Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cardiovascular Terms
Cardiovascular Terms
Uploaded by
Torio Kristine Anne P.0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageThe document discusses the structure and function of the heart and circulatory system. It describes the double circulatory system with pulmonary and systemic circuits. It also outlines the layers of the heart walls, functioning of the valves, electrical conduction system, cardiac cycle phases, and key metrics like cardiac output and stroke volume. Key anatomical parts are defined like the atria, ventricles, arteries, veins, and capillaries. Common monitoring values like blood pressure and electrical signals are also explained.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses the structure and function of the heart and circulatory system. It describes the double circulatory system with pulmonary and systemic circuits. It also outlines the layers of the heart walls, functioning of the valves, electrical conduction system, cardiac cycle phases, and key metrics like cardiac output and stroke volume. Key anatomical parts are defined like the atria, ventricles, arteries, veins, and capillaries. Common monitoring values like blood pressure and electrical signals are also explained.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageCardiovascular Terms
Cardiovascular Terms
Uploaded by
Torio Kristine Anne P.The document discusses the structure and function of the heart and circulatory system. It describes the double circulatory system with pulmonary and systemic circuits. It also outlines the layers of the heart walls, functioning of the valves, electrical conduction system, cardiac cycle phases, and key metrics like cardiac output and stroke volume. Key anatomical parts are defined like the atria, ventricles, arteries, veins, and capillaries. Common monitoring values like blood pressure and electrical signals are also explained.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
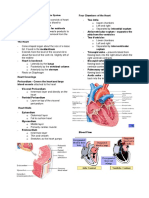
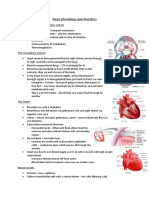
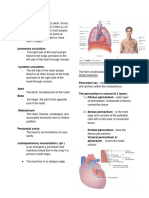
Pulmonary circuit- blood from heart become Tunica interna- inner layer/endothelium
oxygenated (from lungs) Tunica media- mostly skeletal muscle,
Systemic circuit- heart pumps oxygenated blood sympathetic nervous system
throughout the body Tunica externa- outer/fibrous connective tissue
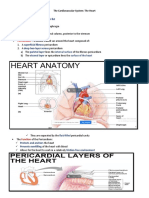
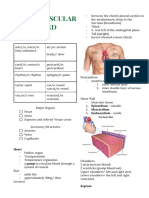
Epicardium- visceral/connective tissue Artery- Smaller lumen since it transports blood
Myocardium- middle/mostly cardiac muscle from the heart
Endocardium- inner/endothelium Vein- Larger lumen
Atria- Receiving chambers) Capillary- Exchange of materials/one cell layer
o Right atrium (deoxy) Vascular shunt – directly connects an arteriole
o Left atrium (Oxy) to a venule
Ventricles- Discharging chambers) True capillaries – exchange vessel
o Right ventricle (PA) Pulse- Pressure wave of blood/ Monitored at
o Left ventricle (aorta) “pressure points”
Heart Valves- No complications/ allowing one Hypotension- Low systolic (below 110 mm
direction of blood HG)/Often associated with illness
Atrioventricular valves- between atria & Hypertension- High systolic (above 140 mm
ventricles valves HG)/Can be dangerous if it is chronic
Semilunar valves- between ventricle & artery
valve
Chordae tendineae (heartstring)- closes to
prevent backflow
Coronary Circulation- Heart supplies blood on
its own
Coronary sinus- Blood empties into the right
atrium via the
Sinoatrial node (right atrium)- Pacemaker
Electrodes- detects electrical signal
P wave: Atrial depolarization ,blood flows to the
atria
QRS complex/waves- ventricular depolarization
T wave: end of electrical activity in
ventricles/ventricular repolarization
Defibrillation- sends electrical signal to correct
heart beat
Cardiac Cycle- Atria contract simultaneously/
Atria relax, then ventricles contract
Systole = contraction
Diastole = relaxation
Ventricular filling- Blood from atria will flow to
the ventricles (atria contracts), if the ventricle are
full, next is isovolumetric contraction
Isovolumetric contraction- Both ventricles
contract
Isovolumetric ejection- Ventricles eject to the
PA and aorta (systole)
Isovolumetric relaxation- Ventricles relax (early
diastole)
Cardiac Output- Amount of blood pumped by
each side of the heart in one minute
Stroke volume- Volume of blood pumped by
each ventricle in one contraction
You might also like
- Squeezed by Alissa Quart "Why Our Families Can't Afford America"Document6 pagesSqueezed by Alissa Quart "Why Our Families Can't Afford America"Zahra AfikahNo ratings yet
- OSTEORADIONECROSISDocument38 pagesOSTEORADIONECROSISAbel AbrahamNo ratings yet
- 1H06B Lectures 1-4 Review CardiacDocument16 pages1H06B Lectures 1-4 Review Cardiachaaris 7khanNo ratings yet
- MPI Painting CodeDocument28 pagesMPI Painting CodeGhayas JawedNo ratings yet
- The Equine Cardiovascular SystemDocument5 pagesThe Equine Cardiovascular SystemSavannah Simone PetrachenkoNo ratings yet
- Biology NMAT Notes AnatomyCirculatory and RespiratoryDocument13 pagesBiology NMAT Notes AnatomyCirculatory and RespiratoryMa. Teresa M. AbainzaNo ratings yet
- Heart Anatomy: LocationDocument45 pagesHeart Anatomy: LocationZaira100% (1)
- Animals Part 1Document129 pagesAnimals Part 1黄心怡No ratings yet
- 3 CVSDocument10 pages3 CVSzabdullahstud1No ratings yet
- ANATOMY Final pt.1Document26 pagesANATOMY Final pt.1Gladys Mae S. BañesNo ratings yet
- Heart AnatomyDocument7 pagesHeart AnatomyArjon BalaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System-Heart: Miss Wheeler Unit 8Document29 pagesCardiovascular System-Heart: Miss Wheeler Unit 8Ngatchou GaelleNo ratings yet
- CARDIOLOGYDocument15 pagesCARDIOLOGYPatty RomeroNo ratings yet
- Anatomy - Cardiovascular System - Part IDocument13 pagesAnatomy - Cardiovascular System - Part IVăn ĐứcNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument5 pagesCirculatory SystemSakshi BishnoiNo ratings yet
- AtriumDocument1 pageAtriumPhilip Ryken YuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Cardiovascular SystemDocument6 pagesChapter 11 Cardiovascular SystemClarisse Anne QuinonesNo ratings yet
- Charter College: T.Miller - 7/2017Document28 pagesCharter College: T.Miller - 7/2017Waqar AhmedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20 Heart and Neck VesselsDocument10 pagesChapter 20 Heart and Neck Vesselsannoja selvaNo ratings yet
- Lect 8. Cardiovascular SystemDocument35 pagesLect 8. Cardiovascular Systemrukhsanatariq299No ratings yet
- Ana CardioDocument3 pagesAna CardioFIONA DANE MAURERANo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument101 pagesCardiovascular SystemBanessa Mae GarcianoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20-Cardiovascular System The HeartDocument44 pagesChapter 20-Cardiovascular System The HeartleoNo ratings yet
- Pedrajeta-Heart and Neck Vessels AssessmentDocument4 pagesPedrajeta-Heart and Neck Vessels AssessmentAndrei PedrajetaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System NotesDocument3 pagesCirculatory System Notesapi-317705375No ratings yet
- Chapter 16 Anatomy of The HeartDocument5 pagesChapter 16 Anatomy of The Heartphotojockey18No ratings yet
- Ch18-Ch19 - NotesDocument5 pagesCh18-Ch19 - NotesCj LinceNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular NotesDocument16 pagesCardiovascular NotesPRAGATI RAINo ratings yet
- Heart and Neck VesselsDocument3 pagesHeart and Neck VesselsMark ElbenNo ratings yet
- Transport System: Biology Unit (12/13) Kedah Matriculation CollegeDocument26 pagesTransport System: Biology Unit (12/13) Kedah Matriculation CollegegajenraoNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument12 pagesCardiovascular SystemDevendra RawatNo ratings yet
- Biology AS Revision: Single Circulatory SystemDocument4 pagesBiology AS Revision: Single Circulatory SystemKieran ArronNo ratings yet
- Basics of The Heart: Katee Beaudry MS 2 - Penn State University College of MedicineDocument24 pagesBasics of The Heart: Katee Beaudry MS 2 - Penn State University College of MedicineAlkhnsa CaifNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology NotesDocument56 pagesAnatomy & Physiology NotesChristina Gonez100% (2)
- Heart Physiology and DisordersDocument9 pagesHeart Physiology and DisordersLottie EvansNo ratings yet
- Ecg Review: Ecgs Made Easy: Section IDocument11 pagesEcg Review: Ecgs Made Easy: Section ISewyel GarburiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology of Heart: BY: Mr. Anurag Lecturer College of Nursing DMC & H, LudhianaDocument56 pagesAnatomy & Physiology of Heart: BY: Mr. Anurag Lecturer College of Nursing DMC & H, Ludhianapreet kaurNo ratings yet
- Heart Anatomy Only StudentsDocument34 pagesHeart Anatomy Only Studentscharlene.jadulcoNo ratings yet
- Exam 4 Study Guide (1386)Document11 pagesExam 4 Study Guide (1386)S. MartinezNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System - Heart IntroDocument6 pagesCardiovascular System - Heart IntroKate Angeline TanNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument34 pagesCardiovascular Systemurooj100% (1)
- Anatomi Radiologi Sistem KardiovaskulerDocument52 pagesAnatomi Radiologi Sistem KardiovaskulerlinoconceicaoNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument10 pagesCardiovascular SystemGlen DaleNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 (Heart)Document10 pagesLecture 5 (Heart)Άγγελος ΧαβέλαςNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System BSN 1Document16 pagesCardiovascular System BSN 1Arianne Jen GenotivaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19 Heart Marie BDocument29 pagesChapter 19 Heart Marie BomarNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Markers-It Is An Enzyme That Increases If You Have Cardiac Muscle Injury. We NeedDocument5 pagesCardiac Markers-It Is An Enzyme That Increases If You Have Cardiac Muscle Injury. We Needcamile buhanginNo ratings yet
- The Emotion That Breaks Your Heart Is Sometimes The Very One That Heals It!Document4 pagesThe Emotion That Breaks Your Heart Is Sometimes The Very One That Heals It!A-Naeem To'mah Al-sawaieNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascularsystem 210913083324Document51 pagesCardiovascularsystem 210913083324mahatoshatrudhan333No ratings yet
- Parts and Function of Heart: Group 5 9 - ActsDocument47 pagesParts and Function of Heart: Group 5 9 - ActsJasmin GarciaNo ratings yet
- Circulation Vocabulary HandoutDocument2 pagesCirculation Vocabulary HandoutGPearce204No ratings yet
- 8 CardiovascularDocument44 pages8 CardiovascularleonardodataguroNo ratings yet
- Local Media1995767886843754234Document10 pagesLocal Media1995767886843754234Haimen BuisanNo ratings yet
- HeartDocument3 pagesHeartTrisha MedidasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Card WPS OfficeDocument19 pagesChapter 12 Card WPS OfficeKaye CepedaNo ratings yet
- Heart Finals ReviewerDocument7 pagesHeart Finals ReviewershannenmaehfajanilanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14.1 - Cardiovascular System - Blood VesselsDocument56 pagesChapter 14.1 - Cardiovascular System - Blood VesselsMichael PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument26 pagesCardiovascular SystemdumbledoreaaaaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System NotesDocument31 pagesCirculatory System NotesJMHenry0% (1)
- Patent Ductus ArteriosusDocument9 pagesPatent Ductus ArteriosusAnonymous QOCn5dNo ratings yet
- Reviwer QuizDocument1 pageReviwer QuizJullien Tañedo MarcelinoNo ratings yet
- Session 5Document41 pagesSession 5tazebNo ratings yet
- Physician'S Order/Progress Notes: 23 S. Avila Male JhonDocument2 pagesPhysician'S Order/Progress Notes: 23 S. Avila Male JhonKrizha Angela Nicolas100% (1)
- Training - Cga ApplicationDocument34 pagesTraining - Cga ApplicationSubhan Muhammad100% (1)
- Model ETR-9200 Automatic Tuning Smarter Logic ControllerDocument26 pagesModel ETR-9200 Automatic Tuning Smarter Logic ControllervhelectronicaNo ratings yet
- Crew Habitability On Mobile Offshore Drilling Units (Modus) : Guide ForDocument87 pagesCrew Habitability On Mobile Offshore Drilling Units (Modus) : Guide ForReza BabriNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Antioxidant Capacity For Scavenging Free Radicals in Vitro A Rational Basis and Practical ApplicationDocument11 pagesAssessment of Antioxidant Capacity For Scavenging Free Radicals in Vitro A Rational Basis and Practical Applicationngoclien93No ratings yet
- Tehri DamDocument31 pagesTehri DamVinayakJindalNo ratings yet
- Academy of American Franciscan HistoryDocument36 pagesAcademy of American Franciscan HistoryCESAR HUAROTO DE LA CRUZNo ratings yet
- Steps To Become A Healthcare Project ManagerDocument2 pagesSteps To Become A Healthcare Project ManagerHPMA globalNo ratings yet
- Capinew Account June13Document7 pagesCapinew Account June13ashwinNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2021-12-18 at 2.26.56 PMDocument1 pageScreenshot 2021-12-18 at 2.26.56 PMTanya NguyenNo ratings yet
- T N M M T N M M: HE EW Essies Anual HE EW Essies AnualDocument8 pagesT N M M T N M M: HE EW Essies Anual HE EW Essies AnualMunna100% (1)
- Wired For: Hit Play For SexDocument7 pagesWired For: Hit Play For SexPio Jian LumongsodNo ratings yet
- Class 11 English Notes Studyguide360Document272 pagesClass 11 English Notes Studyguide360IsnatainiNo ratings yet
- XT Mobile Shear: Reference GuideDocument12 pagesXT Mobile Shear: Reference GuidePrudzNo ratings yet
- SRHR - FGD With Young PeopleDocument3 pagesSRHR - FGD With Young PeopleMandira PrakashNo ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter PHILO ReviewerDocument1 page2nd Quarter PHILO ReviewerTrisha Joy Dela Cruz80% (5)
- ECA DatabaseDocument22 pagesECA DatabaseRidhwan JamaludinNo ratings yet
- Calculating Parenteral FeedingsDocument5 pagesCalculating Parenteral FeedingsekramsNo ratings yet
- Heterocyclic Aromatic CompoundsDocument67 pagesHeterocyclic Aromatic CompoundsTuyenHHC100% (1)
- Early Alt-RAMEC and Facial Mask Protocol in Class III MalocclusionDocument9 pagesEarly Alt-RAMEC and Facial Mask Protocol in Class III MalocclusionNievecillaNeiraNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6Document32 pagesLecture 6Nilesh PanchalNo ratings yet
- Seed Extraction MethodsDocument3 pagesSeed Extraction MethodsPreetam NayakNo ratings yet
- PreviewpdfDocument79 pagesPreviewpdfcrisuanNo ratings yet
- Dental Implant Site Preparation - A Review: C.J.Venkatakrishnan, S.Bhuminathan and Chitraa.R.ChandranDocument4 pagesDental Implant Site Preparation - A Review: C.J.Venkatakrishnan, S.Bhuminathan and Chitraa.R.ChandranLouis HutahaeanNo ratings yet
- TN-4620190912122 Form21B Signed PDFDocument1 pageTN-4620190912122 Form21B Signed PDFDHEEN MEDICALSNo ratings yet
- Ancient Egyptian Agriculture - WikipediaDocument39 pagesAncient Egyptian Agriculture - WikipediaDiawara HawkeyeNo ratings yet
- Frenkel's ExerciseDocument40 pagesFrenkel's ExerciseManiu EmeseNo ratings yet