Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Medieval History Prelims Booster Consolidated 14135642 2023 04 22
Medieval History Prelims Booster Consolidated 14135642 2023 04 22
Uploaded by
AMSCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Themes in Indian History - Part - 1 Through MindmapsDocument39 pagesThemes in Indian History - Part - 1 Through MindmapsABHISHEK SINGH100% (1)
- Odisha GK Study IqDocument53 pagesOdisha GK Study Iqumakanta panigrahyNo ratings yet
- Prophetic Visions of Future EventsDocument63 pagesProphetic Visions of Future EventsSyncOrSwim67% (6)
- 8 Erotic Nights - Passionate Encounters That Inspire Great Sex For A Lifetime by Charla HathawayDocument180 pages8 Erotic Nights - Passionate Encounters That Inspire Great Sex For A Lifetime by Charla HathawayJanny23SD46% (50)
- ChronologyDocument14 pagesChronologyRajat XanderNo ratings yet
- Rizal ExercisesDocument11 pagesRizal Exerciseskathryn soriano91% (11)
- In Christ Alone PDFDocument3 pagesIn Christ Alone PDFAldrin PaguiriganNo ratings yet
- John Llewelyn The Middle Voice of Ecological Conscience A Chiasmic Reading of Responsibility in The Neighborhood of Levinas Heidegger and OthersDocument161 pagesJohn Llewelyn The Middle Voice of Ecological Conscience A Chiasmic Reading of Responsibility in The Neighborhood of Levinas Heidegger and OthersLucilla Guidi100% (1)
- Medieval History Notes by AnishDocument51 pagesMedieval History Notes by AnishAnish Rahul100% (1)
- P1 - Harshavardhana - 12945273 - 2022 - 12 - 19 - 18 - 31Document17 pagesP1 - Harshavardhana - 12945273 - 2022 - 12 - 19 - 18 - 31Kumar GauravNo ratings yet
- Imperial Cholas - 14126667 - 2022 - 12 - 19 - 18 - 30Document43 pagesImperial Cholas - 14126667 - 2022 - 12 - 19 - 18 - 30Kumar GauravNo ratings yet
- Ancient Indian HistoryDocument7 pagesAncient Indian Historykomal komalNo ratings yet
- P4 - Later Vedic Period - 5906828 - 2022 - 12 - 19 - 18 - 30Document14 pagesP4 - Later Vedic Period - 5906828 - 2022 - 12 - 19 - 18 - 30Kumar GauravNo ratings yet
- P1-Sangam Age - Sangam Literature - 12945291 - 2022 - 12 - 19 - 18 - 30Document21 pagesP1-Sangam Age - Sangam Literature - 12945291 - 2022 - 12 - 19 - 18 - 30Kumar GauravNo ratings yet
- P2 - Harshavardhana - 12945278 - 2022 - 12 - 19 - 18 - 32Document10 pagesP2 - Harshavardhana - 12945278 - 2022 - 12 - 19 - 18 - 32Kumar GauravNo ratings yet
- Ancient History Prelims Booster Consolidated PDF 14224663 2023 04Document53 pagesAncient History Prelims Booster Consolidated PDF 14224663 2023 04AMSNo ratings yet
- Ancient History - Prelims Booster Consolidated - A4 - 18767013 - 2024 - 01 - 01 - 12 - 41Document54 pagesAncient History - Prelims Booster Consolidated - A4 - 18767013 - 2024 - 01 - 01 - 12 - 41tarun choudharyNo ratings yet
- Neha Bhosle - GS Static Notes PDFDocument183 pagesNeha Bhosle - GS Static Notes PDFBhavya Prakash YadavNo ratings yet
- Short Notes IAS PQRN Indian History Puaird - 4787 - 1681447014Document101 pagesShort Notes IAS PQRN Indian History Puaird - 4787 - 1681447014Harish MeenaNo ratings yet
- History of Medieval IndiaDocument21 pagesHistory of Medieval IndiaRobin SharmaNo ratings yet
- All Important Terms History (CDS, Capf, Upsc-Cse)Document2 pagesAll Important Terms History (CDS, Capf, Upsc-Cse)Shubham KhairnarNo ratings yet
- Buddhism & JainismDocument38 pagesBuddhism & JainismWHO AM I100% (1)
- Art & Culture Prelims NotesDocument38 pagesArt & Culture Prelims NotesSuraj Kathayat100% (1)
- Medieval History With Important Facts BY KRISHDocument50 pagesMedieval History With Important Facts BY KRISHVamshi Krishna Acharya100% (1)
- L IV E: Indian PolityDocument111 pagesL IV E: Indian PolityALLU SRISAINo ratings yet
- Polity Laxmikant Short NotesDocument120 pagesPolity Laxmikant Short NotesKundanNo ratings yet
- History: Current AffairsDocument11 pagesHistory: Current AffairsAditi chokha iNo ratings yet
- Ancient History Notes by AnishDocument24 pagesAncient History Notes by AnishAnish Rahul100% (2)
- Medieval History - GS Foundation - Class Notes - Sunya IASDocument92 pagesMedieval History - GS Foundation - Class Notes - Sunya IASGoldNo ratings yet
- PEP - Handout - Modern History 1Document27 pagesPEP - Handout - Modern History 1anon_463330020No ratings yet
- History Ghatna Chakra PointerDocument9 pagesHistory Ghatna Chakra PointerSarcastic LawyerNo ratings yet
- Geography Handout 8Document24 pagesGeography Handout 8Gagandeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Modern History - Prelims Booster Consolidated - 14134705 - 2022 - 12!19!19 - 56Document123 pagesModern History - Prelims Booster Consolidated - 14134705 - 2022 - 12!19!19 - 56Kumar GauravNo ratings yet
- ANCIENT HISTORY Prelims Notes: Pugalur Incsription (1st Century AD) - Mentions 3 Madhuban Plate Inscription - HarshaDocument33 pagesANCIENT HISTORY Prelims Notes: Pugalur Incsription (1st Century AD) - Mentions 3 Madhuban Plate Inscription - HarshaMeghana RajputNo ratings yet
- New 1 Modern History - Basic LevelDocument38 pagesNew 1 Modern History - Basic LevelofferNo ratings yet
- Key Terms - Ancient, Medieval & Modern HistoryDocument28 pagesKey Terms - Ancient, Medieval & Modern HistoryAditya DwivediNo ratings yet
- Modern - History Unique Shiksha SampleDocument26 pagesModern - History Unique Shiksha SampleJoseph SmithNo ratings yet
- Peasant-Movements 41307Document2 pagesPeasant-Movements 41307Joey saravanaNo ratings yet
- Modern History EvernoteDocument18 pagesModern History EvernoteKuldeep SinghNo ratings yet
- India Physical: Chapter - 1Document11 pagesIndia Physical: Chapter - 1Ankit SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- UPSCGeography GSNotesDocument979 pagesUPSCGeography GSNotesSamira ThakurNo ratings yet
- Polity Notes For PrelimsDocument90 pagesPolity Notes For PrelimsVivekanand sahooNo ratings yet
- Ancient History Old Ncert NotesDocument16 pagesAncient History Old Ncert Notesmanish krNo ratings yet
- Economics Prelims Notes GenDocument93 pagesEconomics Prelims Notes Gensrk08072003No ratings yet
- Indian History Chronology - Ancient India To Modern India - Clear IASDocument5 pagesIndian History Chronology - Ancient India To Modern India - Clear IASRahul KumarNo ratings yet
- Iasbaba'S Prelims Exclusive PROGRAM (PEP) 2022: Medieval History HandoutsDocument11 pagesIasbaba'S Prelims Exclusive PROGRAM (PEP) 2022: Medieval History HandoutsGagandeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Ancient HistoryDocument65 pagesAncient HistoryRavi kumarNo ratings yet
- Geography Handout 10Document25 pagesGeography Handout 10Gagandeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Modern History Revision Notes - IxambeeDocument25 pagesModern History Revision Notes - IxambeeTanish KalraNo ratings yet
- History Handout 14Document19 pagesHistory Handout 14Gagandeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Trick Best TrickDocument21 pagesTrick Best Trickfindsatya88No ratings yet
- History Handout 15Document14 pagesHistory Handout 15Gagandeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Ancient and Medieval Indian History Notes by Ias - NetworkDocument102 pagesAncient and Medieval Indian History Notes by Ias - NetworkSai CharanNo ratings yet
- Indian Polity Mind Maps EbookDocument7 pagesIndian Polity Mind Maps EbookAbhi Singh50% (2)
- TABLESDocument22 pagesTABLESpranita kaleNo ratings yet
- History Handout 10Document49 pagesHistory Handout 10Gagandeep KumarNo ratings yet
- GK BookDocument13 pagesGK BookJatin VatsNo ratings yet
- Modern Indian History 2022Document30 pagesModern Indian History 2022prakash gujarNo ratings yet
- Governor General/Viceroy Period Points To RememberDocument5 pagesGovernor General/Viceroy Period Points To Rememberkittu_sivaNo ratings yet
- Medival History Notes TamilnaduDocument8 pagesMedival History Notes Tamilnadumanish krNo ratings yet
- Modern Indian HistoryDocument203 pagesModern Indian HistoryRaktim DasNo ratings yet
- Modern History Ready Reckoner 2019 PDFDocument80 pagesModern History Ready Reckoner 2019 PDFPrafull Bhandari0% (1)
- Polity Repeated Themes & Repeated Topics 2013 2022 IAS PCS PathshalaDocument7 pagesPolity Repeated Themes & Repeated Topics 2013 2022 IAS PCS Pathshalaekta rawatNo ratings yet
- India Map Physiographic Divisions of IndiaDocument11 pagesIndia Map Physiographic Divisions of IndiaSanjana SinghNo ratings yet
- Medieval History (12th Sept) - 25339664 - 2024 - 01 - 20 - 11 - 47Document105 pagesMedieval History (12th Sept) - 25339664 - 2024 - 01 - 20 - 11 - 47alok singhNo ratings yet
- 02 Maths Formula (Aditya Ranjan)Document8 pages02 Maths Formula (Aditya Ranjan)AMSNo ratings yet
- Ancient History Prelims Booster Consolidated PDF 14224663 2023 04Document53 pagesAncient History Prelims Booster Consolidated PDF 14224663 2023 04AMSNo ratings yet
- 47 - (REASONING) (CALENDAR) Calender Practice Sheet 01Document3 pages47 - (REASONING) (CALENDAR) Calender Practice Sheet 01AMSNo ratings yet
- Pet 2022Document35 pagesPet 2022AMSNo ratings yet
- PET Special Ancient History Hand Written NotesDocument25 pagesPET Special Ancient History Hand Written NotesAMSNo ratings yet
- Modern History NotesDocument24 pagesModern History NotesAMSNo ratings yet
- Chemestry Hand Written Notes For PET Exam 2022Document44 pagesChemestry Hand Written Notes For PET Exam 2022AMSNo ratings yet
- The Objective and Subjective HGADocument13 pagesThe Objective and Subjective HGAMidnite Scholar50% (2)
- Freedom of Religion CasesDocument30 pagesFreedom of Religion CasesKeangela LouiseNo ratings yet
- God and MoneyDocument3 pagesGod and Moneyhotchick_19No ratings yet
- Holy Marriages and Their Outcomes Depicted On Near East Cylinder Seals Tom Van BakelDocument9 pagesHoly Marriages and Their Outcomes Depicted On Near East Cylinder Seals Tom Van BakelSrini KalyanaramanNo ratings yet
- Thieves of Fire - Rimbaud, Adūnīs, and Arab PoeticsDocument14 pagesThieves of Fire - Rimbaud, Adūnīs, and Arab Poeticsxsim57100% (1)
- Lisboa2023 WYD Press Release WYD LogoDocument2 pagesLisboa2023 WYD Press Release WYD LogohoahairauNo ratings yet
- MergeDocument30 pagesMergevegavergiagaraNo ratings yet
- Vaggione Archaeus 2002Document4 pagesVaggione Archaeus 2002CAStmNo ratings yet
- Significance of The Bird Albatross in The Rime of The Ancient MarinerDocument3 pagesSignificance of The Bird Albatross in The Rime of The Ancient Marinerشاكر محمود عبد فهدNo ratings yet
- ART 2 - Axiology On The Integration of Knowledge Islam andDocument7 pagesART 2 - Axiology On The Integration of Knowledge Islam andMing Teck TanNo ratings yet
- Novena PrayerDocument22 pagesNovena PrayerMia LamosteNo ratings yet
- AlcuinDocument8 pagesAlcuinA Richard AllenNo ratings yet
- The Chrysalids NOTESDocument26 pagesThe Chrysalids NOTESVishesh MattaiNo ratings yet
- Evergreen PPSC, FPSC, NTS and OTS MCQS SolvedDocument155 pagesEvergreen PPSC, FPSC, NTS and OTS MCQS Solvednabeel ahmadNo ratings yet
- Interview of Papaji by Christopher TitmussDocument19 pagesInterview of Papaji by Christopher TitmussKali AneeNo ratings yet
- Daftar Absensi Uas Analisis Sistem Tenaga Listrik Kode Seksi 5118Document2 pagesDaftar Absensi Uas Analisis Sistem Tenaga Listrik Kode Seksi 5118DaryAntoNo ratings yet
- The Scarletletter Chapter SummaryDocument3 pagesThe Scarletletter Chapter SummaryvalerieehartmanNo ratings yet
- 18 Maha Shakthi PeetamDocument1 page18 Maha Shakthi PeetamSree RajaRajeshwari PeetamNo ratings yet
- C. L. C. Certified Life Coach Christian Life Coaching Christ As My (Our) Life CoachDocument37 pagesC. L. C. Certified Life Coach Christian Life Coaching Christ As My (Our) Life CoachPaula Manalo-Suliguin100% (1)
- Political Islam - Religion and Politics in The Arab World PDFDocument252 pagesPolitical Islam - Religion and Politics in The Arab World PDFNadeem IqbalNo ratings yet
- 3751 Class 9hindi Poem 1 Saakhi by Kabir DasDocument6 pages3751 Class 9hindi Poem 1 Saakhi by Kabir DasShauryaNo ratings yet
- John Chrysostom, Basil The Great - The Orthodox Liturgy (1982, Oxford University Press) - Libgen - LiDocument231 pagesJohn Chrysostom, Basil The Great - The Orthodox Liturgy (1982, Oxford University Press) - Libgen - Li罗月圆No ratings yet
- 156109785009-AL-BASEERA 3 (Vol. 2 - Issue. 1) JUN-2013Document23 pages156109785009-AL-BASEERA 3 (Vol. 2 - Issue. 1) JUN-2013potato potatoNo ratings yet
- Maurice de Wulf, History of Medieval PhilosophyDocument544 pagesMaurice de Wulf, History of Medieval Philosophylomaxx21100% (7)
- 2.05 HOLD CLP Expanded OutlinesDocument74 pages2.05 HOLD CLP Expanded OutlinesJENINE VICTORIANONo ratings yet
Medieval History Prelims Booster Consolidated 14135642 2023 04 22
Medieval History Prelims Booster Consolidated 14135642 2023 04 22
Uploaded by
AMSOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Medieval History Prelims Booster Consolidated 14135642 2023 04 22
Medieval History Prelims Booster Consolidated 14135642 2023 04 22
Uploaded by
AMSCopyright:
Available Formats
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
Growth of feudalism
● following the breakup of roman empire in 6th century
● king >> chief (vassal of king) >> sub-vassals
● chiefs had fief = tracts of land
● kind could in theory take fief of disloyal vassal, but not practically done
● serfdom
○ serf was peasant, couldnt marry, migrate, change profession without
permission of lord
● manor = castle where lord lived
● lord to maintain law and order, dispense justice
● army was decentralised to lords who had to maintain fixed force of cavalry and
infantry for the service of king
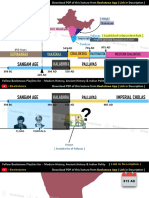
Northern India : age of three empires (800-1000)
pala >> eastern india
pratihara >> western india + upper gangetic valley
rashtrakuta >> deccan, lasted longest among the three
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
Palas
● Founded by gopala, 750 AD
● He was elected king by notable men to end anarchy
● rule of dharampalmarked by tripartite struggle for the control of kannauj and
northern india
○ revived nalanda university
○ founded vikramshila university, on banks of ganga
● arab merchant sulaiman has written account of pala dynasty
○ large military force, not sure whether feudal or standing
● great patrons of buddhist learning and religion, patronage to saivism and
vaishnavism as well
○ built many viharas
● close cultural and economic relations with Tibet and SE asia
● pala administration
○ bhukti (province) under uparika
○ mandal or visaya under visayapati
pratiharas or gurjara pratiharas
● originated from gurjaras who were pastoralists and fighters, like jats
● founder mostly Nagbhata I 730 AD
● greatest ruler = Bhoja / mihir bhoja
○ devotee of vishnu, adopted title of "adivaraha"
● Al masudi visited empire, calls it Al-Jujr
● had best cavalry in country (proximity to arab)
● great patrons of learning and literature = Rajshekhar lived in court of mahipala,
grandson of bhoja
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
Chalukya dynasty
● Western chalukya dynasty (main) 543 AD to 757 AD and again from 975 AD
to 1189 AD
● founder pulakesin I
● Eastern chalukya ruled vengi in eastern andhra pradesh from early 7th to
early 11th century
● achievement of Pulakesin II defeated Harshavardhana on the banks of the
river Narmada.
● Kirtivarman II was the last of the rulers of the Chalukyas.
● He was defeated by Dantidurga, the founder of the Rashtrakuta dynasty in
757 AD
● chalukya dynasty at its peak - maharashtra, karnataka, andhra pradesh. parts
of gujarat and madhya pradesh
● highly centralised administration, village autonomy absent
● great maritime power
rashtrakutas
● founded by dantidurga, capital at manyakhet or malkhed 735 AD
● greatest rulers = Govinda III and amoghavarsha
● govinda III = an inscription mentions that he "terrified kerala, pandya and chola
kings and caused pallavas to wither"
● amoghavarsha wrote first kannada book on poetics - kavirajamarg
● Al masudi writes about this too
● patronised shaivism, vaishnavism and jainism; tolerant religious policy
● Krishna I built famous rock cut temple of shiva (kailasha temple) at ellora in 9th
CE
● patronised sanskrit and jain literature
Apabhramsa corrupt languages, which were fore-runners of modern languages
political organisation and ideas of above three
● king's position generally hereditary, rules of succession not rigid
● the position of ministers was also generally hereditary
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
● Antahpur = officials of royal households
● empires consisted of areas directly administered as well as by vassal chiefs
● directly administered territories in pala and pratihara empire divided into
○ bhuktis (provinces) governed by uparika (collect land revenue, maintain
L&O)
○ mandala or visaya (district) headed by visyapati (same)
○ pattala = unit below visaya
○ village
● directly administered territories in rashtrakutas empire divided into
○ rashtras
○ visaya = district
○ bhukti = under visaya
○ village
● law and order in towns responsibility of koshta pal or kotwal
● Rise in deccan of hereditary revenue officers called nad gavundas or desa
gramakutas
● patronage to all religions, persecuted none
The Tripartite Struggle for control of northern India took place in the ninth century.
South India : The Chola Empire (900-1200)
● founder = vijayalaya in middle 9th CE
● occupied delta of kaveri river
● the greatest chola rulers were Rajaraja (985-1014) and his son Rajendra I (1014-
1044)
● Rajaraja
○ invaded sri lanka and annexed its northern part to its empire
○ conquest maldives
● Rajendra I
○ completely overrun pandya and chera countries, included them in his
empire
○ conquest of sri lanka complete
○ marched across kalinga to bengal, crossed ganga and defeated two local
kings, followed in reverse the same route followed by samudragupta
■ assumed title "gangaikondachola" to commemorate
■ built new capital near mouth of kaveri and called it
gangaikondacholapuram
○ naval expeditions in SE asia
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
○ Due to strength of chola navy in bay of bengal, it was called for some time
"chola lake"
● relations with china
● encouragement to local self government
● declined early 13th CE
● vetti tax taken not in cash but in form of forced labour
chola government
● king >> council of ministers
● chola state divided into 4 mandalams or provinces
● nadu basic unit of administration = consisted of number of villages
● nadus grouped into valanadus
● officials paid by grant of lands
● attention to irrigation, survey of land to fix governments share
● Ur was assembly of village, of non brahmins
● sabha or mahasabha was gathering of adult men in brahmana villages (they
were agraharams), sabha had varied powers
cultural life
● growth and climax of bhakti movement
● temple architecture attained climax
● Nayanars and Alwars, devotees of shiva and vishnu respectively flourisged in
tamil kingdoms between 6th CE and 9th CE
● Tirumurai = often called fifth veda, 12th century writings of saivite saints, songs in
praise of shiva
○ tevaram is part of tirumurai
Sena dynasty
● Founded by Vassal of palas, Hemant sena in very early 11th century
● Ballala Sena (1160-1178) introduced the social reforms in Bengal known as
Kulinism
● Bengal region
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
Eastern Ganga dynasty
● The Western Gangas ruled in Mysore state (Gangavadi) from about 250 to about
1004 CE. The Eastern Gangas ruled Kalinga from 1028 to 1434–35.
● Built Puri Temple, Sun temple Konark
● After them came Gajapati dynasty
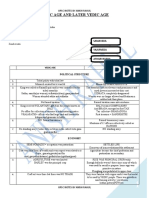
Early medieval India
● After death of Harsha (606 to 647 CE), no political unity in north India for next
five centuries
Rajput kingdoms 7th -12th
● Began from seventh and eighth century till Muslim conquest in 12th century
● Were main defenders of Hindu religion and culture in period of Muslim
aggression
● They are considered descendants of foreign invaders and Indian kshatriya
● Indianised and absorbed into Indian culture
● Made war their chief occupation
● Trade and agriculture also prospered
● Built strong forts
● There were many Rajput kingdoms: Gurjara pratihara, chauhan, paramaras
● Gurjara pratihara were the earliest Rajput rulers. Its first great ruler was
Harishchandra
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
Weakness
● Constant infighting weakened them
● Never United against common enemy
● Lack of political oversight and constant rivalries prevented any combined
opposition to Muslim invaders
Arab conquest of sind 712 AD
● Muhammad bin qasim, who was commander in chief of one of the caliph set up
by followers of prophet Muhammad, Umayyad kingdom (the other being
abbasid) invaded sind in 712 AD
● He won, gave sind status of zimmis (protected subject)
● Did not interfere in the lives and property of the people
The Muslims could not expand further into India due to powerful Pratiharas in the
western India
By the end of 9th century, abbasid caliphate declined = The turkish governors estb
independent kingdom and caliph became only ritual authority.
One of these governors >> alptigin, whose capital was ghazni. Mahmud of ghazni is
his descendent
Mahmud of ghazni (AD 997 - 1030)
Importance:
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
● Said to have made 17 raids into India
● Raids were aimed at plundering rich temples and cities of north India
● His empire extended from punjab in the east to caspian sea on West. Samarkand
in north to Gujarat in south
● The ghaznivad empire roughly included persia, transoxiana, Afghanistan and
punjab
Transoxiana: modern day portions of Central asia
● Firdausi was eminent poet in his court, who wrote shah namah.
● Alberuni was also in his court, write kitab-i-hind, an account on India
● He paved way for afgans and turks for further conquest in India because he
destroyed the Hindu shahi kingdom guarding India's frontiers
Muhammad Ghuri
● Started as vassal of Ghazni but independent later
● Brought ghazni under his control
● Unlike mahmud of ghazni, he wanted to conquer India and expand empire
in this direction
Battle of Tarain 1191-1192
● Muhammad Ghuri vs confederation of Rajputs under Prithviraj Chauhan
● Muhammad Ghuri defeated
● Humiliated Ghuri came again with a larger army and won second battle of Tarain
Importance of second battle of Tarain
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
● Deadly blow to political prestige of Rajputs
● First Muslim kingdom firmly estb in India at ajmer
● Ghuri left his favourite general qutb ud din aibak to make further conquest in
India
Causes of failures of Hindu kingdoms
● Lacked unity
● Divided by factions
● Mutual conflicts between Rajput princes
● Turkish did not have superior weapons
● Military method outdated and inferior than Muslims
● Indians relied on elephants and Muslims possessed quick moving cavalries
● Muslim army was better organised and had able leaders
● Hindus were always in a defensive position
● Muslim's religious zeal and greed for greater wealth of India provided them
stimulus
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
Slave Dynasty 1206 - 1290
● Also called mamluk Dynasty, mamluk was quranic term for slave
Three dynasties were established during this period:
● Qutbi Dynasty 1206 - 1211 founded by qutb ud din aibak
● First ilbary Dynasty 1211 - 1266 founded by iltutmish
● Second ilbary Dynasty 1266 - 1290 founded by balban
Qutbuddin aibak 1206 - 1211
● Was a slave of Muhammad Ghuri who made him governor of his Indian
possessions
● Declared independence after the death of Ghuri
● Founded the slave Dynasty as well as Delhi sultanate
● Assumed title of sultan and made lahore as capital
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
● Muslim writers call him laksh baksh meaning giver of lakhs, he gave liberal
donations
● Patronised great scholar hasan nizami
● Started the construction of qutb minar (238 ft) after the name of sufi saint
qutbuddin bakhtiyar
● built Quwwat-ul-Islam mosque; started construction of Arhai din ka jhopra
● Died playing chaugan meaning polo
Iltutmish 1211 - 1236
● Belonged to ilbary tribe hence his Dynasty named as ilbary Dynasty
● He was sold as slave to qutbuddin aibak
● Aibak appointed him as iqtadar (governor) of gwalior
● In 1211 he defeated Aram Baksh, son of aibak and became sultan
● Mongol policy of iltutmish saved India from the wrath of Chengiz khan
● Received letter of recognition (mansur) from Abbasid caliph in 1229 by which he
became legal Sovereign ruler of India
● Nominated his daughter Razia as successor
● Thus Heriditary succession to Delhi sultanate was initiated by iltutmish
● Introduced arabic coinage into India and silver tanka became standard coin in
medieval India
● Created new class of ruling elite of forty powerful military leaders called The
Forty
● first Muslim sovereign to rule from Delhi
● first to introduce land assignment called Iqtadari
○ Iqtadari system did not confer any ownership in land and it was subject to
transfer.
Era of Balban 1246 - 1287
● Ghiyasuddin Balban, also known as ulugh khan
● Enhanced the power of monarchy
● Served as regent or naib to his Javai Sultan Nasiruddin mahmud (son of
iltutmish)
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
● Married his daughter to Sultan
● In 1266 Nasiruddin Mahmud died without any issues and Balban ascended the
throne
● Knew that the threat to sultanate was The Forty and determined to break them
● According to Balban, sultan was god's shadow on earth and recipient of divine
grace
● Introduced rigorous court discipline and new customs such as prostration and
kissing sultan's feet to prove his superiority over nobles
● Introduced persian festival nauroz to impress nobles and people with his wealth
and power
● Indian Muslim were not given imp post in the government
● Appointed spies to monitor activities of nobles
● Instead of expanding his kingdom, he paid more attention to restoration of law
and order
● Estb separate military dept called diwan i arz
● Roads became safe to travel as he severely punished plunderers
● In north West mongols reappeared and Balban sent his son prince mahmud, he
got killed
● Balban could not safeguard India from the mongol invasion
Khalji Dynasty 1290 - 1320
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
● Advent of khalji Dynasty marked the zenith of Muslim imperialism in India
Jalaluddin khalji
● Generous and lenient but not weak
● His son in law : Alauddin khalji
Alauddin Khalji 1296 - 1316
● Took harsh measures to ensure that his reign was free from rebellions
● was the first Sultan who invaded South India.
● believed in the Divine Right Theory of Kingship
Reforms of Alauddin Khalji
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
● army
○ Maintained large permanent standing army
○ Introduced system of dagh - branding of horses and prepared huliya -
descriptive list of soldiers
○ Strict review of army from time to time
● markets
○ Introduced market reforms: established four separate markets, each under
control of high officer called shahana i mandi
○ Grain was stored in government store houses
○ Regulations were issued to fix price of all commodities
○ Secret agents, munhiyans to send reports to Sultan regarding functioning
of the markets
○ Took important steps in land revenue administration
○ First sultan in Delhi who ordered for measurement of land
● culture
○ Patronised poets like amir khusrau and amir hasan
○ Built alai darwaza, an entrance to qutb minar
○ Constructed new capital at siri
● Separate department called diwani riyasat created under Naib i riyasat
Tughlaq Dynasty 1320 - 1414
● Founder : ghiyasuddin tughlaq
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
Muhammad bin tughlaq 1325 - 1351
● Only Delhi sultan who received comprehensive literary, religious and
philosophical education
● Introduced a token currency
● Capital change from Daulatabad to Delhi (1326-27)
Agricultural reforms
● Gave takkavi loans (loans for cultivation) to farmers to buy seed and extend
cultivation
● Separate department of agriculture, diwan i kohi was estb
● Prepared of famine code for the help of famine people
Firoz tughlaq 1351 - 1388
● Khan i jahan : prime minister of Delhi sultanate
● Built famous town firoz shah kotla
Administrative reforms
● Strictly followed the advice of ulemas in running the administration
● Pleased nobles and assured Heriditary succession to their properties
● Thus iqta system was not only revived but also made Heriditary
● Jizya was strictly imposed on non Muslims
● First sultan to impose irrigation tax
● Diwan i khairat created to take care of orphans and children
● Treated hindus as second grade citizens
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
● Intolerant towards shia Muslims and sufis as he was guided by ulemas
Death of firoz in 1388 led to disintigration of Delhi sultanate. This led to invasion of
Timur in 1398.
Sayyids 1414 - 1451
● Before his departure from India, Timur appointed Khizr khan as governor of
multan
● He captured Delhi and estb Sayyid Dynasty
● Tried to consolidate Delhi but in vain
● Sayyids were succeeded by Lodis
Lodis 1451 - 1526
● Were afgans
● Buhlul Lodi was first Afgan ruler while his predecessor were all turks
● Buhlol lodi succeeded by his son sikandar lodi
Sikandar lodi 1489 - 1517
● Greatest of three lodi Sovereigns
● He was a bigot
● Destroyed many Hindu temples and imposed many restrictions on Hindus
● founded city of agra
Ibrahim lodi
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
● Greatly displeased by the arrogance of Ibrahim lodi, Daulat khan (governor of
Punjab) invited babar to invade India
● Babar defeated ibrahim lodi in first battle of Panipat in 1526
India under Delhi sultanate
Administration
● Their administrative system made powerful impact on Indian provincial kingdoms
and later on Mughal system of administration
● Delhi sultanate was Islamic state with religion islam
● Sultans considered themselves reps of caliph
● Iltutmish, Muhammad bin tughlaq and firoz tughlaq obtained mansur or letter of
permission from caliph
● No clear succession law during this period, all sons had equal claim
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
Central government
● Naib: practically enjoyed all powers of sultan and exercised control over all
departments
● Next to Naib was wazir:heading finance department called Diwani wizarat
● Military department: diwani ariz, headed by ariz i mumalik. He was not
commander in chief of the army, sultan was. This department was first set up by
Balban
● Diwani rasalat: department of religious affairs, headed by sadr
● Head of judicial department: qazi
● Hindus were governed by their own personal laws and their cases were
dispensed by village panchayats
● Diwan i insha: department of correspondence
Local government
● Provinces under Delhi sultanate: iqtas
● Governors of the provinces were called muqtis or walis
● Provinces were divided into shiqsand further, parganas
● Shiq was under control of shiqdar
● Parganasconsists of number of villages was headed by amil
● Village was basic unit of administration, village headman was called muqaddam
or chaudhary
● Patwari : village accountant
Economy
● Lands were classified into three categories
○ Iqta land: assigned to officials as iqtas instead of payment for their
services
○ Khalisa land: under direct control of sultan and revenue generated was
spent for maintenance of royal courts and royal households
○ Inam land : land granted to religious leaders or institutions
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
● Peasant had miserable condition. Paid one third of produce as land revenue,
sometimes half.
○ However, tughlaqs took efforts to enhance agricultural production by
providing takkavi loans
○ Muhammad bin tughlaq created separate department of agriculture:
Diwani kohi
● Process of urbanisation gained momentum
● Cotton textile and silk industry flourished
● Paper industry, leather making, metal crafts and carpet weaving flourished
Coinage:
● Gold coins or dinars became popular during reign of Alauddin Khalji after his
south indian conquests
● Iltutmish issued several types of tankas
● Muhammad bin tughlaq issued token currency and issued several types of gold
and silver coins
Social life
● Little change in the structure of Hindu society
● Traditional caste system prevelant
● Subversion of women and sati continued
● Muslim society remained divided into several ethnic and racial groups
● Hindus were considered zimmis or protected people, forced to pay jizya tax
Art and architecture
● Turqs introduced:
○ Arches
○ Domes
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
○ Lofty towers or minarets
○ Decorations using arabic script
Music
● New musical instruments sarangi and rabad introduced
Literature
● Ziauddin barani's Tarikh i firoz shahi contains history of tughlaq Dynasty
● Minhaj us siraj wrote tabaqat i nasari, a general history of Muslim Dynasty up to
1260
● Amir khusrau's
○ Invented sitar
○ He evolved new style of light music Qawwali by Blending Hindu and
iranian system.
○ introduced many new ragas such as ghora and sanam
○ created new style of persian poetry called sabaq i hind
○ khazain ul futuh speaks about Alauddin's conquest
○ Tughlaq nama deals with rise of ghiyasuddin tughlaq
● Zia nakshabi was first to translate sanskrit stories into persian
● In arabic, Alberuni's kitab ul hind is most famous work
● firdausi wrote shah namah
Distinctive characteristics of islam:
● Monotheism
● Equality and brotherhood of man
● Rejections of rituals and Class divisions
Sufism
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
● Liberal reform movement within islam
● Origin in persia and spread in India in 11th century
● sama sufi musical recitations
Main points
● Liberal reform movement within Islam, origin Persia
● form of islamic mysticism stresses on asceticism
● First sufi saint : shaikh ismail of lahore
● 2 broad sufi orders = bashara and beshara
● 12 silsila under basharas - imp = chisti and suharawadi
○ Famous nizamuddin auliya belonged to chishti order
● in order to realise god, you have to destroy yourself - called fanaa (annihilation)
● be humble, considerate, control desires
● Stressed on love and devotion as effective means of realisation of God
● Love of God meant love of humanity
● Service to humanity as service of God
● Self discipline essential condition to gain knowledge of God
● Laid stress on inner purity
● One must have guidance of pir or guru, without which spiritual development is
not possible
Bhakti movement
● started 7th 8th century in kerala and TN; reached north india 15th century
● TN and kerala = alwars and nayanars
● karnataka = basavanna, akkamahadevi, allama prabhu
● maharashtra = jnandeva, namdev and tukaram
● north india = ramananda, chaitanya, guru nanak, kabir, ravidas, mirabai
causes of rise of bhakti movmt
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
1. evil practices of hinduism
2. fear of spread of islam
3. caste system
4. complicated ritualism
5. need for fulfilling method of worship and salvation
Sankara Ramanuja
Doctrine of advaita Doctrine of vishishtadwaita
God is nirgunabrahmana (god is God is sagunabrahmana
without attributes)
(god with attributes)
God, soul, matter are not real Real
Advocated prabattimarga or path of
self surrender to god
Madhava 13th century, karnataka
● Propogated dvaita
● there is difference between atman (individual soul) and brahman (ultimate reality,
god)
● his philosophy = tattvavada = arguments from a realist viewpoint
● World is not an illusion but reality
● God, soul, matter are unique in nature
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
● 3 correct means of knowledge =pratyaksha (perception), anumana(inference)
and shabda (of expert)
Tulsidas composed ramacharitramanas, hindi version of ramayana
Ramananda, kabir, nanak
● Did not believe in rituals or ceremonies
● Condemned polytheism and believed in one God
● Denounced idolatry
● Bhakti as the only means of salvation
● Emphasized fundamental unity of all religions
Ramananda
● First to employ vernacular medium to preach his ideas
● Born at Allahabad
● His two important contributions to bhakti tradition:
○ Simplification of worship
○ Emancipation of people from traditional caste rules
● Opposed caste system
● Kabir was his disciple
Kabir (15th century)
● His objective was to reconcile Hindus and Muslims and establish harmony
between them
● Denounced idolatry and rituals
● Laid emphasis on equality of man before god
● Emphasized on essential oneness of all religions
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
● Devotion as effective means to salvation
Guru nanak
● Founder of Sikh religion
● Disciple of kabir
● Denounced cast distinctions and rituals
● 'abide pure amidst the impurities of the world'
● Dedicated himself to establish harmony between Hindus and Muslims
Chaitanya (1486-1534)
● Krishna cult
● Preached universal brotherhood of man
● Condemned all religion and caste based distinctions
● From bengal
Gnanadeva
● Founder of bhakti movement in Maharashtra
● It was called Maharashtra dharma
● His commentary on bhagavatgita: gnaneswari
● Other bhakti saints: tukaram, namadeva, ekanatha
Importance of bhakti movement
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
● Provided impetus for the development of regional languages such as Hindi,
marathi, Bengali, kannada etc. Through these languages they directly appealed
to the masses
● Lower classes were raised to a position of great importance
● Importance of women in society increased as movement gave equal importance
to them
● Gave people a simple religion
● introduced social giving like seva and dana
● community kitchens with free food
● believed in non violence
● helping poor farmers and feeding poor people
● free hostels for poor
● promoting folk culture
Music
Literature
1. Bhajan Kirtan
2. Quwwali 1. Rajasthani lang. — Pad
3. Meerabai’s Pads 2. Kannada - Vacchan
4. Akka Mahadevi’s Vacchan 3. Songs in bhajans and qawwali
5. Amir Khusro’s Sitar in Braj Bhasha (Urdu +khadi
6. Sattaria and Jhatra @Assam & boli)
Bengal 4. Divyaprabhandann — TN Alvars
7. Swami Haridas — Krishna | | Nathmuni
Vishnupada | teacher of Tansen | 5. Tanaram @south
Dhrupad style
8. Srimanta Shankardeva — Bhaona
| Assam
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
Mughal empire
Political history
Babur 1526 - 1530
● Founder of Mughal empire in India = timurid dynasty
● Original name : zahiruddin muhammad
● was descendent of changez and timur
● On 21st April 1526 first battle of Panipat took place. Ibrahim lodi got defeated
● Battle of khanua (near agra) 1527, babur vs rana sangha of mewar, babur
victorious
● significance
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
○ by controlling kabul and qandhar = gateway for attack in india, security to
india from external invasion for 200 years
○ greater indian share in trans-asian trade
○ era of small kingdoms ended as gunpowder and artillery became popular,
which were expensive
● begs means soldiers
Estimate of babur
● Turki was his mother tongue
● Great scholar in arabic and persian language
● He wrote his memoir: tuzuk i baburi in turki language. It provides vivid account of
India
● also wrote masnavi
● Was also a naturalist and described flora and fauna of India
● introduced new mode of warfare = combination of cavalry and artillery
● introduced new concept of state - CBC
○ based on strength and prestige of crown,
○ absence of bigotry and
○ fostering of culture and arts
Humayun 1530 - 1540
● Humayun means fortune, but he remained most unfortunate ruler of Mughal
empire
● Battle of chausa, 1539, sher khan (later sher shah suri) (Afgan leader) destroyed
Mughal army
● Battle of kanauj, 1540, same happened chakana
Humayun 1555 - 1556
● In 1555, he defeated afgans and recovered the Mughal throne
● He died in 1556 because he fell from the staircase of his library
● Was not a good general or warrior, was kind and generous
● Was a student of mathematics, astronomy and astrology
● Loved painting and wrote poetry in persian language
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
Sur interregnum 1540 - 1555
● Founder of sur Dynasty was sher shah, whose original name was farid. He
served under Afgan ruler of Bihar, who gave him title of sher shah for his bravery
Sher shah suri 1540 - 1545
● Waged extensive wars with Rajputs and expanded his empire
● His empire included whole of north India except assam, Nepal, Kashmir and
Gujarat
Sher shah's administration
King was assisted by four important ministers:
Diwan i wizarat Also called wazir, incharge of revenue and finance
Diwan i ariz Incharge of army
Diwan i rasalat Foreign minister
Diwan i insha Minister of communication
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
● All cultivable land was divided into three : good, middle, bad
● Introduced new silver coins called 'dam', they were in circulation till 1835
● Improved communications by laying four highways
● built sarai for convenience of travelers = hotel
● his roads and sarais are called arteries of his empire
● restored grand trunk road - from indus to sonargao in bengal
● Police was efficiently reorganised and crime was less during his reign = estb law
and order
● reforms for growth of trade and commerce
● currency reforms, attempted to fix standard weights and measures
● borrowed many ideas like branding of horses from allauddin khalji
● introduced the system of ‘Patta’ (title agreement) and Qubuliat (agreement of the
land).
● overall sound administration
● jizya continued though
Estimate of sher shah
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
● Pious Muslim, tolerant towards others
● Employed Hindus in important offices
● Built a mausoleum at sasaram
● Malik Muhammad jayasi wrote padmavat at during his reign
● his excessive centralisation of authority weakness
Akbar 1556 - 1605
● Defeated hemu (commander in chief of afgans) in second battle of Panipat in
1556
Akbar's Rajput policy
● Religious toleration
● Beneficial to both Mughal and Rajputs
Akbar's religious policy
● Abolished pilgrimage tax and abolished jizya (per capita yearly tax historically
levied on non Muslim subjects)
● Constructed ibadat khana at his new capital fatehpur sikri
● Disliked the interference of ulemas in political matters
● In 1579, he issued 'infallibility decree': required ulema to recognise him as
supreme authority in religious matters
● emphasised concept of sulh i kul or peace and harmony among religions
● In 1582, he promulgated new religion, din ilahi or tauhid i ilahi
○ mixture of different religions
○ Contained good points of all faith
○ Upholds no dogma
○ Basis was rational
○ Aimed at bridging the gulf that separated different religions
○ Did not compel anyone to accept his new faith, it's followers were only 15,
including birbal
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
cultural development
● first who had time and means to construct on large scale
● agra fort, red sandstone
● buland darwaza built to commemmorate akbars victory in gujarat
● Panch Mahal is constructed by Akbar in Fatehpur Sikri
● persian prose and poetry reached climax
● patronised tansen who composed many ragas
abul fazl 3 volume history of akbar reign, titled akbar nama
● first deals with akbars ancestors
● second events of akbar reign
● third is ain i akbari deals with akbar administration
social reform
● raised age of marriage 14 for girls, 16 for boys
● widow remarriage legalised
● against anyone having more than one wife
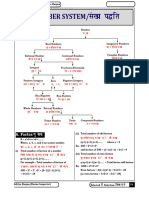
Land revenue administration
● Land revenue system of akbar was called zabti or bandobast system
● Improvised version of zabti system was given by raja todarmal called dahsala
system (not 10 year settlement, note difference)
○ The revenue was fixed based on average yield of land assessed on the
basis of past ten years
● other systems of assessment BaGhaNa Kan- batai or ghalla bakshi and nasaq
or kankut (means estimation)
● Land was divided into four categories:
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
Polaj Cultivated every year
Parauti Once in two years
Chachar Once in three or four
years
Banjar Once in five or more
years
Mansabdari system
● adopted by akbar in his administration
● Lowest rank was 10 and highest 5000 for nobles. Princes of royal blood had
even higher ranks
● Ranks were divided into two : zat and sawar
○ Zat means personal and it fixed personal status of a person
○ Sawar means no of horsemen that were required to maintain
● Mansab rank was not Heriditary
● All appointments, promotion, dismissal was made directly by the emperor
● borrowed from Persia.
● prevalent during the reign of Babur and Humayun, akbar made important
changes to make it efficient
● The duties of a mansabdar were not in accordance with the mansab or position
he held
administration more or less same as before, didnt make much changes
Jahangir 1605 - 1627
● Beheaded guru arjun, fifth sikh guru
● painting reached climax under jahangir
● pietra dura = floral designs with semi precious stones; use started in jahangir
reign
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
● A Baoli (Water tank) at Arab ki Sarai: built by Jahangir and is within Humayun's
tomb
Shah jahan 1627 - 1658
● Last years of shah jahan were clouded with bitter war of succession among his
four sons
● Aurangzeb emerged victorious
● mosque building reached climax under shah jahan
Aurangzeb 1658 - 1707
● Assumed the title alamgir, world conqueror
● aurangzeb was accomplished veena player; had banished singing in court but
not musical instruments;
● largest no of books on classical indian music in persian written during his reign
Deccan policy
● Deccan policy of Mughals started from the reign of akbar
● Aurangzeb after becoming Mughal emperor annexed deccan kingdoms, which
were the barriers between maratha and Mughals. Thus direct confrontation
between the two ensued.
Religious policy
● Staunch and orthodox sunni muslim
● Ideal was to transform India into Muslim state
● Special officer called muhtasib created to enforce moral codes
● Drinking, cultivation and use of bhang prohibited
● Discontinued practice of jharokha darshan
● Banned Construction of Hindu temples, destroyed Hindu temples
● In 1679, reimposed pilgrim and jizya tax
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
● Not tolerant of other Muslim sects, partly this is a reason to invade deccan
sultanate who were of shia faith
● Executed ninth sikh guru tez bahadur, this transformed sikh community into
warring community
Personality and character of aurangzeb
● In his private life he was industrious and disciplined
● Earned money for his personal expense by copying quran and selling those
copies
● Didn't consume wine
● Proficient in arabic and persian language
Vijayanagara and bahmani kingdoms
Vijayanagara empire
Sources
● Four dynasties: SaSTA
○ Sangama
○ Saluva
○ Tuluva
○ Aravidu
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
Ruled vijayanagara from AD 1336 to 1672
Sources of study of vijayanagara:
● Literary
● Archaeological
● Numismatics
Indigenous literature of this period:
Krishnadevaraya Amukhthamalyada, jambavati
kalyanam and ushaparinayam
Gangadevi Maduravijayam
Allasani peddanna Manucharitam, harikathasaram
Foreign travelers who visited Vijayanagara empire:
Morocco Ibn Battuta
Venice Nicolo de conti
Persia Abdul Razzak
Portugal Domingo paes
Portugal Fernando nuniz
All above gave valuable accounts of Socio-Economic conditions of vijayanagara empire
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
● Srirangam copper plate of Devaraya II provide geneology and achievements of
vijayanagara rulers
Political history
● Vijayanagara was founded by harihara and bukka of sangama Dynasty in 1336
● Vijayanagara is a city on south bank of tungabhadra river
● Later on, hoysala kingdom and sultanate of Madurai was brought under control of
vijayanagara empire
● Greatest ruler of sangama Dynasty was Deva raya II
● Conflict between vijayanagara kingdom and bahmani kingdom lasted for many
years. Deva raya II could not win over bahmani sultans
● After deva raya II died, sangama Dynasty became weak
Thereafter, Saluva Dynasty was founded by Saluva narasimha who ruled for a brief
period 1486 - 1509
Krishna deva raya (reigned from 1509–1529)
● Belonged to tuluva Dynasty founded by vira narasimha
● His first task was to check against invading bahmani forces
● Though a vaishnavite, he respected all religions
● Was a great patron of art and literature and was known as Andhra bhoja
● Eight eminent scholars, known as ashtadiggajas were at his royal court. Allasani
peddanna was the greatest and was called andhrakavita pitamaga
● He authored telugu work- amukhthamalyada and sanskrit works- jambavati
kalyanam and ushaparinayam
● Repaired most of the temples of South India
● Built famous vittalaswamy and hazara Ramaswamy temple at vijayanagara
● Built new city called nagalapuram in memory of his queen nagaladevi
Battle of talaikotta
● 1565
● Rama raya (General of the Vijayanagara army and later founder of aravidu
Dynasty) vs combined forces of bijapur, ahmednagar, golconda and bidar
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
● Combined forces won
● This battle also known as raksasa thangadi
Last ruler of vijayanagara empire was Sriranga III
Administration
● Well organised
● King enjoyed absolute authority in executive, legislative and judicial matters
● Succession to throne Heriditary
● King assisted by council of ministers
● Empire was divided into different administrative units called mandalams, nadus,
sthalas and gramas
● Governor of mandalam >> mandaleshwara or nayak
● Rulers gave full powers to local authorities in administration
● Land revenue = one sixth of produce
● Army well organised and efficient. Top grade military officers known as Nayaks
or Poligars. They were granted amaram (lands) for their service
Social life
● Allasani peddanna refers to existence of four castes in manucharitam
● Prevalance of slavery : nicola conti, Italian merchant
● Sangama rulers were chiefly saivaites and virupaksha was their family deity.
Other dynasties were vaishnavite
● Religious freedom enjoyed by everyone
● Position of women did not improve
● Attachment of dancing girls to temples was in practice
● Devdasi system flourished
● Sati was honoured and polygamy prevalent in royal families
Economic condition
● Agriculture chief occupation of people
● One of the wealthiest part of the world at that time
● Chief gold coin was the varaha
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
● Art of shipbuilding had developed
Cultural contributions GoKaS
● Chief characteristics of vijayanagara architecture:
○ Construction of tall gopuram or gateways
○ Kalyanmandapam with carved pillars in temple premises. Horse most
common animal on these pillars
● Many amman shrines were added to the already existing temples in this period
Most important temples
● Vittalaswamy and hazara Ramaswamy temple in hampi best example
● Varadharaja and ekamparanatha temple at kanchipuram
● Different languages like sanskrit, telugu, kannada and Tamil flourished
● Peak of literary development was reached under krishna deva raya, he himself
was a scholar in sanskrit and telugu
Bahmani kingdom
● Founder: allauddin bahman shah, also known as hasan gangu in 1347
● Capital: gulbarga
● Successes of bahmani ruler Muhammad shah was due to advices and services
of chief minister mahmud gawan
○ given title of malik-uj-tujjar
● By 1526, bahmani kingdom disintegrated into 5 independent sultanate:
Ahmednagar, bijapur, berar, golconda and bidar. All known as deccan sultanate
Vijayanagara vs bahmani clash = tungabhadra doab, krishna godavari doab and
marathwada country (konkan area)
why vijayanagara kingdom were unable to overrun tungabhadra doab or control
bahmani offensive in the area = bahmani had alliances with warangal rulers
PRELIMS BOOSTER by Bookstawa ( Youtube Channel )
You might also like
- Themes in Indian History - Part - 1 Through MindmapsDocument39 pagesThemes in Indian History - Part - 1 Through MindmapsABHISHEK SINGH100% (1)
- Odisha GK Study IqDocument53 pagesOdisha GK Study Iqumakanta panigrahyNo ratings yet
- Prophetic Visions of Future EventsDocument63 pagesProphetic Visions of Future EventsSyncOrSwim67% (6)
- 8 Erotic Nights - Passionate Encounters That Inspire Great Sex For A Lifetime by Charla HathawayDocument180 pages8 Erotic Nights - Passionate Encounters That Inspire Great Sex For A Lifetime by Charla HathawayJanny23SD46% (50)
- ChronologyDocument14 pagesChronologyRajat XanderNo ratings yet
- Rizal ExercisesDocument11 pagesRizal Exerciseskathryn soriano91% (11)
- In Christ Alone PDFDocument3 pagesIn Christ Alone PDFAldrin PaguiriganNo ratings yet
- John Llewelyn The Middle Voice of Ecological Conscience A Chiasmic Reading of Responsibility in The Neighborhood of Levinas Heidegger and OthersDocument161 pagesJohn Llewelyn The Middle Voice of Ecological Conscience A Chiasmic Reading of Responsibility in The Neighborhood of Levinas Heidegger and OthersLucilla Guidi100% (1)
- Medieval History Notes by AnishDocument51 pagesMedieval History Notes by AnishAnish Rahul100% (1)
- P1 - Harshavardhana - 12945273 - 2022 - 12 - 19 - 18 - 31Document17 pagesP1 - Harshavardhana - 12945273 - 2022 - 12 - 19 - 18 - 31Kumar GauravNo ratings yet
- Imperial Cholas - 14126667 - 2022 - 12 - 19 - 18 - 30Document43 pagesImperial Cholas - 14126667 - 2022 - 12 - 19 - 18 - 30Kumar GauravNo ratings yet
- Ancient Indian HistoryDocument7 pagesAncient Indian Historykomal komalNo ratings yet
- P4 - Later Vedic Period - 5906828 - 2022 - 12 - 19 - 18 - 30Document14 pagesP4 - Later Vedic Period - 5906828 - 2022 - 12 - 19 - 18 - 30Kumar GauravNo ratings yet
- P1-Sangam Age - Sangam Literature - 12945291 - 2022 - 12 - 19 - 18 - 30Document21 pagesP1-Sangam Age - Sangam Literature - 12945291 - 2022 - 12 - 19 - 18 - 30Kumar GauravNo ratings yet
- P2 - Harshavardhana - 12945278 - 2022 - 12 - 19 - 18 - 32Document10 pagesP2 - Harshavardhana - 12945278 - 2022 - 12 - 19 - 18 - 32Kumar GauravNo ratings yet
- Ancient History Prelims Booster Consolidated PDF 14224663 2023 04Document53 pagesAncient History Prelims Booster Consolidated PDF 14224663 2023 04AMSNo ratings yet
- Ancient History - Prelims Booster Consolidated - A4 - 18767013 - 2024 - 01 - 01 - 12 - 41Document54 pagesAncient History - Prelims Booster Consolidated - A4 - 18767013 - 2024 - 01 - 01 - 12 - 41tarun choudharyNo ratings yet
- Neha Bhosle - GS Static Notes PDFDocument183 pagesNeha Bhosle - GS Static Notes PDFBhavya Prakash YadavNo ratings yet
- Short Notes IAS PQRN Indian History Puaird - 4787 - 1681447014Document101 pagesShort Notes IAS PQRN Indian History Puaird - 4787 - 1681447014Harish MeenaNo ratings yet
- History of Medieval IndiaDocument21 pagesHistory of Medieval IndiaRobin SharmaNo ratings yet
- All Important Terms History (CDS, Capf, Upsc-Cse)Document2 pagesAll Important Terms History (CDS, Capf, Upsc-Cse)Shubham KhairnarNo ratings yet
- Buddhism & JainismDocument38 pagesBuddhism & JainismWHO AM I100% (1)
- Art & Culture Prelims NotesDocument38 pagesArt & Culture Prelims NotesSuraj Kathayat100% (1)
- Medieval History With Important Facts BY KRISHDocument50 pagesMedieval History With Important Facts BY KRISHVamshi Krishna Acharya100% (1)
- L IV E: Indian PolityDocument111 pagesL IV E: Indian PolityALLU SRISAINo ratings yet
- Polity Laxmikant Short NotesDocument120 pagesPolity Laxmikant Short NotesKundanNo ratings yet
- History: Current AffairsDocument11 pagesHistory: Current AffairsAditi chokha iNo ratings yet
- Ancient History Notes by AnishDocument24 pagesAncient History Notes by AnishAnish Rahul100% (2)
- Medieval History - GS Foundation - Class Notes - Sunya IASDocument92 pagesMedieval History - GS Foundation - Class Notes - Sunya IASGoldNo ratings yet
- PEP - Handout - Modern History 1Document27 pagesPEP - Handout - Modern History 1anon_463330020No ratings yet
- History Ghatna Chakra PointerDocument9 pagesHistory Ghatna Chakra PointerSarcastic LawyerNo ratings yet
- Geography Handout 8Document24 pagesGeography Handout 8Gagandeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Modern History - Prelims Booster Consolidated - 14134705 - 2022 - 12!19!19 - 56Document123 pagesModern History - Prelims Booster Consolidated - 14134705 - 2022 - 12!19!19 - 56Kumar GauravNo ratings yet
- ANCIENT HISTORY Prelims Notes: Pugalur Incsription (1st Century AD) - Mentions 3 Madhuban Plate Inscription - HarshaDocument33 pagesANCIENT HISTORY Prelims Notes: Pugalur Incsription (1st Century AD) - Mentions 3 Madhuban Plate Inscription - HarshaMeghana RajputNo ratings yet
- New 1 Modern History - Basic LevelDocument38 pagesNew 1 Modern History - Basic LevelofferNo ratings yet
- Key Terms - Ancient, Medieval & Modern HistoryDocument28 pagesKey Terms - Ancient, Medieval & Modern HistoryAditya DwivediNo ratings yet
- Modern - History Unique Shiksha SampleDocument26 pagesModern - History Unique Shiksha SampleJoseph SmithNo ratings yet
- Peasant-Movements 41307Document2 pagesPeasant-Movements 41307Joey saravanaNo ratings yet
- Modern History EvernoteDocument18 pagesModern History EvernoteKuldeep SinghNo ratings yet
- India Physical: Chapter - 1Document11 pagesIndia Physical: Chapter - 1Ankit SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- UPSCGeography GSNotesDocument979 pagesUPSCGeography GSNotesSamira ThakurNo ratings yet
- Polity Notes For PrelimsDocument90 pagesPolity Notes For PrelimsVivekanand sahooNo ratings yet
- Ancient History Old Ncert NotesDocument16 pagesAncient History Old Ncert Notesmanish krNo ratings yet
- Economics Prelims Notes GenDocument93 pagesEconomics Prelims Notes Gensrk08072003No ratings yet
- Indian History Chronology - Ancient India To Modern India - Clear IASDocument5 pagesIndian History Chronology - Ancient India To Modern India - Clear IASRahul KumarNo ratings yet
- Iasbaba'S Prelims Exclusive PROGRAM (PEP) 2022: Medieval History HandoutsDocument11 pagesIasbaba'S Prelims Exclusive PROGRAM (PEP) 2022: Medieval History HandoutsGagandeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Ancient HistoryDocument65 pagesAncient HistoryRavi kumarNo ratings yet
- Geography Handout 10Document25 pagesGeography Handout 10Gagandeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Modern History Revision Notes - IxambeeDocument25 pagesModern History Revision Notes - IxambeeTanish KalraNo ratings yet
- History Handout 14Document19 pagesHistory Handout 14Gagandeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Trick Best TrickDocument21 pagesTrick Best Trickfindsatya88No ratings yet
- History Handout 15Document14 pagesHistory Handout 15Gagandeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Ancient and Medieval Indian History Notes by Ias - NetworkDocument102 pagesAncient and Medieval Indian History Notes by Ias - NetworkSai CharanNo ratings yet
- Indian Polity Mind Maps EbookDocument7 pagesIndian Polity Mind Maps EbookAbhi Singh50% (2)
- TABLESDocument22 pagesTABLESpranita kaleNo ratings yet
- History Handout 10Document49 pagesHistory Handout 10Gagandeep KumarNo ratings yet
- GK BookDocument13 pagesGK BookJatin VatsNo ratings yet
- Modern Indian History 2022Document30 pagesModern Indian History 2022prakash gujarNo ratings yet
- Governor General/Viceroy Period Points To RememberDocument5 pagesGovernor General/Viceroy Period Points To Rememberkittu_sivaNo ratings yet
- Medival History Notes TamilnaduDocument8 pagesMedival History Notes Tamilnadumanish krNo ratings yet
- Modern Indian HistoryDocument203 pagesModern Indian HistoryRaktim DasNo ratings yet
- Modern History Ready Reckoner 2019 PDFDocument80 pagesModern History Ready Reckoner 2019 PDFPrafull Bhandari0% (1)
- Polity Repeated Themes & Repeated Topics 2013 2022 IAS PCS PathshalaDocument7 pagesPolity Repeated Themes & Repeated Topics 2013 2022 IAS PCS Pathshalaekta rawatNo ratings yet
- India Map Physiographic Divisions of IndiaDocument11 pagesIndia Map Physiographic Divisions of IndiaSanjana SinghNo ratings yet
- Medieval History (12th Sept) - 25339664 - 2024 - 01 - 20 - 11 - 47Document105 pagesMedieval History (12th Sept) - 25339664 - 2024 - 01 - 20 - 11 - 47alok singhNo ratings yet
- 02 Maths Formula (Aditya Ranjan)Document8 pages02 Maths Formula (Aditya Ranjan)AMSNo ratings yet
- Ancient History Prelims Booster Consolidated PDF 14224663 2023 04Document53 pagesAncient History Prelims Booster Consolidated PDF 14224663 2023 04AMSNo ratings yet
- 47 - (REASONING) (CALENDAR) Calender Practice Sheet 01Document3 pages47 - (REASONING) (CALENDAR) Calender Practice Sheet 01AMSNo ratings yet
- Pet 2022Document35 pagesPet 2022AMSNo ratings yet
- PET Special Ancient History Hand Written NotesDocument25 pagesPET Special Ancient History Hand Written NotesAMSNo ratings yet
- Modern History NotesDocument24 pagesModern History NotesAMSNo ratings yet
- Chemestry Hand Written Notes For PET Exam 2022Document44 pagesChemestry Hand Written Notes For PET Exam 2022AMSNo ratings yet
- The Objective and Subjective HGADocument13 pagesThe Objective and Subjective HGAMidnite Scholar50% (2)
- Freedom of Religion CasesDocument30 pagesFreedom of Religion CasesKeangela LouiseNo ratings yet
- God and MoneyDocument3 pagesGod and Moneyhotchick_19No ratings yet
- Holy Marriages and Their Outcomes Depicted On Near East Cylinder Seals Tom Van BakelDocument9 pagesHoly Marriages and Their Outcomes Depicted On Near East Cylinder Seals Tom Van BakelSrini KalyanaramanNo ratings yet
- Thieves of Fire - Rimbaud, Adūnīs, and Arab PoeticsDocument14 pagesThieves of Fire - Rimbaud, Adūnīs, and Arab Poeticsxsim57100% (1)
- Lisboa2023 WYD Press Release WYD LogoDocument2 pagesLisboa2023 WYD Press Release WYD LogohoahairauNo ratings yet
- MergeDocument30 pagesMergevegavergiagaraNo ratings yet
- Vaggione Archaeus 2002Document4 pagesVaggione Archaeus 2002CAStmNo ratings yet
- Significance of The Bird Albatross in The Rime of The Ancient MarinerDocument3 pagesSignificance of The Bird Albatross in The Rime of The Ancient Marinerشاكر محمود عبد فهدNo ratings yet
- ART 2 - Axiology On The Integration of Knowledge Islam andDocument7 pagesART 2 - Axiology On The Integration of Knowledge Islam andMing Teck TanNo ratings yet
- Novena PrayerDocument22 pagesNovena PrayerMia LamosteNo ratings yet
- AlcuinDocument8 pagesAlcuinA Richard AllenNo ratings yet
- The Chrysalids NOTESDocument26 pagesThe Chrysalids NOTESVishesh MattaiNo ratings yet
- Evergreen PPSC, FPSC, NTS and OTS MCQS SolvedDocument155 pagesEvergreen PPSC, FPSC, NTS and OTS MCQS Solvednabeel ahmadNo ratings yet
- Interview of Papaji by Christopher TitmussDocument19 pagesInterview of Papaji by Christopher TitmussKali AneeNo ratings yet
- Daftar Absensi Uas Analisis Sistem Tenaga Listrik Kode Seksi 5118Document2 pagesDaftar Absensi Uas Analisis Sistem Tenaga Listrik Kode Seksi 5118DaryAntoNo ratings yet
- The Scarletletter Chapter SummaryDocument3 pagesThe Scarletletter Chapter SummaryvalerieehartmanNo ratings yet
- 18 Maha Shakthi PeetamDocument1 page18 Maha Shakthi PeetamSree RajaRajeshwari PeetamNo ratings yet
- C. L. C. Certified Life Coach Christian Life Coaching Christ As My (Our) Life CoachDocument37 pagesC. L. C. Certified Life Coach Christian Life Coaching Christ As My (Our) Life CoachPaula Manalo-Suliguin100% (1)
- Political Islam - Religion and Politics in The Arab World PDFDocument252 pagesPolitical Islam - Religion and Politics in The Arab World PDFNadeem IqbalNo ratings yet
- 3751 Class 9hindi Poem 1 Saakhi by Kabir DasDocument6 pages3751 Class 9hindi Poem 1 Saakhi by Kabir DasShauryaNo ratings yet
- John Chrysostom, Basil The Great - The Orthodox Liturgy (1982, Oxford University Press) - Libgen - LiDocument231 pagesJohn Chrysostom, Basil The Great - The Orthodox Liturgy (1982, Oxford University Press) - Libgen - Li罗月圆No ratings yet
- 156109785009-AL-BASEERA 3 (Vol. 2 - Issue. 1) JUN-2013Document23 pages156109785009-AL-BASEERA 3 (Vol. 2 - Issue. 1) JUN-2013potato potatoNo ratings yet
- Maurice de Wulf, History of Medieval PhilosophyDocument544 pagesMaurice de Wulf, History of Medieval Philosophylomaxx21100% (7)
- 2.05 HOLD CLP Expanded OutlinesDocument74 pages2.05 HOLD CLP Expanded OutlinesJENINE VICTORIANONo ratings yet