Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2 ACNunit2 - Partial
2 ACNunit2 - Partial
Uploaded by
Vikas SrivastavOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2 ACNunit2 - Partial
2 ACNunit2 - Partial
Uploaded by
Vikas SrivastavCopyright:
Available Formats
Layer 2 Switching
Layer 2 switches segment a network into multiple collision domains
and interconnect devices within a workgroup, such as a group of PCs.
The heart of a Layer 2 switch is its Media Access Control (MAC)
address table.
When a switch is first powered up, its MAC address table is empty.
Vivek Sethi (DIT) Advanced Computer Networks 10th Jan. 2023 38 / 71
Layer 2 Switching
Figure: MAC.
Vivek Sethi (DIT) Advanced Computer Networks 10th Jan. 2023 39 / 71
Layer 3 Switching
A Layer 3 switch is really a router with some of the functions
implemented in hardware to improve performance.
Vivek Sethi (DIT) Advanced Computer Networks 10th Jan. 2023 40 / 71
Functions of a Layer 3 Switch
Learning routes and keeping the best path to each destination in a
routing table.
Sending the packet out of the appropriate interface, along the best
path. This is also called switching the packet.
Communicating with other routers to exchange routing information.
Allowing devices on different LANs to communicate with each other
and with distant devices.
Blocking broadcasts.
Vivek Sethi (DIT) Advanced Computer Networks 10th Jan. 2023 41 / 71
Layer 4 Switching
Switching based on the protocol and port numbers.
It ensure, for example, that certain types of traffic get higher priority
on the network or take a specific path.
Vivek Sethi (DIT) Advanced Computer Networks 10th Jan. 2023 42 / 71
Multilayer Switching
Multilayer switching, as its name implies, allows switching to take
place at different protocol layers.
Switching can be performed only on Layers 2 and 3, or it can also
include Layer 4.
MLS is based on network flows.
A network flow is a unidirectional sequence of packets between a
source and a destination.
A network flow can be identified by source and destination IP
addresses, protocol numbers, and port numbers as well as the
interface on which the packet enters the switch.
Vivek Sethi (DIT) Advanced Computer Networks 10th Jan. 2023 43 / 71
Components of Multilayer Switching
MLS Route Processor (MLS-RP): Performs traditional features of
routing.
MLS Switching Engine (MLS-SE):The MLS-enabled switch that can
offload some of the packet-switching functionality from the MLS-RP.
Multilayer Switching Protocol (MLSP): Used by the MLS-RP and the
MLS-SE to communicate with each other.
Vivek Sethi (DIT) Advanced Computer Networks 10th Jan. 2023 44 / 71
Components of Multilayer Switching
Figure: Multilayer Switch.
Vivek Sethi (DIT) Advanced Computer Networks 10th Jan. 2023 45 / 71
Functionality of multilayer switch
In the case of the first packet in the flow, SE forwards the frame to
the RP.
The MLS-RP receives the frame, decapsulates (unwraps) the frame,
and determines the destination of a packet.
RP creates a new frame for the packet - decrementing the TTL field,
recalculating the IP header checksum, update source MAC address of
this frame as the MAC address of the RP, update destination MAC
address of this frame as the MAC address of the destination device
(or next-hop router).
The RP then sends the frame to the SE.
The SE therefore makes the MLS cache entry using information from
the frame.
Vivek Sethi (DIT) Advanced Computer Networks 10th Jan. 2023 46 / 71
Cisco Express Forwarding
Cisco Express Forwarding (CEF), like MLS , aims to speed the data
routing and forwarding process in a network.
CEF uses two components to optimize the lookup of the information
required to route packets: the Forwarding Information Base (FIB) for
the Layer 3 information and the adjacency table for the Layer 2
information.
CEF creates an FIB by maintaining a copy of the forwarding
information contained in the IP routing table.
The adjacency table contains Layer 2 frame header information,
including next-hop addresses, for all FIB entries.
Vivek Sethi (DIT) Advanced Computer Networks 10th Jan. 2023 47 / 71
Functioning of Cisco Express Forwarding
When a packet arrives, the route is determined using FIB table.
Then, the next-hop information is retrieved using the adjacency table.
Vivek Sethi (DIT) Advanced Computer Networks 10th Jan. 2023 48 / 71
Switching Security
Switches play an active role in network security by providing various
security features.
Vivek Sethi (DIT) Advanced Computer Networks 10th Jan. 2023 49 / 71
Security Attacks
MAC Address Flooding: An attacker can send frames with fake,
randomly-generated source and destination MAC addresses to the switch.
Figure: Attack.
Vivek Sethi (DIT) Advanced Computer Networks 10th Jan. 2023 50 / 71
Security Attacks
DHCP starvation attack: An attacker floods the DHCP server with
DHCP requests to use all the available IP addresses that the DHCP
server can issue. After these IP addresses are issued, the server
cannot issue any more addresses, and this situation produces a
denial-of-service (DoS) attack.
DHCP spoofing attack: An attacker configures a fake DHCP server
on the network to issue DHCP addresses to clients.
DHCP starvation is often used before a DHCP spoofing attack to
deny service to the legitimate DHCP server, making it easier to
introduce a fake DHCP server into the network.
Vivek Sethi (DIT) Advanced Computer Networks 10th Jan. 2023 51 / 71
Security Attacks
Figure: DHCP Attack.
Vivek Sethi (DIT) Advanced Computer Networks 10th Jan. 2023 52 / 71
Security Attacks
Telnet Attack: The Telnet protocol is insecure and can be used by an
attacker to gain remote access to a Cisco network device.
There are tools available that allow an attacker to launch a brute
force password-cracking attack against the ports on the switch.
Vivek Sethi (DIT) Advanced Computer Networks 10th Jan. 2023 53 / 71
Switch Security
Various security features are used in the switch for preventing the attacks.
Vivek Sethi (DIT) Advanced Computer Networks 10th Jan. 2023 54 / 71
Switch Port Security
Secure Unused Ports: The first step in port security is to be aware of
ports that are not currently being used on the switch.
The second step is to disable all unused ports on a switch.
Vivek Sethi (DIT) Advanced Computer Networks 10th Jan. 2023 55 / 71
DHCP Snooping
DHCP snooping: It determines which devices attached to switch
ports can respond to DHCP requests.
Switch ports can be identified as trusted and untrusted.
Trusted ports can source any type of DHCP message.
Untrusted ports can source DHCP requests only.
Vivek Sethi (DIT) Advanced Computer Networks 10th Jan. 2023 56 / 71
DHCP Snooping
Figure: DHCP Snooping.
Vivek Sethi (DIT) Advanced Computer Networks 10th Jan. 2023 57 / 71
Port Security
Port security : Cisco port security limits the number of valid MAC
addresses allowed on a port.
If the number of MAC addresses allowed on the port is limited to one,
then only the device with that specific MAC address can successfully
connect to the port.
If a port is configured as a secure port and the maximum number of
MAC addresses is reached, any additional attempts to connect by
unknown MAC addresses will generate a security violation.
Vivek Sethi (DIT) Advanced Computer Networks 10th Jan. 2023 58 / 71
SSH
Secure Shell (SSH) is a protocol that provides a secure (encrypted)
management connection to a remote device.
SSH should replace Telnet for management connections.
SSH provides security for remote connections by providing strong
encryption when a device is authenticated (username and password)
and also for the transmitted data between the communicating devices.
Vivek Sethi (DIT) Advanced Computer Networks 10th Jan. 2023 59 / 71
IPv4 Network Design - Two-Level Addressing
Figure: Two-Level Addressing.
Vivek Sethi (DIT) Advanced Computer Networks 10th Jan. 2023 60 / 71
IPv4 Network Design - Two-Level Addressing
Vivek Sethi (DIT) Advanced Computer Networks 10th Jan. 2023 61 / 71
IPv4 Network Design - Three-Level Addressing
Vivek Sethi (DIT) Advanced Computer Networks 10th Jan. 2023 62 / 71
IPv4 Network Design - Subnetting
Vivek Sethi (DIT) Advanced Computer Networks 10th Jan. 2023 63 / 71
IPv4 Network Design - Subnetting
Vivek Sethi (DIT) Advanced Computer Networks 10th Jan. 2023 64 / 71
IPv4 Network Design - Subnetting
Vivek Sethi (DIT) Advanced Computer Networks 10th Jan. 2023 65 / 71
Hierarchical IP Address Design and Summarization
A hierarchical IP address design means that addresses are assigned in
a hierarchical manner, rather than randomly.
Routers maintain summarized routes only, instead of unnecessary
details in their routing tables.
Routing updates become smaller and therefore use less bandwidth on
the network.
Vivek Sethi (DIT) Advanced Computer Networks 10th Jan. 2023 66 / 71
Hierarchical IP Address Design and Summarization
When Router A sends its routing table to the other routers, it has no
choice but to send all its routes.
Vivek Sethi (DIT) Advanced Computer Networks 10th Jan. 2023 67 / 71
Hierarchical IP Address Design and Summarization
Notice, for example, that all the subnets under Router A start with 10.1,
while all under Router B start with 10.2. Therefore, the routers can
summarize the subnets.
Vivek Sethi (DIT) Advanced Computer Networks 10th Jan. 2023 68 / 71
Hierarchical IP Address Design and Summarization
Consider a network in which Router A has the following subnet routes in
its routing table: 192.168.3.64/28, 192.168.3.80/28, 192.168.3.96/28, and
192.168.3.112/28. Router B in the same network has the following subnet
routes in its routing table: 192.168.3.0/28, 192.168.3.16/28,
192.168.3.32/28, and 192.168.3.48/28. What is the summary route for
Router A’s subnets?
Vivek Sethi (DIT) Advanced Computer Networks 10th Jan. 2023 69 / 71
Hierarchical IP Address Design and Summarization
Vivek Sethi (DIT) Advanced Computer Networks 10th Jan. 2023 70 / 71
RIP Routing Protocol
Routing Information Protocol (RIP) is a dynamic routing protocol
that uses hop count as a routing metric to find the best path between
the source and the destination network.
In RIP, infinity is defined as 16, which means that the RIP is useful
for smaller networks or small autonomous systems. The maximum
number of hops that RIP can contain is 15 hops, i.e., it should not
have more than 15 hops as 16 is infinity.
In a routing table, the first column is the destination, or we can say
that it is a network address.
The next column contains the address of the router to which the
packet is to be sent to reach the destination.
Vivek Sethi (DIT) Advanced Computer Networks 10th Jan. 2023 71 / 71
You might also like
- CCNA 1 v7.0 Final Exam Answers Full - Introduction To NetworksDocument64 pagesCCNA 1 v7.0 Final Exam Answers Full - Introduction To NetworkssamiNo ratings yet
- CCNA 1 Exam Final en AnglaisDocument54 pagesCCNA 1 Exam Final en AnglaisRoland FoyemtchaNo ratings yet
- CCNA 1+2+3+4 v5Document87 pagesCCNA 1+2+3+4 v5Ajmal QalaNo ratings yet
- A1800 ALPHA Meter: DLMS Protocol Implementation PG42-1019DDocument86 pagesA1800 ALPHA Meter: DLMS Protocol Implementation PG42-1019DFredy BenavidesNo ratings yet
- IT Questions Bank Final ExamDocument77 pagesIT Questions Bank Final ExamfeyisaNo ratings yet
- CCNA 1 v7.0 Final Exam Answers Full - Introduction To NetworksDocument49 pagesCCNA 1 v7.0 Final Exam Answers Full - Introduction To NetworksChristian StyriaNo ratings yet
- CCNA 1 v7.0 Final Exam Answers Full - Introduction To NetworksDocument48 pagesCCNA 1 v7.0 Final Exam Answers Full - Introduction To NetworksRazvan AlexandruNo ratings yet
- CCNA 1 Full Introduction To Networks PDFDocument46 pagesCCNA 1 Full Introduction To Networks PDFRazvan AlexandruNo ratings yet
- Interview Question and Answers of CCNADocument14 pagesInterview Question and Answers of CCNAPraveen Prakasan100% (1)
- CCNA 1 v7.0 ITN Final Exam Answers Free - 2Document51 pagesCCNA 1 v7.0 ITN Final Exam Answers Free - 2ivy.rpNo ratings yet
- CCNA 1 v70 Final Exam Answers Full Introduction To Networks PDFDocument56 pagesCCNA 1 v70 Final Exam Answers Full Introduction To Networks PDFDallandyshe CenaNo ratings yet
- CCNA 1 v70 Final Exam Answers Full Introduction To NetworksDocument56 pagesCCNA 1 v70 Final Exam Answers Full Introduction To NetworksKreshnik KolaNo ratings yet
- Atestare ARCDocument4 pagesAtestare ARCVictor ColtaNo ratings yet
- CCNA (200-301) Certification Practice Exam Answers (ENSA v7.0)Document54 pagesCCNA (200-301) Certification Practice Exam Answers (ENSA v7.0)samiNo ratings yet
- Section 1 Network Fundamentals CCNA 200-125 TheoryDocument21 pagesSection 1 Network Fundamentals CCNA 200-125 Theoryergu vfuko fghuiNo ratings yet
- CCNA 1 Final ExamDocument54 pagesCCNA 1 Final ExamAdha Estu RizqiNo ratings yet
- Sysnet Notes: Basic CCNA Interview Questions AND AnswersDocument8 pagesSysnet Notes: Basic CCNA Interview Questions AND AnswersReddy SumanthNo ratings yet
- CCNA1 Practice Final ExamDocument16 pagesCCNA1 Practice Final Examak1lNo ratings yet
- DCCNDocument10 pagesDCCNDEABELA GAMING 2No ratings yet
- CCNA 2 (v5.1 + v6.0) Chapter 4 Exam Answers Full PDFDocument20 pagesCCNA 2 (v5.1 + v6.0) Chapter 4 Exam Answers Full PDFZoran100% (1)
- Net Answer SheetDocument88 pagesNet Answer SheetKevin Miguel PadugananNo ratings yet
- CN Lab Manual 2018Document121 pagesCN Lab Manual 2018Suresh RamanujamNo ratings yet
- Ccna 1 R&S: Introduction To Networks Final Exam v5.0 2013Document22 pagesCcna 1 R&S: Introduction To Networks Final Exam v5.0 2013Dani PiñolNo ratings yet
- IT212 - Data Communic5ations and Networking 2 (Cisco 2 New)Document91 pagesIT212 - Data Communic5ations and Networking 2 (Cisco 2 New)Chuster Adriano100% (1)
- Internet Protocol MulticastDocument19 pagesInternet Protocol MulticastAbhijit ThakurNo ratings yet
- CCNA 1 RS Introduction To Networks Final Exam v50 2013Document15 pagesCCNA 1 RS Introduction To Networks Final Exam v50 2013daniel_afpNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks (CS425) : Unix Socket ProgrammingDocument4 pagesComputer Networks (CS425) : Unix Socket ProgrammingAnish VeettiyankalNo ratings yet
- Networking PRACTICALDocument24 pagesNetworking PRACTICALMohit GusainNo ratings yet
- Using IP Multicasting With The TMS320C6000 Network Developer's Kit (NDK)Document12 pagesUsing IP Multicasting With The TMS320C6000 Network Developer's Kit (NDK)Rahim Ali QamarNo ratings yet
- Assessment System4.1Document9 pagesAssessment System4.1JustjosephNo ratings yet
- CCNA 2 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 4 Exam Answers 2019 - 100% FullDocument23 pagesCCNA 2 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 4 Exam Answers 2019 - 100% Fullreem goNo ratings yet
- Final Exam ITNDocument18 pagesFinal Exam ITNImanuel HarefaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Networks Version 70 ITNv7 Practice Final Exam AnswersDocument27 pagesIntroduction To Networks Version 70 ITNv7 Practice Final Exam AnswersTemam MohammedNo ratings yet
- CCNA LabManual NewDocument142 pagesCCNA LabManual Newyashveer100% (1)
- Network Layer - Protocols, Concepts: NET 101 - Lec06Document64 pagesNetwork Layer - Protocols, Concepts: NET 101 - Lec06Judy Ann FloresNo ratings yet
- Netmetric Ccna Study GuideDocument51 pagesNetmetric Ccna Study GuideSUSHOBHAN CHAKRABARTINo ratings yet
- Computer Networks (CS425) : Unix Socket ProgrammingDocument4 pagesComputer Networks (CS425) : Unix Socket ProgrammingPiuNo ratings yet
- Bondo NetworkDocument8 pagesBondo NetworkジュニアJNo ratings yet
- Internet Protocol MulticastDocument17 pagesInternet Protocol MulticastPatricio QueglesNo ratings yet
- Network A2 V2Document52 pagesNetwork A2 V2Selma AsaliNo ratings yet
- Ccna Notes KitDocument81 pagesCcna Notes KitMukesh BhakarNo ratings yet
- Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Is A Mechanism in High-PerformanceDocument6 pagesMultiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Is A Mechanism in High-Performancetasnim tamannaNo ratings yet
- Module3 Part CDocument17 pagesModule3 Part CAnithasrirangaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4 SolDocument7 pagesAssignment 4 Soljazib1921No ratings yet
- CCNA 2 Pretest Exam Answers v5Document81 pagesCCNA 2 Pretest Exam Answers v5Pate Ssmma Ikanivoka100% (2)
- Hct6000 Tcpip OptionDocument14 pagesHct6000 Tcpip OptionGerman DfrNo ratings yet
- CCNA1 - 3 V7 Final ExamDocument167 pagesCCNA1 - 3 V7 Final ExamTsehayou SieleyNo ratings yet
- Mahlatse Iven Somela Unique Number: 640309 Student Number: 60232811 ICT1532: Assignment 1 Section ADocument9 pagesMahlatse Iven Somela Unique Number: 640309 Student Number: 60232811 ICT1532: Assignment 1 Section Amahlatse iven somelaNo ratings yet
- Bosch - Networking Essentials and Basic ConceptsDocument10 pagesBosch - Networking Essentials and Basic ConceptsFábio Dos ReisNo ratings yet
- Chapter3-Network Basics in CCDocument24 pagesChapter3-Network Basics in CChaithamokour11No ratings yet
- CCNA 1 Practice Final Exam V4Document30 pagesCCNA 1 Practice Final Exam V4miljkoyuNo ratings yet
- CCNA 3 v7.0 Modules 9 - 12Document20 pagesCCNA 3 v7.0 Modules 9 - 12arvie montemayorNo ratings yet
- Cisco Pass4Sure 640-822 v2013-05-02 by FadiDocument155 pagesCisco Pass4Sure 640-822 v2013-05-02 by FadiIris DebergesNo ratings yet
- Study Guide ExpandedDocument7 pagesStudy Guide ExpandedGabby ShearerNo ratings yet
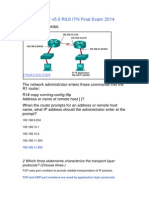
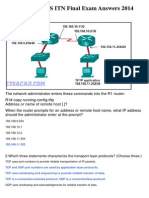
- CCNA 1 v5.0 R&S ITN Final Exam Answers 2014Document22 pagesCCNA 1 v5.0 R&S ITN Final Exam Answers 2014jonmicNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks Lab ManualDocument61 pagesComputer Networks Lab Manualjenisha100% (2)
- CCNA1var.2 100p 12Document7 pagesCCNA1var.2 100p 12tibimaNo ratings yet
- Bisf 2207 Past Paper RevisedDocument6 pagesBisf 2207 Past Paper RevisedvictorsebstarNo ratings yet
- CCNA 1 Chapter 10 V4.0 AnswersDocument9 pagesCCNA 1 Chapter 10 V4.0 AnswersAbdullah Al HawajNo ratings yet
- Ccna1-Final 2 v4.0Document18 pagesCcna1-Final 2 v4.0rajnox100% (6)
- Implementing Canvas Open SourceDocument24 pagesImplementing Canvas Open Sourcechristopher-bennellNo ratings yet
- 19.3 Zte Gpon Onu f804 DatasheetDocument1 page19.3 Zte Gpon Onu f804 DatasheetJosé AcostaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 10 InternetDocument3 pagesLesson Plan 10 InternetsimonettixNo ratings yet
- Real Estate Management SystemDocument9 pagesReal Estate Management SystemShmoney SherifNo ratings yet
- Manoj KumarDocument3 pagesManoj Kumarmanojsingh474No ratings yet
- Cisco IOS Quality of Service Solutions Command ReferenceDocument1,105 pagesCisco IOS Quality of Service Solutions Command ReferencepmdongreNo ratings yet
- Modern Asian APT Groups TTPs Report EngDocument370 pagesModern Asian APT Groups TTPs Report EngJavier Panete PérezNo ratings yet
- Firefox - About - ConfigDocument2 pagesFirefox - About - ConfigesshorNo ratings yet
- FL Dcufi 4.0.1 LG-1Document361 pagesFL Dcufi 4.0.1 LG-1Wilson DanielNo ratings yet
- Pegasus Research PaperDocument15 pagesPegasus Research PaperMargaNo ratings yet
- L'Oreal BrandstormDocument3 pagesL'Oreal Brandstormankush aroraNo ratings yet
- Welcome To The Adobe Partner Connection Reseller ProgramDocument1 pageWelcome To The Adobe Partner Connection Reseller ProgramMario Andres B.No ratings yet
- The Need For Security: Our Bad Neighbor Makes Us Early Stirrers, Which Is Both Healthful and Good HusbandryDocument46 pagesThe Need For Security: Our Bad Neighbor Makes Us Early Stirrers, Which Is Both Healthful and Good HusbandryNivi SenthilNo ratings yet
- GPYGP PPT For 25 26 Apr09Document26 pagesGPYGP PPT For 25 26 Apr09api-3702832No ratings yet
- Nguyen Casey DBQ LimitingDocument3 pagesNguyen Casey DBQ Limitingapi-222058980No ratings yet
- Polymers - Chemistry ProjectDocument28 pagesPolymers - Chemistry ProjectKaku Bwj67% (3)
- Group Report 1Document5 pagesGroup Report 1Rosita Jamiliana 1DNo ratings yet
- Baitul Maal Watamwil: Program Kerja (BMT Al Jun)Document20 pagesBaitul Maal Watamwil: Program Kerja (BMT Al Jun)akademik smkaljunNo ratings yet
- Junos Security Admin GuideDocument452 pagesJunos Security Admin GuideregabriNo ratings yet
- Installing XP After Vista or 7 - Easybcd - Neosmart Technologies WikiDocument3 pagesInstalling XP After Vista or 7 - Easybcd - Neosmart Technologies WikirjefrisonNo ratings yet
- Computer Network - CS610 Power Point Slides Lecture 01Document19 pagesComputer Network - CS610 Power Point Slides Lecture 01Ibrahim ChoudaryNo ratings yet
- Idealtech PricelistDocument5 pagesIdealtech PricelistAmmar MurabbiNo ratings yet
- Virtual Communities and Social CapitalDocument16 pagesVirtual Communities and Social CapitalChayma BouaoiinaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer Assignment - 2: 1. Differentiate Between Printers and Plotters? PrinterDocument19 pagesIntroduction To Computer Assignment - 2: 1. Differentiate Between Printers and Plotters? Printerapi-19653075No ratings yet
- NmapDocument14 pagesNmapamird12No ratings yet
- CCH SDCCH DimensioningDocument2 pagesCCH SDCCH DimensioningpavlodeNo ratings yet
- Data Center EVPN-VXLAN Fabric Architecture GuideDocument291 pagesData Center EVPN-VXLAN Fabric Architecture GuideLi KangNo ratings yet
- 30wknm15 Week30 2015Document119 pages30wknm15 Week30 2015Kunal Singh100% (1)
- 2e-How To Use A Search Engine To Search The Internet PDFDocument3 pages2e-How To Use A Search Engine To Search The Internet PDFMarco Mariano100% (1)