Professional Documents
Culture Documents
How To Calculate Resultant Vector Using Parallelogram Law of Forces - Definition
How To Calculate Resultant Vector Using Parallelogram Law of Forces - Definition
Uploaded by
Ranggarizkysptr 22Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
How To Calculate Resultant Vector Using Parallelogram Law of Forces - Definition
How To Calculate Resultant Vector Using Parallelogram Law of Forces - Definition
Uploaded by
Ranggarizkysptr 22Copyright:
Available Formats
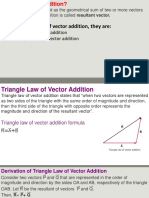
How to Calculate Resultant Vector using Parallelogram Law of Forces - Definition,
Formula, Example
Definition:
Parallelogram is a schematic figure with two set of similar sides. Parallelogram Law of Forces states that if any two given
forces acting at a point are indicated in magnitude and direction by the two contiguous sides of a parallelogram, then their
outcome is signified in magnitude and direction by the diagonal passing through the point, where magnitude specifies the
vectors size or quantity and direction specifies how the vector is directed from one location to another.
Formula:
Where,
R = Magnitude of resultant vector
α = Direction of resultant vector
P = Magnitude of vector P
Q = Magnitude of vector Q
θ = Angle between two vectors
Example :
Consider that in a parallelogram, the magnitude of a vector P as 3N, another magnitude of vector Q as 4N and angle
between two vectors is 30 degrees. Calculate the resultant force vector using parallelogram law of forces
Given,
Magnitude of vector [P] = 3N,
Magnitude of vector [Q] = 4N,
Angle = 30 degrees
To find,
Resultant force vector using parallelogram law of forces
Step 1:
Substitute the value of P and Q in the formula,
2 2
R = √3 + 4 + (2 x 3 x 4 x cos(30))
R = √9 + 16 + 20.7846
R = 6.77N
Step 2:
Let us now calculate the value of α.
tan α = (4 x sin 30) / ( 3 + 4 cos 30)
tan α = 4 x 0.5 / (3 + ( 4 x 0.866))
tan α = 0.309405941
α = tan -1 (0.309405941)
α = 17.2 o
You might also like
- Physics Lab Report 2.0 Resultant and Equilibrant ForcesDocument3 pagesPhysics Lab Report 2.0 Resultant and Equilibrant ForcesIan Garcia0% (1)
- Chapter 2&3Document22 pagesChapter 2&3RN Builder IpohNo ratings yet
- MechanicsDocument31 pagesMechanicsUsman PervaizNo ratings yet
- A A A PMV Fma F Eq F MB A : Addition of VectorsDocument2 pagesA A A PMV Fma F Eq F MB A : Addition of VectorsWillSmithNo ratings yet
- ME 1204: Engineering Statics: Dr. Faraz JunejoDocument86 pagesME 1204: Engineering Statics: Dr. Faraz JunejoTayabaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document5 pagesLecture 2Bredley SilvaNo ratings yet
- Standard SI PrefixesDocument11 pagesStandard SI PrefixesprimalNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics: Scalars, VectorsDocument70 pagesEngineering Mechanics: Scalars, VectorsMuhammad FahadNo ratings yet
- PH 103 Fall 2008:, Third Week: Scalars and VectorsDocument9 pagesPH 103 Fall 2008:, Third Week: Scalars and VectorsAli AhmadNo ratings yet
- Maths Project 2Document8 pagesMaths Project 2Raj MallickNo ratings yet
- Stanes School ShibiDocument8 pagesStanes School ShibiShibiNo ratings yet
- BC 9A Note PagesDocument5 pagesBC 9A Note PagesCarson ReskeNo ratings yet
- Note On Vector AnalysisDocument37 pagesNote On Vector AnalysisNabil MunshiNo ratings yet
- VectorDocument3 pagesVectorRohitNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document56 pagesChapter 2akml dnielNo ratings yet
- Solid Mechanics TMEE3642chapter1and2Document70 pagesSolid Mechanics TMEE3642chapter1and2Godwin IzaaksNo ratings yet
- Mathematical DescriptionDocument109 pagesMathematical DescriptionBiswarup BurmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Force Vectors Scalars and VectorsDocument6 pagesChapter 2 - Force Vectors Scalars and VectorsMahesh RamtekeNo ratings yet
- Idebe Physics - 3 New 2024Document241 pagesIdebe Physics - 3 New 2024r38836592100% (1)
- Moment 1Document7 pagesMoment 1flav kthNo ratings yet
- Vectors Note 2Document30 pagesVectors Note 2dhausa basnetNo ratings yet
- Laws of Mechanics - 1661861760647Document17 pagesLaws of Mechanics - 1661861760647ericmuendo351No ratings yet
- 5.VECTORS ex 5.1Document33 pages5.VECTORS ex 5.1prathameshamle05No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Force Vectors Scalars and VectorsDocument6 pagesChapter 2 - Force Vectors Scalars and VectorstcsNo ratings yet
- Parallelogram LawDocument8 pagesParallelogram LawSriram MuruganNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Force Systems PDFDocument17 pagesUnit 1 Force Systems PDFpeter vanderNo ratings yet
- Vector Analysis PDFDocument5 pagesVector Analysis PDFasdfghjNo ratings yet
- Vector CalculusDocument113 pagesVector CalculusHergene FanerNo ratings yet
- Determinant: Det (A) Det A - A - 2 × 2Document23 pagesDeterminant: Det (A) Det A - A - 2 × 2David RicardoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document67 pagesLecture 2nnsNo ratings yet
- Chapter One Lecture3Document12 pagesChapter One Lecture3Arian SoleimanNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS Year 11 First Term Slides 2023-2024Document167 pagesPHYSICS Year 11 First Term Slides 2023-2024adedoyindasilva26No ratings yet
- VectorsDocument48 pagesVectorsUltra Gamer (sishant)No ratings yet
- Application, Its Magnitude, and Its DirectionDocument12 pagesApplication, Its Magnitude, and Its DirectionJohn Laurence Gonzaga AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Forces & EquilibriumDocument54 pagesChapter 2 Forces & EquilibriumIsabelNo ratings yet
- 1-Vector Analysis-Algebra and Basics of Vector SY 2020-2021 - ECEDocument46 pages1-Vector Analysis-Algebra and Basics of Vector SY 2020-2021 - ECEMarc RiveraNo ratings yet
- Coordinate Systems Used To Describe The Position of A Point in Space Common Coordinate Systems AreDocument1 pageCoordinate Systems Used To Describe The Position of A Point in Space Common Coordinate Systems AreKyra Mae UrbanoNo ratings yet
- CG-Part2 PPSXDocument58 pagesCG-Part2 PPSXmocit51855No ratings yet
- Determi AntsDocument27 pagesDetermi AntsEyas A-e ElHashmiNo ratings yet
- To Study Parallelogram Law of VectorDocument12 pagesTo Study Parallelogram Law of VectorAayush PawarNo ratings yet
- Module 2 VectorsDocument31 pagesModule 2 Vectorsnamjoon kimNo ratings yet
- Dynamics - Curvilinear MotionDocument43 pagesDynamics - Curvilinear Motionawethaf9876No ratings yet
- Scalar Quantities: A 2 I 2 I ADocument13 pagesScalar Quantities: A 2 I 2 I ARajat HattewarNo ratings yet
- Movement Equations 2 Chap2Document19 pagesMovement Equations 2 Chap2sam mslNo ratings yet
- Lec 1Document40 pagesLec 1Naughty GunnerNo ratings yet
- 3 - Dimensional Geometry - Day - 4: Equation of A Line in Three DimensionsDocument6 pages3 - Dimensional Geometry - Day - 4: Equation of A Line in Three Dimensionsmanisha choudharyNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 - Forces and EquilibriumDocument53 pagesCHAPTER 2 - Forces and EquilibriumLin YanNo ratings yet
- VectorDocument5 pagesVectorSeema JainNo ratings yet
- 3-Euclidean Vector SpacesDocument97 pages3-Euclidean Vector SpacesslowjamsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Force VectorsDocument20 pagesChapter 2 Force VectorsTOS CCLNo ratings yet
- Advanced Engineering Mathematics: Submitted By: Jeb Gumban Submitted To: Engr. Jocelyn DomingoDocument17 pagesAdvanced Engineering Mathematics: Submitted By: Jeb Gumban Submitted To: Engr. Jocelyn DomingoSasuke UchihaNo ratings yet
- Motion in PlaneDocument20 pagesMotion in PlanekartikthedashingNo ratings yet
- L1 Chapter - IDocument54 pagesL1 Chapter - IKrishnaveni Subramani S100% (1)
- Intro To MechDocument12 pagesIntro To MechJChris EsguerraNo ratings yet
- E3 Vector AdditionDocument6 pagesE3 Vector AdditionMahir MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Motion in Plane For High School StudentsDocument23 pagesMotion in Plane For High School StudentsPratik.KNo ratings yet
- Module 2 VectorsDocument16 pagesModule 2 VectorsKrizel CalasaraNo ratings yet
- Chapter IDocument17 pagesChapter IMD NAYM MIANo ratings yet
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)