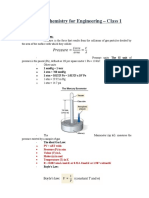
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Safety Verifications: - Geometry of The Hangers
Safety Verifications: - Geometry of The Hangers
Uploaded by
Alvaro SaldamandoCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Canon EOS Rebel T2i/550D For Dummies: Cheat SheetDocument21 pagesCanon EOS Rebel T2i/550D For Dummies: Cheat SheetMoyeen Uddin Hasan100% (2)
- Trapezoidal Sheet As A Bracing Preventing Flat Trusses From Out-Of-Plane BucklingDocument7 pagesTrapezoidal Sheet As A Bracing Preventing Flat Trusses From Out-Of-Plane BucklingWilliam Pol100% (1)
- Design of Concrete-Filled Steel Tubular Members According To The Australian Standard As 5100 Model and CalibrationDocument18 pagesDesign of Concrete-Filled Steel Tubular Members According To The Australian Standard As 5100 Model and Calibrationoui6592No ratings yet
- ASTM D3500-90 (Tension Test) PDFDocument6 pagesASTM D3500-90 (Tension Test) PDFAsri Marwa Syabana100% (1)
- G S C - S D: Lobal Tability of Able Tayed EcksDocument9 pagesG S C - S D: Lobal Tability of Able Tayed EcksTran Tien DungNo ratings yet
- Optimal Design of Long-Span Steel Portal Frames Using Fabricated BeamsDocument11 pagesOptimal Design of Long-Span Steel Portal Frames Using Fabricated Beamsalexkoch2No ratings yet
- Shear Truss Analogy For Concrete MembersDocument11 pagesShear Truss Analogy For Concrete MembersMashudha SulthanaNo ratings yet
- Buitengragt BridgeDocument4 pagesBuitengragt BridgeJohn AndersonNo ratings yet
- Static Instability Analysis of Long-Span Cable-Stayed Bridges With Carbon Fiber Composite Cable Under Wind LoadDocument8 pagesStatic Instability Analysis of Long-Span Cable-Stayed Bridges With Carbon Fiber Composite Cable Under Wind Loadshimic32000No ratings yet
- Pile Caps With Inclined Shear Reinforcement and Steel FibersDocument12 pagesPile Caps With Inclined Shear Reinforcement and Steel FibersLana Gomes CastroNo ratings yet
- CI4210 ShushkewichDocument21 pagesCI4210 ShushkewichjmdominguezcabelloNo ratings yet
- Circular Slab Estimation of SteelDocument3 pagesCircular Slab Estimation of SteelGaddam Padmaja ReddyNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Sheet Steel Diaphragms in The UK Calculation of Sheet Steel Diaphragms in The UKDocument44 pagesCalculation of Sheet Steel Diaphragms in The UK Calculation of Sheet Steel Diaphragms in The UKthreedlabsNo ratings yet
- Extended-Design and Analysis of A Network Arch BridgeDocument10 pagesExtended-Design and Analysis of A Network Arch BridgehansNo ratings yet
- Design of Haunched Composite Connections For Long-Span Beam ConstructionDocument10 pagesDesign of Haunched Composite Connections For Long-Span Beam ConstructioncasanovavnNo ratings yet
- Stability Analysis of Box-Girder Cable-Stayed BridgesDocument6 pagesStability Analysis of Box-Girder Cable-Stayed BridgesDhimas Surya NegaraNo ratings yet
- L-2 Design of Steel Roof Truss As Per SP38888Document21 pagesL-2 Design of Steel Roof Truss As Per SP38888Kanak YadavNo ratings yet
- PHD Useful PaperDocument362 pagesPHD Useful Paperpc.backupwasimNo ratings yet
- Investigation of Free In-Plane Vibration of Curved Bridges: Navid HeidarzadehDocument10 pagesInvestigation of Free In-Plane Vibration of Curved Bridges: Navid HeidarzadehpuenteprefabricadoNo ratings yet
- Theoretical and Exper Study Steel PropsDocument7 pagesTheoretical and Exper Study Steel PropsAnonymous ePcnZoBENo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0263823116307108 MainDocument15 pages1 s2.0 S0263823116307108 MainLeonardoNo ratings yet
- Design of Prestressed Concrete Piles For Seismic Loads Adds A NewDocument3 pagesDesign of Prestressed Concrete Piles For Seismic Loads Adds A NewMahindaNo ratings yet
- Esperimental StudyDocument9 pagesEsperimental Studyrafaelrp22009No ratings yet
- Arch BridgesDocument20 pagesArch BridgesPankaj_Taneja_96840% (1)
- Analytical Study On Safety Level of Stay Cables of Cable Stayed BridgeDocument8 pagesAnalytical Study On Safety Level of Stay Cables of Cable Stayed Bridgesushil deshmukhNo ratings yet
- Yimeng 2000Document20 pagesYimeng 2000dipeshbarua55No ratings yet
- Bruhn 73 C4Document28 pagesBruhn 73 C4brhNo ratings yet
- Prestressed Steel Beam: Figure 4.2-Sliding BearingDocument4 pagesPrestressed Steel Beam: Figure 4.2-Sliding BearingMarcelo AlvesNo ratings yet
- High Strength Steel in Seismic Resistant Building FramesDocument6 pagesHigh Strength Steel in Seismic Resistant Building Framesuhu_plus6482No ratings yet
- Buckling Behavior of Cold-Formed Scaffolding TubesDocument17 pagesBuckling Behavior of Cold-Formed Scaffolding TubesHaseeb KhanNo ratings yet
- 8884 PDFDocument10 pages8884 PDF081382991318No ratings yet
- Sergio Pellegrino University of Cambridge, Cambridge, UK: Deployment. The Reverse Transformation Is Called RetractionDocument35 pagesSergio Pellegrino University of Cambridge, Cambridge, UK: Deployment. The Reverse Transformation Is Called RetractionRupesh DangolNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Design Outline: 3.1 ObjectiveDocument10 pagesPreliminary Design Outline: 3.1 Objectivemohamed ahmedNo ratings yet
- Chapter-4 Design of Column & Column BaseDocument26 pagesChapter-4 Design of Column & Column Basezakai zakiNo ratings yet
- 595 05-Notes PDFDocument14 pages595 05-Notes PDFfilipeNo ratings yet
- Zirakian, 2005Document9 pagesZirakian, 2005carlosNo ratings yet
- Pseudo-Dynamic Test of A Full-Scale CFT/BRB Frame: Part 2 - Construction and TestingDocument15 pagesPseudo-Dynamic Test of A Full-Scale CFT/BRB Frame: Part 2 - Construction and TestingDiego Matias Burgos FuentesNo ratings yet
- Nguyen Trung HieuDocument6 pagesNguyen Trung HieuAhmed DahirNo ratings yet
- Journal of Constructional Steel Research: N. Jamaluddin, D. Lam, X.H. Dai, J. YeDocument11 pagesJournal of Constructional Steel Research: N. Jamaluddin, D. Lam, X.H. Dai, J. YeRaja GopalNo ratings yet
- Welded Built-Up Columns, April 1966: Lehigh PreserveDocument95 pagesWelded Built-Up Columns, April 1966: Lehigh PreservemohanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7: Columns and Strut: Failure of A ColumnDocument10 pagesChapter 7: Columns and Strut: Failure of A ColumnAshish KumarNo ratings yet
- Rules of Thumb For Steel DesignDocument7 pagesRules of Thumb For Steel DesignjaberfirasNo ratings yet
- RC I&II, SD &bridge Eng Model-Tutoarial ExamDocument63 pagesRC I&II, SD &bridge Eng Model-Tutoarial ExamWendimu TolessaNo ratings yet
- Extended-Design and Analysis of A Network Arch BridgeDocument11 pagesExtended-Design and Analysis of A Network Arch BridgeSebastian KanNo ratings yet
- Extended Abstract - Design and Analysis of A Network Arch BridgeDocument11 pagesExtended Abstract - Design and Analysis of A Network Arch BridgeSebastian KanNo ratings yet
- NAME351: L-3ff-1/NAME Date: 07/06/2014Document21 pagesNAME351: L-3ff-1/NAME Date: 07/06/2014Kabir ShafayatNo ratings yet
- Shear Capacity of Reinforced Concrete Slabs Under Concentrated LoadsDocument8 pagesShear Capacity of Reinforced Concrete Slabs Under Concentrated Loads정주호No ratings yet
- Longitudinal Stiffeners On Compression Panels: CIVL 7690Document64 pagesLongitudinal Stiffeners On Compression Panels: CIVL 7690Arul JONo ratings yet
- (5hdo $%HG/QHN DQG (0ludpehooDocument8 pages(5hdo $%HG/QHN DQG (0ludpehooRaquel CarmonaNo ratings yet
- Critical Lateral-Torsional Buckling Moments of Steel Web-TaperedDocument8 pagesCritical Lateral-Torsional Buckling Moments of Steel Web-TaperedLệnh BùiNo ratings yet
- Seismic Response of Bridges With Sliding and Elastomeric Isolation BearingsDocument7 pagesSeismic Response of Bridges With Sliding and Elastomeric Isolation BearingsciscoNo ratings yet
- Inelastic Versus Elastic Displacement-Based Intensity Measures For Seismic AnalysisDocument5 pagesInelastic Versus Elastic Displacement-Based Intensity Measures For Seismic Analysismercab15No ratings yet
- Balanced Force Charles Et Al IEJ 1998Document7 pagesBalanced Force Charles Et Al IEJ 1998abcder1234No ratings yet
- Efficiency Reduction Due To Shear Lag On Bolted Cold-Formed Steel AnglesDocument13 pagesEfficiency Reduction Due To Shear Lag On Bolted Cold-Formed Steel AnglesMaryam Al-SalmiyahNo ratings yet
- Structural Steel DesignDocument32 pagesStructural Steel Designshaluka100% (1)
- Cable Shape & Strength: Telford and The Flat Form BridgeDocument15 pagesCable Shape & Strength: Telford and The Flat Form Bridgerene boisselleNo ratings yet
- Analisis de Vibracion Grua Torre PDFDocument10 pagesAnalisis de Vibracion Grua Torre PDFdanielcolina1613No ratings yet
- Free Vibration and Modal Analysis of Tower Crane Using SAP2000 and ANSYS PDFDocument10 pagesFree Vibration and Modal Analysis of Tower Crane Using SAP2000 and ANSYS PDFİsmailNo ratings yet
- Design of Portal FramesDocument35 pagesDesign of Portal FramesPranav Prabhakar100% (2)
- A Short Guide to the Types and Details of Constructing a Suspension Bridge - Including Various Arrangements of Suspension Spans, Methods of Vertical Stiffening and Wire Cables Versus Eyebar ChainsFrom EverandA Short Guide to the Types and Details of Constructing a Suspension Bridge - Including Various Arrangements of Suspension Spans, Methods of Vertical Stiffening and Wire Cables Versus Eyebar ChainsNo ratings yet
- Instructions on Modern American Bridge BuildingFrom EverandInstructions on Modern American Bridge BuildingNo ratings yet
- Welding Procedure Qualification Record (WPQR) (ISO 15614-1-2017)Document3 pagesWelding Procedure Qualification Record (WPQR) (ISO 15614-1-2017)ramesh rajaNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Stability - An IntroductionDocument4 pagesIntermediate Stability - An IntroductiondylaraniNo ratings yet
- Chemistry For Engineering - Class 1: 1. GasesDocument9 pagesChemistry For Engineering - Class 1: 1. GasesMai Sơn DươngNo ratings yet
- C2 Cement Consistency PasteDocument9 pagesC2 Cement Consistency PasteSyukri Abd KadirNo ratings yet
- Deflections of Beams: Geometric MethodDocument22 pagesDeflections of Beams: Geometric MethodMicko LaneluzNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power Plant: 17 Mechanical by Engr. Ans Ahmed Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument29 pagesThermal Power Plant: 17 Mechanical by Engr. Ans Ahmed Department of Mechanical EngineeringTarvesh Kumar100% (1)
- Ashwin Ushas CorpDocument9 pagesAshwin Ushas CorpMengfang LiNo ratings yet
- Appl Phys B 63 451 1996 Tunable ArF Laser For VUV GenerationDocument11 pagesAppl Phys B 63 451 1996 Tunable ArF Laser For VUV Generation3209185626No ratings yet
- SUPERDRY - Superior Container Desiccants and DehumidifiersDocument2 pagesSUPERDRY - Superior Container Desiccants and DehumidifiersSrina SriNo ratings yet
- Toluene Material 2520 BalanceDocument5 pagesToluene Material 2520 Balanceapi-3714811No ratings yet
- Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA)Document43 pagesFailure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA)Muhammad Bilal100% (4)
- LAB VIVA Questions and AnswersDocument6 pagesLAB VIVA Questions and AnswersNilambar YadavNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics Class 12 Notes Chemistry Chapter 4 - CBSE LabsDocument5 pagesChemical Kinetics Class 12 Notes Chemistry Chapter 4 - CBSE Labsavinash kishoreNo ratings yet
- SRM Valliammai Engineering College: Department of Civil Engineering (M.E - Structural Engineering)Document17 pagesSRM Valliammai Engineering College: Department of Civil Engineering (M.E - Structural Engineering)Exciting DataNo ratings yet
- Che 2Document25 pagesChe 2Jaynie Lee VillaranNo ratings yet
- Resonance and Damping NOTESDocument1 pageResonance and Damping NOTESThash ANo ratings yet
- MPVN BrochureDocument32 pagesMPVN Brochurefernando_naciamentNo ratings yet
- Part 2 Week 9 - Treatment PlanningDocument50 pagesPart 2 Week 9 - Treatment PlanningdanNo ratings yet
- 2019 Edition Changes: National Board Inspection Code-Part-3Document39 pages2019 Edition Changes: National Board Inspection Code-Part-3NAVANEETH NAVANINo ratings yet
- Referensi PUR - Urethane Surface coating-BlockedISO (Baxenden) - 20160802 PDFDocument6 pagesReferensi PUR - Urethane Surface coating-BlockedISO (Baxenden) - 20160802 PDFFahmi Januar AnugrahNo ratings yet
- Table For For C-Q C-Q & & C-B C-B Compressors Compressors Series SeriesDocument1 pageTable For For C-Q C-Q & & C-B C-B Compressors Compressors Series SeriesALF1975ANo ratings yet
- 3.28 & 3.29 Kawat Las Nikko Steel 312 2,6 X 350 MM & 3,2 X 350 MMDocument1 page3.28 & 3.29 Kawat Las Nikko Steel 312 2,6 X 350 MM & 3,2 X 350 MMumarNo ratings yet
- DLP SCIENCE 4 Q4 Practice Safety Precautions On The Effects of The SunDocument6 pagesDLP SCIENCE 4 Q4 Practice Safety Precautions On The Effects of The SunMark-Christopher Roi Pelobello MontemayorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Part 2 - Slides 01 To 27 - Hydrostatic Thrust On Plane SurfaceDocument14 pagesChapter 2 - Part 2 - Slides 01 To 27 - Hydrostatic Thrust On Plane SurfaceNely ZulfatulNo ratings yet
- CW For 14.10.2021Document9 pagesCW For 14.10.2021boyi yangNo ratings yet
- Johnson - York - Marine - Chiller - UnitsDocument2 pagesJohnson - York - Marine - Chiller - UnitsAldryn AdatoNo ratings yet
- Computer Simulation of Explosion Crater in Dams With Different Buried Depths of ExplosiveDocument8 pagesComputer Simulation of Explosion Crater in Dams With Different Buried Depths of ExplosiveliushaozengNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet For Barred Tee 010719 PDFDocument1 pageData Sheet For Barred Tee 010719 PDFkandraNo ratings yet
Safety Verifications: - Geometry of The Hangers
Safety Verifications: - Geometry of The Hangers
Uploaded by
Alvaro SaldamandoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Safety Verifications: - Geometry of The Hangers
Safety Verifications: - Geometry of The Hangers
Uploaded by
Alvaro SaldamandoCopyright:
Available Formats
5
For the main longitudinal beam it was The arch height and the hangers were
used the same tube section of the arch, a CHS designed simultaneously due to the fulfilment
(Circular Hollow Section) with D = 1250 mm of the 5.0 m minimum required gabarit over the
and t = 25 mm, for aesthetic reasons mainly, sidewalks kerb. Since there was a maximum
and two secondary longitudinal box-girders height (1/4 of the span) defined by the study of
beams were set on both cantilever tips, to stiff other Bowstring cases, 30 m high was the
the grid steel structure and better redistribute chosen solution. From that, several designs
the hangers forces through the deck. were made for the hanger’s geometry, leading
to an inclined Net solution of Figure 4.4.
Figure 4.4 – Geometry of the hangers
4.3. MATERIALS AND ACTIONS
Figure 4.2 – Transversal girders cross-section
The materials adopted were the
The transversal beams were base on
concrete C35/45 for the deck slab; steel
important works like the Puente de la
reinforcement bars A500; steel grade
Exposición in Valencia or Pont de [3]
S420 NH/NHL for all deck girders and grade
l’Observatoire in Liège (Figure 4.3), from the [3]
S460 NH/NHL for the arch; and steel S355
famous architect Santiago Calatrava, leading
or S460 for the hangers.
to a maximum and minimum cross-section
For every step of the design, the actions
presented on Figure 4.2.
(dead loads, hangers installed forces, live
loads and fatigue) were considered. With all
the permanent actions in play, it is able to
[4] [5]
verify the ULS and fatigue , as well as the
ULS and stability of the arch.
5. SAFETY VERIFICATIONS
Figure 4.3 – Pont de l’Observatoire in Belgium To determine the required area of
reinforcement in the concrete deck slab, the
The chosen cross-section for the arch,
shell bending moments were obtained by with
the same as the main longitudinal beam, was a
a 3D finite beam/shell elements analysis
CHS (D = 2500 mm and t = 80 mm) since it’s
model. The longitudinal slab cracking was
going to be heavily compressed and subjected
relevant to the slab behaviour, and a fictitious
to high bending moments in every direction.
You might also like
- Canon EOS Rebel T2i/550D For Dummies: Cheat SheetDocument21 pagesCanon EOS Rebel T2i/550D For Dummies: Cheat SheetMoyeen Uddin Hasan100% (2)
- Trapezoidal Sheet As A Bracing Preventing Flat Trusses From Out-Of-Plane BucklingDocument7 pagesTrapezoidal Sheet As A Bracing Preventing Flat Trusses From Out-Of-Plane BucklingWilliam Pol100% (1)
- Design of Concrete-Filled Steel Tubular Members According To The Australian Standard As 5100 Model and CalibrationDocument18 pagesDesign of Concrete-Filled Steel Tubular Members According To The Australian Standard As 5100 Model and Calibrationoui6592No ratings yet
- ASTM D3500-90 (Tension Test) PDFDocument6 pagesASTM D3500-90 (Tension Test) PDFAsri Marwa Syabana100% (1)
- G S C - S D: Lobal Tability of Able Tayed EcksDocument9 pagesG S C - S D: Lobal Tability of Able Tayed EcksTran Tien DungNo ratings yet
- Optimal Design of Long-Span Steel Portal Frames Using Fabricated BeamsDocument11 pagesOptimal Design of Long-Span Steel Portal Frames Using Fabricated Beamsalexkoch2No ratings yet
- Shear Truss Analogy For Concrete MembersDocument11 pagesShear Truss Analogy For Concrete MembersMashudha SulthanaNo ratings yet
- Buitengragt BridgeDocument4 pagesBuitengragt BridgeJohn AndersonNo ratings yet
- Static Instability Analysis of Long-Span Cable-Stayed Bridges With Carbon Fiber Composite Cable Under Wind LoadDocument8 pagesStatic Instability Analysis of Long-Span Cable-Stayed Bridges With Carbon Fiber Composite Cable Under Wind Loadshimic32000No ratings yet
- Pile Caps With Inclined Shear Reinforcement and Steel FibersDocument12 pagesPile Caps With Inclined Shear Reinforcement and Steel FibersLana Gomes CastroNo ratings yet
- CI4210 ShushkewichDocument21 pagesCI4210 ShushkewichjmdominguezcabelloNo ratings yet
- Circular Slab Estimation of SteelDocument3 pagesCircular Slab Estimation of SteelGaddam Padmaja ReddyNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Sheet Steel Diaphragms in The UK Calculation of Sheet Steel Diaphragms in The UKDocument44 pagesCalculation of Sheet Steel Diaphragms in The UK Calculation of Sheet Steel Diaphragms in The UKthreedlabsNo ratings yet
- Extended-Design and Analysis of A Network Arch BridgeDocument10 pagesExtended-Design and Analysis of A Network Arch BridgehansNo ratings yet
- Design of Haunched Composite Connections For Long-Span Beam ConstructionDocument10 pagesDesign of Haunched Composite Connections For Long-Span Beam ConstructioncasanovavnNo ratings yet
- Stability Analysis of Box-Girder Cable-Stayed BridgesDocument6 pagesStability Analysis of Box-Girder Cable-Stayed BridgesDhimas Surya NegaraNo ratings yet
- L-2 Design of Steel Roof Truss As Per SP38888Document21 pagesL-2 Design of Steel Roof Truss As Per SP38888Kanak YadavNo ratings yet
- PHD Useful PaperDocument362 pagesPHD Useful Paperpc.backupwasimNo ratings yet
- Investigation of Free In-Plane Vibration of Curved Bridges: Navid HeidarzadehDocument10 pagesInvestigation of Free In-Plane Vibration of Curved Bridges: Navid HeidarzadehpuenteprefabricadoNo ratings yet
- Theoretical and Exper Study Steel PropsDocument7 pagesTheoretical and Exper Study Steel PropsAnonymous ePcnZoBENo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0263823116307108 MainDocument15 pages1 s2.0 S0263823116307108 MainLeonardoNo ratings yet
- Design of Prestressed Concrete Piles For Seismic Loads Adds A NewDocument3 pagesDesign of Prestressed Concrete Piles For Seismic Loads Adds A NewMahindaNo ratings yet
- Esperimental StudyDocument9 pagesEsperimental Studyrafaelrp22009No ratings yet
- Arch BridgesDocument20 pagesArch BridgesPankaj_Taneja_96840% (1)
- Analytical Study On Safety Level of Stay Cables of Cable Stayed BridgeDocument8 pagesAnalytical Study On Safety Level of Stay Cables of Cable Stayed Bridgesushil deshmukhNo ratings yet
- Yimeng 2000Document20 pagesYimeng 2000dipeshbarua55No ratings yet
- Bruhn 73 C4Document28 pagesBruhn 73 C4brhNo ratings yet
- Prestressed Steel Beam: Figure 4.2-Sliding BearingDocument4 pagesPrestressed Steel Beam: Figure 4.2-Sliding BearingMarcelo AlvesNo ratings yet
- High Strength Steel in Seismic Resistant Building FramesDocument6 pagesHigh Strength Steel in Seismic Resistant Building Framesuhu_plus6482No ratings yet
- Buckling Behavior of Cold-Formed Scaffolding TubesDocument17 pagesBuckling Behavior of Cold-Formed Scaffolding TubesHaseeb KhanNo ratings yet
- 8884 PDFDocument10 pages8884 PDF081382991318No ratings yet
- Sergio Pellegrino University of Cambridge, Cambridge, UK: Deployment. The Reverse Transformation Is Called RetractionDocument35 pagesSergio Pellegrino University of Cambridge, Cambridge, UK: Deployment. The Reverse Transformation Is Called RetractionRupesh DangolNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Design Outline: 3.1 ObjectiveDocument10 pagesPreliminary Design Outline: 3.1 Objectivemohamed ahmedNo ratings yet
- Chapter-4 Design of Column & Column BaseDocument26 pagesChapter-4 Design of Column & Column Basezakai zakiNo ratings yet
- 595 05-Notes PDFDocument14 pages595 05-Notes PDFfilipeNo ratings yet
- Zirakian, 2005Document9 pagesZirakian, 2005carlosNo ratings yet
- Pseudo-Dynamic Test of A Full-Scale CFT/BRB Frame: Part 2 - Construction and TestingDocument15 pagesPseudo-Dynamic Test of A Full-Scale CFT/BRB Frame: Part 2 - Construction and TestingDiego Matias Burgos FuentesNo ratings yet
- Nguyen Trung HieuDocument6 pagesNguyen Trung HieuAhmed DahirNo ratings yet
- Journal of Constructional Steel Research: N. Jamaluddin, D. Lam, X.H. Dai, J. YeDocument11 pagesJournal of Constructional Steel Research: N. Jamaluddin, D. Lam, X.H. Dai, J. YeRaja GopalNo ratings yet
- Welded Built-Up Columns, April 1966: Lehigh PreserveDocument95 pagesWelded Built-Up Columns, April 1966: Lehigh PreservemohanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7: Columns and Strut: Failure of A ColumnDocument10 pagesChapter 7: Columns and Strut: Failure of A ColumnAshish KumarNo ratings yet
- Rules of Thumb For Steel DesignDocument7 pagesRules of Thumb For Steel DesignjaberfirasNo ratings yet
- RC I&II, SD &bridge Eng Model-Tutoarial ExamDocument63 pagesRC I&II, SD &bridge Eng Model-Tutoarial ExamWendimu TolessaNo ratings yet
- Extended-Design and Analysis of A Network Arch BridgeDocument11 pagesExtended-Design and Analysis of A Network Arch BridgeSebastian KanNo ratings yet
- Extended Abstract - Design and Analysis of A Network Arch BridgeDocument11 pagesExtended Abstract - Design and Analysis of A Network Arch BridgeSebastian KanNo ratings yet
- NAME351: L-3ff-1/NAME Date: 07/06/2014Document21 pagesNAME351: L-3ff-1/NAME Date: 07/06/2014Kabir ShafayatNo ratings yet
- Shear Capacity of Reinforced Concrete Slabs Under Concentrated LoadsDocument8 pagesShear Capacity of Reinforced Concrete Slabs Under Concentrated Loads정주호No ratings yet
- Longitudinal Stiffeners On Compression Panels: CIVL 7690Document64 pagesLongitudinal Stiffeners On Compression Panels: CIVL 7690Arul JONo ratings yet
- (5hdo $%HG/QHN DQG (0ludpehooDocument8 pages(5hdo $%HG/QHN DQG (0ludpehooRaquel CarmonaNo ratings yet
- Critical Lateral-Torsional Buckling Moments of Steel Web-TaperedDocument8 pagesCritical Lateral-Torsional Buckling Moments of Steel Web-TaperedLệnh BùiNo ratings yet
- Seismic Response of Bridges With Sliding and Elastomeric Isolation BearingsDocument7 pagesSeismic Response of Bridges With Sliding and Elastomeric Isolation BearingsciscoNo ratings yet
- Inelastic Versus Elastic Displacement-Based Intensity Measures For Seismic AnalysisDocument5 pagesInelastic Versus Elastic Displacement-Based Intensity Measures For Seismic Analysismercab15No ratings yet
- Balanced Force Charles Et Al IEJ 1998Document7 pagesBalanced Force Charles Et Al IEJ 1998abcder1234No ratings yet
- Efficiency Reduction Due To Shear Lag On Bolted Cold-Formed Steel AnglesDocument13 pagesEfficiency Reduction Due To Shear Lag On Bolted Cold-Formed Steel AnglesMaryam Al-SalmiyahNo ratings yet
- Structural Steel DesignDocument32 pagesStructural Steel Designshaluka100% (1)
- Cable Shape & Strength: Telford and The Flat Form BridgeDocument15 pagesCable Shape & Strength: Telford and The Flat Form Bridgerene boisselleNo ratings yet
- Analisis de Vibracion Grua Torre PDFDocument10 pagesAnalisis de Vibracion Grua Torre PDFdanielcolina1613No ratings yet
- Free Vibration and Modal Analysis of Tower Crane Using SAP2000 and ANSYS PDFDocument10 pagesFree Vibration and Modal Analysis of Tower Crane Using SAP2000 and ANSYS PDFİsmailNo ratings yet
- Design of Portal FramesDocument35 pagesDesign of Portal FramesPranav Prabhakar100% (2)
- A Short Guide to the Types and Details of Constructing a Suspension Bridge - Including Various Arrangements of Suspension Spans, Methods of Vertical Stiffening and Wire Cables Versus Eyebar ChainsFrom EverandA Short Guide to the Types and Details of Constructing a Suspension Bridge - Including Various Arrangements of Suspension Spans, Methods of Vertical Stiffening and Wire Cables Versus Eyebar ChainsNo ratings yet
- Instructions on Modern American Bridge BuildingFrom EverandInstructions on Modern American Bridge BuildingNo ratings yet
- Welding Procedure Qualification Record (WPQR) (ISO 15614-1-2017)Document3 pagesWelding Procedure Qualification Record (WPQR) (ISO 15614-1-2017)ramesh rajaNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Stability - An IntroductionDocument4 pagesIntermediate Stability - An IntroductiondylaraniNo ratings yet
- Chemistry For Engineering - Class 1: 1. GasesDocument9 pagesChemistry For Engineering - Class 1: 1. GasesMai Sơn DươngNo ratings yet
- C2 Cement Consistency PasteDocument9 pagesC2 Cement Consistency PasteSyukri Abd KadirNo ratings yet
- Deflections of Beams: Geometric MethodDocument22 pagesDeflections of Beams: Geometric MethodMicko LaneluzNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power Plant: 17 Mechanical by Engr. Ans Ahmed Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument29 pagesThermal Power Plant: 17 Mechanical by Engr. Ans Ahmed Department of Mechanical EngineeringTarvesh Kumar100% (1)
- Ashwin Ushas CorpDocument9 pagesAshwin Ushas CorpMengfang LiNo ratings yet
- Appl Phys B 63 451 1996 Tunable ArF Laser For VUV GenerationDocument11 pagesAppl Phys B 63 451 1996 Tunable ArF Laser For VUV Generation3209185626No ratings yet
- SUPERDRY - Superior Container Desiccants and DehumidifiersDocument2 pagesSUPERDRY - Superior Container Desiccants and DehumidifiersSrina SriNo ratings yet
- Toluene Material 2520 BalanceDocument5 pagesToluene Material 2520 Balanceapi-3714811No ratings yet
- Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA)Document43 pagesFailure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA)Muhammad Bilal100% (4)
- LAB VIVA Questions and AnswersDocument6 pagesLAB VIVA Questions and AnswersNilambar YadavNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics Class 12 Notes Chemistry Chapter 4 - CBSE LabsDocument5 pagesChemical Kinetics Class 12 Notes Chemistry Chapter 4 - CBSE Labsavinash kishoreNo ratings yet
- SRM Valliammai Engineering College: Department of Civil Engineering (M.E - Structural Engineering)Document17 pagesSRM Valliammai Engineering College: Department of Civil Engineering (M.E - Structural Engineering)Exciting DataNo ratings yet
- Che 2Document25 pagesChe 2Jaynie Lee VillaranNo ratings yet
- Resonance and Damping NOTESDocument1 pageResonance and Damping NOTESThash ANo ratings yet
- MPVN BrochureDocument32 pagesMPVN Brochurefernando_naciamentNo ratings yet
- Part 2 Week 9 - Treatment PlanningDocument50 pagesPart 2 Week 9 - Treatment PlanningdanNo ratings yet
- 2019 Edition Changes: National Board Inspection Code-Part-3Document39 pages2019 Edition Changes: National Board Inspection Code-Part-3NAVANEETH NAVANINo ratings yet
- Referensi PUR - Urethane Surface coating-BlockedISO (Baxenden) - 20160802 PDFDocument6 pagesReferensi PUR - Urethane Surface coating-BlockedISO (Baxenden) - 20160802 PDFFahmi Januar AnugrahNo ratings yet
- Table For For C-Q C-Q & & C-B C-B Compressors Compressors Series SeriesDocument1 pageTable For For C-Q C-Q & & C-B C-B Compressors Compressors Series SeriesALF1975ANo ratings yet
- 3.28 & 3.29 Kawat Las Nikko Steel 312 2,6 X 350 MM & 3,2 X 350 MMDocument1 page3.28 & 3.29 Kawat Las Nikko Steel 312 2,6 X 350 MM & 3,2 X 350 MMumarNo ratings yet
- DLP SCIENCE 4 Q4 Practice Safety Precautions On The Effects of The SunDocument6 pagesDLP SCIENCE 4 Q4 Practice Safety Precautions On The Effects of The SunMark-Christopher Roi Pelobello MontemayorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Part 2 - Slides 01 To 27 - Hydrostatic Thrust On Plane SurfaceDocument14 pagesChapter 2 - Part 2 - Slides 01 To 27 - Hydrostatic Thrust On Plane SurfaceNely ZulfatulNo ratings yet
- CW For 14.10.2021Document9 pagesCW For 14.10.2021boyi yangNo ratings yet
- Johnson - York - Marine - Chiller - UnitsDocument2 pagesJohnson - York - Marine - Chiller - UnitsAldryn AdatoNo ratings yet
- Computer Simulation of Explosion Crater in Dams With Different Buried Depths of ExplosiveDocument8 pagesComputer Simulation of Explosion Crater in Dams With Different Buried Depths of ExplosiveliushaozengNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet For Barred Tee 010719 PDFDocument1 pageData Sheet For Barred Tee 010719 PDFkandraNo ratings yet