Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 viewsAdvanced Concrete Technology - PDF 22
Advanced Concrete Technology - PDF 22
Uploaded by
MohsinThis document discusses the history and chemistry of cement production. Some key developments include the introduction of rotary kilns in 1880 which allowed for higher volume production. Standards for cement were published in the UK and US in 1880. The basic chemistry of cement involves four main oxides - calcium oxide, silica, alumina, and iron oxide. Cement production is a chemical process industry that requires close control and monitoring of chemistry to ensure consistent properties in the final product.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Ullmann S Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry - 2011 - Appl - Ammonia 2 Production ProcessesDocument88 pagesUllmann S Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry - 2011 - Appl - Ammonia 2 Production ProcessesJulius SuhermanNo ratings yet
- Failure of Inner Shell of Double Walled Atmospheric Ammonia TankDocument9 pagesFailure of Inner Shell of Double Walled Atmospheric Ammonia Tankvaratharajan g rNo ratings yet
- BS 806 Boiler PipingDocument153 pagesBS 806 Boiler PipingAmrit Pal SinghNo ratings yet
- Standards For Cement, Aggregate, Gupsum. Definitions, Requirements and Test MethodsDocument33 pagesStandards For Cement, Aggregate, Gupsum. Definitions, Requirements and Test MethodsfoxmancementNo ratings yet
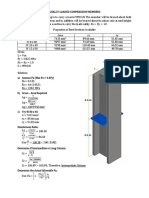
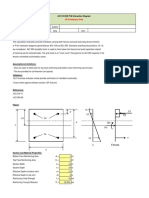
- C Assumed Fa 890 X 10 138.2Document11 pagesC Assumed Fa 890 X 10 138.2Dominic FloresNo ratings yet
- Cement and Concrete Presentation LafargeDocument131 pagesCement and Concrete Presentation LafargeJohnnie Strydom100% (1)
- Short Note of Cement ChemistryDocument14 pagesShort Note of Cement Chemistrynk_kanchkar80% (5)
- Hydration of A Belite-Calcium Sulfoaluminate-Ferrite Cement: AetherDocument7 pagesHydration of A Belite-Calcium Sulfoaluminate-Ferrite Cement: AetherAhmet SevinçNo ratings yet
- Cement: Its Chemistry and PropertiesDocument13 pagesCement: Its Chemistry and PropertiesarylananylaNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Alkalis On The Properties of Portland Cement: Anbar Journal For Engineering SciencesDocument14 pagesThe Effect of Alkalis On The Properties of Portland Cement: Anbar Journal For Engineering Sciencesmosinghi AmosNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1 1.1. Cement - Scenario - HistoryDocument12 pagesChapter - 1 1.1. Cement - Scenario - HistoryjimsonNo ratings yet
- 36 - Process Characteristics of Clinker and Cement Production - Cluster Workshop Hamburg 2107 - 10 - 26 - PresentedDocument30 pages36 - Process Characteristics of Clinker and Cement Production - Cluster Workshop Hamburg 2107 - 10 - 26 - PresentedIrshad Hussain100% (1)
- SECTION 03310-1 Portland Cement Rev 1Document10 pagesSECTION 03310-1 Portland Cement Rev 1Abdalrahman AntariNo ratings yet
- Material VotorantimDocument15 pagesMaterial VotorantimTomaz GonzalesNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Alkalis On The Properties of Portland CementDocument15 pagesThe Effect of Alkalis On The Properties of Portland CementfaheemqcNo ratings yet
- Cement Production Basic Knowledge-ShangDocument21 pagesCement Production Basic Knowledge-Shangadrian3591No ratings yet
- Concrete Technology 1Document7 pagesConcrete Technology 1Mohammad AliNo ratings yet
- Lecture1 PortlandCement IntroductionDocument39 pagesLecture1 PortlandCement IntroductioneseemNo ratings yet
- Ammonia Production - A Century of Safety, Health & Environmental ImprovementsDocument16 pagesAmmonia Production - A Century of Safety, Health & Environmental ImprovementsGrootNo ratings yet
- Topics: A Glimpse Into Sustainable Ternary-Blended Cements of The FutureDocument19 pagesTopics: A Glimpse Into Sustainable Ternary-Blended Cements of The FutureEmilioLimberArredondoOyolaNo ratings yet
- Magaldi Bottom Ash RecyleDocument17 pagesMagaldi Bottom Ash RecyleAnonymous wIPMQ5rhNo ratings yet
- Types of Cement and Testing of Cement: IiiiiDocument39 pagesTypes of Cement and Testing of Cement: IiiiiKalidass BackNo ratings yet
- Opportunities For Use of Bauxite Residue in Special CementsDocument46 pagesOpportunities For Use of Bauxite Residue in Special CementsyinglvNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2. State of The Art (Revised)Document65 pagesCHAPTER 2. State of The Art (Revised)Humbert Day-LewisNo ratings yet
- Modern Cements: Industrial RevolutionDocument5 pagesModern Cements: Industrial RevolutionHareesh HariNo ratings yet
- Portland, Blended and Other Hydraulic Cement: Design and Control of Concrete Mixtures - Chapter 3Document97 pagesPortland, Blended and Other Hydraulic Cement: Design and Control of Concrete Mixtures - Chapter 3Juan MartinezNo ratings yet
- Strength, Water Absorption and Density of Cellular Light Weight Concrete (Foam Brick)Document5 pagesStrength, Water Absorption and Density of Cellular Light Weight Concrete (Foam Brick)Green MyanmarNo ratings yet
- Eurobitumen Presentation 2016Document24 pagesEurobitumen Presentation 2016RashidNo ratings yet
- Ullmanns 2 PDFDocument88 pagesUllmanns 2 PDFCaroline Midori AkamatsuNo ratings yet
- Cement, Slag, Pozzolan, & Silica FumeDocument60 pagesCement, Slag, Pozzolan, & Silica Fumeog_double8699No ratings yet
- BS-1881-110 CONCRETE Making Test Cylinders From Fresh Con PDFDocument12 pagesBS-1881-110 CONCRETE Making Test Cylinders From Fresh Con PDFAshraf TomizehNo ratings yet
- Complete Stress-Strain Behavior of Ecological Ultra-High-Performance Cementitious Composite Under Uniaxial CompressionDocument12 pagesComplete Stress-Strain Behavior of Ecological Ultra-High-Performance Cementitious Composite Under Uniaxial CompressionkashifNo ratings yet
- Concrete Fundamentals: Stages in Cement DevelopmentDocument9 pagesConcrete Fundamentals: Stages in Cement DevelopmentAafan ShahidNo ratings yet
- V4s44A Cement Specification StandardsDocument18 pagesV4s44A Cement Specification StandardsDilnesa EjiguNo ratings yet
- Cniai 34686 0003Document45 pagesCniai 34686 0003Nirosha Dilrangi PereraNo ratings yet
- Cement Manufacturing Process - Civil EngineeringDocument8 pagesCement Manufacturing Process - Civil EngineeringScott the LION SigaukeNo ratings yet
- Cystal UreaDocument6 pagesCystal UreaDMwasNo ratings yet
- Tehnologija BetonaDocument58 pagesTehnologija BetonaOglasi Za SveNo ratings yet
- Art - Influence of The Cement Type On The Resistance of Concrete To Feed AcidsDocument9 pagesArt - Influence of The Cement Type On The Resistance of Concrete To Feed AcidsDEIVYD HEIVYSON DIOGENES COSTANo ratings yet
- Cement Chemistry L1Document23 pagesCement Chemistry L1Bharat Singh100% (2)
- Cement Industry Towards Sustainability: June 2004Document7 pagesCement Industry Towards Sustainability: June 2004Veena PasumarthyNo ratings yet
- Execution of A Cement Project From Faugi Cement1 1Document32 pagesExecution of A Cement Project From Faugi Cement1 1Ahmer SohailNo ratings yet
- Foam ConcreteDocument12 pagesFoam Concretealexnlima852No ratings yet
- Cement ChemistryDocument89 pagesCement Chemistrysameh ibrahemNo ratings yet
- Andrussow HCN Process With Ammonia RecycleDocument5 pagesAndrussow HCN Process With Ammonia RecycleKarolina Wieszczycka100% (1)
- CPD Paper 1-CementDocument12 pagesCPD Paper 1-CementBenedicto Bright MunthaliNo ratings yet
- Cement: EN 197-1 States That, Cement Is A Hydraulic Binder, I.E. A Finely Ground Inorganic Material WhichDocument33 pagesCement: EN 197-1 States That, Cement Is A Hydraulic Binder, I.E. A Finely Ground Inorganic Material WhichPrantoNo ratings yet
- 19th Century CementDocument4 pages19th Century Cementnaeem.soomro13No ratings yet
- AlccofineDocument9 pagesAlccofineMadan Mohan ReddyNo ratings yet
- Concrete CO2e ValuesDocument6 pagesConcrete CO2e ValuesasasqzNo ratings yet
- Development and Uses of Hard-Grade Asphalt and of High-Modulus Asphalt Mixes in FranceDocument20 pagesDevelopment and Uses of Hard-Grade Asphalt and of High-Modulus Asphalt Mixes in FranceJackelin TolozaNo ratings yet
- Agglomeration of Iron OresDocument41 pagesAgglomeration of Iron OresAnonymous NxpnI6jC100% (1)
- BIS Standards & CodesDocument12 pagesBIS Standards & CodeskalpanaadhiNo ratings yet
- Astm C595-C595M-16Document8 pagesAstm C595-C595M-16Jesus Luis Arce GuillermoNo ratings yet
- Concrete Technology: Ce 40/L Construction Materials and TestingDocument30 pagesConcrete Technology: Ce 40/L Construction Materials and TestingGabriel VergaraNo ratings yet
- Civ CementDocument35 pagesCiv Cementdeepan.pandyaNo ratings yet
- 7 - Concrete-1 PDFDocument73 pages7 - Concrete-1 PDFjinnaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document59 pagesChapter 2GK LSNo ratings yet
- IV ConcreteDocument30 pagesIV ConcretecamilleNo ratings yet
- The end of concrete: Pros and cons of an unsuccesful technologyFrom EverandThe end of concrete: Pros and cons of an unsuccesful technologyRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Cementitious Materials for Nuclear Waste ImmobilizationFrom EverandCementitious Materials for Nuclear Waste ImmobilizationRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Fisher EW Series (EWD/EWS/EWT) Sliding - Stem Control Valves Through NPS 12x8Document36 pagesFisher EW Series (EWD/EWS/EWT) Sliding - Stem Control Valves Through NPS 12x8Marcelo Alves Dos SantosNo ratings yet
- TESA Hinges For Firebreak DoorsDocument1 pageTESA Hinges For Firebreak DoorsBelal AliNo ratings yet
- Partially Replacing Cockle ShellDocument8 pagesPartially Replacing Cockle ShellUmange RanasingheNo ratings yet
- SPDIDocument501 pagesSPDIEugene Odullada MangaringNo ratings yet
- 8.3 Dodge Washdown Ball BearingsDocument16 pages8.3 Dodge Washdown Ball Bearingsrrobles011No ratings yet
- 13 Very Important Type Tests of A Low Voltage Switchgear Carried Out by The ManufacturerDocument10 pages13 Very Important Type Tests of A Low Voltage Switchgear Carried Out by The ManufacturerAhmed BoussoffaraNo ratings yet
- Project Report - CNG CylindersDocument23 pagesProject Report - CNG CylindersNaresh DhakerNo ratings yet
- Young's Modulus of FibersDocument10 pagesYoung's Modulus of Fiberspractice rosNo ratings yet
- Shafts Subjected To Axial Load in Axial Load in Addition To Combined Torsion and Bending Torsion and Bending LoadsDocument7 pagesShafts Subjected To Axial Load in Axial Load in Addition To Combined Torsion and Bending Torsion and Bending LoadsChetan PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Long Welded Rails: Indian Railways Institute of Civil Engineering PuneDocument136 pagesLong Welded Rails: Indian Railways Institute of Civil Engineering Punevikas_sidhana1628No ratings yet
- Wire Drawing Shearing Processes FinalDocument19 pagesWire Drawing Shearing Processes FinalJairam AtluriNo ratings yet
- LTP Ja Sa Etr 01 Nov 18 Phong CmtedDocument19 pagesLTP Ja Sa Etr 01 Nov 18 Phong CmtedTham PhongNo ratings yet
- Style J: (Potted Preferred) (Grommet & Ferrule, Contact Us)Document3 pagesStyle J: (Potted Preferred) (Grommet & Ferrule, Contact Us)JdhdkdidbdjdubdnjfbebeirhrbNo ratings yet
- 02-SAMSS-006 Extend Revision CycleDocument17 pages02-SAMSS-006 Extend Revision CycleSyed Zain AliNo ratings yet
- KingpinDocument2 pagesKingpinrobertNo ratings yet
- خواص صخور المكمن رقم 9Document31 pagesخواص صخور المكمن رقم 9maamoun ramyNo ratings yet
- Series 7000 - Tolerances, Testing and Quality ControlDocument27 pagesSeries 7000 - Tolerances, Testing and Quality ControlKamagara Roland AndrewNo ratings yet
- BOLTCALC ResultsDocument3 pagesBOLTCALC ResultsAnis SuissiNo ratings yet
- RCC SLAB 11-12 Rate AnalysisDocument2 pagesRCC SLAB 11-12 Rate AnalysisRiazahemad B Jagadal0% (1)
- Construction Technology .KDocument247 pagesConstruction Technology .KHarshit Kumar SahuNo ratings yet
- ASTM A210 Seamless Boiler and Superheater Tubes PDFDocument5 pagesASTM A210 Seamless Boiler and Superheater Tubes PDFPAULNo ratings yet
- ACI-350 P-M Interaction 1.1Document6 pagesACI-350 P-M Interaction 1.1Edgardo ArriesgadoNo ratings yet
- SputteringDocument29 pagesSputteringHebin RoyNo ratings yet
- ES9-58-1 STD Paint For Turbomachinery-Addendum Rev PDocument4 pagesES9-58-1 STD Paint For Turbomachinery-Addendum Rev PganeshNo ratings yet
- Horizontal Directionl Drilling 02466 - 1Document14 pagesHorizontal Directionl Drilling 02466 - 1Gamal AhmedNo ratings yet
- Fire Risk Assessment ReportDocument19 pagesFire Risk Assessment ReportAnonymous qPiTKbU100% (1)
- Basic Refrigeration CycleDocument12 pagesBasic Refrigeration CycleApet GriffinNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Strut-and-Tie Modeling Applied To Dapped Beam With OpeningDocument6 pagesEvaluation of Strut-and-Tie Modeling Applied To Dapped Beam With OpeningMarcel SteoleaNo ratings yet
- BS en 50264-3-1-2008Document28 pagesBS en 50264-3-1-2008Shivangi BhardwajNo ratings yet
Advanced Concrete Technology - PDF 22
Advanced Concrete Technology - PDF 22
Uploaded by
Mohsin0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views1 pageThis document discusses the history and chemistry of cement production. Some key developments include the introduction of rotary kilns in 1880 which allowed for higher volume production. Standards for cement were published in the UK and US in 1880. The basic chemistry of cement involves four main oxides - calcium oxide, silica, alumina, and iron oxide. Cement production is a chemical process industry that requires close control and monitoring of chemistry to ensure consistent properties in the final product.
Original Description:
Original Title
Advanced Concrete Technology.pdf 22
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses the history and chemistry of cement production. Some key developments include the introduction of rotary kilns in 1880 which allowed for higher volume production. Standards for cement were published in the UK and US in 1880. The basic chemistry of cement involves four main oxides - calcium oxide, silica, alumina, and iron oxide. Cement production is a chemical process industry that requires close control and monitoring of chemistry to ensure consistent properties in the final product.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views1 pageAdvanced Concrete Technology - PDF 22
Advanced Concrete Technology - PDF 22
Uploaded by
MohsinThis document discusses the history and chemistry of cement production. Some key developments include the introduction of rotary kilns in 1880 which allowed for higher volume production. Standards for cement were published in the UK and US in 1880. The basic chemistry of cement involves four main oxides - calcium oxide, silica, alumina, and iron oxide. Cement production is a chemical process industry that requires close control and monitoring of chemistry to ensure consistent properties in the final product.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
Cements 1/5
lower strength limits. The European Standard for Common Cements (EN 197-1) is outlined
in section 1.6.3.
2000– Multistage combustion – emission control
New horizontal cement mill technology
High-pressure roll press for cement pregrinding
Automatic kiln control using expert systems
1980 High-efficiency separator introduced for cement grinding
Precalciner process developed
1960 X-ray fluorescence (XRF) rapid chemical analysis
Suspension preheater process introduced
1940 Lepol (nodule) process introduced
Introduction of pneumatic blending silos for raw meal
1920 First electrostatic precipitator installed in cement works
1900 Paper sacks introduced for cement
1880 British (BS 12) and ASTM (C9) standards published
Rotary kilns introduced
Tube grinding mills for cement
1860 Method for carbonate of lime developed
J. Grant introduced tensile strength test for cement
1840 W. Aspdin bottle kiln plant at Northfleet
1820 Patent for Portland Cement granted to J. Aspdin
Figure 1.1 Landmarks in Portland cement production.
1.3 Chemistry of clinker manufacture
1.3.1 Raw materials
Cement making is essentially a chemical process industry and has much in common with
the manufacture of so-called heavy chemicals such as sodium hydroxide and calcium
chloride. Close control of the chemistry of the product is essential if cement with consistent
properties is to be produced. This control applies not only to the principal oxides which
are present but also to impurities, which can have a marked influence on both the
manufacturing process and cement properties.
As illustrated in Figure 1.2, a chemical analysis of Portland cement clinker shows it to
consist mainly of four oxides: CaO (lime), SiO2 (silica), Al2O3 (alumina) and Fe2O3 (iron
oxide). In order to simplify the description of chemical composition, a form of shorthand
is used by cement chemists in which the four oxides are referred to respectively as C, S,
A and F.
Expressing the chemical analysis in the form of oxides, rather than the individual
elements of silicon (Si), calcium (Ca) etc., has the advantage that the analysis total should
You might also like
- Ullmann S Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry - 2011 - Appl - Ammonia 2 Production ProcessesDocument88 pagesUllmann S Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry - 2011 - Appl - Ammonia 2 Production ProcessesJulius SuhermanNo ratings yet
- Failure of Inner Shell of Double Walled Atmospheric Ammonia TankDocument9 pagesFailure of Inner Shell of Double Walled Atmospheric Ammonia Tankvaratharajan g rNo ratings yet
- BS 806 Boiler PipingDocument153 pagesBS 806 Boiler PipingAmrit Pal SinghNo ratings yet
- Standards For Cement, Aggregate, Gupsum. Definitions, Requirements and Test MethodsDocument33 pagesStandards For Cement, Aggregate, Gupsum. Definitions, Requirements and Test MethodsfoxmancementNo ratings yet
- C Assumed Fa 890 X 10 138.2Document11 pagesC Assumed Fa 890 X 10 138.2Dominic FloresNo ratings yet
- Cement and Concrete Presentation LafargeDocument131 pagesCement and Concrete Presentation LafargeJohnnie Strydom100% (1)
- Short Note of Cement ChemistryDocument14 pagesShort Note of Cement Chemistrynk_kanchkar80% (5)
- Hydration of A Belite-Calcium Sulfoaluminate-Ferrite Cement: AetherDocument7 pagesHydration of A Belite-Calcium Sulfoaluminate-Ferrite Cement: AetherAhmet SevinçNo ratings yet
- Cement: Its Chemistry and PropertiesDocument13 pagesCement: Its Chemistry and PropertiesarylananylaNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Alkalis On The Properties of Portland Cement: Anbar Journal For Engineering SciencesDocument14 pagesThe Effect of Alkalis On The Properties of Portland Cement: Anbar Journal For Engineering Sciencesmosinghi AmosNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1 1.1. Cement - Scenario - HistoryDocument12 pagesChapter - 1 1.1. Cement - Scenario - HistoryjimsonNo ratings yet
- 36 - Process Characteristics of Clinker and Cement Production - Cluster Workshop Hamburg 2107 - 10 - 26 - PresentedDocument30 pages36 - Process Characteristics of Clinker and Cement Production - Cluster Workshop Hamburg 2107 - 10 - 26 - PresentedIrshad Hussain100% (1)
- SECTION 03310-1 Portland Cement Rev 1Document10 pagesSECTION 03310-1 Portland Cement Rev 1Abdalrahman AntariNo ratings yet
- Material VotorantimDocument15 pagesMaterial VotorantimTomaz GonzalesNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Alkalis On The Properties of Portland CementDocument15 pagesThe Effect of Alkalis On The Properties of Portland CementfaheemqcNo ratings yet
- Cement Production Basic Knowledge-ShangDocument21 pagesCement Production Basic Knowledge-Shangadrian3591No ratings yet
- Concrete Technology 1Document7 pagesConcrete Technology 1Mohammad AliNo ratings yet
- Lecture1 PortlandCement IntroductionDocument39 pagesLecture1 PortlandCement IntroductioneseemNo ratings yet
- Ammonia Production - A Century of Safety, Health & Environmental ImprovementsDocument16 pagesAmmonia Production - A Century of Safety, Health & Environmental ImprovementsGrootNo ratings yet
- Topics: A Glimpse Into Sustainable Ternary-Blended Cements of The FutureDocument19 pagesTopics: A Glimpse Into Sustainable Ternary-Blended Cements of The FutureEmilioLimberArredondoOyolaNo ratings yet
- Magaldi Bottom Ash RecyleDocument17 pagesMagaldi Bottom Ash RecyleAnonymous wIPMQ5rhNo ratings yet
- Types of Cement and Testing of Cement: IiiiiDocument39 pagesTypes of Cement and Testing of Cement: IiiiiKalidass BackNo ratings yet
- Opportunities For Use of Bauxite Residue in Special CementsDocument46 pagesOpportunities For Use of Bauxite Residue in Special CementsyinglvNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2. State of The Art (Revised)Document65 pagesCHAPTER 2. State of The Art (Revised)Humbert Day-LewisNo ratings yet
- Modern Cements: Industrial RevolutionDocument5 pagesModern Cements: Industrial RevolutionHareesh HariNo ratings yet
- Portland, Blended and Other Hydraulic Cement: Design and Control of Concrete Mixtures - Chapter 3Document97 pagesPortland, Blended and Other Hydraulic Cement: Design and Control of Concrete Mixtures - Chapter 3Juan MartinezNo ratings yet
- Strength, Water Absorption and Density of Cellular Light Weight Concrete (Foam Brick)Document5 pagesStrength, Water Absorption and Density of Cellular Light Weight Concrete (Foam Brick)Green MyanmarNo ratings yet
- Eurobitumen Presentation 2016Document24 pagesEurobitumen Presentation 2016RashidNo ratings yet
- Ullmanns 2 PDFDocument88 pagesUllmanns 2 PDFCaroline Midori AkamatsuNo ratings yet
- Cement, Slag, Pozzolan, & Silica FumeDocument60 pagesCement, Slag, Pozzolan, & Silica Fumeog_double8699No ratings yet
- BS-1881-110 CONCRETE Making Test Cylinders From Fresh Con PDFDocument12 pagesBS-1881-110 CONCRETE Making Test Cylinders From Fresh Con PDFAshraf TomizehNo ratings yet
- Complete Stress-Strain Behavior of Ecological Ultra-High-Performance Cementitious Composite Under Uniaxial CompressionDocument12 pagesComplete Stress-Strain Behavior of Ecological Ultra-High-Performance Cementitious Composite Under Uniaxial CompressionkashifNo ratings yet
- Concrete Fundamentals: Stages in Cement DevelopmentDocument9 pagesConcrete Fundamentals: Stages in Cement DevelopmentAafan ShahidNo ratings yet
- V4s44A Cement Specification StandardsDocument18 pagesV4s44A Cement Specification StandardsDilnesa EjiguNo ratings yet
- Cniai 34686 0003Document45 pagesCniai 34686 0003Nirosha Dilrangi PereraNo ratings yet
- Cement Manufacturing Process - Civil EngineeringDocument8 pagesCement Manufacturing Process - Civil EngineeringScott the LION SigaukeNo ratings yet
- Cystal UreaDocument6 pagesCystal UreaDMwasNo ratings yet
- Tehnologija BetonaDocument58 pagesTehnologija BetonaOglasi Za SveNo ratings yet
- Art - Influence of The Cement Type On The Resistance of Concrete To Feed AcidsDocument9 pagesArt - Influence of The Cement Type On The Resistance of Concrete To Feed AcidsDEIVYD HEIVYSON DIOGENES COSTANo ratings yet
- Cement Chemistry L1Document23 pagesCement Chemistry L1Bharat Singh100% (2)
- Cement Industry Towards Sustainability: June 2004Document7 pagesCement Industry Towards Sustainability: June 2004Veena PasumarthyNo ratings yet
- Execution of A Cement Project From Faugi Cement1 1Document32 pagesExecution of A Cement Project From Faugi Cement1 1Ahmer SohailNo ratings yet
- Foam ConcreteDocument12 pagesFoam Concretealexnlima852No ratings yet
- Cement ChemistryDocument89 pagesCement Chemistrysameh ibrahemNo ratings yet
- Andrussow HCN Process With Ammonia RecycleDocument5 pagesAndrussow HCN Process With Ammonia RecycleKarolina Wieszczycka100% (1)
- CPD Paper 1-CementDocument12 pagesCPD Paper 1-CementBenedicto Bright MunthaliNo ratings yet
- Cement: EN 197-1 States That, Cement Is A Hydraulic Binder, I.E. A Finely Ground Inorganic Material WhichDocument33 pagesCement: EN 197-1 States That, Cement Is A Hydraulic Binder, I.E. A Finely Ground Inorganic Material WhichPrantoNo ratings yet
- 19th Century CementDocument4 pages19th Century Cementnaeem.soomro13No ratings yet
- AlccofineDocument9 pagesAlccofineMadan Mohan ReddyNo ratings yet
- Concrete CO2e ValuesDocument6 pagesConcrete CO2e ValuesasasqzNo ratings yet
- Development and Uses of Hard-Grade Asphalt and of High-Modulus Asphalt Mixes in FranceDocument20 pagesDevelopment and Uses of Hard-Grade Asphalt and of High-Modulus Asphalt Mixes in FranceJackelin TolozaNo ratings yet
- Agglomeration of Iron OresDocument41 pagesAgglomeration of Iron OresAnonymous NxpnI6jC100% (1)
- BIS Standards & CodesDocument12 pagesBIS Standards & CodeskalpanaadhiNo ratings yet
- Astm C595-C595M-16Document8 pagesAstm C595-C595M-16Jesus Luis Arce GuillermoNo ratings yet
- Concrete Technology: Ce 40/L Construction Materials and TestingDocument30 pagesConcrete Technology: Ce 40/L Construction Materials and TestingGabriel VergaraNo ratings yet
- Civ CementDocument35 pagesCiv Cementdeepan.pandyaNo ratings yet
- 7 - Concrete-1 PDFDocument73 pages7 - Concrete-1 PDFjinnaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document59 pagesChapter 2GK LSNo ratings yet
- IV ConcreteDocument30 pagesIV ConcretecamilleNo ratings yet
- The end of concrete: Pros and cons of an unsuccesful technologyFrom EverandThe end of concrete: Pros and cons of an unsuccesful technologyRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Cementitious Materials for Nuclear Waste ImmobilizationFrom EverandCementitious Materials for Nuclear Waste ImmobilizationRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Fisher EW Series (EWD/EWS/EWT) Sliding - Stem Control Valves Through NPS 12x8Document36 pagesFisher EW Series (EWD/EWS/EWT) Sliding - Stem Control Valves Through NPS 12x8Marcelo Alves Dos SantosNo ratings yet
- TESA Hinges For Firebreak DoorsDocument1 pageTESA Hinges For Firebreak DoorsBelal AliNo ratings yet
- Partially Replacing Cockle ShellDocument8 pagesPartially Replacing Cockle ShellUmange RanasingheNo ratings yet
- SPDIDocument501 pagesSPDIEugene Odullada MangaringNo ratings yet
- 8.3 Dodge Washdown Ball BearingsDocument16 pages8.3 Dodge Washdown Ball Bearingsrrobles011No ratings yet
- 13 Very Important Type Tests of A Low Voltage Switchgear Carried Out by The ManufacturerDocument10 pages13 Very Important Type Tests of A Low Voltage Switchgear Carried Out by The ManufacturerAhmed BoussoffaraNo ratings yet
- Project Report - CNG CylindersDocument23 pagesProject Report - CNG CylindersNaresh DhakerNo ratings yet
- Young's Modulus of FibersDocument10 pagesYoung's Modulus of Fiberspractice rosNo ratings yet
- Shafts Subjected To Axial Load in Axial Load in Addition To Combined Torsion and Bending Torsion and Bending LoadsDocument7 pagesShafts Subjected To Axial Load in Axial Load in Addition To Combined Torsion and Bending Torsion and Bending LoadsChetan PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Long Welded Rails: Indian Railways Institute of Civil Engineering PuneDocument136 pagesLong Welded Rails: Indian Railways Institute of Civil Engineering Punevikas_sidhana1628No ratings yet
- Wire Drawing Shearing Processes FinalDocument19 pagesWire Drawing Shearing Processes FinalJairam AtluriNo ratings yet
- LTP Ja Sa Etr 01 Nov 18 Phong CmtedDocument19 pagesLTP Ja Sa Etr 01 Nov 18 Phong CmtedTham PhongNo ratings yet
- Style J: (Potted Preferred) (Grommet & Ferrule, Contact Us)Document3 pagesStyle J: (Potted Preferred) (Grommet & Ferrule, Contact Us)JdhdkdidbdjdubdnjfbebeirhrbNo ratings yet
- 02-SAMSS-006 Extend Revision CycleDocument17 pages02-SAMSS-006 Extend Revision CycleSyed Zain AliNo ratings yet
- KingpinDocument2 pagesKingpinrobertNo ratings yet
- خواص صخور المكمن رقم 9Document31 pagesخواص صخور المكمن رقم 9maamoun ramyNo ratings yet
- Series 7000 - Tolerances, Testing and Quality ControlDocument27 pagesSeries 7000 - Tolerances, Testing and Quality ControlKamagara Roland AndrewNo ratings yet
- BOLTCALC ResultsDocument3 pagesBOLTCALC ResultsAnis SuissiNo ratings yet
- RCC SLAB 11-12 Rate AnalysisDocument2 pagesRCC SLAB 11-12 Rate AnalysisRiazahemad B Jagadal0% (1)
- Construction Technology .KDocument247 pagesConstruction Technology .KHarshit Kumar SahuNo ratings yet
- ASTM A210 Seamless Boiler and Superheater Tubes PDFDocument5 pagesASTM A210 Seamless Boiler and Superheater Tubes PDFPAULNo ratings yet
- ACI-350 P-M Interaction 1.1Document6 pagesACI-350 P-M Interaction 1.1Edgardo ArriesgadoNo ratings yet
- SputteringDocument29 pagesSputteringHebin RoyNo ratings yet
- ES9-58-1 STD Paint For Turbomachinery-Addendum Rev PDocument4 pagesES9-58-1 STD Paint For Turbomachinery-Addendum Rev PganeshNo ratings yet
- Horizontal Directionl Drilling 02466 - 1Document14 pagesHorizontal Directionl Drilling 02466 - 1Gamal AhmedNo ratings yet
- Fire Risk Assessment ReportDocument19 pagesFire Risk Assessment ReportAnonymous qPiTKbU100% (1)
- Basic Refrigeration CycleDocument12 pagesBasic Refrigeration CycleApet GriffinNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Strut-and-Tie Modeling Applied To Dapped Beam With OpeningDocument6 pagesEvaluation of Strut-and-Tie Modeling Applied To Dapped Beam With OpeningMarcel SteoleaNo ratings yet
- BS en 50264-3-1-2008Document28 pagesBS en 50264-3-1-2008Shivangi BhardwajNo ratings yet