagesWeek 7 8Koko Yanne'No ratings yet
- 1 IntroductionDocument44 pages1 IntroductionFaek NaemNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 7 Median Quartile of Grouped DataDocument10 pagesWorksheet 7 Median Quartile of Grouped DataIsaac-elmar Agtarap100% (1)
- JournalDocument6 pagesJournalAriel SumagaysayNo ratings yet
- International Standards For Size at Birth PDFDocument3 pagesInternational Standards For Size at Birth PDFKenya Karina Soto RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Q4 Week 1 2Document26 pagesQ4 Week 1 2John Michael TismoNo ratings yet
- 2 Distributional Quantities and Risk MeasuresDocument18 pages2 Distributional Quantities and Risk MeasuresgameplayevgerkNo ratings yet
- Baseline Diameter of The Inferior Vena Cava Measured With Sonography in Euvolemic ChildrenDocument9 pagesBaseline Diameter of The Inferior Vena Cava Measured With Sonography in Euvolemic ChildrenMario TGNo ratings yet
- Full Download Ebook PDF Social Statistics For A Diverse Society 7th Edition PDFDocument41 pagesFull Download Ebook PDF Social Statistics For A Diverse Society 7th Edition PDFjames.speed848100% (37)
- PHE Tool For Common PH Stats and CIsDocument13 pagesPHE Tool For Common PH Stats and CIsThaigroup CementNo ratings yet
- Level Tekanan Darah AnakDocument4 pagesLevel Tekanan Darah AnakFajar JuliansyahNo ratings yet
- BM-707 & BM-607 MID AssignmentDocument4 pagesBM-707 & BM-607 MID AssignmentNoumanQasmiNo ratings yet